Gambling in Macau: Difference between revisions
Added {{merge from}} tag to article (TW) |
Reverted to revision 591048037 by 92.20.51.239 (talk): Wikipedia:Copy-paste. (TW) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{merge from|Macau gaming law|discuss=Talk:Gambling in Macau#Proposed merge with Macau gaming law|date=March 2014}} |
|||
{{Use British English|date=January 2012}} |
{{Use British English|date=January 2012}} |
||
{{Use dmy dates|date=January 2012}} |
{{Use dmy dates|date=January 2012}} |
||
| Line 20: | Line 19: | ||
In 2002, the Macau government ended the monopoly system and 3 (later 6) casino operating concessions (and subconcessions) are granted to [[Sociedade de Jogos de Macau]] (SJM, an 80% owned subsidiary of STDM), [[Wynn Resorts]], [[Las Vegas Sands]], [[Galaxy entertainment|Galaxy Entertainment Group]], the partnership of [[MGM Mirage]] and [[Pansy Ho Chiu-king]], and the partnership of Melco and PBL. Today, there are 16 casinos operated by the STDM, and they are still crucial in the casino industry in Macau, but in 2004, the opening of the [[Sands Macau]] ushered in the new era. |
In 2002, the Macau government ended the monopoly system and 3 (later 6) casino operating concessions (and subconcessions) are granted to [[Sociedade de Jogos de Macau]] (SJM, an 80% owned subsidiary of STDM), [[Wynn Resorts]], [[Las Vegas Sands]], [[Galaxy entertainment|Galaxy Entertainment Group]], the partnership of [[MGM Mirage]] and [[Pansy Ho Chiu-king]], and the partnership of Melco and PBL. Today, there are 16 casinos operated by the STDM, and they are still crucial in the casino industry in Macau, but in 2004, the opening of the [[Sands Macau]] ushered in the new era. |
||
In 5 October 2011 Macau casino stocks plummeted after a massive sell-off early in the week over fears of tighter credit and an economic slowdown in China. Gaming giant SJM saw shares fall as much as 20% to HK$11.28, while Galaxy Entertainment tumbled 21% to HK$9.18. US-based casino enterprises were also hit hard during the decline with Sands China and Wynn Macau both falling 14%. The benchmark Hang Seng Index was down 4%. Fears of an economic slowdown in export-driven China have resulted from turmoil in Europe and the United States, according to analysts, casusing a credit squeeze that will make it harder for Macau’s high rollers to borrow money for gambling. According to Bloomberg, an estimated two-thirds of Macau’s gambling revenues come from high-spending, mainland Chinese who gamble with borrowed money from "junket operators," which are tourist agencies that provide travel packages and loans to gamblers. Despite the credit fears and stock market decline, Macau gambling revenues continue to soar with 60% growth recorded in 2010. Macau casino stocks had risen 20% this year before the sell-off, and analysts remain optimistic on the region's prospects for the next year.<ref>http://www.pokerupdate.com/news/business-and-finance/macau-casino-stocks-plummet/</ref> A week later Macau casino stocks rebounded after a report revealed gambling revenues grew 39% in September. US-based Sands China posted the biggest gain, up 26%, while Wynn Macau and MGM China both jumped more than 20%. Galaxy Entertainment (up 18%), Melco International Development (15%) and SJM Holdings (16%) also recorded increases. Hong Kong’s benchmark Hang Seng Index rose more than 4% to 18,131. In addition to a rebound in Macau casino stocks, junket operator (a tourist agency that provides travel packages and loans to gamblers) Asia Entertainment and Resources announced that revenues soared 189% to $1.92 billion. Chairman Lam Man Pou told CalvinAyre: "While we are aware of recent concerns that have been raised about the Macau VIP business, we can firmly say we have not seen any decrease in demand or growth in terms of the VIP market."<ref>http://www.pokerupdate.com/news/business-and-finance/macau-casino-stocks-rebound/</ref> |
|||
On 1 March 2012 it was revelead the Macau Gambing market was worth $3 Billin. Macau, currently the preferred location for nose-bleed stakes poker games, has seen its gaming revenues rise by 22% to $3 billion during February, according to a report in the Las Vegas Review-Journal. The special administrative region of China is host to some of the big casino operators such as Wynn and MGM resorts, who stand to continue to cash in on a thriving tourist trade in the East. The online poker player community is buzzing with news of soft games and high winrates in contrast to the tougher games in Las Vegas and Online. Many are making the trip to Macau to take advantage of favourable exchange rates and a high standard of living: the former Portuguese colony has the second highest life expectancy in the world.<ref>http://www.pokerupdate.com/news/business-and-finance/in-brief-macau-gaming-market-worth-3-billion/</ref> |
|||
In 2014 Macau’s gaming sector did not have a great start to the year, with January’s revenue growth having fallen below the estimates of economic analysts. That led to a fear of a potential slowdown in the growth of the world’s largest gaming area after a record-breaking year of revenue in 2013. Those fears will likely be gone after February’s revenue figures were released this week. The figures show that Macau’s gaming revenue for the month of February totalled US$4.8 million, a 40% increase from the month before. That was an amount that actually exceeded analysts’ expectations, which were between 29 and 35 percent. February’s gaming revenue was also the highest ever monthly revenue recorded in Macau, which was previously US$4.57 million in October last year. Macau saw a major spike in the number of tourists from the Chinese mainland throughout February, in particular during Chinese New Year celebrations in the first week of the month.<ref>http://www.pokerupdate.com/news/industry-and-market-analysis/february-a-revenue-record-breaker-for-macau/</ref> |
|||
==Economic aspects== |
==Economic aspects== |
||
Revision as of 16:49, 28 March 2014
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2006) |
| Economy of Macau |
|---|
 |
| Currency and identity |
| Resources |
| Companies |
| Other Macau topics |


Gambling in Macau has been legal since the 1850s when the Portuguese government legalised the activity in the colony. Since then, Macau has become known worldwide as the "Monte Carlo of the Orient".
Gambling tourism is Macau's biggest source of revenue, making up about 50% of the economy. Visitors are made up largely of Chinese nationals from the mainland and Hong Kong. With the entry of large foreign casinos from Las Vegas and Australia, Macau overtook the Las Vegas Strip in gaming revenues in 2007.
Until Western-style casino games were introduced in the 20th century, only Chinese games were played, the most popular being Fan-Tan. Generally, gambling in Macau can be divided into three different categories: casino games and greyhound racing. There is also sports betting and a number of lotteries. At the present time, Macau does not license online gaming operations.
History
In an attempt to generate revenues for the government, gambling in Macau was legalised around 1850. In the late 19th century, the government introduced a licensing system for the fantan houses (Chinese gambling houses). It is reported that over 200 gambling houses were required to pay gambling rent to the government.[1] The second casino monopoly concession was granted to the Tai Heng[2] Company in 1937.[3] The company was, however, too conservative to fully exploit the economic potential of gambling. The industry saw a major breakthrough in 1962 when the government granted the Sociedade de Turismo e Diversões de Macau (STDM), a syndicate jointly formed by Hong Kong and Macau businessmen, the monopoly rights to all forms of gambling. The STDM introduced western-style games and modernised the marine transport between Macau and Hong Kong, bringing millions of gamblers from Hong Kong every year.[1] The license was extended in 1986 for another 15 years but expired at the end of 2001.
Macau was transferred to the People's Republic of China in 1999 and became a special administrative region of China. During this transition, there were no changes to gambling policy in Macau.[4]
In 2002, the Macau government ended the monopoly system and 3 (later 6) casino operating concessions (and subconcessions) are granted to Sociedade de Jogos de Macau (SJM, an 80% owned subsidiary of STDM), Wynn Resorts, Las Vegas Sands, Galaxy Entertainment Group, the partnership of MGM Mirage and Pansy Ho Chiu-king, and the partnership of Melco and PBL. Today, there are 16 casinos operated by the STDM, and they are still crucial in the casino industry in Macau, but in 2004, the opening of the Sands Macau ushered in the new era.
Economic aspects
The so-called "Monte Carlo of the Orient", Macau's economy relies heavily on gambling. Nowadays, the gambling industry generates over 40% of the GDP of Macau. Since the early 1960s, around 50% of Macau's official revenue has been driven by gambling. The percentage remained steady until the late 1990s. In 1998, 44.5% of total government revenue was produced by the direct tax on gambling. Then there was a 9.1% decrease in 1999, probably due to internet gaming. After the handover of the Macau from Portugal to China, the SAR released gambling licenses to other companies in order to eliminate the monopoly played by the STDM. In 2002, the government signed concession contracts with two Macau gaming companies, Wynn Resort Ltd. and Galaxy Casino. This opened the gambling market for competition and increased government tax revenue significantly. It also attracted more tourists to Macau. At this moment, according to official statistics, gambling taxes form 70% of Macau's government income.[5]
Many forms of gambling are legal there, such as blackjack, baccarat, roulette, boule, Sic bo, Fan Tan, keno and slot machines.
However, the gambling industry is also a source of instability in the Macau economy, as the nature of gambling business is not susceptible to technological advancement or productivity growth. The gambling business is still dependent on the prosperity of other Asian economies, especially that of Hong Kong.
Gambling forms
Gaming policy
Detailed law is enforced in Macau to ensure "qualified operation of gambling" in Macau. The details are listed in Law 16/2001 (regime jurídico da exploração de jogos de fortuna ou azar em casino), and other laws regulating the activity of gaming promoters and credit for gaming.
The Gaming Inspection and Coordination Bureau (known as DICJ) is the main government unit that oversees the operation of different gaming activities.
Under Macau law, it stated that a permit issued by the Gaming Inspection and Coordination Bureau is required for the operation of lotteries sales, lucky draw or similar activities, and the initial procedure in the application on the operation of lotteries sales, lucky draw, or similar activities is to submit a notification to the relevant government department ten days prior to the application.
Casinos
Macau has 33 casinos, of which the biggest is The Venetian Macau. Twenty-three casinos are located on the Macau Peninsula and ten on Taipa Island. They all operate under a government franchise and under a common set of rules.
The main casino operators in Macau are SJM Holdings, Galaxy Entertainment and Las Vegas Sands with respective revenues of 9.7, 4.8, and 4.2 billion in 2011.[6]
Poker was introduced only in August 2007, in an electronic table format at Galaxy Starworld casino using PokerPro tables from PokerTek, Inc The first live poker tournament was the Asia Pacific Poker Tour Macau event in November 2007. Shortly thereafter, in January 2008, the government of Macau published the official rules for Texas hold 'em poker games in Macau. In February 2008, Grand Lisboa Casino added the first live-dealer cash game tables in Macau. In May 2008, 'PokerStars Macau' opened at Grand Waldo Casino. In November 2008, Texas Holdem' Poker opened at Wynn Macau and the "Learn to Play" table is available. 'PokerStars Macau' moved to a new location at the Grand Lisboa Casino in March 2009. Today, Wynn Macau, StarWorld, and the Venetian offer live-dealer cash game poker tables. In 2013 PokerStars announced PokerStars Live at the City of Dreams Macau Poker once was but is no longer offered at Grand Lisboa and Hard Rock.[7]
Gambling has been legal in Macau for a long time beginning around 1850 where there was a licensing system for gambling houses until 1863. Beginning in 1934, casinos' ownership and operation was centralised where through private negotiations, some franchises monopolised the operation right of all casinos. The casino industry has been controlled by the STDM monopoly for 39 years but, this changed in 2001 when casino licenses were offered to other casino operators, including American companies such as Las Vegas Sands (Sheldon Adelson) and Wynn Resorts (Steve Wynn) and then later on May 18, 2004, the Sands Macau casino opened near the Macau Ferry Terminal.
See: Overview of Casinos and attractions in Macau
| Name | Opening Hours | Size | Special Features |
| Casino Lisboa | 24 hours | 107 slots and 146 table games (190,000 sq ft) | Hotel with 1,000 rooms and 6 restaurants |
| Casa Real Casino | 24 hours | 123 slots and 53 table games (36,000 sq ft) | Hotel with 381 rooms and 2 restaurants |
| Grandview Casino | 24 hours | 51 table games | Hotel with 407 rooms and 2 restaurants |
| Casino Macau Palace | 24 hours | 51 slots and 12 table games (11,120 sq ft) | None |
| Altira Macau | 24 hours | 550 slots and 220 table games | Hotel with 216 VIP rooms |
| Jai Alai Casino | 24 hours | 208 slots and 61+ table games, 4 VIP rooms (67,075 sq ft) | None |
| Kam Pek Casino | 24 hours | 71 slots and 24 table games; 4 VIP rooms (34,320 sq ft) | None |
| Kingsway Hotel & Casino | 12:00 pm – 4:00 am | 20 slots and 8 table games (11,755 sq ft) | Hotel with 410 rooms |
| Grand Lapa Hotel | 12:00 pm – 4:00 am | 59 slots and 11 table games (12,140 sq ft) | Hotel with 437 rooms and 6 restaurants |
| Mocha Clubs | 24 hours | 1000 slots (number of tables unknown) | None |
| New Century Hotel & Casino | 24 hours | 19 table games | Hotel with 554 rooms |
| The Legend Club | 24 hours | 108 slots and 12 table games; 1 VIP room (15,000 sq ft) | None |
| Sands Macao | 24 hours | 405 slots and 270 gaming tables (165,000 sq ft) | 51 suite VIP hotel |
| Golden Dragon Casino | 24 hours | 137 slots, 123 gaming machines and 85 gaming tables, 15 VIP rooms | 483 deluxe guest rooms including 84 harbour view rooms and 45 signature suites |
| Greek Mythology Casino | 24 hours | 228 tables (to be upgraded to 500), 100 slot machines (160,000 sq ft) | 554 rooms at the New Century Hotel |
| MGM Macau | 24 hours | 345 gaming tables and 1035 slot machines | 600-room hotel |
| Wynn Macau | 24 hours | 375 slot machines and 212 gaming tables (246,000 sq ft) | Integrated resort with 600 rooms and restaurants |
| The Venetian Macao, Cotai strip | 24 hours | 3400 slot machines and 800 gaming tables (550,000 square feet of casino space) | Integrated resort with 3000 suites, convention and retail space |
| Babylon Casino – Fisherman's Wharf | 1100–2300 | ||
| Casino Crystal Palace at Hotel Lisboa | 36 slots (14,100 sq ft) | Makccarat tables | |
| Diamond Casino at Holiday Inn | 6 + 1 VIP Room, 32 slot machines (6,900 sq ft) | ||
| Emperor Palace Casino | 64 gaming table on 3 floors of casino concourse & 8 VIP Halls, 365 slot machines | ||
| Fortuna Casino | 35 gaming tables | ||
| Galaxy Rio Casino | 80 tables, 150 slots, 4 VIP rooms | 450 rooms, 65 suites | |
| Galaxy Starworld | 24 Hours | 300 tables, 371 slots | StarWorld Hotel |
| Galaxy Waldo Hotel and Casino | 24 Hours | 63 tables, 8 VIP rooms, 100 slots | 161 rooms |
| Pharaoh's Palace Casino | 24 Hours | 109 tables 5 VIP rooms, 383 slots (9000 sq ft) | 3 Presidential suites, 448 Rooms and Suites at The Landmark |
| Ponte 16 | 24 Hours | 150 tables, 5 VIP halls and 20 rooms | |
| Casino Marina at Tapia | 20 tables, 4 VIP rooms, 37 slots 45,900 | 312 rooms and suites at Marina Hotel | |
| Crown Casino, Taipa – u/c | 220 (80 VIP), 183,000 sq ft (17,000 m2) gaming space 500 slots | ||
| MJC Casino, Taipa | 19 tables, 2 VIP rooms, 15,800 sq ft (1,470 m2) | 3 Deluxe Rooms and 22 Junior Suites and 1 Presidential Suite and 352 Standard Rooms and 26 Suites | |
| City of Dreams | 24 Hours | 420,000-square-foot (39,000 m2) gaming floor containing 550 gaming tables and 1500 machines; 85,000 square feet (7,900 m2) of retail space; Theatre of Dreams (1,700 seaters) | 366-room Hard Rock Hotel and 290 suites Crown Towers Hotel, Cotai. Grand Hyatt Macau (971 rooms). |
| Galaxy Cotai Mega Resort, Cotai | 450 tables, 1000 slot | 2000 hotel rooms, 50 restaurants, an artificial beach, a wave pool | |
| Galaxy Grand Waldo, Cotai | 168 tables, 25 machines, 350 slots (120000 sq ft) | ||
| Casino Oceanus | 32,000 m2 on 3 floors containing 269 gaming tables and 569 machines[8] | special facade, closest casino to the ferry terminal directly connected by a pedestrian bridge |
Horse racing
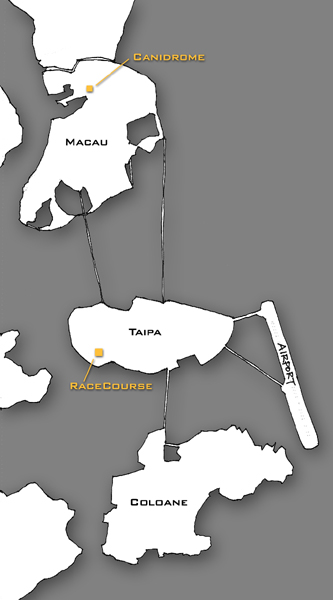
Other than casinos, there is betting at the Macau Jockey Club and the dog-racing Canidrome.
Horse-racing mainly takes place every Tuesday and Saturday or Sunday at the race-course on the Taipa Island of Macau. The race-course has an area of 450,000 square metres and 18,000 seats for gamblers, and is open only for people over 18 years of age.
The Macau Jockey Club was formerly the Macau Trotting Club. In 1991, it was acquired by a consortium led by Stanley Ho. The Macau Jockey Club is one of the largest private employers of Macau with around 1,400 employees and around 1,100 part-timers.
| Year | Number of Visitors | overall betting turnover |
| 89/90 | 268,561 | 462,642,000 |
| 90/91 | 305,957 | 637,308,000 |
| 91/92 | 349,845 | 979,940,000 |
| 92/93 | 353,730 | 1,296,616,000 |
| 93/94 | 324,953 | 1,296,133,000 |
| 94/95 | 367,185 | 1,521,334,000 |
| 95/96 | 376,487 | 2,285,331,000 |
| 96/97 | 352,440 | 2,635,168,000 |
| 97/98 | 369,957 | 3,421,173,000 |
| 98/99 | 325,444 | 3,576,040,000 |
| 99/00 | 306,319 | 3,567,430,000 |
| 00/01 | 284,569 | 4,019,742,000 |
| 01/02 | 330,298 | 3,263,321,000 |
| 02/03 | 308,168 | 3,297,540,000 |
Ways of betting
- On-course Betting
There are over 210 betting terminals "on-course". All terminals can perform sell and pay functions. Punters may bet in Hong Kong dollars or Macau patacas. Bets are accepted up to the start of each race. Punters may place a bet by oral instructions or by filling a ticket.
- Off-course Betting
There are over 80 betting terminals in the Off-Course Betting Centres. 14 Off-course Betting Centres are located in popular districts of Macau and Taipa.
- Internet betting
The Internet betting service commenced on 20 September 2003. Customers can review the Club's internet betting website at www.macauhorsebet.com.
- Telephone Services
There are over 600 telephone service terminals and a total of over 38,000 telebet accounts. The winning dividend of account holders may at their instructions be automatically transferred to their bank accounts.
- Fast Access Terminals (FAT)
Launched in June 1997, the personal betting terminal, FAT (Fast Access Terminal) offers betting, calculation of bet units, record tracking of bets, account enquiry, withdrawal instructions and other related information on races such as declaration and race-odds. Close to 1,000 customers are currently using FAT.
- Hong Kong Service Centres
Three service centres are now set up in Hong Kong including Shaukeiwan Service Centre, Sheung Wan Service Centre and Mongkok Service Centre.
Greyhound Racing
Greyhound Racing takes place at the Canidrome on Avenida General Castelo Branco (see image above for the location of the canidrome). These races are held on Mondays, Thursdays, Fridays and weekends starting from 7:45 pm and there are 16 games on every racing evenings. Admission is MOP$10 (usable for betting) for the public stand. Boxes are MOP$80 (Monday to Thursday) and MOP$120 (Friday to Sunday and Public Holidays) with a minimum charge of MOP$30 per person. Bar, snack-bars and restaurant facilities are available.
Players can bet inside the greyhound racing centre, or in off-course betting centres located in the Hotel Lisboa, Jai-Alai Palace and Kam Pek Casino.
Gambling and society
The casino industry is viewed by some as harmful to society. A high crime rate was one of the biggest problems that Macau's colonial Portuguese government had to face. Since Macau's return to China's rule in 1999, the public security situation has markedly improved. With the growth of the casino industry, a business called "bate-ficha" was developed and it is usually run by different triad societies. The bate-ficha business is an element of triad involvement in Macau's gambling industry. Bate-ficha involves selling customers "dead chips" that cannot be exchanged for cash in the casinos, but only by bate-ficha men or women, who are officially known as "gaming promoters" or "middlemen." for a commission.
Triad involvement in Macau casinos makes a serious social impact on the local area. It attracts the attention of Chinese gangsters, whose deadly battles over the fortunes to be made from racketeering and extortion in the territory are a continuing problem. As different triad societies compete for controlled territory in the casinos and on the streets, disputes between societies occur from time to time. These are often settled in violent ways. Even worse, triad societies have grown so powerful in Macau that there was a trend that people tried to seek help from these societies rather than from the police. Although the situation has improved since the 1999 handover to China, the problem is still entrenched in the local area.
See also
References
- ^ a b Chan, S. S. (2000). The Macau Economy. Macau: Publications Centre, University of Macau. ISBN 99937-26-03-6.
- ^ "Macau Gaming Summary". UNLV Center for Gaming Research. Retrieved 19 April 2012.
- ^ Macau Yearbook 2007. Government Information Bureau of the Macau SAR. 2007. ISBN 978-99937-56-09-5.
- ^ "All you need to know, Macau Hotel". Gambling Info. Retrieved 27 June 2011.
- ^ Bloomberg, Macau Casinos Top Las Vegas as Adelson, Wynn, Battle Stanley Ho, 1 March 2007
- ^ "Main casino operators in Macau". Travel & Gamble Online Magazine.
- ^ http://www.intensegambling.com/casinos/macau/best-poker-rooms/
- ^ video on www.oceanus.asia