Nakhon Pathom province
Nakhon Pathom
จังหวัดนครปฐม | |
|---|---|
(Clockwise from top left) Phra Pathom Chedi, Sanam Chandra Palace, Phutthamonthon Buddhism Park, Don Wai floating market, Thai Human Imagery Museum, Prince Mahidol Hall of Mahidol University Salaya Campus | |
 Map of Thailand highlighting Nakhon Pathom Province | |
| Country | Thailand |
| Capital | Mueang Nakhon Pathom |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Charnana Iamsang (since 2017) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,168 km2 (837 sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 66th |
| Population (2018)[2] | |
| • Total | 917,053 |
| • Rank | Ranked 25th |
| • Density | 423/km2 (1,100/sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 8th |
| Human Achievement Index | |
| • HAI (2017) | 0.6354 "high" Ranked 12th |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 73xxx |
| Calling code | 034 & 02 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-73 |
| Website | www |
Nakhon Pathom (Template:Lang-th, pronounced [náʔkʰɔ̄ːn pā.tʰǒm], (Pronunciation)) is one of the central provinces (changwat) of Thailand. Neighbouring provinces are (from north clockwise) Suphan Buri, Ayutthaya, Nonthaburi, Bangkok, Samut Sakhon, Ratchaburi and Kanchanaburi. The capital city of Nakhon Pathom Province is Nakhon Pathom.
Nakhon Pathom Province is home to the Phra Pathom Chedi, a chedi commissioned by King Mongkut (Rama IV) and completed by King Chulalongkorn (Rama V) in 1870. The chedi is a reminder of the long vanished Dvaravati civilization that once flourished here and by tradition Nakhon Pathom is where Buddhism first came to Thailand.[citation needed] The province itself is known for its many fruit orchards.[4]
Geography
Nakhon Pathom is a small province 56 km from Bangkok. It is in the alluvial plain of central Thailand and is drained by the Tha Chin River (sometimes called the Nakhon Chai Si), a tributary of the Chao Phraya River. There are many canals that have been dug for agriculture. The capital city of Bangkok has grown until it borders Nakhon Pathom.
Climate
Nakhon Pathom province has a tropical savanna climate (Köppen climate classification category Aw). Winters are dry and warm. Temperatures rise until May. Mansoon season runs from May through October, with heavy rain and somewhat cooler temperatures during the day, although nights remain warm. Climatological data for the years 2012 - 2013: It's maximum temperature is 40.1 °C (104.2 °F) in April 2013 and the lowest temperature is 12.0 °C (53.6 °F) in December 2013. The highest average temperature is 37.4 °C (99.3 °F) in April 2013 and the minimum average temperature is 16.5 °C (61.7 °F) in December 2013. The average relative humidity is 75% and the minimum relative humidity is 22%. Annual rainfall is 1,095 millimeters. The number of rainy days was 134 days for the year 2013.
Toponymy
The name derives from the Pali words Nagara Pathama, meaning 'first city', and Nakhon Pathom is often referred as Thailand's oldest city.[citation needed] Archaeological remains have been linked to the (pre-Thai) Dvaravati kingdom, dating to the 6th through 11th centuries.[4]
History
Nakhon Pathom Province centuries ago was a coastal city on the route between China and India; due to sedimentation from the Chao Phraya River, the coastline moved much farther to sea. When the Tha Chin River changed its course, the city lost its main water source and thus was for hundreds of years deserted, the population moving to a city called Nakhon Chai Si (or Sri Wichai). King Mongkut (Rama IV) ordered the restoration of the Phra Pathom Chedi, which was then crumbling and abandoned in the jungle. A city gradually formed around it, bringing new life to Nakhon Pathom. A museum presents the archaeological record of the city's history.[5]
Major settlement of the province included immigration beginning in the reign of King Buddha Loetla Nabhalai (Rama II), which included Khmer villages (e.g., Don Yai Hom), the Lan Na-populated (Baan Nua) and Lao Song villages (e.g., Don Kanak), as well as a major influx of southern Chinese in the late-1800s and early-1900s. Today Nakhon Pathom attracts people from all over Thailand, most notably from Bangkok and Isan, plus Burmese migrant workers. The province includes industrial zones, major university towns, government offices relocated from Bangkok, and agricultural and transport hubs.[4]
Economy
In mid-2019, the Department of Airports (DOA) proposed the construction of a new airport in the province, to relieve pressure on Bangkok's two existing airports. The 20 billion baht airport would occupy 3,500 rai of land in Bang Len District and Nakhon Chai Si District. Its capacity would be 25 million passengers annually. If approved, construction would start in 2023 and the airport would be operational by 2025 or 2026.[6] When fully built-out, the airport will accommodate 80-100 seat aircraft flying between Bangkok and second-tier provinces to ease congestion at Suvarnabhumi and Don Mueang airports. The project site has low population density, only 200 households on 400 plots of land.[7]
Symbols
The provincial seal shows Phra Pathom Chedi, at 127 meters the tallest pagoda in the world.[citation needed] It is in the center of the city of Nakhon Pathom, and has been an important Buddhist center since the 6th century. The current building was created by King Mongkut in 1860. On the pagoda a royal crown is depicted, the symbol for King Mongkut's work on reconstructing the pagoda.
The provincial flag is blue with the yellow provincial seal in the middle of the flag.[8]
The provincial tree is Chan, scientific name Diospyros decandra. The provincial slogan is "sweet pomelos, delicious rice, beautiful young ladies".[4]
Administrative divisions
Provincial government


The province is divided into seven districts (amphoes). The districts are further subdivided into 106 subdistricts (tambons) and 904 villages (mubans).[9]
Local government
As of 26 November 2019 there are[10]: one Nakhon Pathom Provincial Administrative Organization - PAO (ongkan borihan suan changwat) and twenty-four municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. The capital Nakhon Pathom has city (thesaban nakhon) status. Further five have town (thesaban mueang) status and eight-teen subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon).[2]
| # | City municipality | 1 | Nakhon Pathom[11] |
| # | Town municipalities | 3 | Rai Khing |
| 1 | Nakhon Pathom | 4 | Krathum Lom |
| 2 | Sam Khwai Taro | 5 | Sam Phran |
| # | Subdistrict mun. | ||
| 1 | Phrong Maduea | 10 | Sam Ngam |
| 2 | Bo Phlap | 11 | Bang Len |
| 3 | Map Khae | 12 | Rang Krathum |
| 4 | Thammasala | 13 | Bang Luang |
| 5 | Don Yai Hom | 14 | Lam Phaya |
| 6 | Kamphaeng Saen | 15 | Om Yai |
| 7 | Nakhon Chai Si | 16 | Bang Kratuek |
| 8 | Khun Kaeo | 17 | Sala Ya |
| 9 | Huai Phlu | 18 | Khlong Yong |
The non-municipal areas are administered by 91 Subdistrict Administrative Organizations - SAO (ongkan borihan suan tambon).
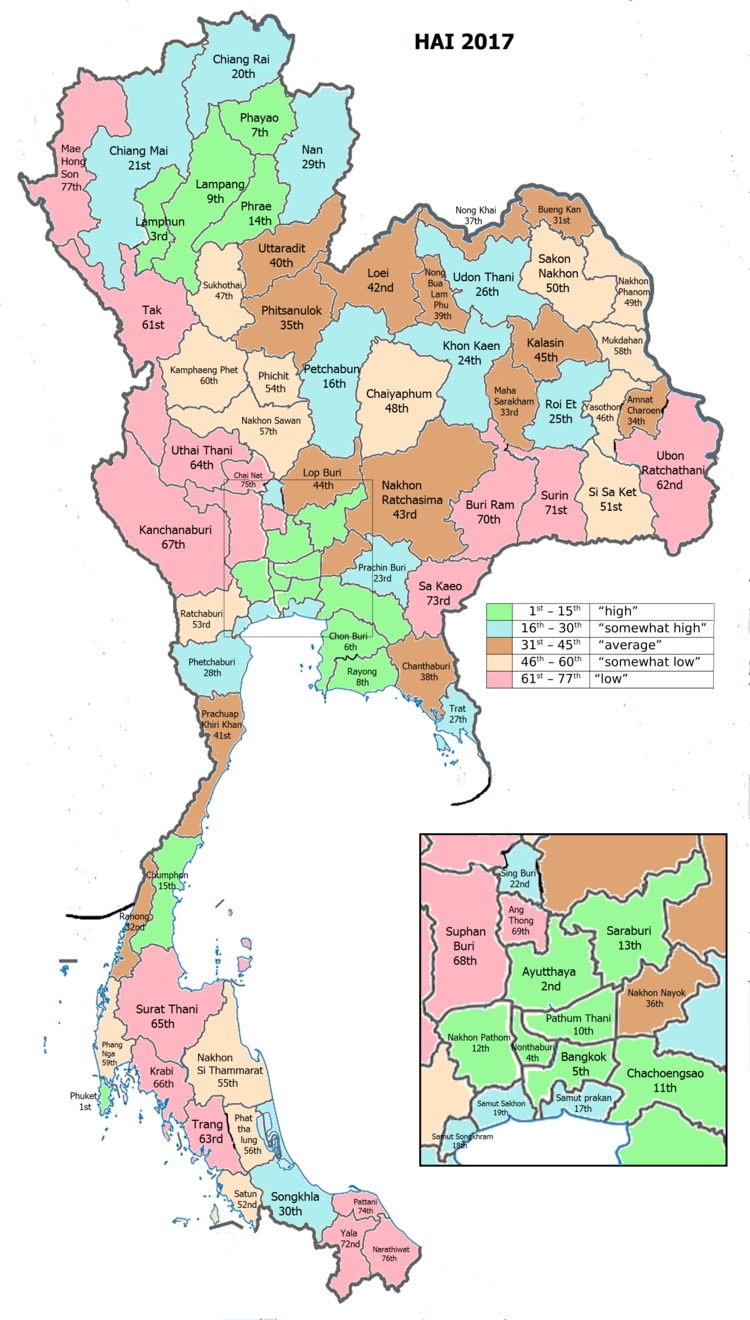
Human achievement index 2017
| Health | Education | Employment | Income |
| 40 | 5 | 22 | 8 |
| Housing | Family | Transport | Participation |

|
 |

|
|
| 56 | 57 | 25 | 62 |
| Province Nakhon Pathom, with an HAI 2017 value of 0.6354 is "high", occupies place 12 in the ranking. | |||
Since 2003, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at sub-national level using the Human achievement index (HAI), a composite index covering all the eight key areas of human development. National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.[3]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 - 15 | "high" |
| 16 - 30 | "somewhat high" |
| 31 - 45 | "average" |
| 45 - 60 | "somewhat low" |
| 61 - 77 | "low" |
| Map with provinces and HAI 2017 rankings |
|
References
- ^ Advancing Human Development through the ASEAN Community, Thailand Human Development Report 2014, table 0:Basic Data (PDF) (Report). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Thailand. pp. 134–135. ISBN 978-974-680-368-7. Retrieved 17 January 2016, Data has been supplied by Land Development Department, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives, at Wayback Machine.
{{cite report}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link)[dead link] - ^ a b "รายงานสถิติจำนวนประชากรและบ้านประจำปี พ.ศ.2561" [Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2018]. Registration Office Department of the Interior, Ministry of the Interior (in Thai). 31 December 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2019.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - ^ a b Human achievement index 2017 by National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB), pages 1-40, maps 1-9, retrieved 14 September 2019, ISBN 978-974-9769-33-1
- ^ a b c d "Official Infos about Nakhon Pathom" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-05-09. Retrieved 2019-08-16.
- ^ "History". Province Nakhon Pathom. nakhonpathom.go.th. 2019. Retrieved 20 November 2019.
- ^ Hongtong, Thodsapol (20 July 2019). "Third Bangkok airport proposed". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 25 July 2019.
- ^ Hongthong, Thodsapol (22 September 2019). "New airport under scrutiny". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 22 September 2019.
- ^ "Logo". Province Nakhon Pathom. nakhonpathom.go.th. 2019. Retrieved 20 November 2019.
- ^ "Information". Province Nakhon pathom. nakhonpathom.go.th. 2019. Retrieved 20 November 2019.
- ^ "Number of local government organizations by province". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 26 November 2019. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
18 Nakhon Pathom: 1 PAO, 1 City mun., 5 Town mun., 18 Subdistrict mun., 91 SAO.
- ^ "พระราชกฤษฎีกา จัดตั้งเทศบาลนครนครปฐม จังหวัดนครปฐม พ.ศ.๒๕๔๒" [Royal Decree Establish of Thesaban Nakhon Nakhon Pathom, Changwat Nakhon Pathom B.E.2542 (1999)] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 116 (110 Kor): 6–9. 10 November 1999. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
Notes
Reports (data) from Thai government are "not copyrightable" (Public Domain), Copyright Act 2537 (1994), section 7.
External links
 Nakhon Pathom travel guide from Wikivoyage
Nakhon Pathom travel guide from Wikivoyage- Province page from the Tourist Authority of Thailand
- Website of province (Thai only)
- Nakhon Pathom provincial map, coat of arms and postal stamp
- Jesada Technik Museum(Thai only)









