24,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol: Difference between revisions
Updating {{chembox}} (no changed fields - added verified revid - updated 'DrugBank_Ref', 'UNII_Ref', 'ChEMBL_Ref', 'ChEBI_Ref', 'KEGG_Ref') per Chem/Drugbox validation (report errors or [[u... |
Added interactive pathway map |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
It is not known whether the compound might also have some physiologically significant activity. Some evidence of a possible receptor has been obtained.<ref name="pmid6981414">{{cite journal |author=Sömjen D, Sömjen GJ, Weisman Y, Binderman I |title=Evidence for 24,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol receptors in long bones of newborn rats |journal=Biochem. J. |volume=204 |issue=1 |pages=31–6 |year=1982 |month=April |pmid=6981414 |pmc=1158312 |doi= |url=}}</ref> |
It is not known whether the compound might also have some physiologically significant activity. Some evidence of a possible receptor has been obtained.<ref name="pmid6981414">{{cite journal |author=Sömjen D, Sömjen GJ, Weisman Y, Binderman I |title=Evidence for 24,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol receptors in long bones of newborn rats |journal=Biochem. J. |volume=204 |issue=1 |pages=31–6 |year=1982 |month=April |pmid=6981414 |pmc=1158312 |doi= |url=}}</ref> |
||
==Interactive pathway map== |
|||
{{VitaminDSynthesis_WP1531|highlight=24,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol}} |
|||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 21:58, 24 January 2012

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(6R)-6-[(1R,3aS,4E,7aR)-4-[(2Z)-2-[(5S)-5-hydroxy-2-methylenecyclohexylidene]ethylidene]-7a-methyl-2,3,3a,5,6,7-hexahydro-1H-inden-1-yl]-2-methylheptane-2,3-diol
| |
| Other names
24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3
(24R)-hydroxycalcifediol (24R)-hydroxycalcidiol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.049.754 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H44O3 | |
| Molar mass | 416.63 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
24,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol, also known as 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and (24R)-hydroxycalcidiol (abbreviated as 24(R),25-(OH)2D3),[1] is a compound which is closely related to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, the active form of vitamin D3, but like vitamin D3 itself and 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 is inactive as a hormone both in vitro[2] and in vivo.[3]
Formation and significance
24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is formed from 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 by the action of P450cc24 (25-hydroxyvitamin D3-24-hydroxylase), which appears to be "a multicatalytic enzyme catalyzing most, if not all, of the reactions in the C-24/C-23 pathway of 25-OH-D3 metabolism."[4] It has been proposed that 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a metabolite of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 which is destined for excretion.[4]
It is not known whether the compound might also have some physiologically significant activity. Some evidence of a possible receptor has been obtained.[5]
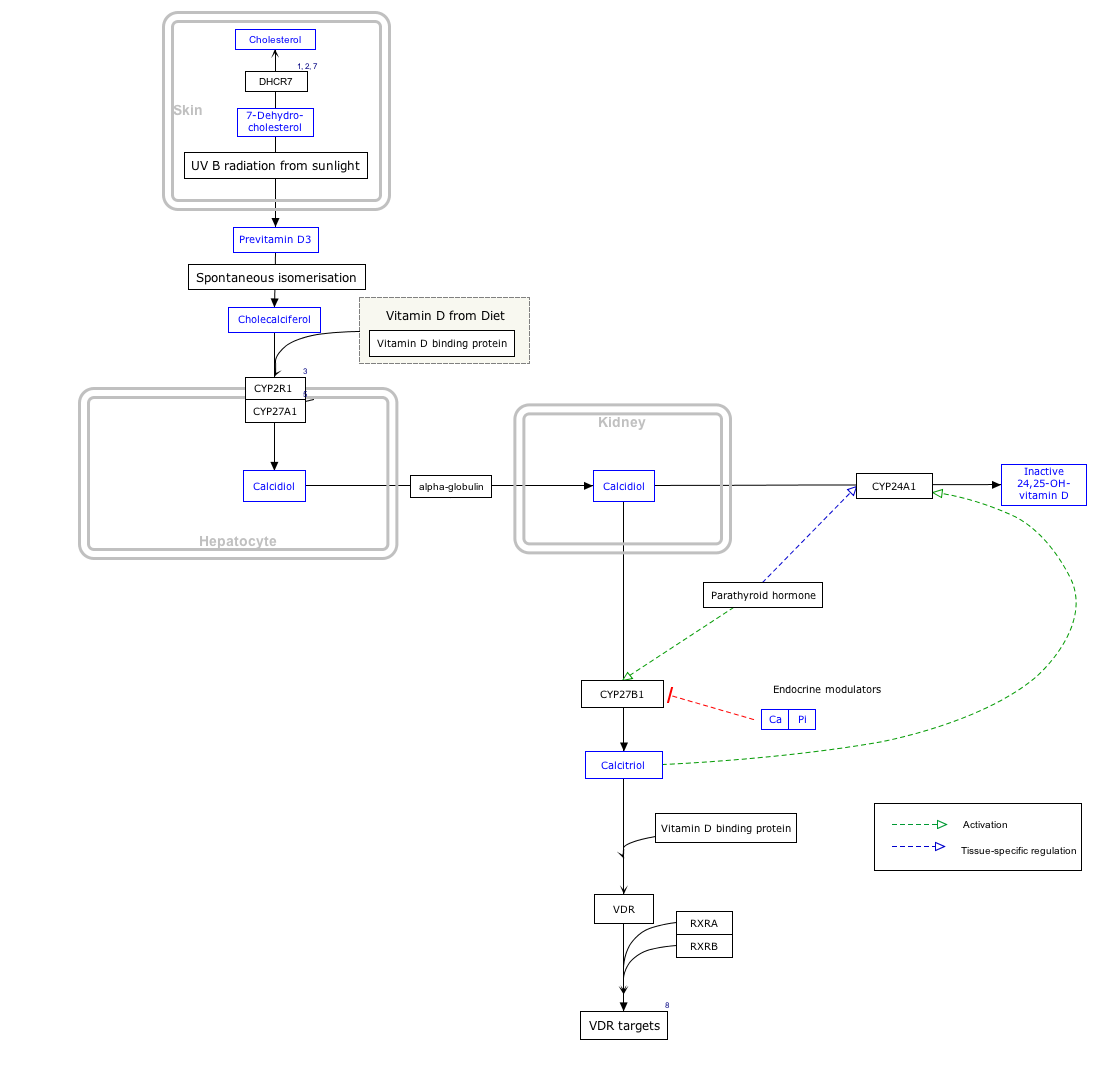
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- ^ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "VitaminDSynthesis_WP1531".
References
- ^ "Nomenclature of Vitamin D. Recommendations 1981. IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature (JCBN)" reproduced at the Queen Mary, University of London website. Retrieved 21 March 2010.
- ^ Sørnes S, Bjøro T, Berg JP, Torjesen PA, Haug E (1994). "Calcitriol attenuates the basal and vasoactive intestinal peptide-stimulated cAMP production in prolactin-secreting rat pituitary (GH4C1) cells." Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 101 (1-2): 183–8. PMID 9397951
- ^ Mortensen BM, Gautvik KM, Gordeladze JO (1993). "Bone turnover in rats treated with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 or 24,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3". Biosci. Rep. 13 (1): 27–39. PMID 8392394
- ^ a b Beckman, Matthew J.; Tadikonda, Praveen; Werner, Elizabeth; Prahl, Jean; Yamada, Sachiko; Deluca, Hector F. (1996). "Human 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3-24-Hydroxylase, a Multicatalytic Enzyme". Biochemistry. 35 (25): 8465–72. doi:10.1021/bi960658i. PMID 8679605.
- ^ Sömjen D, Sömjen GJ, Weisman Y, Binderman I (1982). "Evidence for 24,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol receptors in long bones of newborn rats". Biochem. J. 204 (1): 31–6. PMC 1158312. PMID 6981414.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Other articles
- Mata-Granados JM, Luque de Castro MD, Quesada Gomez JM (2008). "Inappropriate serum levels of retinol, alpha-tocopherol, 25 hydroxyvitamin D3 and 24,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 levels in healthy Spanish adults: simultaneous assessment by HPLC". Clin. Biochem. 41 (9): 676–80. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2008.02.003. PMID 18313404.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)