Endomysium
Appearance
| Endomysium | |
|---|---|
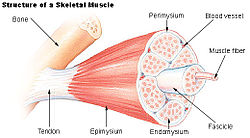 Structure of a skeletal muscle. (Endomysium labeled at bottom center.) | |
| Identifiers | |
| TA98 | A04.0.00.043 |
| TA2 | 2007 |
| TH | H3.03.00.0.00004 |
| FMA | 9729 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The endomysium, meaning within the muscle, is a layer of connective tissue that ensheaths a muscle fiber and is composed mostly from reticular fibers. It also contains capillaries, nerves, and lymphatics. It overlies the muscle fiber's cell membrane: the Sarcolemma.
The term cardiac skeleton is sometimes considered synonymous with endomysium[clarification needed], but sometimes cardiac skeleton refers to the combination of the endomysium and perimysium.
Anti-endomysial antibodies (EMA) are present in celiac disease. They do not cause any direct symptoms to muscles, but detection of EMA is useful in the diagnosis of the disease.[1]
See also
References
- ^ Pruessner HT (1998). "Detecting celiac disease in your patients". Am Fam Physician. 57 (5): 1023–34, 1039–41. PMID 9518950.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)
External links
- UIUC Histology Subject 777
- Template:EMedicineDictionary
- Illustration at wku.edu
- Anatomy photo: Musculoskeletal/muscle/skeletal1/skeletal3 - Comparative Organology at University of California, Davis
- MedEd at Loyola histo/practical/muscle/hp7-42.html
