United Nations Convention Against Transnational Organized Crime: Difference between revisions
→Description: Titles of protocols |
|||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
*[[Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women and Children]]. |
*[[Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women and Children]]. |
||
*[[Protocol Against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air]]. |
*[[Protocol Against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air]]. |
||
*[[Protocol Against the Illicit Manufacturing and Trafficking in Firearms]]. |
*[[Protocol Against the Illicit Manufacturing of and Trafficking in Firearms]]. |
||
All four of these instruments contain elements of the current international law on [[human trafficking]], [[arms trafficking]] and [[money laundering]]. The [[United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime]] (UNODC) acts as custodian of the UNTOC and its protocols.<ref>{{Cite web|title=United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (Palermo Convention) {{!}} veritaszim|url=http://www.veritaszim.net/node/839|website=www.veritaszim.net|access-date=2020-05-30}}</ref> |
All four of these instruments contain elements of the current international law on [[human trafficking]], [[arms trafficking]] and [[money laundering]]. The [[United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime]] (UNODC) acts as custodian of the UNTOC and its protocols.<ref>{{Cite web|title=United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (Palermo Convention) {{!}} veritaszim|url=http://www.veritaszim.net/node/839|website=www.veritaszim.net|access-date=2020-05-30}}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 20:30, 30 August 2022
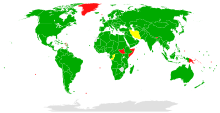 Signed and ratified or acceded
Only signed
Non-party | |
| Type | Organized crime; international criminal law |
|---|---|
| Drafted | 15 November 2000 |
| Signed | 12 December 2000 |
| Location | Palermo, Italy |
| Effective | 29 September 2003 |
| Condition | 40 ratifications |
| Signatories | 147 |
| Parties | 190 |
| Depositary | Secretary-General of the United Nations |
| Languages | Arabic, Chinese, English, French, Russian, and Spanish |
The United Nations Convention Against Transnational Organized Crime (UNTOC, also called the Palermo Convention) is a 2000 United Nations-sponsored multilateral treaty against transnational organized crime.
History
The convention was adopted by a resolution of the United Nations General Assembly on 15 November 2000. India joined on 12 December 2002.[1]
The Convention came into force on 29 September 2003. According to Leoluca Orlando, Mayor of Palermo, the convention was the first international convention to fight transnational organized crime, trafficking of human beings, and terrorism.[2]
In 2014, the UNTOC strengthened its policies regarding wildlife smuggling.[3] Botswana signed the Anti-Human Trafficking Act of 2014 to comply with UNTOC on the human smuggling protocol.[4]
In 2017, as Japan prepared the organization of the 2019 Rugby World Cup, and the 2020 Summer Olympics and Paralympics, it faced the issue of not being fully compliant with the UNTOC, thus jeopardizing its eligibility to organize those events.[5]
In February 2018, Afghanistan introduced a new penal code which made the country's laws UNTOC-compliant for the first time.[6]
Description
UNTOC's three supplementary protocols (the Palermo Protocols) are:[7]
- Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women and Children.
- Protocol Against the Smuggling of Migrants by Land, Sea and Air.
- Protocol Against the Illicit Manufacturing of and Trafficking in Firearms.
All four of these instruments contain elements of the current international law on human trafficking, arms trafficking and money laundering. The United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) acts as custodian of the UNTOC and its protocols.[8]
The UNTOC is the main legal international instrument to fight organized crime, but its efficiency depends on each member's ability to implement the organization's framework.[9] As an example, the UNTOC requires a minimum sentence of four years imprisonment for transnational organised criminal offences.[10]
Parties
As of 19 September 2017, it has 190 parties,[11] which includes 185 United Nations member states, the Cook Islands, the Holy See, Niue, the State of Palestine, and the European Union. The nine UN member states that are not party to the convention are (* indicates that the state has signed but not ratified the convention):
In June 2018, the Iranian Parliament approved the bill to join UNTOC, but 10 days later Ali Khamenei, Supreme Leader of Iran, called the bill "unacceptable" and blocked its progress.[12][13] In January 2019, the bill was still being debated between the Parliament and the Guardian Council.[14]
See also
- European Public Prosecutor
- International Criminal Police Organization
- ISO 37001 Anti-bribery management systems
- United Nations Convention against Corruption
References
- ^ India signs the UN Convention against Transnational Organised Crime (UNTOC), Mea.gov.in, 23 December 2002 (accessed on 18 August 2019)
- ^ Loredana Pianta, Researchers simulate mafia and terrorism recruitment, Phys.org, 25 July 2019 (accessed on 30 July 2019)
- ^ >Wildlife trafficking to become a ‘serious crime’ under UNTOC, Worldecr.com, 20 February 2014 (accessed on 18 August 2019)
- ^ Tshepo Mongwa, Botswana Makes Progress, Allafrica.com, 12 September 2018 (accessed on 18 August 2019)
- ^ Japan and an Anti-Crime Bill, Nytimes.com, 1 June 2017 (accessed on 18 August 2019)
- ^ Afghanistan: UN mission welcomes new penal code, urges measures to protect women from violence, Un.org, 22 February 2018 (accessed on 18 August 2019)
- ^ "UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION AGAINST TRANSNATIONAL ORGANIZED CRIME AND THE PROTOCOLS THERETO" (PDF). UNITED NATIONS OFFICE ON DRUGS AND CRIME. 2004. p. V. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- ^ "United Nations Convention against Transnational Organized Crime (Palermo Convention) | veritaszim". www.veritaszim.net. Retrieved 30 May 2020.
- ^ Laura Adal, Organised crime in Africa / Weak laws make tackling organised crime harder, Enactafrica.org, 8 November 2018 (accessed on 18 August 2019)
- ^ Carina Bruwer, Lions, tigers and bears: Wildlife trafficking in the age of globalisation, Dailymaverick.co.za, 20 February 2019 (accessed on 18 August 2019)
- ^ UN Convention against Transnational Organized Crime: Treaty status
- ^ Palermo Bills Suspended, Radiofarda.com, 25 Juily 2018 (accessed on 30 July 2019)
- ^ Iran's Watchdog Rejects Bills To Join U.N. Crime Conventions, Radiofarda.com, 15 July 2018 (accessed on 30 July 2019)
- ^ Iran Postpones Approval Of UN Convention Against Transnational Crime, Radiofarda.com, 19 January 2019 (accessed on 30 July 2019)
External links
- Organized crime
- United Nations treaties
- Treaties concluded in 2000
- Child labour treaties
- Treaties entered into force in 2003
- Treaties of the Afghan Transitional Administration
- Treaties of Albania
- Treaties of Algeria
- Treaties of Andorra
- Treaties of Angola
- Treaties of Antigua and Barbuda
- Treaties of Argentina
- Treaties of Armenia
- Treaties of Australia
- Treaties of Austria
- Treaties of Azerbaijan
- Treaties of the Bahamas
- Treaties of Bahrain
- Treaties of Bangladesh
- Treaties of Barbados
- Treaties of Belarus
- Treaties of Belgium
- Treaties of Belize
- Treaties of Benin
- Treaties of Bolivia
- Treaties of Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Treaties of Botswana
- Treaties of Brazil
- Treaties of Brunei
- Treaties of Bulgaria
- Treaties of Burkina Faso
- Treaties of Burundi
- Treaties of Cambodia
- Treaties of Cameroon
- Treaties of Canada
- Treaties of Cape Verde
- Treaties of the Central African Republic
- Treaties of Chad
- Treaties of Chile
- Treaties of the People's Republic of China
- Treaties of Colombia
- Treaties of the Comoros
- Treaties of the Cook Islands
- Treaties of Costa Rica
- Treaties of Ivory Coast
- Treaties of Croatia
- Treaties of Cuba
- Treaties of Cyprus
- Treaties of the Czech Republic
- Treaties of the Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Treaties of Denmark
- Treaties of Djibouti
- Treaties of Dominica
- Treaties of the Dominican Republic
- Treaties of Ecuador
- Treaties of Egypt
- Treaties of El Salvador
- Treaties of Equatorial Guinea
- Treaties of Eritrea
- Treaties of Estonia
- Treaties of Ethiopia
- Treaties of Fiji
- Treaties of Finland
- Treaties of France
- Treaties of Gabon
- Treaties of the Gambia
- Treaties of Georgia (country)
- Treaties of Germany
- Treaties of Ghana
- Treaties of Greece
- Treaties of Grenada
- Treaties of Guatemala
- Treaties of Guinea
- Treaties of Guinea-Bissau
- Treaties of Guyana
- Treaties of Haiti
- Treaties of the Holy See
- Treaties of Honduras
- Treaties of Hungary
- Treaties of Iceland
- Treaties of India
- Treaties of Indonesia
- Treaties of Iraq
- Treaties of Ireland
- Treaties of Israel
- Treaties of Italy
- Treaties of Jamaica
- Treaties of Japan
- Treaties of Jordan
- Treaties of Kazakhstan
- Treaties of Kenya
- Treaties of Kiribati
- Treaties of Kuwait
- Treaties of Kyrgyzstan
- Treaties of Laos
- Treaties of Latvia
- Treaties of Lebanon
- Treaties of Lesotho
- Treaties of Liberia
- Treaties of the Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
- Treaties of Liechtenstein
- Treaties of Lithuania
- Treaties of Luxembourg
- Treaties of Madagascar
- Treaties of Malawi
- Treaties of Malaysia
- Treaties of the Maldives
- Treaties of Mali
- Treaties of Malta
- Treaties of the Marshall Islands
- Treaties of Mauritania
- Treaties of Mauritius
- Treaties of Mexico
- Treaties of the Federated States of Micronesia
- Treaties of Monaco
- Treaties of Mongolia
- Treaties of Montenegro
- Treaties of Morocco
- Treaties of Mozambique
- Treaties of Myanmar
- Treaties of Namibia
- Treaties of Nauru
- Treaties of Nepal
- Treaties of the Netherlands
- Treaties of New Zealand
- Treaties of Nicaragua
- Treaties of Niger
- Treaties of Nigeria
- Treaties of Niue
- Treaties of North Korea
- Treaties of Norway
- Treaties of Oman
- Treaties of Pakistan
- Treaties of the State of Palestine
- Treaties of Panama
- Treaties of Paraguay
- Treaties of Peru
- Treaties of the Philippines
- Treaties of Poland
- Treaties of Portugal
- Treaties of Qatar
- Treaties of South Korea
- Treaties of Moldova
- Treaties of Romania
- Treaties of Russia
- Treaties of Rwanda
- Treaties of Samoa
- Treaties of San Marino
- Treaties of São Tomé and Príncipe
- Treaties of Saudi Arabia
- Treaties of Senegal
- Treaties of Serbia and Montenegro
- Treaties of Seychelles
- Treaties of Singapore
- Treaties of Slovakia
- Treaties of Slovenia
- Treaties of South Africa
- Treaties of Spain
- Treaties of Sri Lanka
- Treaties of Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Treaties of Saint Lucia
- Treaties of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Treaties of Sierra Leone
- Treaties of the Republic of the Sudan (1985–2011)
- Treaties of Suriname
- Treaties of Eswatini
- Treaties of Sweden
- Treaties of Switzerland
- Treaties of Syria
- Treaties of Tajikistan
- Treaties of North Macedonia
- Treaties of Thailand
- Treaties of East Timor
- Treaties of Togo
- Treaties of Tonga
- Treaties of Trinidad and Tobago
- Treaties of Tunisia
- Treaties of Turkey
- Treaties of Turkmenistan
- Treaties of Uganda
- Treaties of Ukraine
- Treaties of the United Arab Emirates
- Treaties of the United Kingdom
- Treaties of Tanzania
- Treaties of the United States
- Treaties of Uruguay
- Treaties of Uzbekistan
- Treaties of Vanuatu
- Treaties of Venezuela
- Treaties of Vietnam
- Treaties of Yemen
- Treaties of Zambia
- Treaties of Zimbabwe
- Treaties entered into by the European Union
- International criminal law treaties
- 2000 in New York (state)
- Treaties adopted by United Nations General Assembly resolutions
- Treaties extended to Aruba
- Treaties extended to the Falkland Islands
- Treaties extended to Gibraltar
- Treaties extended to the Cayman Islands
- Treaties extended to the British Virgin Islands
- Treaties extended to the Isle of Man
- Treaties extended to the Netherlands Antilles
- Treaties extended to Hong Kong
- Treaties extended to Macau
- Treaties extended to Guernsey
- Treaties extended to Jersey
- Treaties extended to Anguilla
- Treaties extended to the Turks and Caicos Islands
