Infraorbital foramen
| Infraorbital foramen | |
|---|---|
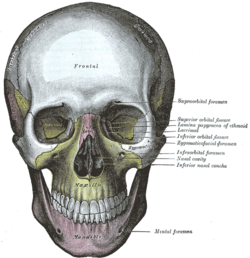 The skull from the front. (Infraorbital foramen labeled at center right, under the eye.) | |
 Articulation of nasal and lacrimal bones with maxilla. (Infraorbital foramen labeled at left.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | foramen infraorbitale |
| TA98 | A02.1.12.008 |
| TA2 | 763 |
| FMA | 57718 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
In human anatomy, the infraorbital foramen is one of two small holes in the skull's upper jawbone (maxillary bone), located below the eye socket and to the left and right of the nose. Both holes are used for blood vessels and nerves. In anatomical terms, it is located below the infraorbital margin of the orbit. It transmits the infraorbital artery and vein, and the infraorbital nerve, a branch of the maxillary nerve. It is typically 6.10 to 10.9 mm (0.240 to 0.429 in) from the infraorbital margin.[1]
Structure
[edit]Forming the exterior end of the infraorbital canal, the infraorbital foramen communicates with the infraorbital groove, the canal's opening on the interior side.
The ramifications of the three principal branches of the trigeminal nerve—at the supraorbital, infraorbital, and mental foramen—are distributed on a vertical line (in anterior view) passing through the middle of the pupil. The infraorbital foramen is used as a pressure point to test the sensitivity of the infraorbital nerve.[2] Palpation of the infraorbital foramen during an extraoral examination or an administration of a local anesthetic agent will cause soreness to the area.[3]
See also
[edit]Additional images
[edit]-
A grizzly bear's skull with the left infraorbital foramina clearly visible
-
1 Anterior ethmoidal foramen, 2 Optic foramen, 3 Superior orbital fissure, 4 Lacrimal sac, 5 Infraorbital groove, 6 Inferior orbital fissure, 7 Infraorbital foramen
References
[edit]- ^ Macedo, VC; Cabrini, RR; Faig-Leite, H (2009). "Infraorbital foramen location in dry human skulls" (PDF). Braz. J. Morphol. Sci. 26 (1): 35–38. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2011-12-03.
- ^ Platzer, Werner (2004). Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Vol. 1: Locomotor System (5th ed.). Thieme. p. 336. ISBN 3-13-533305-1.
- ^ Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 55
External links
[edit]- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)
- Anatomy photo:29:os-0506 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center (closeup)
- Anatomy figure: 22:02-08 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center (distance)
- Upstate.edu
- "Anatomy diagram: 34256.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-12-27.


