Shi'er lü
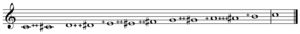
Shí-èr-lǜ (Chinese: 十二律, [ʂɻ̩̌.âɚ lŷ], 12 pitches) (twelve-pitch scale) is a standardized gamut of twelve notes.[1] Also known, rather misleadingly, as the Chinese chromatic scale it is one kind of chromatic scale used in ancient Chinese music. The Chinese scale uses the same intervals as the Pythagorean scale, based on 2:3 ratios (8:9, 16:27, 64:81, etc.). The gamut or its subsets were used for tuning and are preserved in bells and pipes.[2]
However, "it should not be imagined that this gamut ever functioned as a scale, and it is erroneous to refer to the 'Chinese chromatic scale', as some Western writers have done. The series of twelve notes known as the twelve lü were simply a series of fundamental notes from which scales could be constructed."[3]
The first reference to, "the standardization of bells and pitch," dates back to around 600 [BCE] while the first description of the generation of the pitches dates back to around 240 [CE].[3]
Note names
- 黄钟 - Huáng Zhōng - tonic/unison - 1 : 1 -
- 大吕 - Dà Lǚ - semitone - 37 : 211 -
- 太簇 - Tài Cù - major second - 32 : 23 -
- 夹钟 - Jiá Zhōng - minor third - 39 : 214 -
- 姑洗 - Gū Xiǎn - major third - 34 : 26 -
- 中吕 - Zhòng Lǚ - perfect fourth - 311 : 217 -
- 蕤宾 - Ruí Bīn - tritone - 36 : 29 -
- 林钟 - Lín Zhōng - perfect fifth - 3 : 2 -
- 夷则 - Yí Zé - minor sixth - 38 : 212 -
- 南吕 - Nán Lǚ - major sixth - 33 : 24 -
- 无射 - Wú Yì - minor seventh - 310 : 215 -
- 应钟 - Yìng Zhōng - major seventh - 35 : 27 -
12 total, which fall within the scope of one octave. (Note that the mathematical method used by the ancient Chinese could never produce a true octave. No matter what is done with numbers involving 1/3, it is impossible to get to 1/2 or to 2.) The next higher frequency in the series of frequencies produced by the Chinese system would be higher than 880 hertz.

See the article by Chen Ying-shi.[4]
See also
Further reading
- Reinisch, Richard (?). Chinesische Klassische Musik, p. 30. Books On Demand. ISBN 978-3-8423-4502-7.
Sources
- ^ Joseph C.Y. Chen (1996). Early Chinese Work in Natural Science: A Re-examination of the Physics of Motion, Acoustics, Astronomy and Scientific Thoughts, p. 96. ISBN 962-209-385-X.
- ^ Chen (1996), p.97.
- ^ a b Needham, Joseph (1962/2004). Science and Civilization in China, Vol. IV: Physics and Physical Technology, p.170-171. ISBN 978-0-521-05802-5.
- ^ 一种体系 两个系统 by 陈应时 (Yi zhong ti-xi, liang ge xi-tong by Chen Ying-shi of the Shanghai Conservatory), Musicology in China, 2002, Issue 4, 中国音乐学,2002,第四 期
External links
- Graham Pont. "Philosophy and Science of Music in Ancient Greece: The Predecessors of Pythagoras and their Contribution", Nexus Network Journal.

