Sorivudine
Appearance
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2015) |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Usevir, Brovavir |
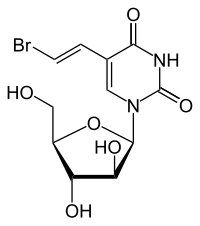
| Other names | BV-araU, Bromovinyl araU, 5-Bromovinyl-araU, 5-[(E)-2-bromoethenyl]-1-[(2R,3S,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]pyrimidine-2,4-dione |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Viral thymidine kinase |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H13BrN2O6 |
| Molar mass | 349.137 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Sorivudine (INN), is a nucleoside analogue antiviral drug, marketed under trade names such as Usevir (Nippon Shoji, Eisai) and Brovavir (BMS).
Pharmacology
Feature
- First-line[citation needed] treatment of herpes drug acyclovir was (Zovirax, Activir) from VZV strong activity of the virus.
- Undergoes gastrointestinal absorption, absorption from the gastrointestinal tract after the most degrading without being excreted in urine.
Mechanism of action
- Sorivudine is phosphorylated by thymidine kinase activity in the body and is absorbed into the virus's DNA instead of the correct nucleoside. It is a competitive inhibitor of DNA polymerase, so the viral DNA cannot be replicated and the virus cannot grow.
Microbiology
Sorivudine is active against most species in the herpesvirus family.
- Herpes simplex virus type I (HSV-1)
- Varicella zoster virus (VZV)
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
Interactions
Sorivudine interacts strongly and in some cases lethally with fluorouracil (5-FU), its prodrugs and related substances. This is based on the metabolite bromovinyluracil (BVU), which irreversibly inhibits the enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) which is necessary for inactivating 5-FU. The closely related drug brivudine has the same interaction.[1]

References
- ^ "UAW – Aus Fehlern lernen - Potenziell tödlich verlaufende Wechselwirkung zwischen Brivudin (Zostex) und 5-Fluoropyrimidinen" (PDF). Deutsches Ärzteblatt (in German). 103 (27). 7 July 2006.
