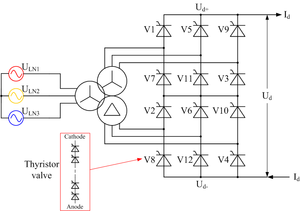
HVDC converter
An HVDC converter converts electric power from high voltage alternating current (AC) to high-voltage direct current (HVDC), or vice versa. HVDC is used as an alternative to AC for transmitting electrical energy over long distances or between AC power systems of different frequencies.[1] HVDC converters capable of converting up to two gigawatts (GW)[2] and with voltage ratings of up to 900 kilovolts (kV)[3] have been built, and even higher ratings are technically feasible. A complete converter station may contain several such converters in series and/or parallel to achieve total system DC voltage ratings of up to 1,100 kV.

Almost all HVDC converters are inherently bi-directional; they can convert either from AC to DC (rectification) or from DC to AC (inversion). A complete HVDC system always includes at least one converter operating as a rectifier (converting AC to DC) and at least one operating as an inverter (converting DC to AC). Some HVDC systems take full advantage of this bi-directional property (for example, those designed for cross-border power trading, such as the Cross-Channel link between England and France).[4] Others, for example those designed to export power from a remote power station such as the Itaipu scheme in Brazil,[5] may be optimised for power flow in only one preferred direction. In such schemes, power flow in the non-preferred direction may have a reduced capacity or poorer efficiency.
Types of HVDC converters
HVDC converters can take several different forms. Early HVDC systems, built until the 1930s, were effectively rotary converters and used electromechanical conversion with motor-generator sets connected in series on the DC side and in parallel on the AC side. However, all HVDC systems built since the 1940s have used electronic (static) converters.
Electronic converters for HVDC are divided into two main categories. Line-commutated converters (HVDC classic) are made with electronic switches that can only be turned on. Voltage-sourced converters are made with switching devices that can be turned both on and off. Line-commutated converters (LCC) used mercury-arc valves until the 1970s,[6] or thyristors from the 1970s to the present day. Voltage-source converters (VSC), which first appeared in HVDC in 1997,[7] use transistors, usually the Insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT).
As of 2012, both the line-commutated and voltage-source technologies are important, with line-commutated converters used mainly where very high capacity and efficiency are needed, and voltage-source converters used mainly for interconnecting weak AC systems, for connecting large-scale wind power to the grid or for HVDC interconnections that are likely to be expanded to become Multi-terminal HVDC systems in future. The market for voltage-source converter HVDC is growing fast, driven partly by the surge in investment in offshore wind power, with one particular type of converter, the Modular Multi-Level Converter (MMC)[8] emerging as a front-runner.
Electromechanical converters
As early as the 1880s, the advantages of DC long-distance transmission were starting to become evident and several commercial power transmission systems were put into operation.[1] The most successful of these used the system invented by René Thury and were based on the principle of connecting several motor-generator sets in series on the DC side. The best-known example was the 200 km, Lyon–Moutiers DC transmission scheme in France, which operated commercially from 1906 to 1936 transmitting power from the Moutiers hydroelectric plant to the city of Lyon.[9] Kimbark[10] reports that this system operated quite reliably; however, the total end to end efficiency (at around 70%) was poor by today's standards. From the 1930s onwards,[6] extensive research started to take place into static alternatives using gas-filled tubes – principally mercury-arc valves but also thyratrons – which held the promise of significantly higher efficiency. Very small mechanical rotary convertors remained in use for niche applications in adverse environments, such as in aircraft and vehicles, as a power conversion method from batteries to the high voltages required for radio and RADAR, until the 1960s and the transistor era.
Line-commutated converters
Most of the HVDC systems in operation today are based on line-commutated converters (LCC). The term line-commutated indicates that the conversion process relies on the line voltage of the AC system to which the converter is connected in order to effect the commutation from one switching device to its neighbour.[11] Line-commutated converters use switching devices that are either uncontrolled (such as diodes) or that can only be turned on (not off) by control action, such as thyristors. Although HVDC converters can, in principle, be constructed from diodes, such converters can only be used in rectification mode and the lack of controllability of the DC voltage is a serious disadvantage. Consequently, in practice all LCC HVDC systems use either grid-controlled mercury-arc valves (until the 1970s) or thyristors (to the present day).
In a line-commutated converter, the DC current does not change direction; it flows through a large inductance and can be considered almost constant. On the AC side, the converter behaves approximately as a current source, injecting both grid-frequency and harmonic currents into the AC network. For this reason, a line-commutated converter for HVDC is also considered as a current-source converter.[11] Because the direction of current cannot be varied, reversal of the direction of power flow (where required) is achieved by reversing the polarity of DC voltage at both stations.
Line Commutated Six-pulse bridge
The basic LCC configuration for HVDC uses a three-phase Graetz bridge rectifier or six-pulse bridge, containing six electronic switches, each connecting one of the three phases to one of the two DC terminals.[12] A complete switching element is usually referred to as a valve, irrespective of its construction. Normally, two valves in the bridge are conducting at any time: one to a phase on the top row and one (from a different phase) on the bottom row. The two conducting valves connect two of the three AC phase voltages, in series, to the DC terminals. Thus, the DC output voltage at any given instant is given by the series combination of two AC phase voltages. For example, if valves V1 and V2 are conducting, the DC output voltage is given by the voltage of phase 1 minus the voltage of phase 3.
Because of the unavoidable (but beneficial) inductance in the AC supply, the transition from one pair of conducting valves to the next does not happen instantly. Rather, there is a short overlap period when two valves on the same row of the bridge are conducting simultaneously. For example, if valves V1 and V2 are initially conducting and then valve V3 is turned on, conduction passes from V1 to V3 but for a short period both of these valves conduct simultaneously.[11] During this period, the DC output voltage is given by the average of the voltages of phases 1 and 2, minus the voltage of phase 3. The overlap angle μ (or u) in an HVDC converter increases with the load current, but is typically around 20° at full load.
 |
 |
During the overlap period, the output DC voltage is lower than it would otherwise be and the overlap period produces a visible notch in the DC voltage.[11] An important effect of this is that the mean DC output voltage decreases as the overlap period increases; hence the mean DC voltage falls with increasing DC current.

The mean DC output voltage of a six-pulse converter is given by:[13]
Where:
- VLLpeak - the peak value of the line to line input voltage (on the converter side of the converter transformer),
- α - the firing angle of the thyristor
- Lc - the commutating inductance per phase
- Id - the direct current
The firing angle α represents the time delay from the point at which the voltage across a valve becomes positive (at which point a diode would start to conduct) and the thyristors being turned on.[11][14] From the foregoing equation, it is clear that as the firing angle increases, the mean DC output voltage decreases. In fact, with a line-commutated converter, the firing angle represents the only fast way of controlling the converter. Firing angle control is used to regulate the DC voltages of both ends of the HVDC system continuously in order to obtain the desired level of power transfer.

The DC output voltage of the converter steadily becomes less positive as the firing angle is increased: firing angles of up to 90° correspond to rectification and result in positive DC voltages, while firing angles above 90° correspond to inversion and result in negative DC voltages.[15] However, the firing angle cannot be extended all the way to 180°, for two reasons. Firstly, allowance must be made for the overlap angle μ, and secondly for an additional extinction angle γ which is needed for the valves to recover their ability to withstand positive voltage after conducting current. The extinction angle γ is related to the turn-off time tq of the thyristors. A typical value of γ is 15°. α, γ and μ are inter-related thus:
(in degrees)
Line Commutated Twelve-pulse bridge
With a phase change only every 60°, considerable harmonic distortion is produced at both the DC and AC terminals when the six-pulse arrangement is used. Large filtering components are needed to restore the waveforms to sinusoidal. An enhancement of the six-pulse bridge arrangement uses 12 valves in a twelve-pulse bridge.[11] A twelve-pulse bridge is effectively two six-pulse bridges connected in series on the DC side and arranged with a phase displacement between their respective AC supplies so that some of the harmonic voltages and currents are cancelled.
The phase displacement between the two AC supplies is usually 30° and is realised by using converter transformers with two different secondary windings (or valve windings). Usually one of the valve windings is star (wye)-connected and the other is delta-connected.[16] With twelve valves connecting each of the two sets of three phases to the two DC rails, there is a phase change every 30°, and the levels of low frequency harmonics are considerably reduced, considerably simplifying the filtering requirements. For this reason the twelve-pulse system has become standard on almost all line-commutated converter HVDC systems, although HVDC systems built with mercury arc valves make provision for temporary operation with one of the two six-pulse groups bypassed.
Mercury arc valves

Early LCC systems used mercury-arc valves, with designs that had evolved from those used on high power industrial rectifiers.[17] A number of adaptations were needed to make such valves suitable for HVDC, in particular the use of anode voltage grading electrodes to minimise the risk of arc-back at the very high reverse voltages experienced in HVDC.[18] Much of the pioneering work in this area was performed in Sweden by Dr Uno Lamm, widely considered the “Father of HVDC” and in whose name the IEEE introduced the “Uno Lamm Award” for outstanding contributions in the field of HVDC.[19] The very long anode columns needed for high voltage applications limited the current which could safely be carried by each anode, so most mercury-arc valves for HVDC used several (most often, four) anode columns in parallel per valve.[6]
Usually, each arm of each six-pulse bridge consisted of only one mercury-arc valve, but two projects built in the former Soviet Union used two or three mercury-arc valves in series per arm, without parallel connection of anode columns.[20]
Mercury arc valves for HVDC were rugged but required high maintenance. Because of this, most mercury-arc HVDC systems were built with bypass switchgear across each six-pulse bridge so that the HVDC scheme could be operated in six-pulse mode for short periods of maintenance.[16][21]
Mercury arc valves were built with ratings of up to 150 kV, 1800 A. The last (and most powerful) mercury arc system installed was that of the Nelson River DC Transmission System in Canada, which used six anode columns in parallel per valve and was completed in 1977.[22][23] The last operating mercury arc system (the HVDC Inter-Island link between the North and South Islands of New Zealand) was shut down in 2012. Mercury arc valves were also used on the following HVDC projects:[24]
- The Elbe Project in Berlin, Germany
- The Moscow–Kashira project in Russia[20]
- The first phase of the Gotland project in Sweden
- The original (160 MW) Cross Channel project between England and France
- The Volgograd–Donbass project linking Russia and Ukraine[20]
- The first phase of the Konti–Skan link between Sweden and Denmark
- The Sakuma frequency converter in Japan
- The first phase of the Italy–Corsica–Sardinia link
- The first phase of the Vancouver Island link in Canada
- The first phase of the Pacific DC Intertie from Oregon to Los Angeles in the United States
- The Kingsnorth link in London, England
- The first phase of the Nelson River DC Transmission System in Canada
Thyristor valves
The thyristor valve was first used in HVDC systems in 1972 on the Eel River Converter Station in Canada.[23] The thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device similar to the diode, but with an extra control terminal that is used to switch the device on at a defined instant. Because thyristors have breakdown voltages of only a few kilovolts each, HVDC thyristor valves are built using large numbers of thyristors connected in series. Additional passive components such as grading capacitors and resistors need to be connected in parallel with each thyristor in order to ensure that the voltage across the valve is shared uniformly between the thyristors. The thyristor plus its grading circuits and other auxiliary equipment is known as a thyristor level.

Each thyristor valve will typically contain tens or hundreds of thyristor levels, each operating at a different (high) potential with respect to earth.[16] The command information to turn on the thyristors therefore cannot simply be sent using a wire connection – it needs to be isolated. The isolation method can be magnetic (using pulse transformers) but is usually optical. Two optical methods are used: indirect and direct optical triggering. In the indirect optical triggering method, the low-voltage control electronics sends light pulses along optical fibres to the high-side control electronics, which derives its power from the voltage across each thyristor. The alternative direct optical triggering method dispenses with most of the high-side electronics, instead using light pulses from the control electronics to switch light-triggered thyristors (LTTs),[25] although a small monitoring electronics unit may still be required for protection of the valve.
As of 2012, thyristor valves had been used on over 100 HVDC schemes, with many more still under construction or being planned. The highest power rating of any single HVDC converter (twelve-pulse bridge) in operation was 2000 MW in 2010, on the ±660 kV Ningdong–Shandong scheme in China. Two such converters are provided at each end of the scheme, which is of conventional bipolar construction.[2] Since 2007 the highest voltage rating of a single HVDC converter has been the ±450 kV NorNed scheme linking Norway to the Netherlands, which has only a single converter at each end in an arrangement that is unusual for an LCC HVDC scheme.[3]
Voltage-source converters
Because thyristors (and mercury rectifiers) can only be turned on (not off) by control action, and rely on the external AC system to effect the turn-off process, the control system only has one degree of freedom – when in the cycle to turn on the thyristor.[11] This limits the usefulness of HVDC in some circumstances because it means that the AC system to which the HVDC converter is connected must always contain synchronous machines in order to provide the timing for the commutating voltage – the HVDC converter cannot feed power into a passive system. This is not a problem supplying additional power to a grid that is already live, but cannot be used as the sole source of power.
With other types of semiconductor device such as the insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT), both turn-on and turn-off timing can be controlled, giving a second degree of freedom. As a result, IGBTs can be used to make self-commutated converters which are closer to a large inverter in operation. In such converters, the polarity of DC voltage is usually fixed and the DC voltage, being smoothed by a large capacitance, can be considered constant. For this reason, an HVDC converter using IGBTs is usually referred to as a voltage-source converter (or voltage-sourced converter[26]). The additional controllability gives many advantages, notably the ability to switch the IGBTs on and off many times per cycle in order to improve the harmonic performance, and the fact that (being self-commutated) the converter no longer relies on synchronous machines in the AC system for its operation. A voltage-sourced converter can therefore feed power to an AC network consisting only of passive loads, something which is impossible with LCC HVDC. Voltage-source converters are also considerably more compact than line-commutated converters (mainly because much less harmonic filtering is needed) and are preferable to line-commutated converters in locations where space is at a premium, for example on offshore platforms.
In contrast to line-commutated HVDC converters, voltage-source converters maintain a constant polarity of DC voltage and power reversal is achieved instead by reversing the direction of current. This makes voltage-source converters much easier to connect into a Multi-terminal HVDC system or “DC Grid”.[27]
HVDC systems based on voltage-source converters normally use the six-pulse connection because the converter produces much less harmonic distortion than a comparable LCC and the twelve-pulse connection is unnecessary. This simplifies the construction of the converter transformer. However, there are several different configurations of voltage-source converter[28] and research is continuing to take place into new alternatives.
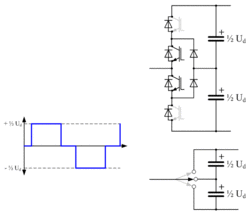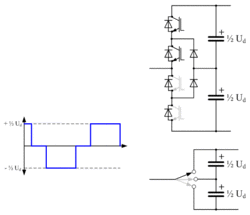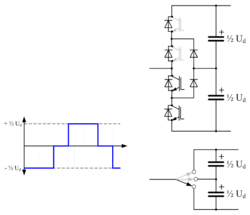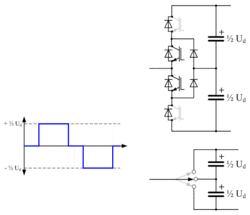
Two-level converter
From the very first VSC-HVDC scheme installed (the Hellsjön experimental link commissioned in Sweden in 1997[7]) until 2012, most of the VSC HVDC systems built were based on the two level converter. The two-level converter is the simplest type of three-phase voltage-source converter[29] and can be thought of as a six pulse bridge in which the thyristors have been replaced by IGBTs with inverse-parallel diodes, and the DC smoothing reactors have been replaced by DC smoothing capacitors. Such converters derive their name from the fact that the voltage at the AC output of each phase is switched between two discrete voltage levels, corresponding to the electrical potentials of the positive and negative DC terminals. When the upper of the two valves in a phase is turned on, the AC output terminal is connected to the positive DC terminal, resulting in an output voltage of +½ Ud with respect to the midpoint potential of the converter. Conversely when the lower valve in a phase is turned on, the AC output terminal is connected to the negative DC terminal, resulting in an output voltage of -½ Ud. The two valves corresponding to one phase must never be turned on simultaneously, as this would result in an uncontrolled discharge of the DC capacitor, risking severe damage to the converter equipment.
 |
 |

The simplest (and also, the highest-amplitude) waveform that can be produced by a two-level converter is a square wave; however this would produce unacceptable levels of harmonic distortion, so some form of Pulse-width modulation (PWM) is always used to improve the harmonic distortion of the converter. As a result of the PWM, the IGBTs are switched on and off many times (typically 20) in each mains cycle.[30] This results in high switching losses in the IGBTs and reduces the overall transmission efficiency. Several different PWM strategies are possible for HVDC[31] but in all cases the efficiency of the two-level converter is significantly poorer than that of a LCC because of the higher switching losses. A typical LCC HVDC converter station has power losses of around 0.7% at full load (per end, excluding the HVDC line or cable) while with 2-level voltage-source converters the equivalent figure is 2-3% per end.
Another disadvantage of the two-level converter is that, in order to achieve the very high operating voltages required for an HVDC scheme, several hundred IGBTs have to be connected in series and switched simultaneously in each valve.[32] This requires specialised types of IGBT with sophisticated gate drive circuits, and can lead to very high levels of electromagnetic interference.
Three-level converter
In an attempt to improve on the poor harmonic performance of the two-level converter, some HVDC systems have been built with three level converters. Three-level converters can synthesize three (instead of only two) discrete voltage levels at the AC terminal of each phase: +½ Ud, 0 and -½ Ud. A common type of three-level converter is the diode-clamped (or neutral-point-clamped) converter, where each phase contains four IGBT valves, each rated at half of the DC line to line voltage, along with two clamping diode valves.[32] The DC capacitor is split into two series-connected branches, with the clamping diode valves connected between the capacitor midpoint and the one-quarter and three-quarter points on each phase. To obtain a positive output voltage (+½ Ud) the top two IGBT valves are turned on, to obtain a negative output voltage (-½ Ud) the bottom two IGBT valves are turned on and to obtain zero output voltage the middle two IGBT valves are turned on. In this latter state, the two clamping diode valves complete the current path through the phase.
 |
 |
In a refinement of the diode-clamped converter, the so-called active neutral-point clamped converter, the clamping diode valves are replaced by IGBT valves, giving additional controllability. Such converters were used on the Murraylink project[33] in Australia and the Cross Sound Cable link in the United States.[34] However, the modest improvement in harmonic performance came at a considerable price in terms of increased complexity, and the design proved to be difficult to scale up to DC voltages higher than the ±150 kV used on those two projects.
Another type of three-level converter, used in some adjustable-speed drives but never in HVDC, replaces the clamping diode valves by a separate, isolated, flying capacitor connected between the one-quarter and three-quarter points.[32] The operating principle is similar to that of the diode-clamped converter. Both the diode-clamped and flying capacitor variants of three-level converter can be extended to higher numbers of output levels (for example, five), but the complexity of the circuit increases disproportionately and such circuits have not been considered practical for HVDC applications.
Modular Multi-Level Converter (MMC)
First proposed for HVDC applications in 2003 by Marquardt[8] and first used commercially in the Trans Bay Cable project in San Francisco,[35] the Modular Multi-Level Converter (MMC) is now becoming the most common type of voltage-source converter for HVDC.[36]
Like the two-level converter and the six-pulse line-commutated converter, a MMC consists of six valves, each connecting one AC terminal to one DC terminal. However, where each valve of the two-level converter is effectively a high-voltage controlled switch consisting of a large number of IGBTs connected in series, each valve of a MMC is a separate controllable voltage source in its own right. Each MMC valve consists of a number of independent converter submodules, each containing its own storage capacitor. In the most common form of the circuit, the half-bridge variant, each submodule contains two IGBTs connected in series across the capacitor, with the midpoint connection and one of the two capacitor terminals brought out as external connections.[35] Depending on which of the two IGBTs in each submodule is turned on, the capacitor is either bypassed or connected into the circuit. Each submodule therefore acts as an independent two-level converter generating a voltage of either 0 or Usm (where Usm is the submodule capacitor voltage). With a suitable number of submodules connected in series, the valve can synthesize a stepped voltage waveform that approximates very closely to a sine-wave and contains very low levels of harmonic distortion.

The MMC differs from other types of converter in that current flows continuously in all six valves of the converter throughout the mains-frequency cycle. As a result, concepts such as “on-state” and “off-state” have no meaning in the MMC. The direct current splits equally into the three phases and the alternating current splits equally into the upper and lower valve of each phase.[35] The current in each valve is therefore related to the direct current Id and alternating current Iac as follows:
Upper valve:
Lower valve:
A typical MMC for an HVDC application contains around 300 submodules connected in series in each valve and is therefore equivalent to a 301 level converter. Consequently, the harmonic performance is excellent and usually no filters are needed. A further advantage of the MMC is that PWM is not necessary, with the result that the power losses are much lower than those of the 2-level converter, at around 1% per end.[37][36][38] Finally, because direct series-connection of IGBTs is not necessary, the IGBT gate drives do not need to be as sophisticated as those for a 2-level converter.
The MMC has two principal disadvantages. Firstly, the control is much more complex than that of a 2-level converter. Balancing the voltages of each of the submodule capacitors is a significant challenge and requires considerable computing power and high-speed communications between the central control unit and the valve. Secondly, the submodule capacitors themselves are large and bulky.[39] A MMC is considerably larger than a comparable-rated 2-level converter, although this may be offset by the saving in space from not requiring filters.
As of 2012 the largest-capacity MMC HVDC system in operation is still the 400 MW Trans Bay Cable scheme but many larger schemes are under construction, including an underground cable interconnection from France to Spain consisting of two 1000 MW links in parallel at a voltage of ±320 kV.[40]
MMC variants
A variant of the MMC, proposed by one manufacturer, involves connecting multiple IGBTs in series in each of the two switches that make up the submodule. This gives an output voltage waveform with fewer, larger, steps than the conventional MMC arrangement. This arrangement is referred to as the Cascaded Two Level (CTL) converter.[37] Functionally it is exactly equivalent to the conventional half-bridge MMC in every respect except for the harmonic performance, which is slightly inferior – although still claimed to be good enough to avoid the need for filtering in most instances.

Another alternative replaces the half bridge MMC submodule described above, with a full bridge submodule containing four IGBTs in an H bridge arrangement, instead of two.[41] The full-bridge variant of MMC allows the submodule capacitor to be inserted into the circuit in either polarity. This confers additional flexibility in controlling the converter and allows the converter to block the fault current which arises from a short-circuit between the positive and negative DC terminals (something which is impossible with any of the preceding types of VSC). Furthermore, it allows the DC voltage to be of either polarity (like a LCC HVDC scheme), giving rise to the possibility of hybrid LCC and VSC HVDC systems. However, the full-bridge arrangement requires twice as many IGBTs and has higher power losses than the equivalent half-bridge arrangement.
Other types of voltage-source converter
Various other types of converter have been proposed, combining features of the two-level and Modular Multi-Level Converters.[42] These hybrid VSC systems aim to achieve the low losses and high harmonic performance of the MMC with a more compact design and greater controllability, but these concepts are still at the research stage.[43]
See also
- High-voltage direct current
- HVDC converter station
- List of HVDC projects
- Rectifier
- Inverter (electrical)
- Mercury-arc valve
- Thyristor
- Insulated-gate bipolar transistor
References
- ^ a b Arrillaga, Jos; High Voltage Direct Current Transmission, second edition, Institution of Electrical Engineers, ISBN 0852969414, 1998, Chapter 1, pp 1-9.
- ^ a b Davidson, C.C., Preedy, R.M., Cao, J., Zhou, C., Fu, J., Ultra-High-Power Thyristor Valves for HVDC in Developing Countries, IET 9th International Conference on AC/DC Power Transmission, London, October 2010.
- ^ a b Skog, J.E., van Asten, H., Worzyk, T., Andersrød, T., Norned – World’s longest power cable, CIGRÉ session, Paris, 2010, paper reference B1-106 Archived 2015-09-23 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Rowe, B.A., Goodrich, F.G., Herbert, I.R., Commissioning the Cross Channel h.v.d.c. link, GEC Review, Vol. 3, No. 2, 1987.
- ^ Praça, A., Arakari, H., Alves, S.R., Eriksson, K., Graham, J., Biledt, G., Itaipu HVDC Transmission System - 10 years operational experience, V SEPOPE, Recife, May 1996.
- ^ a b c Peake, O., The History of High Voltage Direct Current Transmission, 3rd Australasian Engineering Heritage Conference 2009
- ^ a b Asplund, G., Svensson, K., Jiang, H., Lindberg, J., Pålsson, R., DC transmission based on voltage source converters, CIGRÉ session, Paris, 1998, paper reference 14-302.
- ^ a b Lesnicar, A., Marquardt, R., An innovative modular multi-level converter topology for a wide power range, IEEE Power Tech Conference, Bologna, Italy, June 2003.
- ^ Black, R.M.,The History of Electric Wires and Cable, Peter Peregrinus, London, 1983, ISBN 0-86341-001-4, p 95
- ^ Kimbark, E.W., Direct current transmission, volume 1, Wiley Interscience, 1971, pp3–4.
- ^ a b c d e f g Arrillaga, Jos; High Voltage Direct Current Transmission, second edition, Institution of Electrical Engineers, ISBN 0-85296-941-4, 1998, Chapter 2, pp 10-55.
- ^ Kimbark, E.W., Direct current transmission, volume 1, Wiley Interscience, 1971, pp 71–128.
- ^ Williams, B.W., Power Electronics - devices, drivers and applications, Macmillan Press, ISBN 0-333-57351-X, 1992, pp 287–291.
- ^ Kimbark, E.W., Direct current transmission, volume 1, Wiley Interscience, 1971, p 75.
- ^ Mohan, N., Undeland, T.M., Robbins, W.P., Power Electronics - converters, applications and design, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 0-471-58408-8, 1995, pp 148-150.
- ^ a b c Arrillaga, Jos; High Voltage Direct Current Transmission, second edition, Institution of Electrical Engineers, ISBN 0-85296-941-4, 1998, Chapter 7, pp 159-199.
- ^ Rissik, H., Mercury-Arc Current Converters, Pitman. 1941.
- ^ Cory, B.J., Adamson, C., Ainsworth, J.D., Freris, L.L., Funke, B., Harris, L.A., Sykes, J.H.M., High voltage direct current converters and systems, Macdonald & Co. (publishers) Ltd, 1965, chapter 3.
- ^ "IEEE list of Uno Lamm award winners". Archived from the original on 2012-12-03. Retrieved 2012-12-20.
- ^ a b c Nekrasov, A.M., Posse, A.V., Work done in the Soviet Union on High-Voltage Long-Distance DC power transmission, A.I.E.E. Transactions, Vol. 78, part 3A, August 1959, pp515–521.
- ^ Calverley T.E., Gavrilovic, A., Last F.H., Mott C.W., The Kingsnorth-Beddington-Willesden DC Link, CIGRÉ session, Paris, 1968, paper 43-04.
- ^ Cogle, T.C.J, The Nelson River Project - Manitoba Hydro exploits sub-arctic hydro power resources, Electrical Review, 23 November 1973.
- ^ a b "List of IEEE Milestones". IEEE Global History Network. IEEE. Retrieved 20 December 2012.
- ^ Compendium of HVDC schemes, CIGRÉ Technical Brochure No. 003 Archived 2014-07-08 at the Wayback Machine, 1987.
- ^ High Voltage Direct Current Transmission – Proven Technology for Power Exchange, Siemens publication.
- ^ High-voltage direct current (HVDC) power transmission using voltage sourced converters (VSC), IEC/TR 62543:2011.
- ^ Callavik, M.,HVDC Grids for offshore and onshore transmission, EWEA Conference, Amsterdam, 2011.
- ^ Voltage sourced converter (VSC) valves for high-voltage direct current (HVDC) power transmission — Electrical testing, IEC 62501:2009, Annex A.
- ^ Mohan, N., Undeland, T.M., Robbins, W.P., Power Electronics - converters, applications and design, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 0-471-58408-8, 1995, pp 225-236.
- ^ Williams, B.W., Power Electronics - devices, drivers and applications, Macmillan Press, ISBN 0-333-57351-X, 1992, pp 359–371.
- ^ Components Testing of VSC System for HVDC Applications, CIGRÉ Technical Brochure No. 447, 2011.
- ^ a b c VSC Transmission, CIGRÉ Technical Brochure No. 269 Archived 2016-02-04 at the Wayback Machine, 2005.
- ^ Mattsson, I., Railing, B.D., Williams, B., Moreau, G., Clarke, C.D., Ericsson, A., Miller, J.J., Murraylink – the longest underground HVDC cable in the world, CIGRÉ session, Paris, 2004, paper reference B4-103.
- ^ Railing, B.D., Miller, J.J., Steckley, P., Moreau, G., Bard, P., Ronström, L., Lindberg, J., Cross Sound Cable project – second generation VSC technology for HVDC, CIGRÉ session, Paris, 2004, paper reference B4-102.
- ^ a b c Westerweller T., Friedrich, K., Armonies, U., Orini, A., Parquet, D., Wehn, S., Trans Bay cable – world's first HVDC system using multilevel voltage-sourced converter, CIGRÉ session, Paris, 2010, paper reference B4-101.
- ^ a b "Design, Modeling and Control of Modular Multilevel Converter based HVDC Systems. - NCSU Digital Repository". www.lib.ncsu.edu. Retrieved 2016-04-17.
- ^ a b Jacobsson, B., Karlsson, P., Asplund, G., Harnefors, L., Jonsson, T., VSC - HVDC transmission with cascaded two-level converters, CIGRÉ session, Paris, 2010, paper reference B4-110.
- ^ Falahi, G.; Huang, A. Q. (2015-09-01). "Design consideration of an MMC-HVDC system based on 4500V/4000A emitter turn-off (ETO) thyristor". 2015 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE): 3462–3467. doi:10.1109/ECCE.2015.7310149. ISBN 978-1-4673-7151-3.
- ^ Davidson, C.C., Trainer, D.R., Innovative concepts for hybrid multi-level converters for HVDC power transmission, IET 9th International Conference on AC and DC Power Transmission, London, 2010.
- ^ INELFE interconnector, Siemens publication.
- ^ MacLeod, N.M., Lancaster, A.C., Oates, C.D.M., The development of a Power Electronic Building Block for use in Voltage Source Converters for HVDC transmission applications, CIGRÉ Colloquium, Bergen, Norway, 2009.
- ^ Voltage Source Converter (VSC) HVDC for Power Transmission – Economic Aspects and Comparison with other AC and DC Technologies, CIGRÉ Technical Brochure No. 492 Archived 2016-02-04 at the Wayback Machine, April 2012, section 2.5.3
- ^ Trainer, D.R., Davidson, C.C., Oates, C.D.M., MacLeod, N.M., Critchley, D.R., Crookes, R.W., A New Hybrid Voltage-Sourced Converter for HVDC Power Transmission, CIGRÉ session, Paris, 2010, paper reference B4-111.
Further reading
- Arrillaga, Jos; High Voltage Direct Current Transmission, second edition, Institution of Electrical Engineers, ISBN 0-85296-941-4, 1998.
- Kimbark, E.W., Direct current transmission, volume 1, Wiley Interscience, 1971.
- Cory, B.J., Adamson, C., Ainsworth, J.D., Freris, L.L., Funke, B., Harris, L.A., Sykes, J.H.M., High voltage direct current converters and systems, Macdonald & Co. (publishers) Ltd, 1965.
- Williams, B.W., Power Electronics - devices, drivers and applications, Macmillan Press, ISBN 0-333-57351-X, 1992.
- Mohan, N., Undeland, T.M., Robbins, W.P., Power Electronics - converters, applications and design, John Wiley & Sons, ISBN 0-471-58408-8, 1995.