1,3-Indandione

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
indane-1,3-dione
| |
| Other names
Indandione
1,3-diketohydrindene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.191 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 146.14 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow solid |
| Density | 1.37 g / cm3 |
| Melting point | 129—132[1][2] °C |
| slight | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
1,3-indandione is an aromatic trans-fixed β-diketone, in standard conditions it is referred to in different sources as colourless or yellowish[3], green[4] or (most commonly) yellow solid. It is an anticoagulant used as a rodenticide.[citation needed]
A valuable contribution in research of 1,3-indandiones and other diketones belongs to a great Latvian chemist Gustavs Vanags.
Structural properties
In the solid 1,3-indandione occurs as a diketone whereas its water solution is partially (~2%) enolized. The enolate anion exhibits significant delocalisation, and the highest electron density is on the second carbon. This explains many of chemical properties of the compound.
Preparation
The well-known method is decarboxilation of the sodium salt of 2-etoxycarbonyl-1,3-indandione, which itself is obtained by Claisen condensation of ethyl acetate and diethyl phthalate (of course another alcohol moieties can be present in the raw materials).
Chemical properties
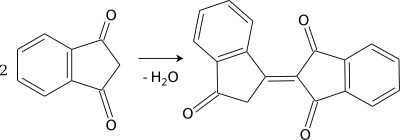
1,3-Indandione is a very strong C-nucleophile. It undergoes self-condensation quite easily, resulting in bindone.
Another example is bromination.
1,3-indandione could be reduced till indanone, 3-hydroxy-1-insanone, 1,3-indanediol or even indane, depending on the method used.
Uses
Certain derivatives are used in human medicine. Some another ones could be promising materials in the photonics field.
See also
References
This article is in the process of being translated from German in the 1,3-indandion-language Wikipedia. In order to reduce edit conflicts, please consider not editing it while translation is in progress. |