Ophthalmic artery
| Ophthalmic artery | |
|---|---|
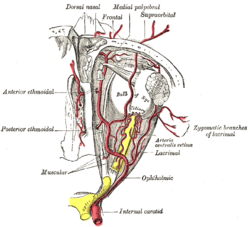 The ophthalmic artery and its branches. | |
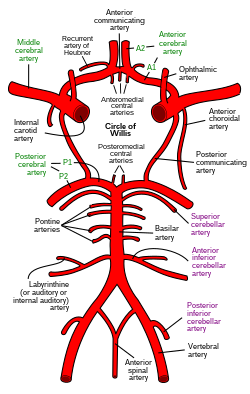 Diagram of the arterial circulation at the base of the brain (inferior view). Ophthalmic artery labeled at upper right. | |
| Details | |
| Source | Internal carotid |
| Branches | Lacrimal artery Supraorbital artery Posterior ethmoidal artery Anterior ethmoidal artery Internal palpebral artery Supratrochlear artery Dorsal nasal artery Long posterior ciliary arteries Short posterior ciliary arteries Anterior ciliary artery Central retinal artery Superior muscular artery Inferior muscular artery |
| Vein | superior ophthalmic, inferior ophthalmic |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria ophthalmica |
| MeSH | D009880 |
| TA98 | A12.2.06.016 |
| TA2 | 4469 |
| FMA | 49868 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The ophthalmic artery (OA) is an artery of the head. It is the first branch of the internal carotid artery distal to the cavernous sinus. Branches of the ophthalmic artery supply all the structures in the orbit around the eye, as well as some structures in the nose, face, and meninges. Occlusion of the ophthalmic artery or its branches can produce sight-threatening conditions.
Structure
The ophthalmic artery emerges from the internal carotid artery.[1] This is usually just after the internal carotid artery emerges from the cavernous sinus. In some cases, the ophthalmic artery branches just before the internal carotid exits the cavernous sinus. The ophthalmic artery emerges along the medial side of the anterior clinoid process. It runs anteriorly, passing through the optic canal inferolaterally to the optic nerve.[1] It can also pass superiorly to the optic nerve in a minority of cases.[2] In the posterior third of the cone of the orbit, the ophthalmic artery turns sharply and medially to run along the medial wall of the orbit.
Because of the obvious importance of the ocular globe, branches of the ophthalmic artery often are subdivided into two groups: those that supply the eyeball (ocular group) and those that supply non-ocular orbital structures (orbital group).[3]
Orbital group
The orbital group, distributing vessels to the orbit and surrounding parts, includes:
- Lacrimal artery A. lacrimalis
- Supraorbital artery A. supraorbitalis
- Posterior ethmoidal artery A. ethmoidalis posterior
- Anterior ethmoidal artery A. ethmoidalis anterior
- Medial palpebral artery A. palpebralis medialis
- Frontal artery, also called the Supratrochlear artery A. supratrochlearis
- Dorsal nasal artery A. dorsalis nasi
Ocular group
The ocular group, distributing vessels to the eye and its muscles, includes:
- Long posterior ciliary arteries Aa. ciliares posteriores longae
- Short posterior ciliary arteries Aa. ciliares posteriores breves
- Anterior ciliary artery A. ciliares anterior
- Central retinal artery A. centralis retinae
- Superior muscular artery A. supraorbitalis
- Inferior muscular artery A. infraorbitalis
Central retinal artery
The central retinal artery is the first, and one of the smaller branches of the ophthalmic artery and runs in the dura mater inferior to the optic nerve. About 12.5mm (0.5 inch) posterior to the globe, the central retinal artery turns superiorly and penetrates the optic nerve, continuing along the center of the optic nerve, entering the eye to supply the inner retinal layers.
Lacrimal artery
The next branch of the ophthalmic artery is the lacrimal artery, one of the largest, arises just as the OA enters the orbit and runs along the superior edge of the lateral rectus muscle to supply the lacrimal gland, eyelids and conjunctiva.
Posterior ciliary arteries
The ophthalmic artery then turns medially, giving off 1 to 5 posterior ciliary arteries (PCA) that subsequently branch into the long and short posterior ciliary arteries (LPCA and SPCA respectively) which perforate the sclera posteriorly in the vicinity of the optic nerve and macula to supply the posterior uveal tract. In the past, anatomists made little distinction between the posterior ciliary arteries and the short and long posterior ciliary arteries often using the terms synonymously. However, recent work by Hayreh has shown that there is both an anatomic and clinically useful distinction.[4] The PCAs arise directly from the OA and are end arteries which is to say no PCA or any of its branches anastomose with any other artery. Consequently, sudden occlusion of any PCA will produce an infarct in the region of the choroid supplied by that particular PCA. Occlusion of a short or long PCA will produce a smaller choroidal infarct, within the larger area supplied by the specific parent PCA.
Muscular branches
The ophthalmic artery continues medially the superior and inferior muscular branches arise either from the ophthalmic artery directly or a single trunk from the ophthalmic artery subsequently divides into superior and inferior branches to supply the extraocular muscles.
Supraorbital artery
The supraorbital artery branches from the ophthalmic artery as it passes over the optic nerve. The supraorbital artery passes anteriorly along the medial border of the superior rectus and levator palpebrae and through the supraorbital foramen to supply muscles and skin of the forehead.
Ethmoidal arteries
After reaching the medial wall of the orbit, the ophthalmic artery again turns anteriorly. The posterior ethmoidal artery enters the nose via the posterior ethmoidal canal and supplies the posterior ethmoidal sinuses and enters the skull to supply the meninges.
The OA continues anteriorly, giving off the anterior ethmoidal artery which enters the nose after traversing the anterior ethmoidal canal and supplies the anterior and middle ethmoidal sinuses, as well as the frontal sinus and also enters the cranium to supply the meninges.
Medial palpebral arteries
The OA continues anteriorly to the trochlea, where the medial palpebral arteries (superior and inferior) arise and supply the eyelids.
Terminal branches
The OA terminates in two branches, the supratrochlear (or frontal) artery and the dorsal nasal artery. Both exit the orbit medially to supply the forehead and scalp.
Function
Branches of the ophthalmic artery supply:
- Frontal belly of the occipitofrontalis muscle
- Inferior oblique muscle
- Inferior rectus muscle
- Lacrimal gland
- Lateral rectus muscle
- Levator palpebrae superioris muscle
- Medial rectus muscle
- Nasalis muscle
- Procerus muscle
- Superior oblique muscle
- Superior rectus muscle
Clinical significance
Severe occlusion of the ophthalmic artery causes ocular ischemic syndrome. As with central retinal artery occlusions, ophthalmic artery occlusions may result from systemic cardiovascular diseases; however, a cherry-red spot is typically absent and the vision is usually worse. Amaurosis fugax is a temporary loss of vision that occurs in two conditions which cause a temporary reduction in ophthalmic artery pressure: orthostatic hypotension and positive acceleration.[5]
Even complete occlusion of the ophthalmic artery may possibly leave the eye without symptoms, probably because of circulatory anastomoses[6]
See also
References
- ^ a b Ehrlich, Rita; Harris, Alon; Wentz, Scott M.; Moore, Nicholas A.; Siesky, Brent A. (2017). "Anatomy and Regulation of the Optic Nerve Blood Flow". Reference Module in Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Psychology. Elsevier. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-809324-5.01301-8. ISBN 978-0-12-809324-5.
- ^ "Medscape: Medscape Access". medscape.com. Retrieved 2015-10-23.
- ^ "Yahoo". education.yahoo.com. Retrieved 2015-10-23.
- ^ Hayreh, SS. "Posterior Ciliary Artery Circulation In Health and Disease" Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 2004 Mar;45(3):749-757. PMID 14985286
- ^ Phelps GK, Phelps CD. "Blood pressure and pressure amaurosis." Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 1975 Mar;14(3):237-40. PMID 1116922
- ^ A case of ophthalmic artery occlusion without manifestation of ocular ischemic syndrome. Authors;SHIMABUKURO MIKIKO (Izumisano City Hosp.) OJI MASATO (Osaka Univ., Med. Sch.) AOMATSU ICHIKO (Osaka Police Hosp.) FUKUI TAKEHIRO (Osaka Police Hosp.) TSUKAMOTO HIROKO (Osaka Police Hosp.) TANAKA YASUO (Osaka Police Hosp.) NISHIKAWA NORIKIYO (Osaka Police Hosp.) KITANISHI KUNIKO (Shiritsuizumiotsubyoin) OZAKI TOSHIYA (Kojunkaiobpkurinikku). Journal Title;Japanese Journal of Clinical Ophthalmology. Journal Code:Z0515B. ISSN 0370-5579. VOL.54;NO.1;PAGE.97-101(2000)
External links
- MedEd at Loyola Neuro/neurovasc/navigation/opht.htm
- Anatomy photo:29:03-0102 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- "Ophthalmic Artery | neuroangio.org". neuroangio.org. Retrieved 2015-10-23.
