Fukushima nuclear accident: Difference between revisions
Shinkolobwe (talk | contribs) m →Reactor unit 4: Minor edit |
|||
| Line 632: | Line 632: | ||
The [[United Nations]] predicted that a radiation [[Plume (hydrodynamics)|plume]] from the stricken Japanese reactors would reach the United States by 18 March. Health and nuclear experts emphasized that dilute radiation in the plume would affect health.<ref>[http://www.nytimes.com/2011/03/17/science/17plume.html?_r=1&hp Scientists Project Path of Radiation Plume] By William J. Broad, 16 March 2011, [[The New York Times]]</ref> A simulation by the Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy shows trace amounts of radioactivity reaching California and Mexico around 19 March.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Nouvelle simulation du nuage de pollution radioactive au Japon|date=2011-03-16|url=http://aeronomie.be/multimedia/video/daiichi3-washout_bira-iasb_animated.gif}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.zamg.ac.at/aktuell/index.php?seite=1&artikel=ZAMG_2011-03-15GMT08:26 |title=Aktuelle Informationen |publisher=ZAMG |date= |accessdate=18 March 2011}}</ref> |
The [[United Nations]] predicted that a radiation [[Plume (hydrodynamics)|plume]] from the stricken Japanese reactors would reach the United States by 18 March. Health and nuclear experts emphasized that dilute radiation in the plume would affect health.<ref>[http://www.nytimes.com/2011/03/17/science/17plume.html?_r=1&hp Scientists Project Path of Radiation Plume] By William J. Broad, 16 March 2011, [[The New York Times]]</ref> A simulation by the Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy shows trace amounts of radioactivity reaching California and Mexico around 19 March.<ref>{{Cite web|title=Nouvelle simulation du nuage de pollution radioactive au Japon|date=2011-03-16|url=http://aeronomie.be/multimedia/video/daiichi3-washout_bira-iasb_animated.gif}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.zamg.ac.at/aktuell/index.php?seite=1&artikel=ZAMG_2011-03-15GMT08:26 |title=Aktuelle Informationen |publisher=ZAMG |date= |accessdate=18 March 2011}}</ref> |
||
[[File:Fukushima trajectory forecast animation from 2011-03-19 to 2011-03-23.gif|thumb|Fukushima trajectory forecast animation from 2011-03-19 to 2011-03-23]] |
|||
Favorable westernly winds have been dominant during most of the first week of the accident. Five days trajectories for the time period 18–22 March run in the NOAA HYSPLIT model (at http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/ 12 UTC 18 March 2011) forecasts air packets that already left from the plant area towards the sea to change their direction towards the coast south of the plant at 19 March mid-day Japanese time. 20 March forecast shows air packets starting from the plant heading towards the Fukushima city and further to the Sendai area. 21 March forecast is to the direction 200 (SSW, South-South-West) like most of the 22nd March. 13 UTC 22 March trajectory (8 p.m. Japanese time) shows change in air flow direction again back towards the sea. Similar air movement is prediction results are presented by Finnish Metorological Institue for 19–20 March 2011<ref>[http://en.ilmatieteenlaitos.fi/japan], Updated 19/3 09:39AM UTC.</ref> |
Favorable westernly winds have been dominant during most of the first week of the accident. Five days trajectories for the time period 18–22 March run in the NOAA HYSPLIT model (at http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/ 12 UTC 18 March 2011) forecasts air packets that already left from the plant area towards the sea to change their direction towards the coast south of the plant at 19 March mid-day Japanese time. 20 March forecast shows air packets starting from the plant heading towards the Fukushima city and further to the Sendai area. 21 March forecast is to the direction 200 (SSW, South-South-West) like most of the 22nd March. 13 UTC 22 March trajectory (8 p.m. Japanese time) shows change in air flow direction again back towards the sea. Similar air movement is prediction results are presented by Finnish Metorological Institue for 19–20 March 2011<ref>[http://en.ilmatieteenlaitos.fi/japan], Updated 19/3 09:39AM UTC.</ref> |
||
Revision as of 16:38, 19 March 2011
This article documents a current event. Information may change rapidly as the event progresses, and initial news reports may be unreliable. The latest updates to this article may not reflect the most current information. (March 2011) |
| File:Fukushima I by Digital Globe 2.jpg Satellite image on 16 March of the four damaged reactor buildings | |
| Date | 11 March 2011 |
|---|---|
| Time | 14:46 JST (UTC+09:00) |
| Location | Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan |
| Coordinates | 37°25′17″N 141°1′57″E / 37.42139°N 141.03250°E |
| Outcome | Level 5 (Units 1, 2, and 3) Level 3 (Unit 4): level 6 (serious accident): |
| Deaths | 2 missing |
| Non-fatal injuries | 37 (none reported as due to radiation contamination)[6] |
The Fukushima I nuclear accidents (福島第一原子力発電所事故, fukushima daiichi genshiryoku hatsudensho jiko) are a series of ongoing equipment failures and releases of radiation at the Fukushima I Nuclear Power Plant, following the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami on 11 March 2011. The plant comprises six separate boiling water reactors maintained by the Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO). Reactors 4, 5, and 6 had been shut down prior to the earthquake for planned maintenance.[7] The remaining reactors were shut down automatically after the earthquake, but the subsequent tsunami flooded the plant, knocking out emergency generators needed to run pumps which cool and control the reactors. The flooding and earthquake damage prevented assistance being brought from elsewhere.
Over the following days there was evidence of partial nuclear meltdowns in reactors 1, 2, and 3; hydrogen explosions destroyed the upper cladding of the buildings housing reactors 1, 3, and 4; an explosion damaged reactor 2's containment; and multiple fires broke out at reactor 4. Fears of radiation leaks led to a 20 km (12-mile) radius evacuation around the plant.
TEPCO employees and workers from other companies not involved in essential work were temporarily evacuated after an explosion was heard in the suppression chamber of reactor building 2.[8] Employees returned after it was confirmed that there had not been a containment breach but evacuated again on 16 March following a spike in radiation.[9][10][11] On Friday 18 March, Japanese officials designated the magnitude of the danger at reactors 1, 2 and 3 at level 5, on the 7 point International Nuclear Event Scale (INES).[12]
The gravity of the disaster is such that many international leaders have expressed concerns. Radiation leaks beyond the plant's boundaries had not been high enough to constitute any significant danger to the public, but the Japanese Government and TEPCO have been criticized for poor communications over the incident.[13][14]
A replacement grid power connection of over a kilometer-long was laid to the plant and power was expected to be reconnected to the 4 damaged reactors on March 20 although it was unclear what condition the various pump and machinery were in after the fires and explosions.[15] On 19 March, food raised in the Fukushima area was banned from sale due to contamination and traces of radioactive iodine were found in drinking water in Tokyo.[16] [17]
Summarised daily events
- 11 March: 14:46 JST (05:46 UTC): Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami. The Japanese government declared a nuclear power emergency due to the failure of the reactor cooling systems in reactors of Fukushima I and evacuated thousands of residents living with 2 km of the reactor.[18][19]
- 12 March: while evidence of partial meltdown of the fuel rods in unit 1 was growing, a hydrogen explosion destroyed the upper section of the building housing unit 1. The explosion injured four workers, but the reactor containment inside the building remained intact.[20][21] Hydrogen and steam had been vented from the reactor to reduce pressure within the containment vessel and built up within the building.[22][23] Operators of the plant began using sea water for emergency cooling, which would permanently damage the reactor.[24] The evacuation zone was extended to 20 km, affecting 170,000–200,000 people, and the government advised residents within a further 10 km to stay indoors.[25][26] The release of fission products from the damaged reactor core, notably radioactive iodine-131, led Japanese officials to distribute prophylactic iodine to people living around Fukushima I and Fukushima II.[27] but only one worker was confirmed to be ill. The US government offered to provide technical assistance in dismantling the fuel rods at plants in which the cooling systems were having problems before the fuel began to overheat, but the offer was refused by the Japanese government.[28]
- 13 March: a partial meltdown was possible at unit 3. As of 13:00 JST, both reactors 1 and 3 were being vented and re-filled with water and boric acid to reduce temperatures and inhibit further nuclear reactions.[29] Unit 2 was possibly suffering lower than normal water level but to be stable, although pressure inside the containment vessel was high.[29] The Japan Atomic Energy Agency announced that it was rating the situation at unit 1 as level 4 (accident with local consequences) on the International Nuclear and Radiological Event Scale.[30][31]
- 14 March: the reactor building for unit 3 exploded[32] injuring eleven people. There was no release of radioactive material beyond that already being vented but blast damage affected water supply to unit 2.[33] The president of the French nuclear safety authority, Autorité de sûreté nucléaire (ASN), said that the accident should be rated as a 5 ( accident with wider consequences) or even a 6 (serious accident) on INES.[34]
- 15 March: damage to temporary cooling systems on unit 2 by the explosion in unit 3 plus problems with its venting system meant that water could not be added, to the extent that unit 2 was in the most severe condition of the three reactors.[35] An explosion in the "pressure suppression room" caused some damage to unit 2’s containment system.[35][36] A fire broke out at unit 4 involving spent fuel rods from the reactor, which are normally kept in the water-filled spent fuel pool to prevent overheating. Radiation levels at the plant rose significantly but subsequently fell back.[37] Radiation equivalent dose rates at one location in the vicinity of unit 3 recorded 400 millisieverts per hour (400 mSv/h).[38][39][30]
- 16 March: At approximately 14:30 on 16 March, TEPCO announced its belief that the fuel rod storage pool of unit 4—which is located outside the containment area[40]-may have begun boiling, raising the possibility that exposed rods could reach criticality.[41] By midday, NHK TV was reporting white smoke rising from the Fukushima I plant, which officials suggested was likely coming from reactor 3. Shortly afterwards, all but a small group[42] of remaining workers at the plant had been placed on standby because of the dangerously rising levels of radioactivity up to 1,000 mSv/h.[11][43] TEPCO had temporarily suspended operations at the facility due to radiation spikes and had pulled all their employees out.[44] A TEPCO press release stated that workers had been withdrawn at 06:00 JST because of abnormal noises coming from one of the reactor pressure suppression chambers.[45] Late in the evening, Reuters reported that water was being poured into reactors 5 and 6.[46]
- 17 March: During the morning, Self-Defense Force helicopters four times dropped water on the spent fuel pools of units 3 and 4.[47] In the afternoon it was reported that the unit 4 spent fuel pool was full with water and none of the fuel rods was exposed.[48] Construction work was started to supply a working external electrical power source to all six units of Fukushima I.[49] Starting at 7 pm, police and fire water trucks with high pressure hoses attempted to spray water into the unit 3 reactor.[50] Japanese authorities informed the IAEA that engineers were laying an external grid power line cable to unit 2. The operation was continuing as of 20:30 UTC.[30]
- 18 March: Pursuant to a request from Tokyo Governor Shintaro Ishihara, Tokyo Fire Department dispatched thirty fire engines with 139 fire-fighters and trained rescue team at approximately 03:00 JST. These include a fire truck with a 22 m water tower; all units will join Japan Defense Forces fire equipment which is already deployed.[51] JDF anticipated utilizing TFD equipment to address low water which was confirmed to exist in unit 4 and also an emergent concern with unit 3, which appeared to be more problematic than previously believed. Winds were forecast to shift to the northeast, which would continue to be toward the sea.[52] For the second consecutive day, high radiation levels had been detected in an area 30 kilometers (18.6 miles) northwest of the damaged Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant. The reading was 150 microsieverts per hour. Human exposure to that level of radiation for six to seven hours would result in absorption of what is considered safe in a year.[53] Japanese authorities upgraded INES ratings for cooling loss and core damage at unit 1 to level 5 and issued the same rating for units 2 and 3.[30] The loss of fuel pool cooling water at unit 4 was classified as level 3.[30] It was anticipated to restore power to units 1 and 2 on 19 March and the other units on 20 March.[54] The president of the Tokyo Electric Power Company, TEPCO.[55] In a 24-period ending at 11 am local time, radiation levels near the plant had declined from 351.4 microsieverts per hour to 265 microsieverts per hour, but it was unclear if the water spraying efforts was the cause of the decrease.[56]
- 19 March: A second group of 100 Tokyo firefighters replaced the previous team. They used a vehicle that can project water from a height of 22 meters for cooling spent nuclear fuel storage pool inside the reactor of Unit 3.[57] Water was sprayed into the reactor for a total of 7 hours during the day. TEPCO reported afterwards that the water had been effective in lowering the temperature around the spent fuel rods to below 100 °C.[58][verification needed]
Fukushima I Nuclear Power Plant
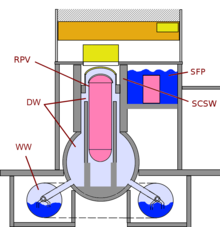
The Fukushima I Nuclear Power Plant is located in the town of Okuma in the Futaba District of Fukushima Prefecture, Japan, about 210 kilometers (130 miles) north of Tokyo.[59] It consists of six light water, boiling water reactors (BWR) designed by General Electric with a combined power of 4.7 gigawatts, making Fukushima I one of the 25 largest nuclear power stations in the world. Fukushima I was the first nuclear plant to be constructed and run entirely by the Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO).
Unit 1 is a 439 MWe type (BWR3) reactor constructed in July 1967. It commenced commercial electrical production on 26 March 1971.[60] It was designed for a peak ground acceleration of 0.18 g (1.74 m/s2) and a response spectrum based on the 1952 Kern County earthquake.[61] Units 2 and 3 are both 784 MW type BWR-4 reactors, Unit 2 commenced operating in July 1974 and Unit 3 in March 1976. All units were inspected after the 1978 Miyagi earthquake when the ground acceleration was 0.125 g (1.22 m/s2) for 30 seconds, but no damage to the critical parts of the reactor was discovered.[61]
Units 1–5 have a Mark 1 type (light bulb torus) containment structure, unit 6 has Mark 2 type (over/under) containment structure.[61] From September 2010, unit 3 has been fueled by mixed-oxide (MOX) fuel.[62]
Cooling requirements
Cooling is needed to remove decay heat even when a plant has been shut down. Nuclear fuel releases a small quantity of heat under all conditions, but the chain reaction when a reactor is operating creates short lived decay products which initially produce roughly 6.6% of full thermal heat (~100 MW for reactors 2 and 3) and then decrease over several days before reaching cold shutdown levels.[63] The nuclear fuel requires 1–3 years of constant active cooling (by flowing water) before the decay heat production gets low enough that effective passive cooling becomes sufficient to avoid excessive heating up to temperatures where the integrity of the fuel is at risk. Boiling water reactors have steam-turbine driven emergency core cooling systems that can be directly operated by steam produced after a reactor shutdown and can inject water directly into the reactor. Using these pumps, boiling water reactors can provide water without electrically driven pumps, but only while the reactor is at pressure. This results in less dependence on emergency generators but only operates so long as the reactor is safely producing steam, and some power is still needed to operate the valves and monitoring systems.
When a reactor is shut down, decay heat is usually removed from the fuel by circulating water over it. High pressure systems circulate water through the reactor pressure vessel and pipework. The heated water is cooled in water-water heat exchangers, the heat passing to sea water circulated through the secondary side of the heat exchangers. In this way the decay heat is pumped out to sea and disperses. The systems which do this are typically called residual heat removal, for normal removal of decay heat during a planned shutdown, or emergency core cooling systems for core cooling after an accident. They may be the same systems, or share pumps, valves, heat exchangers etc.

At the time of the earthquake on 11 March, units 1, 2, and 3 were operating and units 4, 5, and 6 were out of service for scheduled maintenance and refueling. When the earthquake occurred, units 1, 2, and 3 were shut down as a standard response to an earthquake, stopping on-site generation of electricity. A few minutes later, incoming electrical supplies from the grid were also lost as a result of the earthquake. Initially on site diesel generators supplied power to the residual heat removal system, cooling the reactor cores as designed. The diesel generators failed shortly after the tsunami, and alternative power arrangements were insufficient to support the control systems for the normal or emergency cooling systems. Had these systems continued to operate, the core temperature would have remained under control, with no damage to the reactor or its fuel, and even with some fuel damaged and partially melted the reactor could have been brought under control. The first attempts to restore electrical connections to the grid to enable the cooling systems to be operated were reported on 17 March. This effort was impeded initially by the tsunami damage in the area of the plant and then by the damage caused by the explosions at the plant.
Merely pumping water into the reactor containment does not get the water into the pressurised reactor vessel and pipework and into contact with the fuel. Fire trucks and water cannon cannot achieve the required pressures. The operators tried to fill the reactor containment with water to cool the molten core if it melted through the steel reactor pressure vessel (or to keep the exterior of the steel reactor pressure vessel cool enough to prevent it from melting, if molten fuel reached the bottom of the steel pressure vessel). This would generate large amounts of steam within the containment. If the Fukushima reactors are fitted with containment coolers - heat exchangers like the residual heat removal heat exchangers - then this steam could be condensed and recirculated. If there are no containment coolers, or they are not working, then the steam would have to be vented and replaced with more water from outside the containment.
A decay heat output of 10 MW (typical of a power reactor a few days after shutdown) has the capacity to boil off over three hundred tonnes of water per day, which puts the requirement for cooling water in context.
Direct effect of the 2011 earthquake and tsunami
The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, categorised as 9.0 MW on the moment magnitude scale occurred on 11 March 2011, at 14:46 Japan Standard Time (JST) off the northeast coast of Japan. On that day, reactor units 1, 2, and 3 were operating, but units 4, 5, and 6 had already been shut down for periodic inspection.[64] When the earthquake was detected, units 1, 2 and 3 underwent an automatic shutdown (called scram).[65]

After the reactors shut down, electricity generation stopped. Normally the plant could use the external electrical supply to power cooling and control systems,[66] but the earthquake had caused major damage to the power grid. Emergency diesel generators started but stopped abruptly at 15:41, ending all AC power supply to the reactors. The plant was protected by a sea wall, but the tsunami topped this sea wall, flooding the low lying generator building.[67][68] Article 10 of the Japanese law on Special Measures Concerning Nuclear Emergency Preparedness, heightened alert condition requires authorities to be informed of such an incident: TEPCO did so immediately and also issued a press release declaring a "First Level Emergency".[65]
After the failure of the diesel generators, emergency power for control systems was supplied by batteries that would last about eight hours.[19] Batteries from other nuclear plants were sent to the site and mobile generators arrived within 13 hours,[69] but work to connect portable generating equipment to power water pumps was still continuing as of 15:04 on 12 March.[18] Generators would normally be connected through switching equipment in a basement area of the buildings, but this basement area had been flooded.[67] After subsequent efforts to bring water to the plant, plans shifted to a strategy of building a new power line and re-starting the pumps, eventually resulting in cable emplacement reported at approximately 08:30 UTC.[70]
Reactor unit 1
Cooling problems at unit 1

On 11 March 2011 at 16:36 JST, a Nuclear Emergency Situation (Article 15 of the Japanese law on Special Measures Concerning Nuclear Emergency Preparedness) was declared when "the status of reactor water coolant injection could not be confirmed for the emergency core cooling systems of Units 1 and 2." The alert was temporarily cleared when water level monitoring was restored for unit 1; however, it was reinstated at 17:07 JST.[71] Potentially radioactive steam was released from the primary circuit into the secondary containment area to reduce mounting pressure.[72]
In the early hours of 12 March TEPCO reported that radiation levels were rising in the turbine building for unit 1[73] and that it was considering venting some of the mounting pressure into the atmosphere, which could result in the release of some radiation.[74] Chief Cabinet Secretary Yukio Edano stated later in the morning the amount of potential radiation would be small and that the prevailing winds were blowing out to sea.[75] At 02:00 JST, the pressure inside the reactor containment was reported to be 600 kPa (6 bar or 87 psi), 200 kPa higher than under normal conditions.[68] At 05:30 JST the pressure inside reactor 1 was reported to be 2.1 times the "design capacity",[76] 820 kPa.[20] Rising heat within the containment area led to increasing pressure, with both cooling water pumps and ventilation fans for driving gases through heat exchangers within the containment dependent on electricity.[77] Releasing gases from the reactor is necessary if pressure becomes too high and has the benefit of cooling the reactor as water boils off, but this also means cooling water is being lost and must be replaced.[67] Assuming no damage to the fuel elements, water inside the reactor should be only very slightly radioactive.
In a press release at 07:00 JST 12 March, TEPCO stated, "Measurement of radioactive material (iodine, etc.) by monitoring car indicates increasing value compared to normal level. One of the monitoring posts is also indicating higher than normal level."[78] Dose or dose-equivalent rates recorded on the main gate rose from 69 nGy/h (for gamma radiation, equivalent to 0.069 µSv/h) at 04:00 JST, 12 March, to 866 nGy/h (equivalent to 0.866 µSv/h) 40 minutes later, before hitting a peak of 385.5 μSv/h at 10:30 JST.[78][79][80][81] At 13:30 JST, workers detected radioactive caesium-137 and iodine-131 near reactor 1,[82] which indicated some of the core's fuel was exposed due to a partial-meltdown or other damage of the nuclear fuel.[83] The NHK website reported that cooling water had lowered so much that parts of the nuclear fuel rods were exposed.[84] Radiation levels at the site boundary exceeded the regulatory limits.[85] Kyodo News Service later reported that partial melting might have occurred.[30][86][87][88] On 14 March 2011, Kyodo News reported radiation levels had continued to increase on the premises, measuring at 02:20 an intensity of 751 μSv/hour on one location and at 02:40 an intensity of 650 μSv/hour at another location on the premises.[89] On 16 March the maximum readings peaked at 10850 μSv/hour.[90]
Explosion of reactor 1 building
At 15:36 JST on 12 March 2011 there was an explosion at Unit 1. Four workers were injured, and the upper shell of the reactor building was blown away leaving in place its steel frame.[91][92] The outer building is designed to provide ordinary weather protection for the areas inside, but not to withstand the high pressure of an explosion or to act as containment for the reactor. In the Fukushima I reactors the primary containment consists of "drywell" and "wetwell" concrete structures immediately surrounding the reactor pressure vessel.[20][93]

Experts soon agreed the cause was a hydrogen explosion.[21][94][95] Almost certainly the hydrogen was formed inside the reactor vessel[21] because of falling water levels, and this hydrogen then leaked into the containment building.[21] Exposed Zircaloy metal clad fuel rods become very hot and can then react with steam oxidising the metal and releasing hydrogen.[96] Safety devices should remove the hydrogen when it is vented before explosive concentrations are reached but these systems failed, or could not be operated due to the shortage of electrical power.
Officials indicated the container of the reactor had remained intact and there had been no large leaks of radioactive material,[20][21] although an increase in radiation levels was confirmed following the explosion.[97][98] ABC News (Australia) reported that according to the Fukushima prefectural government, radiation dose rates at the plant reached 1.015 micro sievert per hour (1.015 µSv/h).[99] Two independent nuclear experts cited design differences between the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant and the Fukushima I Nuclear Power Plant,[100][101] one of them saying he did not believe that a Chernobyl-style disaster will occur.[100]
The IAEA stated on 13 March that four workers had been injured by the explosion at the Unit 1 reactor, and that three injuries were reported in other incidents at the site. They also reported one worker was exposed to higher-than-normal radiation levels but that fell below their guidance for emergency situations.[102]
Seawater used for cooling
At 20:05 on 12 March 2011, under the terms of the Nuclear Regulation Act, paragraph 3, article 64 and a directive issued by the Prime Minister, the Japanese government ordered seawater to be injected into Unit 1 in an ultimate effort to cool the degraded reactor core.[18] At 21:00 JST TEPCO announced they planned to cool the reactor with seawater (started at 20:20 JST), adding boric acid to act as a neutron absorber to prevent a criticality accident.[103][104] The water was to take five to ten hours to fill the reactor core, after which the reactor would cool down in around ten days.[21] At 23:00 JST TEPCO announced due to the quake at 22:15,[105] workers had temporarily suspended filling of the reactor but filling resumed after a short while.[20][106] The last resort decision to recirculate seawater as coolant in the reactor implied de facto to contaminate the inner core with corrosive salts (mainly NaCl) and matters in suspension, meaning the reactor would have to be decommissioned anyway.[24]
NISA reported that injection of seawater into the Reactor Pressure Vessel through the fire extinguisher system commenced at 11:55 on 13 March.[107] At 01:10 on 14 March injection of seawater was halted because all available water in the plant pools had run out (similarly, feed to unit 3 was halted). Water supply was restored at 03:20.[107]
NISA stated 70% of the fuel rods were damaged in news reports the morning of 16 March.[108]
On 18 March work was proceeding to install a new electrical distribution panel in an office adjacent to unit 1 which was to supply power from a transmission grid transformer at unit 2. It was anticipated power would be restored to units 1 and 2 by the following Saturday (19 Mar).[109]
Reactor unit 2
Unit two was operational during the earthquake and experienced the same cooling procedures directly after the earthquake (power supply by diesel engine, which failed after about an hour), and stable water levels were reported. Some power was achieved by mobile power units, while preparations were made to perform pressure venting.[20][110] A report in the New York Times suggested that plant officials initially concentrated efforts on a damaged fuel storage pool at unit 2, distracting attention from problems arising at the other reactors.[111]
Cooling problems at unit 2
On 14 March, at 15:29 JST the Jiji news agencies reported that the cooling functions at reactor unit 2 had stopped and that the cooling water levels in the reactor were falling.[112][113] This happened when fuel for pumps ran out.[114] Jiji news agencies later reported that nuclear fuel rods at reactor unit 2 were fully exposed and there was a risk of a full meltdown at reactor unit 2.[115] Jiji later reported that according to TEPCO, a meltdown cannot be ruled out.[116]
At 22:29 JST, workers had succeeded in refilling half the reactor with water. However, at that time, part of the rods were still exposed, and technicians could not rule out the possibility that fuel rods had melted. Work was in hand to demolish parts of the walls of reactor building 2 to allow the escape of hydrogen and hopefully prevent another explosion.[117] At 21:37 JST the measured radiation rates at the gate of the plant had reached a maximum of 3.13 millisievert per hour, which was enough to reach the annual limit for non-nuclear workers in twenty minutes,[117] but had fallen back to 0.326 millisieverts per hour by 22:35.[118]
It was believed that around 23:00 JST the 4 m long fuel rods in the reactor were fully exposed for the second time.[117][119] At 00:30 JST of 15 March, NHK ran a live press conference with TEPCO stating that the water level had sunk under the rods once again and pressure in the vessel was raised. The utility said that the hydrogen explosion at unit 3 might have caused a glitch in the cooling system of unit 2: Four out of five water pumps being used to cool unit 2 reactor had failed after the explosion at unit 3. In addition, the last pump had briefly stopped working.[120] To replenish the water, the contained pressure would have to be lowered first by opening a valve of the vessel. The unit's air flow gauge was accidentally turned off and, with the gauge turned off, flow of water into the reactor was blocked leading to full exposure of the rods.[117][121]
As of 04:11 JST, 15 March, water was being pumped into the reactor of unit 2 again.[122] At 10:38 JST, 15 March, water level was reported to be at 1.20 meters and rising.[123]
Explosion in reactor 2 building
An explosion was heard after 06:14 JST[124] on 15 March in unit 2, possibly damaging the pressure-suppression system, which is at the bottom part of the containment vessel.[125][126] The radiation level was reported to exceed the legal limit and the plant's operator started to evacuate all non-essential workers from the plant.[127] Only a minimum crew of 50 men, also referred to as the Fukushima 50, was left at the site.[128] Soon after, radiation equivalent dose rates had risen to 8.2 mSv/h[129] around two hours after the explosion and again down to 2.4 mSv/h, shortly after.[130] Three hours after the explosion, the rates had risen to 11.9 mSv/h.[131]
While admitting that the suppression pool at the bottom of the containment vessel had been damaged in the explosion, causing a drop of pressure there, Japanese nuclear authorities emphasized that the containment had not been breached as a result of the explosion and contained no obvious holes.[132]
In a news conference on 15 March the director general of the IAEA, Yukiya Amano, said that there was a "possibility of core damage" at the No. 2 unit of the damaged Fukushima power plant. He went on to add that the damage was estimated as being "less than five percent".[133] The Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency stated 33% of the fuel rods were damaged, in news reports the morning of 16 March.[108]
Work was to continue through the night aimed at reconnecting mains power to the reactor from the transmission grid once water spraying of unit 3 ceased at 20:09 on 17 March.[134] By midday on 19 March grid power had been connected to the existing transformer at unit 2 but work continued to connect the transformer to the new distribution panel installed in a nearby building.[135]
Reactor unit 3
Unlike the other five reactor units, reactor 3 runs on mixed uranium and plutonium oxide, or MOX fuel, making it potentially more dangerous in an incident due to the neutronic effects of plutonium on the reactor and the carcinogenic effects[136] in the event of release to the environment.[86][137][138] Units 3 and 4 have a shared control room.[139]
Cooling problems at unit 3
Early on 13 March 2011, an official of the Japan Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency told a news conference that the emergency cooling system of Unit 3 had failed, spurring an urgent search for a means to supply cooling water to the reactor vessel in order to prevent a meltdown of its reactor core.[140] At 05:38 there was no means of adding coolant to the reactor due to loss of power. Work to restore power and vent pressure continued.[141] At one point, the top three meters of mixed oxide (MOX) fuel rods were not covered by coolant.[142]
At 07:30 JST, TEPCO prepared to release radioactive steam, indicating that "the amount of radiation to be released would be small and not of a level that would affect human health"[143] and manual venting took place at 08:41 and 09:20.[110] At 09:25 JST on 13 March 2011, operators began injecting water containing boric acid into the primary containment vessel (PCV) via a fire pump.[144][145] When water levels continued to fall and pressure to rise, the injected water was switched to sea water at 13:12.[141] By 15:00 it was noted that despite adding water the level in the reactor did not rise and radiation had increased.[146] A rise was eventually recorded but the level stuck at 2 m below the top of reactor core. Other readings suggested that this could not be the case and the gauge was malfunctioning.[110]
Injection of sea water into the PCV was discontinued at 01:10 on 14 March because all the water in the reserve pool had been used up. Supplies were restored by 03:20 and injection of water resumed.[145] On the morning of 15 March 2011 (JST), Secretary Edano announced that according to the TEPCO, at one location near reactor units 3 and 4, radiation at an equivalent dose rate of 400 mSv/h was detected,[38][39][30] but this might have been due to debris from the explosion in unit 4.[147]
Explosion of reactor 3 building
At 12:33 JST on 13 March 2011, the chief spokesman of the Japanese government, Yukio Edano said hydrogen was building up inside the outer building of Unit 3 just as had occurred in Unit 1, threatening the same kind of explosion.[148] At 11:15 JST on 14 March 2011, the envisaged explosion of the building surrounding reactor 3 of Fukushima 1 occurred, due to the ignition of built up hydrogen gas.[149][150] The Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency of Japan reported, as with Unit 1, the top section of the reactor building was blown apart, but the inner containment vessel was not breached. The explosion was larger than that in Unit 1 and felt 40 kilometers away. Pressure readings within the reactor remained steady at around 380 kPa at 11:13 and 360 kPa at 11:55 compared to nominal levels of 400 kPa and a maximum recorded of 840 kPa. Water injection continued. Radiation rates of 0.05 mSv//h were recorded in the service hall and of 0.02 mSv/h at the plant entrance.[151] Eleven people were reported injured in the blast.[152][153]
Spent fuel pool
Around 10:00 JST, 16 March, NHK helicopters flying 30 km away videotaped white fumes rising from the Fukushima I facility. Officials suggested that the reactor 3 building was the most likely source, and said that its containment systems may have been breached.[154] The control room for reactors 3 and 4 was evacuated at 10:45 JST but staff were cleared to return and resume water injection into the reactor at 11:30 JST.[139] At 16:12 JST Self Defence Force (SDF) Chinook helicopters were preparing to pour water on unit 3, where white fumes rising from the building was believed to be water boiling away from the fuel rod cooling pond on the top floor of the reactor building, and on unit 4 where the cooling pool was also short of water. The mission was cancelled when helicopter measurements reported radiation levels of 50 mSv.[155][156] At 21:06 pm JST government reported that major damage to reactor 3 was unlikely but that it nonetheless remained their highest priority.[157] Early on 17 March, TEPCO requested another attempt by the military to put water on the reactor using a helicopter[158] and four helicopter drops of seawater took place around 10:00 JST.[159] The riot police used a water cannon to spray water onto the top of the reactor building and then were replaced by members of the SDF with spray vehicles.[134][134] On 18 March a crew of firemen took over the task with six fire engines each spraying 6 tons of water in 40 minutes. 30 further hyper rescue vehicles were involved in spraying operations.[160]
Reactor unit 4
At the time of the earthquake unit 4 had been shut down for a scheduled periodic inspection since 30 November 2010. All 548 fuel rods had been transferred in December 2010 from the reactor to the spent fuel pool on an upper floor of the reactor building[161] where they were held in racks containing boron to damp down any nuclear reaction.[147] The pool is used to store rods for some time after removal from the reactor and now contains 1,479 rods.[162] Recently active fuel rods produce more decay heat than older ones.[163] At 04:00 JST on Monday 14 March, water in the pool had reached a temperature of 84 °C compared to a normal value of 40-50 °C.[147] IAEA was advised that the temperature value remained 84 °C at 19:00 JST on 15 March, but as of 18 March, no further information was reported.[30][107]
Explosion of reactor 4 building
At approximately 06:00 JST on 15 March, an explosion—thought to have been caused by hydrogen accumulating near the spent fuel pond—damaged the 4th floor rooftop area of the Unit 4 reactor as well as part of the adjacent Unit 3.[164][165] At 09:40 JST, the Unit 4 spent fuel pool caught fire, likely releasing radioactive contamination from the fuel stored there.[166][167] TEPCO said workers extinguished the fire by 12:00.[168][169] As radiation levels rose, some of the employees still at the plant were evacuated.[170]
On the morning of 15 March 2011 (JST), Secretary Edano announced that according to the Tokyo Electric Power Company, radiation dose equivalent rates measured from the reactor unit 4 reached 100 mSv per hour.[38][39] Government speaker Edano has stated that there was no continued release of "high radiation".[171]
Japan's nuclear safety agency reported two holes, each 8 meters square (64 m2 or 689 sq. feet) in a wall of the outer building of the number 4 reactor after an explosion there.[172] Further, at 17:48 JST it was reported that water in the spent fuel pool might be boiling.[173][174]
As of 15 March 2011 21:13 JST, radiation inside unit 4 had increased so much inside the control room that employees could not stay there permanently any more.[175] Seventy staff remained on site but 800 had been evacuated.[176] By 22:30 JST, TEPCO was reported to be unable to pour water into No. 4 reactor's storage pool for spent fuel.[147] At around 22:50 JST, it was reported that TEPCO was considering using helicopters to drop water on the spent fuel storage pool.[176][177][178] However, TEPCO delayed using the option of helicopters because of concerns over safety and effectiveness. TEPCO went on to consider the use of high-pressure fire hoses instead.[179]
A fire was discovered at 05:45 JST on 16 March in the north west corner of the reactor building by a worker taking batteries to the central control room of unit 4.[180][181] This was reported to the authorities, but on further inspection at 06:15 no fire was found. Other reports stated that the fire was under control.[182] At 11:57 JST, TEPCO released a photograph of No.4 reactor showing that "a large portion of the building's outer wall has collapsed."[183] Technicians reportedly considered spraying boric acid on the building from a helicopter.[184][185]
Water sprayed into the pool of unit No. 4 is disappearing faster than evaporation can explain and some suspect that a hole is leaking water from that pool.[186][187]
Possibility of criticality in the spent fuel pool

At approximately 14:30 on 16 March, TEPCO announced its belief that the storage pool—which is located outside the containment area[40]—may have begun boiling, raising the possibility that exposed rods would reach criticality.[41][189] BBC commented that criticality would not mean a nuclear bomb-like explosion, but a sustained release of radioactive materials would be a possible scenario.[41] Around 20:00 JST it was planned to use a police water cannon to spray water on unit 4.[190]
On 16 March the chairman of United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), Gregory Jaczko, said in Congressional testimony that the NRC believed all of the water in the spent fuel pool had boiled dry.[191] "1,097 tons of spent fuel rods are stored there."[192] Japanese nuclear authorities and TEPCO contradicted this report, but later in the day Jaczko stood by his claim saying it had been confirmed by sources in Japan.[193] At 1 pm TEPCO claimed that helicopter observation indicated that the pool had not boiled off.[194] The French Institut de radioprotection et de sûreté nucléaire agreed with this assessment, stating that helicopter crews decided to divert their water dumps to Unit 3 on the basis of their visual inspection of Unit 4.[195]
On 18 March, Japan was reportedly planning to import about 150 tons of boric acid, a neutron poison, from South Korea and France to counter the threat of recriticality.[196]
Reactor units 5 and 6
Both reactors were off line at the time the earthquake struck (reactor 5 had been shut down on 3 January 2011 and reactor 6 on 14 August 2010), although they were still fueled, unlike reactor 4 where the fuel rods had been removed prior to the earthquake.[162]
Government spokesman Edano stated on 15 March that reactors 5 and 6 were being closely monitored, as cooling processes were not functioning well.[171][197] At 09:16 JST the removal of roof panels from reactor buildings 5 and 6 was being considered in order to allow any hydrogen build-up to escape.[30] At 21:00 on 15 March, water levels in unit 5 were reported to be 2 m above fuel rods, but were falling at a rate of 8 cm per hour.
On 17 March, Unit 6 was reported to have operational diesel-generated power and this was to be used to power pumps in unit 5 to run the Make up Water Condensate System (MUWC) to supply more water.[30] Preparations were made to inject water into the reactor pressure vessel once mains power could be restored to the plant,[134] but water levels in the reactors were said to be declining.[30] It was estimated that grid power might be restored on 20 March through cables laid from a new temporary supply being constructed at units 1 and 2.[54]
Information provided to the IAEA indicated that storage pool temperatures at both units 5 and 6 remained steady around 60–68 °C between 19:00 JST 14 March and 21:00 JST 18 March, rising slowly.[30] On 18 March reactor water levels remained around 2m above the top of fuel rods.[54][107] It was confirmed that panels had been removed from the roofs of units 5 and 6 to allow any hydrogen gas to escape.[30] At 04:22 on 19 March the second unit of emergency generator A for unit 6 was restarted and is being used to operate pump C of the residual heat removal system in unit 5 to cool the spent fuel storage pool.[198]
Central fuel storage areas
The central fuel storage pond containing 6375 fuel assemblies was 'secured' and temperatures are 55 °C. The dry cask storage showed 'no signs of abnormal situation'.[199]
Reactor status summary
The Japan Atomic Industrial Forum (JAIF) has developed a status summary table for the Fukushima nuclear power plants and is publishing updates twice each day.[200][201][202][203][204][205][206][207]
| No immediate concern | Concern | Severe Condition |
| Status of Fukushima I at 19 March 10:00 JST (19 March 01:00 UTC)[207] |
Unit 1 | Unit 2 | Unit 3 | Unit 4 | Unit 5 | Unit 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power output (MWe) | 460 | 784 | 784 | 784 | 784 | 1,100 |
| Type of reactor | BWR-3 | BWR-4 | BWR-4 | BWR-4 | BWR-4 | BWR-5 |
| Core fuel assemblies[209] | 400 | 548 | 548 | 0[162] | 548 | 764 |
| Spent fuel assemblies[162] | 292 | 587 | 514 | 1,479 | 826 | 1,136 |
| Decay heat of spent fuel[210] | 60 kW | 400 kW | 200 kW | 2,000 kW | 700 kW | 600 kW |
| Fuel type | Low-enriched uranium | Low-enriched uranium | Mixed-oxide (MOX) and low-enriched uranium | Low-enriched uranium | Low-enriched uranium | Low-enriched uranium |
| Status at earthquake | In service | In service | In service | Outage (scheduled) | Outage (scheduled) | Outage (scheduled) |
| Fuel integrity | Damaged | Damaged | Damaged | Spent fuel damaged | Not damaged | Not damaged |
| Reactor pressure vessel integrity | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Not damaged (defueled) | Not damaged | Not damaged |
| Containment integrity | Not damaged | Damage suspected | Might not be damaged | Not damaged | Not damaged | Not damaged |
| Core cooling system 1 (ECCS/RHR) | Not functional | Not functional | Not functional | Not necessary (defueled) | Not necessary | Not necessary |
| Core cooling system 2 (RCIC/MUWC) | Not functional | Not functional | Not functional | Not necessary (defueled) | Operating[54] | Operating[54] |
| Building integrity | Severely damaged | Slightly damaged, also panel removed to prevent hydrogen explosion | Severely damaged | Severely damaged | Panel removed to prevent hydrogen explosion | Panel removed to prevent hydrogen explosion |
| Pressure vessel, water level | Fuel exposed partially or fully | Fuel exposed partially or fully | Fuel exposed partially or fully | Safe (defueled) | Safe | Safe |
| Pressure vessel, pressure | Stable | Unknown | Stable | Safe (defueled) | Safe | Safe |
| Containment pressure | Unknown | Low | Low | Safe | Safe | Safe |
| Seawater injection into core | Continuing | Continuing | Continuing | Not necessary (defueled) | Not necessary | Not necessary |
| Seawater injection into containment vessel | Continuing | To be decided | Continuing | Not necessary | Not necessary | Not necessary |
| Containment venting | Temporarily stopped | Temporarily stopped | Temporarily stopped | Not necessary | Not necessary | Not necessary |
| Integrity of fuel in Spent Fuel Pool (SFP) | Water injection considered | (no data) | SFP water level low, Water injection continuing |
SFP water level low, preparing water injection, Hydrogen from the pool exploded |
SFP temperature increasing, 68 °C on 18 March 21:00 JST[54] |
SFP temperature increasing, 65 °C on 18 March 21:00 JST[54] |
| INES | Level 5 | Level 5 | Level 5 | Level 3 | – | – |
| Level 5 estimate from Japanese NISA; Level 6 estimate by the French nuclear authority and the Finnish[4] nuclear authorities[2][211][212] | ||||||
| Environmental effect (NPS border) | 304 μSv/hour (0.304 mSv/h) at 03:30 on 19 March | |||||
| Evacuation radius | 20 km from Nuclear Power Station (NPS). People who live between 20 km to 30 km from the Fukushima I Nuclear Power Station are to stay indoors. USA, Australia and Sweden have instructed their citizens to evacuate a radius of minimum 80 km. Spain advises to leave an area of 120 km, Germany advises to leave even the metropolitan area of Tokyo, and South Korea advises to leave farther than 80 km and plans to evacuate by all possible means.[213][214] Travel to Japan is very low, but additional flights are chartered to evacuate foreigners. Official evacuation of Japan was started by several nations.[215] | |||||
Solutions considered or attempted
| Effective | Partially effective | Not effective | Not applicable or unknown |
| Solution | General effectiveness | Specific effectiveness | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor cores | Spent fuel pools | |||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |||
| Backup diesel generators:
The backup diesel generators operated initially. |
Disabled by the tsunami a half hour after the earthquake. One generator on unit 6 was brought back into operation partially powering units 5 and 6.[216] The generators for the SFPs of Units 5 and 6 were reconnected and the pools are at 65.5 and 62 degreees Celsius.[217] As of Saturday 19 March, the diesel generators are also pumping water to fill the reactor cores.[218][219] | |||||||||||||
| Backup batteries:
The backup batteries maintained control functions and limited cooling systems for 8 hours after the generators failed. |
Effective, until they ran out. The operators failed to connect portable generators before the 8 hours ran out, thereby allowing unit 3 to overheat and nearly melt down. However limited cooling was not designed to stabilise reactors indefinitely even if batteries were recharged.[220] | |||||||||||||
| Mobile power units:
Normally, the reactors’ cooling systems pump water through the core containment areas and spent fuel pools. Due to the power loss after the earthquake, mobile power units were sent to the plant.[216][221] General Electric reported through spokesperson Michael Tetuan that they are sending 10 gas turbine generators to help replace lost power generating capacity but GE did not know where these turbines would be used.[221] |
Mobile power units were unable to restore power to reactor pumps but power for control functions was generally maintained. Without full power, most cooling systems did not function which led to overheating and water levels dropped below safe levels. Eventually, additional sea water had to be added along with the release of radioactive steam.[216] Switchgear in basement rooms had been damaged by flooding. | Centralized monitoring instruments | ||||||||||||
| Repair power lines to restart pumps:
New and repaired power lines are being completed that could provide power to the original cooling systems and pumps.[222] The original water pumps may be inoperable due to damage from injected sea water, the earthquake, tsunami or explosions.[223] |
On 17 March a power line was laid near but not connected to Reactor No. 2.[224] TEPCO plans all cable for No. 1 and 2 will be laid on Friday and both reactors will be connected to power on Saturday.[225] Meanwhile, on Friday a distributor panel was installed at Reactor No. 1 and this will next be connected to a transformer at Reactor No. 2. TEPCO connected a power line and confirmed that electricity can be supplied. It will supply power to the Units in this order: 2, 1, 3 and 4; starting with Unit 2 because its electrical system is the least damaged.[226] | |||||||||||||
| Emergency cooling systems:
The Emergency Core Cooling System (ECCS) includes: High Pressure Coolant Injection System (HPCI), Reactor Core Isolation Cooling System (RCIC), Automatic Depressurization System (ADS), Low Pressure Core Spray System (LPCS), Low Pressure Coolant Injection System (LPCI), Depressurization Valve System (DPVS), Passive Containment Cooling System (PCCS), and Gravity Driven Cooling System (GDCS).[220] |
Which cooling systems failed is unclear but the RCIC operated initially and the HPCI worked until the toruses overheated.[220] | |||||||||||||
| Cooling core containment areas by adding sea water:
Sea water is being "manually" "injected" into the Reactor Pressure Vessel of units 1, 2 and 3 via fire extinguisher system line. Neutron absorbing boric acid has been injected with the sea water.[216] |
Sea water cooling has been partially effective for cooling reactor core but fuel damage has taken place. At one point available water in site pools ran out.[216] White smoke or steam was reported rising from Unit 2.[227] | |||||||||||||
| Spraying water into spent fuel pools with water cannon and fire engines:
Riot police, military and firemen working in shifts to reduce radiation exposure used water cannons and fire engines to spray water[228] onto the roofs and into the spent fuel pools of reactor unit Number 3 although it is unclear if any water reached the spent fuel pool.[223][229][230] Officials considered spraying water onto the roof of unit Number 4 also.[230] |
Steam emanated from the roof of unit 3 after spraying which suggested that spraying was at least partially successful in reaching overheated spent fuel rods.[223][231] Radiation levels dropped slightly after the steam had dissipated suggesting the cooling may have been successful.[231]
Inspection during helicopter water drops indicated there was water in the pool of Unit 4; so, spraying on Friday 19 March focused on Unit 3.[199] Water sprayed into the pool of unit No. 4 is disappearing faster than evaporation can explain and some suspect that a hole is leaking water from that pool.[186][187] |
|||||||||||||
| Helicopter dumping of sea water into spent fuel pools:
Helicopters used for forest fire suppression dumped sea water onto the reactors.[230] |
Strong winds prevented effective targeting of the dumped water since high radiation levels prevented the helicopters from flying low.[223][230] Furthermore, footage captured appeared to show much of the water dispersing in mid-air weakening the intensity of the water to cool the overheating reactor.[232] | |||||||||||||
| Boron:
Officials have considered insertion or targeted aerial dropping of boric acid, boronated plastic beads or boron carbide pellets into the spent fuel pools to absorb neutrons.[233][234] |
France is flying 95 tonnes of boron to Japan on Thursday.[235] | |||||||||||||
| Liquid metal cooling:
On 17 March, KyivPost reported that a Ukrainian group of specialists who were involved in the aftermath of the Chernobyl nuclear disaster proposed low-melting and chemically neutral metal, such as tin, to cool the fuel rods even if molten or damaged. [236] Chopped tin can be injected in the reactor through the existing cooling water pipes with compressed inert gas, helium or argon. Melted tin creates a crust (low vapor pressure), cools the reactor and delays the decay products recovery. Liquid metal cooled reactors need no pump which makes them long-term capable. |
This solution has similarities with the 2400 metric tonnes of lead (see also Lead-cooled fast reactor) used to successfully cooling and covering the Chernobyl nuclear plant but avoids the toxic lead.[237] Liquid metal cooled reactors were used in several Soviet submarines which shows additional basic feasibility.
It also avoids the danger of additional explosions caused by water breaking down to hydrogen and oxygen starting at temperatures around 800 °C due to Thermolysis.[238] A team of Ukrainian nuclear specialists is ready to fly out for realizing this in practice. The Japanese Embassy was informed. |
|||||||||||||
| "Sarcophagus":
On 18 March, Reuters reported[239] that Hidehiko Nishiyama, Japan's nuclear agency spokesman when asked about burying the reactors in sand and concrete, said: "That solution is in the back of our minds, but we are focused on cooling the reactors down." |
Even 1800 metric tonnes of sand and clay used in the Chernobyl disaster acted worse as thermal insulators and accumulated heat.[240]
So first a non-evaporating coolant like liquid (and minimum surface-frozen) metal has to be applied, and after temperature has decreased, a sarcophagus. |
|||||||||||||
Radiation levels and radioactive contamination
Secretary Edano on 15 March 2011 said that radiation rates had been measured as high as "30 mSv/h" between units 2 and 3, as high as "400 mSv/h"[38] near unit 3, between it and unit 4, and "100 mSv/h" near unit 4. He said, "there is no doubt that unlike in the past, the figures are the level at which human health can be affected."[241] Prime Minister Naoto Kan urged people living between 20 and 30 kilometers of the plant to stay indoors, "The danger of further radiation leaks (from the plant) is increasing," Kan warned the public at a press conference, while asking people to "act calmly".[242][243]
A spokesman for Japan's nuclear safety agency said TEPCO had told it that radiation levels in Ibaraki, between Fukushima and Tokyo, had risen. "The level does not pose health risks," the spokesman said. The Tokyo metropolitan government said it has detected radioactive material, such as iodine and cesium, up to 40 times normal levels in Saitama, near Tokyo.[241][242] Radiation levels in Tokyo were at one point measured at 0.8 μSv/hour although they were later measured at "about twice the normal level".[244] Later, on 15 March 2011, Edano reported that radiation levels were lower. A changed wind direction dispersed radiation away from the land and back over the Pacific Ocean.[245] Thousands of Tokyo residents are reported to have left for cities further south, although Edano insisted that levels in Greater Tokyo were not hazardous.[246]
On 16 March power plant staff were briefly evacuated after smoke rose above the plant and radiation levels measured at the gate surged to 10 mSv/h[247]. Media reported 1,000 mSv/h close to the leaking reactor, with radiation levels subsequently dropping back to 800–600 millisieverts.[11] Japan's defence ministry criticized the nuclear safety agency and TEPCO after some of its troops were possibly exposed to radiation when working on the site.[248] Japan's ministry of science measured radiation levels of up to 0.33 mSv/h 20 kilometers northwest of the power plant.[249]
On 17 March IAEA radiation monitoring over 47 cities, showed that levels of radiation in Tokyo had not risen. They had received no new radiation level information from the Fukushima power plant site. Although at some locations around 30 km from the Fukushima plant, the dose rates rose significantly in the preceding 24 hours (in one location from 80 to 170 μSv/h and in another from 26 to 95 μSv/h), but levels varied according to the direction from the plant.[250]
International commentators were divided in their analysis of the scale of the danger, with French Foreign Minister, Alain Juppe, saying that the threat was "extremely high" while others said it was too early to make comparisons to the 1986 Chernobyl disaster.[246]
On 18 March IAEA clarified that, contrary to several news reports, the IAEA to date has not received any notification from the Japanese authorities of people sickened by radiation contamination.[6]
Wind and radioactive cloud
The United Nations predicted that a radiation plume from the stricken Japanese reactors would reach the United States by 18 March. Health and nuclear experts emphasized that dilute radiation in the plume would affect health.[251] A simulation by the Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy shows trace amounts of radioactivity reaching California and Mexico around 19 March.[252][253]

Favorable westernly winds have been dominant during most of the first week of the accident. Five days trajectories for the time period 18–22 March run in the NOAA HYSPLIT model (at http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/ 12 UTC 18 March 2011) forecasts air packets that already left from the plant area towards the sea to change their direction towards the coast south of the plant at 19 March mid-day Japanese time. 20 March forecast shows air packets starting from the plant heading towards the Fukushima city and further to the Sendai area. 21 March forecast is to the direction 200 (SSW, South-South-West) like most of the 22nd March. 13 UTC 22 March trajectory (8 p.m. Japanese time) shows change in air flow direction again back towards the sea. Similar air movement is prediction results are presented by Finnish Metorological Institue for 19–20 March 2011[254]
Effects on human health
Radiation exposure of up to 0.17 millisieverts per hour (mSv/h) (measured Thursday, down to 0.15 mSv/h Friday) has been reported 30 km (19 miles) away from the damaged nuclear reactors. This is within the 20 to 30 km "stay in your house" zone being used. Experts say exposure to this amount of radiation for 6 to 7 hours would result in absorption of the maximum level considered safe for one year. [255] For comparison, one chest x-ray is about 0.1 mSv. Some residents have been in the area for 1 week. An acute exposure to radiation is much more harmful than the same dose spread out over a longer period of time, making comparisons between short-term and yearly doses problematic. One exception to this rule is that exposure to penetrating radiation is less harmful than long term exposure to ingested or inhaled radioactive dust. People can mitigate their exposure to radiation through a variety of protection techniques.
Normal background radiation varies from place to place but delivers a dose equivalent in the vicinity of 2.4 mSv/year annually, or about 0.3 µSv/h.[256][257] The international limit for radiation exposure for nuclear workers is 20 mSv per year, averaged over five years, with a limit of 50 mSv in any one year,[257] however for workers performing emergency services EPA guidance on dose limits is 100 mSv when "protecting valuable property" and 250 mSv when the activity is "life saving or protection of large populations."[258] A 250 mSv dose is estimated to increase one's lifetime risk of developing fatal cancer from about 20% to about 21%,[259] and chronic exposure of 100 mSv per year is the "lowest level at which any increase in cancer is clearly evident," according to the International Commission on Radiological Protection.[260] Symptoms of radiation poisoning typically emerge with a 1000 mSv total dose over a day.[261]
Radiation dose rates at one location between reactor units 3 and 4 was measured at 400 mSv/h at 10:22 JST, 13 March, causing experts to urge rapid rotation of emergency crews as a method of limiting exposure to radiation.[262] 1,000 mSv/h were reported (but not confirmed by the IAEA)[30] close to the leaking reactor units on 16 March, prompting a temporary evacuation of plant workers, with radiation levels subsequently dropping back to 800-600 millisieverts.[11] Prior to the accident, the maximum permissible dose for Japanese nuclear workers was 100 mSv in any one year, but on 15 March 2011, the Japanese Health and Labor Ministry increased that annual limit to 250 mSv, for emergency situations.[263][264]
Isotopes of possible concern
Radioactive isotopes of iodine and caesium have been detected at Saitama, near Tokyo.[242] These isotopes can have serious effects on health, depending on the quantity inhaled or ingested.
The isotope iodine-131 is easily absorbed by the thyroid. Persons exposed to releases of I-131 involving melted fuel at nuclear power plants have a higher risk for developing thyroid cancer or thyroid disease, or both. Children are particularly more vulnerable to I-131 than adults. Increased risk for thyroid neoplasm remains elevated for at least 40 years after exposure.[265] Potassium iodide tablets prevent iodine-131 absorption.[265] CBS news reported that the number of doses of potassium iodide available to the public in Japan was inadequate to meet the perceived needs for an extensive radioactive contamination event.[266]
Caesium-137 is also a particular threat because it behaves like potassium and is taken-up by the cells throughout the body. Prussian blue helps the body secrete caesium-137.[266][267] Cs-137 can cause acute radiation sickness, and increase the risk for cancer because of exposure to high-energy gamma radiation.[268] Internal exposure to Cs-137, through ingestion or inhalation, allows the radioactive material to be distributed in the soft tissues, especially muscle tissue, exposing these tissues to the beta particles and gamma radiation and increasing cancer risk.[268]
Strontium-90 behaves like calcium, and tends to deposit in bone and blood-forming tissue (bone marrow).[269] 20-30% of ingested Sr-90 is absorbed and deposited in the bone.[269] Internal exposure to Sr-90 is linked to bone cancer, cancer of the soft tissue near the bone, and leukemia.[269] Risk of cancer increases with increased exposure to Sr-90.[262][269]
Plutonium is also present in the MOX fuel of the Unit 3 reactor and in spent fuel rods,[270] although there has been no official indication that plutonium has been detected outside the reactors. Officials at the International Atomic Energy Agency say the presence of MOX fuel does not add significantly to the dangers.[271] Plutonium-239 is particularly long-lived and toxic with a half-life of 24,000 years, and if it escaped in smoke from a burning reactor and contaminated soil downwind, it would remain hazardous for tens of thousands of years.[271]
Rush for iodine
Fear of radiation from Japan prompted a global rush for iodine pills, including in the United States,[272] Canada, Russia,[273] Korea,[274] China,[275] and Malaysia.[276] There is a rush for iodized salt in China.[275] A rush for iodine antiseptic solution appeared in Malaysia. WHO warned against consumption of iodine pills without consulting a doctor and also warned against drinking iodine antiseptic solution.[276] The United States Pentagon said troops are receiving potassium iodide before missions to areas where possible radiation exposure is likely.[277]
The World Health Organisation (WHO) says it has received reports of people being admitted to poison centres around the world after taking iodine tablets in response to fears about harmful levels of radiation coming out of the damaged nuclear power plant in Fukushima. WHO Western Pacific environmental officer, Steven Iddings, said, "This treatment is really meant for people who are close up, perhaps workers who are associated with the response in Japan."[278]
U.S. military
The U.S. Navy dispatched aircraft carrier USS Ronald Reagan and other vessels flew a series of helicopter operations.[279][280] A US military spokesperson had said that low-level radiation was detected both by navy ships and their accompanying aircraft, forcing a change of course of the 7th fleet, en route to Sendai.[281] USS Ronald Reagan and sailors onboard were exposed to "a month's worth of natural background radiation from the sun, rocks or soil"[282] in an hour and the carrier was repositioned.[283] 17 U.S. sailors were decontaminated after they and the 3 helicopters they were on were found to have been contaminated with low levels of radioactive particulates.[284]
The USS George Washington was docked for maintenance in Yokosuka Naval Base, about 280 km (175 mi) from the plant, when instruments detected the radiation at 07:00 JST, 15 March 2011, the Navy said in a statement.[285] At 320 km (200 mi) from Fukushima, Rear Admiral Richard Wren stated that the nuclear crisis in Fukushima is happening too far from Yokosuka to even warrant a discussion about evacuating base residents.[286] Daily monitoring and limited precautionary measures were recommended for Yokosuka and Atsugi bases: limiting outdoor activities and securing external ventilation systems.[287]
Reaction in Japan
Evacuations

After the declaration of a nuclear emergency by the Government at 19:03 on 11 March, the Fukushima prefecture ordered the evacuation of an estimated 1,864 people within a distance of 2 km from the plant. This was extended to 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) and 5,800 people at 21:23 by a directive to the local governor from the Prime Minister, together with instructions for residents within 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) of the plant to stay indoors.[18][19] The evacuation was expanded to a 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) radius at 5:44 on 12 March, and then to 20 kilometres (12 mi) at 18:25, shortly before ordering use of sea water for emergency cooling.[18][288]
The Guardian reported at 17:35 JST on 12 March that NHK advised residents of the Fukushima area "to stay inside, close doors and windows and turn off air conditioning. They were also advised to cover their mouths with masks, towels or handkerchiefs" as well as not to drink tap water.[289] Air traffic has been restricted in a 20-kilometre (12 mi) radius around the plant, according to a NOTAM.[290] The BBC has reported as of 22:49 JST (13:49 GMT) "A team from the National Institute of Radiological Sciences has been dispatched to Fukushima as a precaution, reports NHK. It was reportedly made up of doctors, nurses and other individuals with expertise in dealing with radiation exposure, and had been taken by helicopter to a base 5 km from the nuclear plant."[291]
Evacuations were also ordered around the nearby Fukushima II (Daini) plant. Residents within 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) were ordered to evacuate at 07:45 on 12 March, again with instructions for those within 10 km to stay indoors. Evacuation was extended to 10 km by 17:39.[18] A journalistic investigation was stopped 60 kilometres (37 mi) from the plants by police.[292] Over 50,000 people were evacuated during 12 March.[293] The figure increased to 170,000–200,000 people on 13 March, after officials voiced the possibility of a meltdown.[25][26]
On the morning of 15 March, the evacuation area was again extended. Prime Minister Naoto Kan issued instructions that any remaining people within a 20 km (12 mile) zone around the plant must leave, and urged that those living between 20 km and 30 km from the site should stay indoors.[294][295] A 30 km no-fly zone has been introduced around the plant.[citation needed]
On 16 March, the U.S. Embassy advised Americans in Japan to leave areas within "approximately 50 miles" (80 km) from the plant. Gregory Jaczko, the chairman of the United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission, said before the United States Congress, believing the Japanese government was not telling the full story, "We would recommend an evacuation to a much larger radius than has currently been provided by Japan."[296] Spain advises to leave an area of 120 km, Germany advises to leave even the metropolitan area of Tokyo, and South Korea advises to leave farther than 80 km and plans to evacuate by all possible means.[213][214] Travel to Japan is very low, but additional flights are chartered to evacuate foreigners. Official evacuation of Japan was started by several nations.[215]
Of 90 bedridden patients moved from a hospital in the town of Futaba-machi, a sample of three patients were tested and shown to have been exposed to radiation. The patients had been waiting outdoors for rescuers before being moved by helicopter at the time an explosion happened.[297][298]
Statements on meltdown possibility
In a press conference, the chief spokesman of the Japanese nuclear authorities was translated into English as having said that a nuclear meltdown may be a possibility at Unit 1.[299] Toshihiro Bannai, director of the international affairs office of Japan's Nuclear and Industrial Safety, in a telephone interview with CNN, stated that a meltdown was possible.[299][300] However, the Japanese prime minister soon indicated that a nuclear meltdown was not in progress and emphasized that the containment of Unit 1 was still intact. After the statement, the government added that the claim of a meltdown had been mistranslated.[299] The temperature inside the reactor was not reported, but Japanese regulators said it was not dropping as quickly as they wanted.[301] At 12:33 JST on 13 March 2011, the Chief Cabinet Secretary of the Japanese government, Yukio Edano, was reported to have confirmed that there was a “significant chance” that radioactive fuel rods had partially melted in Unit 3 and Unit 1, or that "it was 'highly possible' a partial meltdown was underway".[26] “I am trying to be careful with words ... This is not a situation where the whole core suffers a meltdown”.[148] Soon after, Edano disclaimed that a meltdown was in progress. He stated that the radioactive fuel rods had not partially melted and he emphasized that there was no danger for the health of the population.[302][303] Cabinet Secretary Edano later said that there were signs that the fuel rods were melting in all three reactors. "Although we cannot directly check it, it's highly likely happening".[304]
The Prime Minister of Japan, Naoto Kan, visited the plant for a briefing on 12 March 2011.[305] He has been frequently quoted in the press, calling for calm and minimizing exaggerated reports of danger.[306]
Accident rating
At 01:17 JST on Sunday 13 March 2011, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency announced that it was rating the Fukushima accidents at Level 4 (accident with local consequences) on the 0–7 International Nuclear Event Scale (INES), below the Three Mile Island (TMI) accident in seriousness[31] which was at Level 5. A rating of four would make the severity of the Fukushima event comparable to Sellafield accidents between 1955 and 1979.[citation needed]
On Monday, 14 March 2011, three Russian experts stated that the nuclear accident should be classified at Level 5, perhaps even Level 6.[307] One day later, the French nuclear safety authority ASN said that the Fukushima plant could be classified as a Level 6.[308]
On the 18 March, Japanese nuclear officials raised the level of the emergency to 5 on the INES scale.[309]
Requests for help
Japan has not been able to formulate and express requests for assistance as rapidly and specifically as aid agencies would hope was the case. [citation needed] Even at the highest level, Elisabeth Byrs, of the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA), stated that "Japan has requested international search and rescue teams, but only a handful." Nevertheless, search and rescue teams have been dispatched on an ad hoc basis, based upon their own assessment and ability to operate.[citation needed]
The Japanese government has asked the United States to provide cooling equipment to the Dai-ichi plant to help resolve the crisis. As of 15 March 2011, the United States had provided Japan with 3,265 kg (7,200 lb) of "special equipment" (a fire truck)[310] to help monitor and assess the situation at the plant.[311][312]
Dearth of information
Prime Minister Kan met with Tokyo Electric Power Company on 15 March and lamented the lack of information . According to press accounts, he bluntly asked, "What the hell is going on?"[313] He has also admitted: '..We could have moved a little quicker in assessing the situation'[314]
Business reaction
In financial markets, the plant operator TEPCO's shares halved in value as it dropped over four consecutive trading days, before rising again on Thursday.[315] Japan's Nikkei 225 stock index fell 6% on Monday. The Nikkei then plunged another 11% on 15 March after the government warned of elevated radiation risks.[316] On 16 March the index recovered 5.7%.[317] On Friday 18 March at 10 am Tokyo time, the G7 group of nations began an unprecedented coordinated currency market intervention to stabilize the value of the yen above 80 JPY/USD.
International reaction
The International reaction to the nuclear accidents has been a humanitarian response to the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, also to those people affected by the events at Fukushima I. The response has also included the expression of concern over the developments at the reactors and the risk of escalation. The accidents have furthermore prompted re-evaluation of existing and planned national nuclear energy programs, with some commentators questioning the future of the nuclear renaissance.[318][319][320][321]
See also
|
|
References
- ^ "FLASH: Japan nuclear safety agency says level 5 incident at Fukushima reactors No. 1, 2, 3, raised from level 4". Huffington Post. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ a b "UPDATE 1-French nuclear agency now rates Japan accident at 6". Reuters. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ Template:Fr declaration by A.-C. Lacoste, president of French Autorité de sûreté nucléaire (ASN) to the French National Assemblee (16 March 2011).
- ^ a b "STUK: Fukushiman turman vakavuus jo kuutosluokkaa" (in Finnish). Helsingin Sanomat. 15 March 2011.
- ^ "Chu Says Japan Crisis May Top Three Mile Island". National Journal.
- ^ a b IAEA Update on Japan Earthquake - website International Atomic Energy Agency, 18 March 2011
- ^ Black, Richard. "BBC News - Reactor breach worsens prospects". BBC News. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Press Release (Mar 16, 2011) Impact to TEPCO's Facilities due to Tohoku-Taiheiyou-Oki Earthquake (as of 2:00 pm)". Tokyo Electric Power Company. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ Fukushima Plant Staff Return To Work After Temporary Break - RTT News
- ^ Oliver, Steph (16 March 2011). "Staff Evacuated From Japanese Nuclear Plant". Sky News Online. Retrieved 16 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d Font size Print E-mail Share 13 Comments. "Radiation spike hinders work at Japan nuke plant". CBS News. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ 'Japan raised nulear alert level' BBC News online 18 March 2011.
- ^ Wagner, Wieland (15 March 2011). "Problematic Public Relations: Japanese Leaders Leave People in the Dark". Spiegel Online. Der Spiegel. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "China urges Japan's openness amid panic buying of salt". Channel NewsAsia. 17 March 2011. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ Stricken Reactors May Get Power Sunday, Wall Street Journal, March 19, 2011
- ^ Japan halts sale of food from near Fukushima, Reuters, Mar 19, 2011
- ^ Japan officials: radioactive iodine in Tokyo water, Businessweek, March 19, 2011
- ^ a b c d e f http://www.nisa.meti.go.jp/english/files/en20110313-3.pdf Seismic Damage Information (19th press communicate released by NISA on 08:30 13 March 2011).
- ^ a b c Inajima, Tsuyoshi; Okada, Yuji (11 March 2011). "Japan Orders Evacuation From Near Nuclear Plant After Quake". Businessweek. Retrieved 11 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f World Nuclear News (12 March 2011). "Battle to stabilise earthquake reactors". World Nuclear News. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f "Japan to fill leaking nuke reactor with sea water". Reuters. 12 March 2011.
- ^ Steve Mirsky Nuclear Experts Explain Worst-Case Scenario at Fukushima Power Plant Scientific American 12 March 2011
- ^ Grossman, Karl (12 March 2011). "Behind the Hydrogen Explosion at the Fukushima Nuclear Plant". Common Dreams NewsCenter. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ a b "Sea water bid to halt meltdown at Fukushima nuclear plant". mirror.co.uk. 11 August 2009. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ a b Associated, The. "The Canadian Press: IAEA says 170,000 people evacuated from area near damaged Japan nuclear plant". Google. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ a b c Mufson, Steven (13 March 2011). "Japanese nuclear plants' operator scrambles to avert meltdowns". The Washington Post. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ Wald, Matthew (13 March 2011). "Partial Meltdowns Presumed at Crippled Reactors". The New York Times. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ "Japan rejected early US help on nuclear disaster: report". MediaCorp Channel NewsAsia. AFP. 18 March 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ a b "press release 8". TEPCO. 13 March 2011. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n "IAEA Update on Japan Earthquake". Retrieved 16 March 2011.
As reported earlier, a 400 millisieverts (mSv) per hour radiation dose observed at Fukushima Daiichi occurred between 1s 3 and 4. This is a high dose-level value, but it is a local value at a single location and at a certain point in time. The IAEA continues to confirm the evolution and value of this dose rate. It should be noted that because of this detected value, non-indispensible staff was evacuated from the plant, in line with the Emergency Response Plan, and that the population around the plant is already evacuated.
- ^ a b Maeda, Risa (12 March 2011). "Japan rates quake less serious than Three Mile Island, Chernobyl". Reuters. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ Justin McCurry (14 March 2011). "Explosion at Japanese nuclear plant". The Guardian. London.
- ^ "White smoke around the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 3 (2nd release)" (Press release). Tokyo Electric Power Company. 14 March 2011.
- ^ [1] Reuters UK 15 March 2011
- ^ a b Hiroko Tabuchi, Keith Bradsher, Matt Wald (14 March 2011). "Japan Faces Prospect of Nuclear Catastrophe as Workers Leave Plant". The New York Times.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Radiation shoots up at Fukushima nuke plant after blast heard Kyodo News 15 March 2010
- ^ "Container damaged, radiation leak feared at Fukushima No.2 reactor". Kyodo News. 15 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d "放射線、福島原発で400ミリシーベルト=「人体に影響及ぼす可能性」-官房長官". jiji press. 15 March 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
{{cite web}}: More than one of|work=and|newspaper=specified (help) - ^ a b c "Radiation levels spike at Japanese nuclear plant". CNN. 15 March 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ a b Japanese emperor 'deeply worried' BBC News
- ^ a b c Surprise 'critical' warning raises nuclear fears
- ^ Mackey, Robert (14 March 2011). "Latest Updates on Japan's Nuclear Crisis and Earthquake Aftermath - NYTimes.com". Japan: Thelede.blogs.nytimes.com. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Japan suspends work at stricken nuclear plant - Yahoo! News". News.yahoo.com. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ Richard Black. "BBC News - Fukushima workers withdraw after radiation spikes". BBC News. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Press Release | Transfer of Fukushima Dai-ichi Power Station Workers". TEPCO. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Fukushima operator: pouring water into No.5, 6 reactors". Reuters. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ 北沢防衛相「自衛隊ヘリの水投下、4回実施」
- ^ "4号機プール内に大量の水、自衛隊ヘリ確認" (in Japanese). Yomiuri Shimbun. 17 March 2011.
- ^ "冷却装置回復へ、原発に送電線引き込み工事開始" (in Japanese). Yomiuri Shimbun. 16 March 2011.
- ^ Takahara, Kanako, and Alex Martin, "Copters, trucks try to cool fuel rod pool", Japan Times, 18 March 2011, p. 1.
- ^ "NHK WORLD English". .nhk.or.jp. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ . "NHK WORLD TV on USTREAM: Official NHK WORLD TV live on USTREAM. NHK WORLD TV is an English language 24-hour international news and information channel. New". Ustream.tv. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) - ^ "NHK WORLD English". nhk.co.jp. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Seismic Damage Information (the 31st Release)" (PDF) (Press release). Japan: Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency. 18 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "Assessment of INES (International Nuclear and Radiological Event Scale) on the incident at Fukushima Daiichi and Fukushima Daini Nuclear Power Station" (Press release). Tokyo Electric Power Company. 18 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ Takahara, Kanako, and Kazuaki Nagata, "Workers battle against time", Japan Times, 19 March 2011, p. 1.
- ^ "More Tokyo firefighters join the battle". NHK. 19 March 2011.
- ^ NHK (Evening news broadcast), 19 March 2011, 19:00.
- ^ "Japan's Bonds Fall for a Second Day as Stock Gain Curbs Demand", San Francisco Chronicle (15 March 2011).
- ^ "Fukushima Daiichi Information Screen". Icjt.org. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ a b c Brady, A. Gerald (1980). Ellingwood, Bruce (ed.). An Investigation of the Miyagi-ken-oki, Japan, earthquake of June 12, 1978. NBS special publication. Vol. 592. United States Department of Commerce, National Bureau of Standards. p. 123.
- ^ "Fukushima to Restart Using MOX Fuel for First Time". Nuclear Street. 17 September 2010. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ DOE fundamentals handbook - Decay heat, Nuclear physics and reactor theory - volume 2 of 2, module 4, page 61
- ^ "Plant Status of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (as of 00:00 March 12th)" (Press release). TEPCO. 12 March 2011. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ a b "Occurrence of a Specific Incident Stipulated in Article 10, Clause 1 of the Act on Special Measures Concerning Nuclear Emergency Preparedness (Fukushima Daiichi)" (Press release). TEPCO. 11 March 2011. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ Japan Atomic Industrial Forum, Inc. "Quake Triggers Evacuation of Residents Surrounding Fukushima-1 NPS" (PDF).
- ^ a b c David Sanger and Matthew Wald, Radioactive Releases in Japan Could Last Months, Experts Say The New York Times 13 March 2011
- ^ a b "Massive earthquake hits Japan". World Nuclear News. 11 March 2011. Retrieved 13 March 2011.; "Japan Earthquake Update (2030 CET)". IAEA Alert Log. International Atomic Energy Agency. 11 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ Maugh II, Thomas H.; Vartabedian, Ralph (11 March 2011). "Damage at two Japan nuclear plants prompts evacuations". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 11 March 2011.; "Japan Earthquake Update (2210 CET)". IAEA Alert Log. International Atomic Energy Agency. 11 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ Magnier, Mark; Demick, Barbara; King, Laura (16 March 2011). "New power line could restore cooling systems at Fukushima Daiichi plant". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "TEPCO press release 3". Tepco. 11 March 2011.
- ^ Radiation 1K times normal at one Japan nuke plant. Content.usatoday.com (3 January 2011). Retrieved on 12 March 2011.
- ^ "Radiation level rising in Fukushima Nuclear Plant turbine building." Nikkei.com. 12 March 2011 JST. Retrieved 18:30 GMT 11 March 2011.
- ^ "(朝日新聞社):福島原発炉内蒸気、外に逃す作業検f討 放射能漏れの恐れ – 社会". Asahi Shimbun (in Japanese). Japan. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ International Business Times. Japan warns of small radiation leak from quake-hit plant Retrieved 11 March 2011, 21:48 (GMT)
- ^ Fukushima reactor pressure may have hit 2.1 times capacity -METI Maeda, Rita, Reuters wire service, quoting Japan Trade Ministry (20:30 GMT) 12 March 2011 (Tokyo time)
- ^ All Things Nuclear • Containment at Fukushima. Allthingsnuclear.org. Retrieved on 12 March 2011.
- ^ a b "Impact to TEPCO's Facilities due to Miyagiken-Oki Earthquake (as of 7 am)". TEPCO News website. 12 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ Nikkei, Radiation Could Already Have Leaked At Nuke Plant. 12 March 2011, 7:20 JST.
- ^ "福島第一原子力発電所モニタリングカーによる計測状況" (PDF). TEPCO (in Japanese). Retrieved 13 March 2011.
69 nGy/h ... 866 nGy/h ... 385.5 μSv/h
- ^ "福島第一原子力発電所の現状について【午後4時40分時点】". TEPCO (in Japanese). 12 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help) - ^ "IAEA update on Japan Earthquake". iaea.org. 2011 [last update]. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
NISA have confirmed the presence of caesium-137 and iodine-131 in the vicinity of Fukushima Daiichi Unit 1. NISA reported an initial increase in levels of radioactivity around the plant earlier today, but these levels have been observed to lessen in recent hours.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|year=(help) - ^ "Possible Meltdown at TEPCO Reactor". Nikkei.com. 12 March 2011.
- ^ Yoshie Furuhashi (12 March 2011). "NHK, "Fukushima 1: Fuel Rods Exposed"". Mrzine.monthlyreview.org. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
As of 11:20, a part of the "fuel assembly" of fuel rods is now exposed above water.
- ^ "TEPCO press release 4". TEPCO News website. 12 March 2011. Archived from the original on 13 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ a b McCurry, Justin (13 March 2011). "Japan nuclear plant faces new threat". The Guardian. UK. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ "【地震】炉心溶融している可能性 福島第一原発" (in Japanese). News.tv-asahi.co.jp. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ "URGENT: Concerns of core partially melting at Fukushima nuke plant | Kyodo News". English.kyodonews.jp. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ Kyodo (14 March 2011). "Radiation level again tops legal limit at Fukushima No. 1 nuke plant". Kyodo News. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "TEPCO press release 4". TEPCO News website. 12 March 2011. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ "福島第1原発で爆発と白煙 4人ケガ" (in Japanese). Nippon Television Network Corporation. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ "TEPCO press release 34". Tepco. 12 March 2011.
- ^ "Drawing of the reactor and explanation of the containments". allthingsnuclear.org. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ Fredrik Dahl, Louise Ireland (12 March 2011). "Hydrogen may have caused Japan atom blast-industry". Reuters. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ "2011/03/13 01:04 – Meltdown Caused Nuke Plant Explosion: Safety Body". E.nikkei.com. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ Nuclear Fuel Behaviour in Loss-of-coolant Accident (LOCA) Conditions (PDF). Nuclear Energy Agency, OECD. 2009. p. 140. ISBN 978-92-64-99091-3.
- ^ "The FINANCIAL – Radiation levels increase at Fukushima No.1 after blast reports". Finchannel.com. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ Meyers, Chris (9 February 2009). "Radiation leaking from Japan's quake-hit nuclear". Reuters. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ "Explosion at quake-hit nuclear plant". ABC News (Australian Broadcasting Corporation). 12 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ a b Richard Jones. ""Thousands undergo radioactive screening after explosion in nuclear power station" by Wil Longbottom". The Daily Mail. London. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ "Fukushima Fallout: How Bad Could It Get?". News.sky.com. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ "IAEA update on Japan Earthquake". iaea.org. 0235 CET, 13 March 2011. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
At Fukushima Daichi, four workers were injured by the explosion at the Unit 1 reactor, and there are three other reported injuries in other incidents. In addition, one worker was exposed to higher-than-normal radiation levels that fall below the IAEA guidance for emergency situations.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ "Impact to TEPCO's Facilities due to Miyagiken-Oki Earthquake (as of 9 pm)". TEPCO. 12 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ "東北地方太平洋沖地震における当社設備への影響について【午後9時現在】". TEPCO (in Japanese). 12 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ "USGS Earthquake Details". USGS. 12 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ "福島第一原子力発電所プラント状況等のお知らせ(3月12日 午後11時現在)" (PDF). TEPCO (in Japanese). 12 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d http://www.nisa.meti.go.jp/english/files/en20110318-2.pdf
- ^ a b "Japan earthquake: Fire erupts again at Fukushima Daiichi reactor; nuclears rods damaged at other reactors". Los Angeles Times. 27 February 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "NHK WORLD English". .nhk.or.jp. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ a b c "Efforts to manage Fukushima Daiichi 3, update 2". World Nuclear News. 13 March 2011. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ "In Stricken Fuel-Cooling Pools, a Danger for the Longer Term". New York Times. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "LIVE: Japan earthquake". BBC News. 14 March 2011.
- ^ "TEPCO press release 3". Tepco. 14 March 2011.
- ^ "URGENT: Fuel rods at No. 2 reactor of Fukushima No. 1 nuke plant fully exposed". Kyodo news. 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Nuclear fuel rods fully exposed at Japan reactor – Jiji". Reuters. 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Meltdown cant be ruled out at Japan reactor". thenews.com. 14 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d "Crisis continues at Fukushima nuclear plant as fuel rods exposed again". Kyodo news. 15 March 2011.
- ^ Post a Job. "Tepco Fears Fuel Rods Melt, Fights to Stabilize Stricken Reactor – Businessweek". BusinessWeek. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ "Fuel rods fully exposed again at Fukushima nuclear power plant". Xinhuanet. 14 March 2011.
- ^ Vastag, Brian (28 February 2011). "Nuclear crisis deepens as third reactor loses cooling capacity – The Washington Post". The Washington Post. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ "Japan on meltdown alert". ABC news(Australia). 15 March 2011.
- ^ "Tokyo Elec resumes work to pump water into No.2 reactor-Kyodo". Reuters. 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Newsticker". tagesschau.de. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ Hiroko Tabuchi, Keith Bradsher, Matt Wald (14 March 2011). "Japan Faces Prospect of Nuclear Catastrophe as Workers Leave Plant". The New York Times.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "URGENT: Blast heard at Fukushima's No.2 reactor: gov't ; Kyodo News". english.kyodonews.jp. 2011. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
The sound of a blast was heard Tuesday morning at the troubled No. 2 reactor of the quake-hit Fukushima No. 1 nuclear power plant, the government said. The incident occurred at 6:10 am and is feared to have damaged the reactor's pressure-suppression system, the Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency said, citing a report from the plant's operator Tokyo Electric Power Co.
- ^ "Japanese nuclear safety agency says explosion heard at Unit 2 of Fukushima Dai-ichi plant Canadian Business Online". canadianbusiness.com. 2011. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Blast heard at Fukushima's No.2 reactor: gov't". Retrieved 14 March 2011.
Shortly after the 6:10 am incident, the radiation level exceeded the legal limit to reach 965.5 micro sievert per hour (about 1 millisievert per hour), and it is feared that the reactor's pressure-suppression system was damaged, the Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency. Tokyo Electric Power Co., the plant's operator, said it is evacuating workers from the plant, except for those necessary for the work to cool the reactor.
- ^ http://www.nytimes.com/2011/03/15/world/asia/15nuclear.html?_r=1&hp
- ^ "URGENT: Radiation shoots up at Fukushima nuke plant after blast heard | Kyodo News". English.kyodonews.jp. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ NHK, 15 March 2011
- ^ "Japanese Government Warns that New Radiation Leak is Harmful to Health | Cleveland Leader". clevelandleader.com. 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ 15 March 2011, Plant operator says reactor seal apparently not holed, Channel News Asia.
- ^ "UN atom chief sees possible Japan plant core damage". Reuters. 11 March 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d "Fukushima I nuclear accidents - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia". En.wikipedia.org. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ http://www.tepco.co.jp/en/press/corp-com/release/11031905-e.html
- ^ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plutonium#Toxicity Plutonium Toxicity
- ^ "Warning of another possible explosion at nuclear plant". radionz.co.nz. 2011 [last update]. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
pluton
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|year=(help) - ^ Digges, Charles (2011 [last update]). "Japan floods overheating reactor with sea water while 140,000 evacuate area as more coolant breakdowns spread – Bellona". bellona.org. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
mixed uranium and plutonium oxide, or MOX fuel, since September.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|year=(help) - ^ a b http://www.nisa.meti.go.jp/english/files/en20110317-1.pdf
- ^ "Japan's Fukushima nuclear plant faces new reactor problem". Reuters. 12 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ a b http://www.nisa.meti.go.jp/english/files/en20110313-4.pdf Seismic Damage Information (20th press communicate released by NISA on 16:30 13 March 2011).
- ^ "Meltdowns may have occurred in two Japan reactors – Channel NewsAsia". channelnewsasia.com. 2011 [last update]. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|year=(help) - ^ "Japan's TEPCO preparing to release radiation from second reactor". Reuters. 12 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ "TEPCO press release 8". Tepco. 13 March 2011.
- ^ a b http://www.nisa.meti.go.jp/english/files/en20110314-1.pdf Seismic Damage Information (22th Release) by NISA on 07:30 14 March 2011).
- ^ "press release 10". Tepco. 13 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d "Radiation leak feared at spent fuel pool, water injection ordered". Kyodo News. 15 March 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ a b "Japan battles to stop nuclear catastrophe". Financial Times. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ "URGENT: Hydrogen blast occurs at Fukushima nuke plant's No. 3 reactor: agency". Kyodo News Agency. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ "180,000 flee as Japan's nuclear crisis intensifies". MSNBC. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ "Second explosion rocks Fukushima Daiichi". World-nuclear-news.org. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ "An explosion caused by hydrogen at unit 3 of Fukushima Dai ichi NPS (3rd release)" (PDF). Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency. 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Second blast at stricken Japan nuclear plant". The Independent. UK. 14 March 2011.
- ^ Japan Says 2nd Reactor May Have Ruptured With Radioactive Release The New York Times 16 March 2010
- ^ 9:51 am GMT 16 Mar 2011. "Video: Helicopters attempt to cool Fukushima nuclear plant from the air". Telegraph. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "NHK WORLD English". .nhk.or.jp. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Major damage unlikely at Japan nuke plant's No.3 reactor - Kyodo | Energy & Oil | Reuters". Af.reuters.com. 9 February 2009. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Tokyo Elec: want military chopper to try again to douse reactor | Energy & Oil | Reuters". Af.reuters.com. 9 February 2009. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ Helicopter starts spraying water on Japan nuclear plant Reuters 17 March 2011
- ^ http://www.nisa.meti.go.jp/english/files/en20110318-3.pdf
- ^ "IAEA Update on Japan Earthquake". Retrieved 17 March 2011.
Unit 4 was shut down for a routine, planned maintenance outage on 30 November 2010. After the outage, all 548 fuel rods from the reactor was transferred to the spent fuel pool.
- ^ a b c d "Status of the Nuclear Reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi Power Plant". The New York Times. 16 March 2011. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ Wright, David. "Spent Fuel Pools at Fukushima". Union of Concerned Scientists. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ "Attempts to refill fuel ponds , update 4". World Nuclear News. 17 March 2011.
- ^ "Press Release | Damage to the Unit 4 Nuclear Reactor Building at Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station". TEPCO. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ IAEA Update on Japan Earthquake
- ^ "Japan spent fuel pond on fire,radioactivity out-IAEA". Reuters. 11 March 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ "IAEA Update". 15 March 2011.
- ^ "World Nuclear News Update". 15 March 2011.
- ^ Posted: 14 Mar 2011 7:39 am ET. "Radiation levels could damage health: Japan – World – CBC News". Cbc.ca. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ a b "Government spokesman: No continued radiation from reactor 4 – Monsters and Critics". Monstersandcritics.com. 17 November 2010. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ "Japan agency: holes found in nuclear reactor building wall". 15 March 2011.
{{cite web}}: Text "Reuters" ignored (help) - ^ "LIVE: Japan earthquake". BBC News. 15 March 2011.
- ^ "Fukushima No. 4 reactor spent fuel pool may be boiling -Kyodo". Reuters. 15 March 2011.
- ^ "Radiation hits dangerous levels at Japan plant control room". Reuters. 11 March 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ a b "Late Tuesday, officials at the plant said they were considering asking for help from the U.S. and Japanese militaries to spray water from helicopters into the pool."http://www.ajc.com/business/radiation-level-soars-after-872556.html
- ^ "Radiation level soars after Japan nuke plant fire". Times Union. 15 November 2009. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ AP (7 April 2010). "Nuclear Officials May Spray Japanese Power Plant With Water by Helicopter". Fox News. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ "Workers Evacuated From Japanese Nuclear Reactor - NCPR News from NPR". Northcountrypublicradio.org. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Press Release | Fire occurrence at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 4 (2nd Release)". TEPCO. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Fire breaks out again at Fukushima's No. 4 reactor". Kyodo News. 16 March 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ AFP: Blasts, new fire escalate Japan's nuclear crisis
- ^ TEPCO releases photo of No.4 reactor
- ^ Tokyo Electric may disperse boric acid over plant by helicopter | Energy & Oil | Reuters
- ^ Crisis Continues at Crippled Japanese Nuclear Power Plants | East Asia and Pacific | English
- ^ a b Vartabedian, Ralph; Barbara Demick; Laura King (18 March 2011). "U.S. nuclear officials suspect Japanese plant has a dire breach". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
{{cite news}}: More than one of|author=and|last=specified (help) - ^ a b Hiroko Tabuchi; Keith Bradsher (18 March 2011). "Frantic Repairs Go On at Plant as Japan Raises Severity of Crisis". The New York Times. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "原発冷却へ警視庁が特殊放水車 福島第一に使用検討" (in Japanese).|date=17 March 2011|source=asahi.com}}
- ^ "Fukushima nuclear plant evacuated after radiation spikes". The Guardian. United Kingdom. 16 March 2011.
The No 4 reactor is an increasing cause for concern. Tepco believes that the storage pool may be boiling, raising the possibility that exposed rods will reach criticality. “The possibility of re-criticality is not zero,” a Tepco spokesman said.
- ^ "Water cannon truck to tackle spent nuclear fuel pool". Reuters. 16 March 2011.
- ^ "No water in spent fuel pool at Japanese plant: U.S.". CTV News. 16 March 2011.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help); Missing or empty|url=(help); Unknown parameter|http://montreal.ctv.ca/servlet/an/local/CTVNews/20110316/nuclear-fuel-rods-110316/20110316/?hub=ignored (help) - ^ Japan nuclear crisis: Meltdown at Fukushima Daiichi plant may now be inevitability (www.nydailynews.com)
- ^ "U.S. Calls Radiation 'Extremely High,' Sees Japan Nuclear Crisis Worsening". The New York Times. 17 March 2011.
- ^ "4号機プール内に大量の水、自衛隊ヘリ確認". Yomiuri Shimbun (in Japanese). Japan. 17 March 2011.
- ^ Jonathan Weisman Did NRC’s Jaczko Misspeak? The Wall Street Journal blogs.wsj.com 17 March 2011
- ^ "Japan Raises Nuclear Crisis Warning Level Retroactively". New York Times. 18 March 2011.
- ^ By the CNN Wire Staff. "Officials: Spent fuel rods may have burned in blaze at nuclear plant – CNN.com". CNN. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ http://www.nisa.meti.go.jp/english/files/en20110319-4.pdf
- ^ a b "Spraying continues at Fukushima Daiichi". 18 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "Status of nuclear power plants in Fukushima as of 12:30 on 16 March" (PDF). JAIF. 16 March 2011. Retrieved 16 March 2011.
- ^ "Status of nuclear power plants in Fukushima as of 19:00 JST on 16 March" (PDF). JAIF. 16 March 2011. Retrieved 16 March 2011.
- ^ "Status of nuclear power plants in Fukushima as of 09:00 JST on 17 March" (PDF). JAIF. 17 March 2011. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ "Status of nuclear power plants in Fukushima as of 16:00 JST on 17 March" (PDF). JAIF. 17 March 2011. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ "Status of nuclear power plants in Fukushima as of 22:00 JST on 17 March" (PDF). JAIF. 17 March 2011. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ "Status of nuclear power plants in Fukushima as of 10:00 JST on 18 March" (PDF). JAIF. 18 March 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Status of nuclear power plants in Fukushima as of 22:00 JST on 18 March". JAIF. 18 March 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ a b "Status of nuclear power plants in Fukushima as of 10:00 JST on 19 March" (PDF). JAIF. 19 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "IAEA Update on Japan Earthquake". International Atomic Energy Agency. 19 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ http://www.tepco.co.jp/en/challenge/energy/pdf-1/nuclear-e.pdf
- ^ BMU, German Federal Ministry of the Environment. "Update on Safety ("Kurzuebersicht ueber aktuelle Sicherheitslage - 18 March 2011 19:00 h MEZ)". Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "Harmful Radiation Leak After Japan Explosion". news.sky.com. 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ Japan earthquake: live - Telegraph
- ^ a b Foreigners stream out of Tokyo Inquirer Headlines
- ^ a b Seoul ready to send planes, ships to evacuate its citizens from Japan Korea Herald
- ^ a b US evacuates nationals from Japan Travel News
- ^ a b c d e "Battle to stabilise earthquake reactors". World Nuclear News. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ "News Brief, 3/18/11, 10 AM EDT". Nuclear Science and Engineering at MIT. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "Progress Update at Fukushima Daiichi – 3/17/11 (3:30 pm EST)". Nuclear Science and Engineering at MIT. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "IAEA Update on Japan Earthquake". International Atomic Energy Agency. 19 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ a b c "Modified version of original post written by Josef Oehmen". Nuclear Science and Engineering at MIT. 14 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ a b Broad, William. "In Stricken Fuel-Cooling Pools, a Danger for the Longer Term". The New York Times. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Choi, Christy (17 March 2011). "New Power Lines Could Help Ease Fukushima Nuke Crisis". Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d Black, Richard. "Choppers and cannon bring no nuclear relief". Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ "Japan steps up cooling operation". Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ "Reactors may restore cooling systems by Sat". 18 March 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Power line connected to crippled nuclear plant". 18 March 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "IAEA Update on Japan Earthquake". International Atomic Energy Agency. 19 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "Japan nuclear crisis and tsunami aftermath - live updates". The Guardian. UK. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ "SDF finishes spraying water on No.3 reactor". Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d McCurry, Justin. "Japan to use water cannon at nuclear plant as international concern grows". Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ a b "Radiation levels lowered after water injection". Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ "Fukushima Fifty 'on suicide mission' to battle N-plant meltdown send haunting messages to families... as radioactive steam pours from wrecked reactor". Daily Mail. UK. 17 March 2011. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ "How would you solve Fukushima?". The Guardian. UK. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ Tokyo Electric may disperse boric acid over plant by helicopter | Energy & Oil | Reuters
- ^ "France rushes 95 tonnes of boron to Japan". The Straits Times. 17 March 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ Ukraine advises Japan to use tin to cool Fukushima reactor KyivPost
- ^ Chernobyl History: Initial response TESEC European Centre of Technological Safety
- ^ Chernobyl veterans advise Japan to cool reactors with tin BCM News
- ^ Saoshiro, Shinichi. "Japan weighs need to bury nuclear plant; tries to restore power". Reuters. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ Chernobyl Accident Appendix 1 World Nuclear Association
- ^ a b "Nuke plant blasts raise radiation threat". Australian Broadcasting Commission. 15 March 2011.
- ^ a b c "Radiation leak feared at nuke plant, people urged to stay indoors". Kyodo News Agency. 15 March 2011.
- ^ "Japan fears damage to reactor container]". Australian Broadcasting Commission. 15 March 2011.
- ^ "Tokyo radiation eases – Newstalk ZB". newstalkzb.co.nz. 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
Tokyo officials say they detected 0.8 of a micro-sievert in the morning, which is about 27 times what's considered normal. Health authorities say it's now fallen to about twice the normal level in Tokyo but they need to keep a close watch on it.
- ^ "More nuclear reactors show signs of trouble". Australian Broadcasting Commission. 15 March 2011.
- ^ a b "Radioactive cloud spreading", [The Australian] 16 March 2011, Peter Alford
- ^ http://www.tepco.co.jp/cc/press/betu11_j/images/110315g.pdf
- ^ Japan grateful to 'hero' nuke workers [Australian Broadcasting Commission]] 16 March 2011
- ^ "NHK WORLD English". www3.nhk.or.jp. 2011 [last update]. Retrieved 16 March 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|year=(help) - ^ [plant.http://www.iaea.org/newscenter/news/tsunamiupdate01.html IAEA Briefing on the Fukushima Nuclear Emergency (17 March 14:00 UTC)] International Atomic Energy Agency
- ^ Scientists Project Path of Radiation Plume By William J. Broad, 16 March 2011, The New York Times
- ^ "Nouvelle simulation du nuage de pollution radioactive au Japon". 16 March 2011.
- ^ "Aktuelle Informationen". ZAMG. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ [2], Updated 19/3 09:39AM UTC.
- ^ NHK WORLD (2011 [last update]). "NHK WORLD English". www3.nhk.or.jp. Retrieved March 19, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|year=(help) - ^ "Radiation in everyday life". IAEA.
- ^ a b http://www.world-nuclear.org/info/inf05.html Nuclear Radiation and Health Effects
- ^ Table 2-2 EPA
- ^ Radiation Effects vs. Limits Massachusetts Office of Health and Human Services citing EPA Table 2-4
- ^ Publication 60 1990 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection - ICRP Publication 60
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
turner421was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Aus2was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Last Defense at Troubled Reactors: 50 Japanese Workers", The New York Times, NY, USA, 2011‐3‐16
{{citation}}:|section=ignored (help); Check date values in:|date=(help) - ^ Gov't ups permissible radiation level, JP: NHK
- ^ a b Radiation Exposure from Iodine 131 Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry
- ^ a b Expert: Japan botching crisis management, iodine distribution CBS News, 16 March 2011, Ken Millstone.
- ^ Toxicological profile for Cesium Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, April 2004
- ^ a b Radioisotope Brief: Cesium-137 (Cs-137) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- ^ a b c d Strontium EPA
- ^ Plutonium threat at Japan reactor, expert warns 14 March 2011, Cnet News
- ^ a b Plutonium In Fuel Rods: Cause For Concern? By Dan Charles, 17 March 2011, NPR.
- ^ Hurd, Rick (17 March 2011). "Amid Japan nuclear drama, Bay Area potassium iodide sales skyrocket". Contra Costa Times. San Jose Mercury News. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "Radiation fears spark rush for iodine pills". CTV News. Canada: CTV Television Network. 15 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "South Korean radiation fear iodine rush". Australia Network News. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ a b Jo Ling Kent (17 March 2011). "Chinese scramble to buy salt as radiation fears grow". CNN. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ a b "Health experts warning over iodine rush". Australia: Herald Sun. 15 March 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "U.S. to send drones over damaged nuke plant". CBS News. 16 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "Worldwide reports of iodine overdoses: WHO". ABC Online. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. 18 March 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "Relief efforts still getting started days after earthquake". Stripes.com. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ BBC.
- ^ Dawson, Chester (14 March 2011). "WSJ online U.S. Military Joins in Quake-Relief Effort". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- ^ Broad, William J. (13 March 2011). "Military Crew Said to Be Exposed to Radiation, but Officials Call Risk in U.S. Slight". New York Times. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ US aircraft carrier reportedly sails into radioactive cloud, Jerusalem Post, 14 March 2011
- ^ Shanker, Thom (14 March 2011).17 in U.S. Navy Treated for Contamination, New York Times
- ^ CNN Wire Staff (15 March 2011). "U.S. Navy aircraft carrier detects radiation". CNN. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ Stars and Stripes, 14 March 2011, Erik Slavin reporting.
- ^ Nuclear Officials May Spray Japanese Power Plant With Water by Helicopter, Fox News, 15 March 2011.
- ^ "Blast destroys part of Japan nuclear plant". CBC.ca. 12 March 2011.
- ^ Glendinning, Lee. "Japan tsunami and earthquake – live coverage | World news | guardian.co.uk". Guardian. UK. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ "Pilot information for Sendai Airport". 12 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ "Radioactive emergency team dispatched". NHK World. 12 March 2011. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ Black, Richard (12 March 2011). "Japan earthquake: Explosion at Fukushima nuclear plant". BBC News. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ Joe Weisenthal (4 March 2011). "Fukushima Nuclear Plant". Businessinsider.com. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
{{cite web}}: Text "12 March 2011, 4:08 am" ignored (help); Text "194,758" ignored (help); Text "259" ignored (help) - ^ Richard Black. "BBC News – Japan quake: Radiation rises at Fukushima nuclear plant". BBC News. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ "Japan's PM urges people to clear 20-km zone around Fukushima NPP (Update-1) | World | RIA Novosti". En.rian.ru. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ Sanger, David E.; Wald, Matthew L.; Tabuchi, Hiroko (17 March 2011). "U.S.: Reactor may spew radiation". The New York Times. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- ^ "10,000 missing in Japanese town | News.com.au". news.com.au. 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
- ^ "Japan: At least 3 exposed to radiation in nuclear station explosion – Israel News, Ynetnews". ynetnews.com. 2011. Retrieved 15 March 2011.
The three residents were among a group of some 90 patients hospitalized in the town of Futaba-machi, and were chosen at random by doctors for tests linked to the nuclear incident, the public broadcaster NHK reported. (AFP)
- ^ a b c Tom, Watkins (13 March 2011). "Official: 'We see the possibility of a meltdown'". CNN. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
"There is a possibility, we see the possibility of a meltdown," said Toshihiro Bannai, director of the agency's international affairs office
- ^ "Japan earthquake: Meltdown may be occurring, Japanese nuclear official says". Los Angeles Times. 27 February 2011. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ Donn, Jeff; Yamaguchi, Mari (13 March 2011). "Japan quake causes emergencies at 5 nuke reactors". MSNBC. Associated Press. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ "Government: No meltdown in Japanese nuclear plant". Monsters and Critics. 13 March 2011. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ "Water injected into Fukushima reactor". The Japan Times Online. Retrieved 13 March 2011.
- ^ "Japanese Officials: Nuclear Fuel Rods Appear to be Melting in 3 Reactors". NationalJournal.com. 14 March 2011.
- ^ "Kan inspects quake-hit nuclear plant in Fukushima". Kyodo News. 12 March 2011. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ Japanese nuclear plant hit by fire and third explosion | World news | "The Guardian"
- ^ Shuster, Simon. "Fire at Fourth Reactor: Is Worse Yet to Come in the Fukushima Nuclear Disaster?". Time Magazine.
- ^ Maitre, Marie. "UPDATE 1-French nuclear agency now rates Japan accident at 6". Reuters. Retrieved 16 March 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Richard Black. "BBC News - Japan earthquake: Fukushima nuclear alert level raised". BBC News. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ "Frantic cooling efforts continue". joongangdaily. 2011. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ Takahara, Kanako, and Kazuaki Nagata, "Meltdown looks more imminent", Japan Times, 16 March 2011, p. 1.
- ^ "The Canadian Press: Obama defends use of nuclear energy despite calamity in Japan". Google. 2011. Retrieved 16 March 2011.
- ^ Halloran, Liz. "Nuclear Information Gap Spreads Doubt, Fear". NPR. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ Rayner, Gordon. "Japan still racing against the clock". Telegraph. Retrieved 19 March 2011.
- ^ "The Tokyo Electric Power Company, Inc.: TYO:9501 quotes & news - Google Finance". Google. 31 January 2011. Retrieved 18 March 2011.
- ^ Tokyo Shares Plunge 13% The Wall Street Journal 15 March 2010
- ^ "Japan's Nikkei 225 rebounds as economic concerns ease", BBC News -
- ^ "Nuclear Renaissance Threatened as Japan’s Reactor Struggles" Bloomberg, 13 March 2011, Retrieved 14 March 2011
- ^ Analysis: Nuclear renaissance could fizzle after Japan quake Reuters, 14 March 2011, Retrieved 14 March 2011
- ^ Japan nuclear woes cast shadow over U.S. energy policy Reuters, published 13 March 2011, accessed 14 March 2011
- ^ Nuclear winter? Quake casts new shadow on reactors MarketWatch, 14 March 2011, retrieved 14 March 2011
External links
- Webcam Fukushima nuclear power plant I
- TEPCO News Releases, Tokyo Electric Power Company
- NISA Information update, Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency, the nuclear safety authority of Japan
- JAIF Information update, Japan Atomic International Forum
- JAEA Information update, Japan Atomic Energy Agency
- IAEA Update on Japan Earthquake, International Atomic Energy Agency
- Second "Explosion" at Reactor No. 3 on YouTube
- Anatomy of a meltdown, Nature
- Weather forecast for the area
- FLEXPART analysis showing particle transport forecast for the northern hemisphere]
