Inhibitor of apoptosis domain
| Inhibitor of Apoptosis domain | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
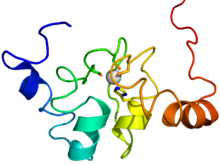 NMR solution structure of the BIR domain of human BIRC2 protein.[1] The protein is rainbow colored cartoon diagram (N-terminus = blue, C-terminus = red) while the coordinated zinc is represented by a grey sphere. | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | BIR | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00653 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001370 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PS50143 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1qbh / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
The inhibitor of apoptosis domain -- also known as IAP repeat, Baculovirus Inhibitor of apoptosis protein Repeat, or BIR -- is a structural motif found in proteins with roles in apoptosis, cytokine production, and chromosome segregation.[2] Proteins containing BIR are known as inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs), or BIR-containing proteins (BIRPs or BIRCs), and include BIRC1 (NAIP), BIRC2 (cIAP1), BIRC3 (cIAP2), BIRC4 (xIAP), BIRC5 (survivin) and BIRC6.[2][3]
BIR domains belong to the zinc-finger domain family and characteristically have a number of invariant amino acid residues, including 3 conserved cysteines and one conserved histidine, which coordinate a zinc ion.[4] They are typically composed of 4-5 alpha helices and a three-stranded beta sheet.
External links
[edit]- Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource motif class LIG_BIR_II_1
- Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource motif class LIG_BIR_III_1
- Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource motif class LIG_BIR_III_2
- Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource motif class LIG_BIR_III_3
- Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource motif class LIG_BIR_III_4
References
[edit]- ^ PDB: 1QBH;Hinds MG, Norton RS, Vaux DL, Day CL (July 1999). "Solution structure of a baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) repeat". Nat. Struct. Biol. 6 (7): 648–51. doi:10.1038/10701. PMID 10404221. S2CID 3194182.
- ^ a b Silke J, Vaux DL (May 2001). "Two kinds of BIR-containing protein - inhibitors of apoptosis, or required for mitosis". J. Cell Sci. 114 (Pt 10): 1821–7. doi:10.1242/jcs.114.10.1821. PMID 11329368.
- ^ Verhagen AM, Coulson EJ, Vaux DL (2001). "Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins and their relatives: IAPs and other BIRPs". Genome Biol. 2 (7): REVIEWS3009. doi:10.1186/gb-2001-2-7-reviews3009. PMC 139420. PMID 11516343.
- ^ Birnbaum MJ, Clem RJ, Miller LK (April 1994). "An apoptosis-inhibiting gene from a nuclear polyhedrosis virus encoding a polypeptide with Cys/His sequence motifs". J. Virol. 68 (4): 2521–8. doi:10.1128/JVI.68.4.2521-2528.1994. PMC 236730. PMID 8139034.
