Samut Sakhon province
Samut Sakhon
สมุทรสาคร | |
|---|---|
Idol and offerings of Phanthai Norasing, a legendary steersman in Ayutthaya period who sacrificed his own life to offer loyalty to the King, Samut Sakhon is believed to be the place where he was executed (above), Salt farming in Samut Sakhon (below) | |
| Nickname: Mahachai | |
 Map of Thailand highlighting Samut Sakhon Province | |
| Country | Thailand |
| Capital | Mueang Samut Sakhon |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Wirasak Wichitsaengsi (since October 2019)[1] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 872 km2 (337 sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 73rd |
| Population (2018)[3] | |
| • Total | 577,964 |
| • Rank | Ranked 44th |
| • Density | 662/km2 (1,710/sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 6th |
| Human Achievement Index | |
| • HAI (2017) | 0.6175 "somewhat high" Ranked 19th |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 74xxx |
| Calling code | 034 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-74 |
| Website | www |
Samut Sakhon (Template:Lang-th, pronounced [sā.mùt sǎː.kʰɔ̄ːn]) is one of the central provinces (changwat) of Thailand, established by the Act Establishing Changwat Samut Prakan, Changwat Nonthaburi, Changwat Samut Sakhon, and Changwat Nakhon Nayok, Buddhist Era 2489 (1946), which came into force on 9 May 1946.[5]
Neighboring provinces are (from the southwest clockwise) Samut Songkhram, Ratchaburi, Nakhon Pathom, and Bangkok. Samut Sakhon is part of the Bangkok Metropolitan Region.
Toponymy
The word samut originates from the Sanskrit word samudra meaning 'ocean', and the word sakhon from Sanskrit sagara meaning 'lake'.
Geography
Samut Sakhon is at the mouth of the Tha Chin Klong River, a distributary of the Chao Phraya River, to the Gulf of Thailand. At the coast are many salt pans used for harvesting sea salt.[6]
Climate
Samut Nakhon province has a tropical savanna climate (Köppen climate classification category Aw). Winters are dry and warm. Temperatures rise until May. The monsoon season runs from May through October, with heavy rain and somewhat cooler temperatures during the day, although nights remain warm. Climatological data for the period 1981–2010: Maximum temperature is 39.7 °C (103.5 °F) in April and May and the lowest temperature is 12.0 °C (53.6 °F) in December. The highest average temperature is 35.4 °C (95.7 °F) in April and the minimum average temperature is 22.0 °C (71.6 °F) in December. Mean annual rainfall is 1648 millimeters. The maximum daily rainfall is 248 millimeters in May. Mean rainy days average 130 days per year.[7]
History
The oldest name of the area is Tha Chin ('Chinese pier'), probably referring to the fact that it was a trading port where Chinese junks arrived.[8] In 1548 the city Sakhon Buri was established, and was renamed Mahachai in 1704 after the khlong Mahachai which was dug then and connected with the Tha Chin River near the town. King Mongkut gave it its current name, but the old name Mahachai is still sometimes used by locals.[9]
Economy and environment
Formerly an agricultural- and fisheries-based province, Samut Sakhon in 2020 has more than 6,000 factories, most of them small, employing fewer than 50 workers, and too small to warrant much attention from Thailand's Pollution Control Department (PCD). Small firms lack the budgets to install the environmental gear that would help protect the environment. As a result, Samut Sakhon is one of the most polluted provinces in the nation.[10]
Soil and water samples from the industrial area of Mueang District were found to be contaminated with high levels of arsenic, lead, cadmium, chromium, zinc, copper, and nickel. High levels of persistent organic pollutants (POPS), byproducts of industrial processes, were present in eggs from free-range chickens. An egg tested by researchers was found to have 84 nanograms per kilogram of dioxins and furans, a level 33 times higher than the safety limit observed by the European Union.[10]
The most polluted air in Thailand in 2018 was found to be in Samut Sakhon Province.[11] According to the PCD, the level of PM2.5 in the provincial atmosphere in 2019 was unusually high, measuring as high as 195 micrograms per cubic metre (µg/m³). During the air pollution "season" of 2018–2019, PM2.5 levels exceeded the PCD's safe threshold of 50 µg/m³ for 41 days.[10]
Samut Sakhon is a leading sea salt producer. According to a survey in 2011, 12,572 rai of salt pans were managed by 242 families in Samut Sakhon.[12]
Symbols

The provincial seal shows a Chinese junk in front of the coast, with a factory and a smoking chimney in the background. Both refer to the old trading tradition as well as the local industries.
The provincial flag is horizontally divided pink/light blue/pink (1:3:1) the provincial seal in the middle.
The provincial brand is a picture of a white factory, a fishing boat, a fish and blue water and a green leaf.
The provincial tree is commonly called blackboard tree or devil's tree (Alstonia scholaris).
The provincial aquatic animal is Pholas orientalis, a bivalve that found in the Gulf of Thailand and Tha Chin estuary especially in the area of the province.
The provincial slogan is "Fishing city, factory town, agricultural ground, historic site".[13]
Administrative divisions
Provincial government


The province is divided into three districts (amphoes). The districts are further subdivided into 40 subdistricts (tambons) and 290 villages (mubans).[14]
Local government
As of 19 December 2019 there are:[15] one Samut Sakhon Provincial Administrative Organization (PAO) (ongkan borihan suan changwat) and fourteen municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. The capital Samut Sakhon and Om Noi have city (thesaban nakhon) status. Two have town (thesaban mueang) status and ten are subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon).[3]
| # | City municipalities | ||
| 1 | Samut Sakhon.[16] | 2 | Om Noi.[17] |
| # | Town municipality | ||
| 1 | Krathum Baen.[18] | 2 | Khlong Maduea.[19] |
| # | Subdistrict mun. | ||
| 1 | Na Di | 6 | Don Kai |
| 2 | Bang Ya Phraek | 7 | Khae Rai |
| 3 | Tha Chin | 8 | Lak Ha |
| 4 | Bang Pla | 9 | Kaset Phatthana |
| 5 | Suan Luang | 10 | Ban Phaeo |
The non-municipal areas are administered by 23 Subdistrict Administrative Organizations (SAO) (ongkan borihan suan tambon).
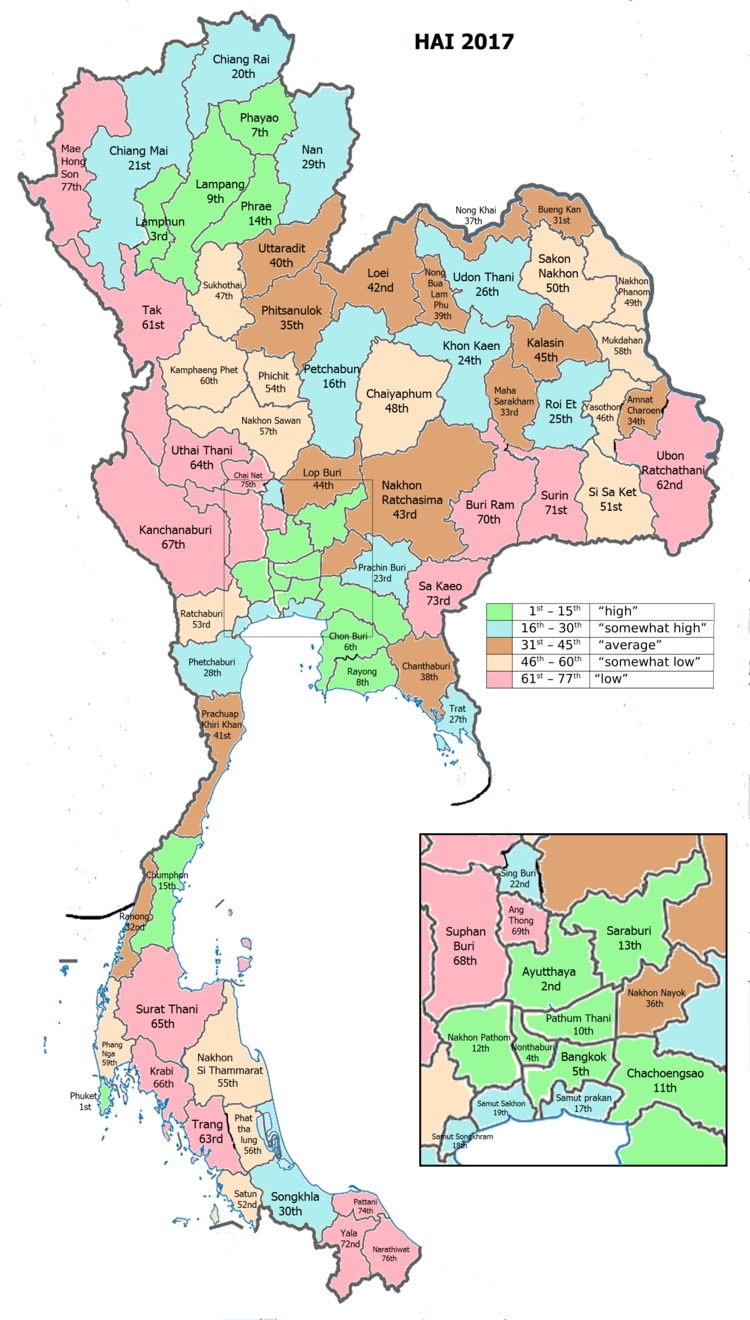
Human achievement index 2017
Since 2003, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at sub-national level using the Human achievement index (HAI), a composite index covering all the eight key areas of human development. National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.[4]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 - 15 | "high" |
| 16 - 30 | "somewhat high" |
| 31 - 45 | "average" |
| 45 - 60 | "somewhat low" |
| 61 - 77 | "low" |
| Map with provinces and HAI 2017 rankings |
|
Notes
Reports (data) from Thai government are "not copyrightable" (Public Domain), Copyright Act 2537 (1994), section 7.
References
- ^ "ประกาศสำนักนายกรัฐมนตรี เรื่อง แต่งตั้งข้าราชการพลเรือนสามัญ" [Announcement of the Prime Minister's Office regarding the appointment of civil servants] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 136 (Special 242 Ngor). 27. 28 September 2019. Retrieved 24 November 2019.
- ^ Advancing Human Development through the ASEAN Community, Thailand Human Development Report 2014, table 0:Basic Data (PDF) (Report). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Thailand. pp. 134–135. ISBN 978-974-680-368-7. Retrieved 17 January 2016, Data has been supplied by Land Development Department, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives, at Wayback Machine.
{{cite report}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link)[dead link] - ^ a b "รายงานสถิติจำนวนประชากรและบ้านประจำปี พ.ศ.2561" [Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2018]. Registration Office Department of the Interior, Ministry of the Interior (in Thai). 31 December 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2019.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help) - ^ a b Human achievement index 2017 by National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB), pages 1-40, maps 1-9, retrieved 14 September 2019, ISBN 978-974-9769-33-1
- ^ พระราชบัญญัติจัดตั้งจังหวัดสมุทรปราการ จังหวัดนนทบุรี จังหวัดสมุทรสาคร และจังหวัดนครนายก พุทธศักราช ๒๔๘๙ [Act Establishing Changwat Samut Prakan, Changwat Nonthaburi, Changwat Samut Sakhon and Changwat Nakhon Nayok, Buddhist Era 2489 (1946)] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 63 (29 Kor): 315–317. 9 May 1946. Retrieved 2 December 2019.
- ^ "Geographic information". Samut Sakhon province. samutsakhon.go.th. 2014. Archived from the original on 25 August 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2019.
- ^ "Climatological data for the period 1981–2010". Thai Meteorological Department. 2011. pp. 16–17. Retrieved 24 November 2019, Data are from nearest weather station Bangkok (32 km)
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - ^ "About Samut Sakhon". Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT). Archived from the original on 22 April 2019. Retrieved 17 May 2019.
- ^ "History". Samut Sakhon Province. 2014. Archived from the original on 25 August 2018. Retrieved 20 November 2019.
- ^ a b c Kongrut, Anchalee (9 February 2020). "Pollution taints seaside community's prosperity". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 10 February 2020.
- ^ "World most polluted cities 2018 (PM2.5)". AirVisual. Retrieved 13 September 2019.
- ^ Wattanavanitvut, Phongthai (10 September 2016). "Salt industry prepares for a shake-up". Bangkok Post. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- ^ "About Us". Samut Sakhon Province. 2014. Archived from the original on 1 November 2015. Retrieved 20 November 2019.
- ^ "Governance". Samut Sakhon province. samutsakhon.go.th. 2014. Retrieved 20 November 2019.
- ^ "Number of local government organizations by province". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 26 November 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
61 Samut Sakhon: 1 PAO, 2 City mun., 2 Town mun., 10 Subdistrict mun., 25 SAO.
- ^ "พระราชกฤษฎีกา จัดตั้งเทศบาลนครสมุทรสาคร จังหวัดสมุทรสาคร พ.ศ.๒๕๔๒" [Royal Decree Establish of Thesaban Nakhon Samut Sakhon, Samut Sakhon Province B.E.2542] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 116 (110 Kor): 2–5. 10 November 1999. Retrieved 20 November 2019.
- ^ "เปลี่ยนแปลงฐานะ เทศบาลเมืองอ้อมน้อย อำเภอกระทุ่มแขน จังหวัดสมุทรสาคร เป็นเทศบาลนครอ้อมน้อย" [Announcement from the Ministry of interior Re: Change of Thesaban Mueang Om Noi, Amphoe Krathum Baen, Changwat Samut Sakhon Is Thesaban Nakhon Om Noi] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 127 (Special Section 149 Ngor): 45. 27 December 2010. Retrieved 20 November 2019.
- ^ "พระราชกฤษฎีกา จัดตั้งเทศบาลนเมืองกระทุ่มแบน จังหวัดสมุทรสาคร พ.ศ.๒๕๓๘" [Royal Decree Establish of Thesaban Mueang Krathum Baen, Samut Sakhon Province B.E.2538] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 112 (40 Kor): 62–65. 24 September 1990. Retrieved 20 November 2019.
- ^ "ประกาศกระทรวงมหาดไทย เรื่อง จัดตั้งองค์การบริหารส่วนตำบลคลองมะเดื่อ อำเภอกระทุ่มแบน จังหวัดสมุทสาคร เป็นเทศบาเมืองคลองมะเดื่อ" [Notification of the Ministry of Interior Re: Establishment of Khlong Maduea Subdistrict Administrative Organization Amphoe Krathum Baen Changwat Samut Sakhon is Thesaban Mueang Khlong Maduea] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 136 (Special 309 Ngor): 23. 19 December 2019. Retrieved 22 December 2019.
External links
 Samut Sakhon travel guide from Wikivoyage
Samut Sakhon travel guide from Wikivoyage- https://web.archive.org/web/20080127154926/http://www.thailex.info/THAILEX/THAILEXENG/lexicon/Copy%20of%20Samut%20Sakon.htm Samut Sakhon provincial map, coat of arms, and postal stamp]








