1977 Irish general election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
147 of 148 seats in Dáil Éireann 74 seats were needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turnout | 76.3% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
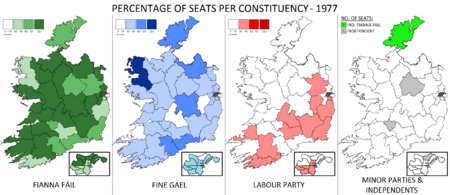 Percentage of seats gained by each of the three major parties, and number of seats gained by smaller parties and independents. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Irish general election of 1977 was held on 16 June 1977 and is regarded as a pivotal point in twentieth-century Irish politics. The general election took place in 42 parliamentary constituencies throughout Southern Ireland for 148 seats in the lower house of parliament, Dáil Éireann. The number of seats in the Dáil was increased by 4 from 144 to 148. The newly elected 148 members of the 21st Dáil assembled at Leinster House on 5 July when a new Fianna Fáil government replaced the incumbent Fine Gael–Labour Party coalition, with Jack Lynch becoming Taoiseach for the second time.
Campaign
In spite of having faced some controversial issues during its term of office, the ruling Fine Gael–Labour Party coalition looked set to defy political history by winning an unprecedented second term. This belief was further augmented following the so-called "Tullymander" of parliamentary constituencies. This refers to the Minister for Local Government James Tully, and his scheme of redrawing every constituency in the country in an effort to maximise the vote for the coalition partners. For instance in Dublin there were thirteen three-seat constituencies. It was hoped that the coalition partners would win two of the seats, leaving Fianna Fáil with only one seat. A similar tactic was used in rural areas where the party was at its strongest.
As a result of this, Fianna Fáil and its leader Jack Lynch believed that they couldn't win the general election. The party drew up a manifesto which offered the electorate a string of financial and economic "sweeteners", encouraging them to vote for Fianna Fáil. Some of the promises that were offered included the abolition of rates on houses, the abolition of car tax and the promise of reducing unemployment to under 100,000. Lynch agreed to the manifesto because he believed that the party needed something dramatic if it were to win the election.
Both The Irish Times and The Irish Press, which was then edited by Tim Pat Coogan, were extremely critical of the government's curtailment of freedom of speech and in particular of the Minister for Posts and Telegraphs Conor Cruise O'Brien, who used these restrictions against the PIRA.
The Fianna Fáil campaign was based on the American model. Inspired by director of elections Séamus Brennan, Lynch travelled the length and breadth of the country, music blaring, accompanied by his followers. His popularity was at its highest, and it soon became clear he might win the election. Lynch's popularity was a big electoral asset. The party slogan "Bring Back Jack" even played on Lynch's huge appeal. But the monetary sweeteners were Fianna Fáil's biggest asset.
In contrast to Fianna Fáil, the government parties of Fine Gael and the Labour Party fought the general election on their record in government. The redrawing of the constituency boundaries also gave them hope for success, however they offered little to the electorate except for the policies they had been pursuing for the previous four years.
While towards the end of the campaign Fianna Fáil were expected to win the general election, nobody predicted the scale of that victory. An unprecedented ten-seat majority in Dáil Éireann for Fianna Fáil saw the National Coalition swept from power in what was at the time the biggest political hurricane in Irish history. Only Éamon de Valera had ever done better, but only once out of 13 elections. Following the election defeat the leaders of Fine Gael and the Labour Party, Liam Cosgrave and Brendan Corish resigned as leaders of their respective parties, the first occasion in which a defeated Taoiseach or Tánaiste had done so.
"Tullymandering" and the unprecedented sweeteners were the cause for the scale of the coalition's defeat. The new government established an independent commission to carry out future boundary revisions.
Result
| Election to the 21st Dáil – 16 June 1977[1][2][3] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Leader | Seats | ± | % of seats |
First pref. votes |
% FPv | ±% | |
| Fianna Fáil | Jack Lynch | 84 | +15 | 56.7 | 811,615 | 50.6 | +4.4 | |
| Fine Gael | Liam Cosgrave | 43 | –11 | 29.0 | 488,767 | 30.5 | –4.6 | |
| Labour | Brendan Corish | 17 | –2 | 11.5 | 186,410 | 11.6 | –2.1 | |
| Sinn Féin The Workers' Party | Tomás Mac Giolla | 0 | New | 0 | 27,209 | 1.7 | – | |
| Irish Republican Socialist | Seamus Costello | 0 | New | 0 | 955 | 0.1 | – | |
| Communist | Michael O'Riordan | 0 | – | 0 | 544 | 0.0 | – | |
| Independent | N/A | 4 | +2 | 2.7 | 87,527 | 5.5 | +2.6 | |
| Spoilt votes | 13,743 | — | — | |||||
| Total | 148 | +4 | 100 | 1,616,770 | 100 | — | ||
| Electorate/Turnout | 2,118,606 | 76.3% | — | |||||
Independents include Independent Fianna Fáil (13,824 votes, 1 seat) and the Community group in Dublin (9,427 votes).
- Fianna Fáil majority government formed.
First time TDs
A total of 42 TDs were elected for the first time:
- Bertie Ahern
- Kit Ahern
- Niall Andrews
- Liam Aylward
- John Boland
- Gerard Brady
- Vincent Brady
- Barry Cogan
- Hugh Conaghan
- Michael Joe Cosgrave
- Michael D'Arcy
- Síle de Valera
- Austin Deasy
- Seán Doherty
- Eddie Filgate
- Jim Fitzsimons
- Pádraig Flynn
- Joe Fox
- John Horgan
- Michael Keating
- Seán Keegan
- Patrick Kerrigan
- Timothy Killeen
- Mark Killilea, Jnr
- Liam Lawlor
- Eileen Lemass
- Tom Leonard
- Terry Leyden
- Michael Lipper
- John Mannion, Jnr
- Charlie McCreevy
- Jim Mitchell
- P. J. Morley
- William O'Brien
- Martin O'Donoghue
- Rory O'Hanlon
- Jim O'Keeffe
- Paddy O'Toole
- Ruairi Quinn
- Albert Reynolds
- Joe Walsh
- Michael Woods
By-elections
Outgoing TDs
- Liam Burke (Lost seat)
- Ruairí Brugha (Lost seat)
- Justin Keating (Lost seat)
- Conor Cruise O'Brien (Lost seat)
- Seán Flanagan (Lost seat)
- Richard Gogan (Lost seat)
- Gus Healy (Retired)
- Brigid Hogan-O'Higgins (Lost seat)
- Eugene Timmons (Lost seat)
See also
- Members of the 21st Dáil
- Government of the 21st Dáil
- Ministers of State of the 21st Dáil
- Gerrymandering in Ireland
References
- ^ "21st Dáil 1977 General Election". ElectionsIreland.org. Retrieved 19 June 2009.
- ^ "Dáil elections since 1918". ARK Northern Ireland. Retrieved 19 June 2009.
- ^ Nohlen, D & Stöver, P (2010) Elections in Europe: A data handbook, pp1009-1017 ISBN 978-3-8329-5609-7


