Sultan Said Khan
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (August 2020) |
| Sultan Said Khan | |
|---|---|
| Khan of Yarkent Khanate (1514–1705) | |
| Reign | 1514–1533 |
| Predecessor | Mansur Khan |
| Successor | Abdurashid Khan |
| Born | 1487 |
| Died | 9 July 1533 near Karakoram Pass, likely Daulat Beg Oldi |
| Religion | Sunni Islam |
Sultan Said Khan (Chinese: 薩亦德; 1487–1533) ruled the Yarkent Khanate from September 1514 to July 1533. He was born in the late 15th century in Moghulistan, and he was a direct descendant of the first Moghul Khan, Tughlugh Timur, who had founded the state of Moghulistan in 1348 and ruled until 1363. The Moghuls were turkicized Mongols who had converted to Islam.
Some English sources refer to this ruler as Abusaid.[1]
Background


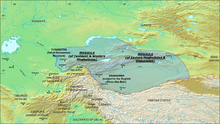

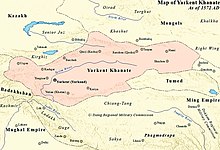

When the Chagatai ulus, which embraced both East and West Turkestan, collapsed, the result was the creation of two different states: Maverannahr in West Turkestan, with its capital at Samarkand, where Timur the Great came to power in 1370, and Moghulistan, with its capital at Almalik, near the present-day town of Gulja, in the Ili valley. Moghulistan embraced settled lands in Eastern Turkestan as well as nomad lands north of Tangri Tagh. The settled lands were known at the time as Manglai Sobe or Mangalai Suyah, which translates as Shiny Land, or Advanced Land Which Faced the Sun. These lands included west and central Tarim oasis-cities, such as Khotan, Yarkand, Yangihisar, Kashgar, Aksu, and Uch Turpan; and hardly involved eastern Tangri Tagh oasis-cities, such as Kucha, Karashahr, Turpan and Kumul, where a local Uyghur administration and Buddhist population still existed. The nomadic areas comprised the present Kyrgyzstan and part of Kazakhstan, including Jettisu, the area of seven rivers.
The ruler of Aksu, the dughlat emir Puladchi, brought a young, 18-year-old, Tughluk Timur from the Ili valley in 1347, and in a kurultai declared him a grandson of Duwa Khan, the great-grandson of Chagatai Khan and ruler of the Chagatai Khanate between 1282 and 1307. Puladchi forced all moghuls to recognize Tughluk as Khan. Khans from Chagatai, the second son of Genghis Khan, to Tughluk Timur are known as "Chagatai khans", and from Tughluk Timur to his descendants as "Moghul khans".
Moghulistan existed around 100 years, and then split into three parts: Yarkand state (mamlakati Yarkand), with its capital at Yarkand, which embraced all the settled lands of Western Kashgaria, still nomad Moghulistan which embraced the nomad lands north of Tengri Tagh, and Uyghurstan which embraced the settled lands of Eastern Kashgaria, Turpan and Kumul Basins. The founder of Yarkand state was Mirza Abu Bakr, who was from the dughlat tribe. In 1465, he raised a rebellion, captured Yarkand, Kashgar, and Khotan, and declared himself an independent ruler, successfully repelling attacks by the Moghulistan rulers Yunus Khan and his son Akhmad Khan, or Ahmad Alaq, named Alach, "Slaughterer", for his war against the kalmyks. In 1462 moghul khan Dost Muhammad took residency in Aksu, denying nomad style of life, and as result Eastern Kashgaria cities, such as Aksu, Uchturpan, Bai, Kucha, Karashar, and also Turpan and Kumul, separated into Eastern Khanate or Uyghurstan.
Dughlat emirs had ruled the country that lay south of Tangri-Tagh in the Tarim Basin from the middle of the thirteenth century, on behalf of Chagatai Khan and his descendants, as their satellites. The first dughlat ruler, who received lands directly from the hands of Chagatai, was amir Babdagan or Tarkhan. The capital of the emirate was Kashgar, and the country was known as Mamlakati Kashgar. Although the emirate, representing the settled lands of Eastern Turkestan, was formally under the rule of the moghul khans, the dughlat emirs often tried to put an end to that dependence, and raised frequent rebellions, one of which resulted in the separation of Kashgar from Moghulistan for almost 15 years (1416–1435).
Mirza Abu Bakr ruled Yarkand for 48 years and his ruling was featured by creation of unique and highly effective penitentiary system, that had no analog in other countries. After discovering, by occasion, 29 large bowls, filled with gold sand and silver coins (Balysh), during excavation in the old city of Yarkand, Mirza Abu Bakr ordered to start excavations throughout the whole country in all old cities of towns and in abounded cities of Taklamakan Desert as well. To get workforce for performing of mass excavations he used convicts, both males and females of any age. The place of site of excavation was named Kazyk and numerous barracks for convicts and the guards were erected, convicts were sent to Kazyks by stages from all over the country and excavation works were continuing the whole year without interruptions. Using this forced labour system he collected during his reign very large amount of treasuries and became the owner of very rare and valuable things, some of them hundreds and thousands years old.
In May 1514, Sultan Said Khan, grandson of Yunus Khan (ruler of Moghulistan between 1462 and 1487) and the third son of Akhmad Khan, made an expedition against Kashgar from Andijan with only 5,000 tribesmen (who represented 9 Moghul tribes- Dughlat, Duhtui, Barlas, Yarki, Ordabegi, Itarchi, Konchi, Churas and Bekchi), and having captured the Yangihisar citadel, that defended Kashgar from south road, took the city, dethroning Mirza Abu Bakr. Soon after, other cities of Yarkand state – Yarkand, Khotan, Aksu, and Uch Turpan – joined him, and recognized Sultan Said Khan as a ruler, creating a union of six cities, called Altishahr. Sultan Said Khan's sudden success is considered to be contributed to by the dissatisfaction of the population with the tyrannical rule of Mirza Abu-Bakr and the unwillingness of the dughlat amirs to fight against a descendant of Chagatai Khan, and who decided, on the contrary, to bring the head of the slain ruler to Sultan Said Khan. This move put an end to almost 300 years of rule (nominal and actual) by the Dughlat emirs in the cities of West Kashgaria (1219–1514). Mirza Abu Bakr fled Yarkand for Ladakh with handful of his followers and 900 donkeys, loaded with his numerous treasuries, and being chased on his heels by Dughlat emirs and also Barlas emirs, sent by Sultan Said Khan. They almost reached him in Karangu Tagh Mountains, but Mirza Abu Bakr managed to escape by killing all 900 donkeys and dumping all treasuries into Karakash River. During flight he found that all garrisons, that he previously deployed in Kashmir and Little Tibet (Ladakh), were deserted by his troops. So, he found it's impossible to stay in Ladakh, he decided to turn back and surrender to Sultan Said Khan but on half-way to Yarkand was captured and slaughtered by Dughlat emirs, who betrayed him.
Life
This section possibly contains original research. (August 2020) |
At this time, almost all of West Turkestan (Maverannahr) was invaded by nomadic Uzbeks of Shaybani Khan, who were killing all the descendants of Timur the Great and Chagatai Khan. Sultan Said Khan saved his life when he moved to Kashgar with his nobles. In 1516, he concluded a peace agreement with his older brother Mansur Khan, the moghul khan of Chalish and Turpan (Uyghurstan), who died in 1543. As a result, the eastern part of the settled country south and partly north of Tangri-Tagh joined his state, including the cities of Bai, Kucha, Chalish (Karashahr), Urum (Urumchi), Turpan, Kumul, and Shazhou (Dunhuang), representing those lands of former Uyghuria (856–1335) that were known as the Fifth Ulus of the Mongol Empire in the middle of the thirteenth century, because the former ruler of Uyghuria, idikut Baurchuk Art Tekin married Altun Begi, the daughter of Genghis Khan, and was declared by Genghis as his fifth son in 1211.[2]
Relations between Yarkand Khanate and Ming dynasty China were not developed, although the far eastern boundaries of Yarkand reached the Jiayuguan Pass at the western end of the Great Wall of China due to holy expeditions of Mansur Khan, including expeditions against the Sarigh Uyghurs – Yellow Uyghurs or Uyghurs of yellow religion, called Yugurs, who worshipped Tibetan Buddhism and took refuge in Gansu province of Ming China in 1529, fleeing the holy warriors of Mansur Khan. This situation can be partly explained by the full extinction of Silk Road trade by this time.[citation needed]



Before his death during almost 20 years of ruling he united all the settled country south of Tangri Tagh, from Kashgar to Kumul, into one centralized state- Yarkand Khanate with a population of the same origin and language. Also such mountainous regions as Kashmir and Bolor became dependencies of Yarkand Khanate, paid tributes and struck silver and golder coins under name "Abul Fath Sultan Said Khan Ghazi". The contemporary writer dughlat amir Mirza Muhammad Haidar stated that it was a time when the Power of Tyranny (the rule of Mirza Abu Bakr) had been changed to the Power of Law and Order during the rule of Sultan Said Khan. Theft of property was considered a high crime and was subject to severe punishment, including execution. Peasants were encouraged to leave their tools in the fields after work, and household owners to keep the doors of their houses unlocked. Foreign traders, upon arrival to any town, could leave their luggage dumped directly on the road and, after taking a rest for several days and returning, they could find their goods in the same place – safe and untouched.[citation needed]
Said Khan had a close relationship with Babur, his cousin and founder of the Mughal Empire across the Himalayas and Karakoram Range from the Yashkent Khanate.[3]
Sultan Said Khan is sometime mentioned with title of Ghazi for his military expeditions.[4] The reign of Sultan Said Khan was heavily influenced by the khojas.[5]
His reign included a campaign in Bolor in 1527–1528 with his son Rashid and Mirza Muhammad Haidar in the command of troops,[6][7] and a raid into Badakhshan in 1529[8] upon the request of its inhabitants, who temporarily were left without ruler when sick Babur recalled his eldest son Humayun Mirza from Badakhshan (ruled Badakhshan in 1520–1528) to Agra to be his successor in case of his death and who recognized Sultan Said Khan rights on Badakhshan as a grandson of Shah Begum. When Sultan Said Khan came to Badakhshan he found that youngest son of Babur Hindal Mirza was already sitting in Zafar fortress, capital of Badakhshan, while Mirza Muhammad Haidar, who was sent to Badakhshan in advance with troops, was besieging the fortress. The siege of the Zafar fortress lasted 3 months during which Babur assembled State Council in Agra and it was decided on it to avoid a war between Moghul Empire and Yarkent Khanate, Hindal Mirza was recalled to Agra and Suleiman Shah, son of the former ruler of Badakhshan Mirza Wais Khan, who died in 1520 and was a son of Timurid Sultan Mahmud Mirza and Sultan Nigar Khanum, daughter of Yunus Khan and Shah Begum, was restored as a lawful ruler of Badakhshan.[citation needed]
Expedition into Ladakh and death
Said Khan launched looting expeditions into Ladakh and Kashmir in 1532.[8] The account of this military expedition was recorded by his general Mirza Muhammad Haidar Dughlat, who was the Sultan's first cousin, in the work of history Tarikh-i-Rashidi (تاریخ رشیدی) (History of Rashid).[9]
In Autumn of 1531 (Safar 938 AH), the Sultan Said Khan left Yarkand with Haidar and a few thousand men. Upon first time crossing the Karakorum, the Sultan encountered severe altitude sickness, but he managed to recover. In the course of a few months of campaigning, they were able to devastate Nubra Valley. As winter approached, they split forces. The Sultan left for Baltistan; Haidar left for Kashmir. In Baltistan, the Sultan encountered a population of friendly Muslims, but he turned them killing and enslaving them, possibly because they were Shiites which was heretic to orthodox Yarkandi Sunnis. On the way to Kashmir, Haider defeated the Dras near Zoji La. In Kashmir, he and his troops were hosted by the king of Srinagar. In the spring, the two parties met up again in Maryul, the Sultan decided to return to Yarkand, but he instructed Haider to conquer Tibet for Islam before his departure.[10][11]
Sultan Said Khan purportedly died at Daulat Beg Oldi while returning to Yarkent.[12][13][4] He died in 1533 of a high-altitude pulmonary edema.[8][14] Henry Walter Bellew argues that the location of his death was here at Daulat Beg Oldi. The news of Sultan's death led to a bloody succession which saw the ascension of Abdurashid Khan. Abdurashid Khan recalled the forces in Tibet and exiled Haidar. By then, Haidar had some successes against the Changpa Tibetans of Baryang, but his forces suffered greatly from the altitude and elements. By the time the army returned to Yarkand, of the starting few thousands, less than a dozen were left. The exiled Haidar received the refuge from his maternal aunt in Badakhshan. He eventually joined the ranks of the Mughal Empire where he wrote the Tarikh-i-Rashidi.[10][11]
Aftermath
Sultan Said Khan was succeeded in Yarkand by his son, Abdur Rashid Khan (Abdurashid Khan), who ruled from 1533 to 1560.
The historian Mirza Muhammad Haidar, in 1546, called the eastern part of the country the "Eastern Khanate or Uyghurstan" in his famous book Tarikh-i- Rashidi, written in Kashmir. The capital of this state was Yarkand, and it was known by the names mamlakati Saidiya, mamlakati Yarkand, and mamlakati Moghuliya in Iranian sources. The last name however was not accurate, because by this time the nomad state of Moghulistan had collapsed. It was eliminated during the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries by nomadic tribes of Kyrgyz, Kazakhs and Jungars, that captured all the Moghul lands north of Tangri Tagh. The remnants of the Moghuls (about 5,000 families mostly from Barlas, Churas and Arlat tribes) moved to Kashgaria and mixed with the local 1,000 000 Uyghur population, although a group of the Moghuls, numbering 30,000 men, joined Babur, a descendant of Timur the Great through his father Omar Sheikh Mirza, and a descendant of Chagatai Khan through his mother Kutluk Nigar Khanum, a daughter of the Moghul Yunus Khan, in Kunduz, in 1512, and helped him in his invasion of India. The Babur state in India was known as the Moghul Empire, and this state recognized Yarkand Khanate in 1529, (when Babur and Sultan Said Khan peacefully settled issue around Badakhshan, that was claimed by both cousins as their hereditary Land) as it did the Shaybanid state in Maverannahr, in 1538.
This country was later known as "Kashgar and Uyghurstan", according to Balkh historian Makhmud ibn Vali ("Bahr al-Asrar", Sea of Mysteries, 1641–1644). Kashgar historian Muhammad Imin Sadr Kashgari called the country Uyghurstan in his book Traces of Invasion (Asar al-futuh) in 1780 (as opposed to Jungaria, which he called Moghulistan, and the Ili River valley, which he called Baghistan, i.e. Land of Gardens). He wrote that this great country embraced a union of six cities south of Tangri Tagh – Kashgar, Yangihisar, Yarkand, Khotan, Aksu (Ardabil), and Uch Turpan (Safidkuh) – the so-called Altishahr, as well as Kucha, Chalish (Karashahr), Turpan and Kumul. According to him, the country collapsed not due to attacks by external enemies, but due to the personal ambitions of its religious leaders, the Khojas. The Khojas were divided into two hostile groups that hated and killed each other – the Ak Taghliks (White Mountaineers) and the Kara Taghliks (Black Mountaineers), who deposed one of the last Moghul Khans, Ismail Khan, in 1678, with the help of invited Kalmyks (Dzungars), and put the whole country under the feet of future invaders, including Dzungar Khanate and Qing dynasty of China, for gaining personal powers.



Family
- Consorts
- Zainab Sultan Khanum, daughter of Mahmud Khan Chaghatai and Said's favourite wife, mother of Ibrahim Khan, Muhsin Khan and Mahmud Yusuf;[15]
- Makhduma Begum, sister of Suqar Bahadur Qaluchi, mother of Abdurashid Khan;[15]
- Habiba Sultan Khanish, daughter of Muhammad Husayn Mirza Dughlat and Khub Nigar Khanum, daughter of Yunus Khan;[15]
- Children
- Abdurashid Khan;
- Ibrahim Khan;
- Muhsin Khan;
- Mahmud Yusuf;
- Badi-ul-Jamal Khanum, married firstly to Baush Sultan of the Uzbeg Kazaks, married secondly to Muhammadi Barlas, a peasant;[15]
Genealogy of Moghul Khans of Yarkent Khanate
In Babr Nama written by Babur, Page 19, Chapter 1; described genealogy of his maternal grandfather Yunas Khan as:
"Yūnas Khān descended from Chaghatāī Khān, the second son of Chīngīz Khān (as follows,) Yūnas Khān, son of Wais Khān, son of Sher-'alī Aūghlān, son of Muḥammad Khān, son of Khiẓr Khwāja Khān, son of Tūghlūq-tīmūr Khān, son of Aīsān-būghā Khān, son of Dāwā Khān, son of Barāq Khān, son of Yīsūntawā Khān, son of Mūātūkān, son of Chaghatāī Khān, son of Chīngīz Khān"[16]
|
Moghulistan (Moghul Khanate) (1347–1543) |
Yarkent Khanate (1514–1705) |
Uyghurstan (Chalish-Turpan-Kumul) (1462–1690) |
Moghulistan (Western and Eastern)
References
- ^ "The Journey of Benedict Goës from Agra to Cathay" – Henry Yule's translation of the relevant chapters of De Christiana expeditione apud Sinas, with detailed notes and an introduction. In: Yule, Henry, ed. (1866). Cathay and the Way Thither: Being a Collection of Medieval Notices of China. Translated by Yule, Henry. Printed for the Hakluyt Society. p. 546.
- ^ Yuan Shi, volume 122 which contains the biography of Baurchuk Art Tekin, composed in 1370 by official Bureau of History in Ming dynasty China as the official chronicle of Yuan dynasty.
- ^ Bano, Majida (2002). "Mughal relations with the Kashghar Khanate". Proceedings of the Indian History Congress. 63: 1116–1119. JSTOR 44158181.
Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire, and Sa'id Khan were cousins, and the relationship was recognised in Babu'r memories. In a sense the Khanate and the Mughal Empire were built together, though there could be no military cooperation between the two, given the heights of the Hamalayas and the Karakoram Range that separated the two states.
- ^ a b Bhattacharji, Romesh (2012). Ladakh: Changing, Yet Unchanged. Rupa Publications. ISBN 978-8129117618.
Some 400 years earlier, in ad 1527, a Yarkandi invader, Sultan Saiad Khan Ghazi (also known as Daulat Beg) of Yarkand, briefly conquered Kashmir after fighting a battle along this pass. He died in 1531 at Daulat Beg Oldi (meaning, where Daulat Beg died) at the foot of the Karakoram pass, after he was returning from an unsuccessful attempt to invade Tibet.
- ^ Grousset, p. 500
- ^ Holdich, Thomas Hungerford (1906). Tibet: The Mysterious. New York: Frederick A. Stokes. p. 61.
- ^ Cacopardo, Alberto M.; Cacopardo, Augusto S. (2001). Gates of Peristan: History, Religion and Society in the Hindu Kush. Rome: Istituto Italiano per l'Africa e l'Oriente. p. 47. ISBN 9788863231496.
Mirza Haidar who led in 934/1527-28 an Islamic incursion into "Balur", describing it as "an infidel country (Kafiristan)" inhabited by "mountaineers" without any "religion or a creed" (Mirza Haidar 1895: 384), located "between Badakhshan and Kashmir" (ibid.: 136).
- ^ a b c Baumer, Christoph (2018). The History of Central Asia: The Age of Decline and Revival. Vol. 4. London: I. B. Tauris. ISBN 978-183860-867-5.
- ^ Bellew, Henry Walter (1875). The History of Káshgharia. Calcutta: Foreign Department Press. pp. 66–67.
(p66) Daulat Beg Uild ... "The lord of the State died" ... (p67) Hydar ... wrote the Tarikhi Rashidi from which these details are derived
- ^ a b Kohli, Harish (2000). Across the Frozen Himalaya: The Epic Winter Ski Traverse from Karakoram to Lipu Lekh. New Delhi: Indus Publishing. pp. 66–67. ISBN 81-7387-106-X.
According to H.W. Bellew, he was no ordinary traveller but a great warrior, a partisan of Babur, the conqueror of Ferghana and the king of Yarkand and Kashgar.
- ^ a b Bellew, Henry Walter (1875). "Kashmir and Kashghar: A Narrative of the Journey of the Embassy to Kashghar in 1873–74". Ludgate Hill: Trübner & Co. pp. 95–98 – via Internet Archive.
- ^ von Le Coq, Albert (2018) [First published 1926]. Buried Treasures of Chinese Turkestan: An Account of the Activities and Adventures of the Second and Third German Turfan Expeditions. Oxford: Routledge. p. 292. ISBN 978-0-429-87141-2.
Daulat Bak Oldi (the royal prince died here), close to the Karakorum pass, is so called because the Sultan Said Khan of Kashgar, on his return from a successful campaign against West Tibet, died here from mountain sickness (Plate 50)
- ^ Howard, Neil; Howard, Kath (2014). "Historic Ruins in the Gya Valley, Eastern Ladakh, and a Consideration of Their Relationship to the History of Ladakh and Maryul". In Lo Bue, Erberto; Bray, John (eds.). Art and Architecture in Ladakh: Cross-Cultural Transmissions in the Himalayas and Karakoram. Leiden: Brill. p. 88. ISBN 9789004271807.
When his Khan decided to return home because of ill health, leaving Mirza Haidar to destroy 'the idol temple of Ursang (i.e. Lhasa)', he 'set out from Maryul in Tibet, for Yarkand'. [...] He 'crossed the pass of Sakri', which must be that above Sakti (not the Kardung pass as Elias and Ross suggest), descended to Nubra and died at a camping place named Daulat Beg Uldi which is two-and-a-half hours below the Karakoram Pass.
- ^ Akimushkin, Oleg F. (2005). "The Alliance of the Chaghataids of Eastern Turkestan and of the Shibanids of Mawarannahr Against the Qazakhs in the Middle of the 16th Century". In Rasuly-Paleczek, Gabriele; Katschnig, Julia (eds.). Central Asia on Display: Proceedings of the VII Conference of the European Society for Central Asian Studies. Vol. 2. Wien: LIT Verlag Münster. p. 29. ISBN 3-8258-8586-0.
On the 16th dhu-l-hiddjja 939/July 9th, 1533, on the way back from campaign in Minor Tibet (Ladakh) the founder of the Moghuliyya-Chaghataid state in Eastern Turkestan, Sultan Said-khan died.
- ^ a b c d Gul-badan Begam (1902). The History of Humāyūn (Humāyūn-nāma). London: Royal Asiatic Society. pp. 213, 235–236, 261, 295.
- ^ Zahiru'd-din Muḥammad Bābur Pādshāh Ghāzi (1922). The Bābur-nāma in English (Memoirs of Bābur). Vol. 1. Translated by Beveridge, Annette Susannah. London: Sold by Luzac & Co. p. 19.
Bibliography
- Mirza Muhammad Haidar Dughlat. Tarikh-i-Rashidi. Translated and edited by Elias & Denison Ross (London, 1898)
- Makhmud ibn Vali. "Bahr al-Asrar" (Sea of mysteries). Written in Balkh in 7 volumes in 1641–1644. Translated from the Balkh original text by B. Akhmedov. (Tashkent, 1977)
- Muhammad Imin Sadr Kashgari. Asar al-futuh (Traces of Invasion). Original manuscript (never published, written in 1780 in Samarkand in Uighur language by the exiled author) in custody of Uzbekistan Academy of Sciences, No.753, in Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
- Kutlukov, M. Mongol rule in Eastern Turkestan. (Moscow, Nauka, 1970)
- Kutlukov, M. About emergence of Yarkand state. (Almaty, Gylym, 1990)
