Oxytocin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌɒks[invalid input: 'ɨ']ˈtoʊsɪn/ |
| Trade names | Pitocin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intranasal, IV, IM |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 30% |
| Metabolism | liver and other oxytocinases |
| Elimination half-life | 1–6 min (IV) ~2 h (intranasal)[2][3] |
| Excretion | Biliary and kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.045 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C43H66N12O12S2 |
| Molar mass | 1007.19 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Oxytocin (Oxt) is a hormone, neuropeptide, and medication.[4][5] As a medication, it is used to cause contraction of the uterus in order to start labor or increase the speed of labor, and to stop bleeding following delivery.[4] For this purpose, it is given either by injection into a muscle or into a vein.[4]
The use of oxytocin as a medication can result in excessive contraction of the uterus that can cause distress in an unborn baby. Common side effects in the mother include nausea and a slow heart rate. Serious side effects include water intoxication with an excessive dose and uterus rupture. Allergic reactions may also occur.[4]
Oxytocin is normally produced in the posterior pituitary.[6] It plays a role in social bonding, sexual reproduction in both sexes, and during and after childbirth.[7] Oxytocin is released into the bloodstream as a hormone in response to stretching of the cervix and uterus during labor and with stimulation of the nipples from breastfeeding.[6] This helps with birth, bonding with the baby, and milk production.[6][8]
Oxytocin was discovered in 1952.[9] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most important medications needed in a basic health system.[10] As of 2014[update], the wholesale cost of the medication is US$0.1–0.56 per dose.[11]
Physiological effects
Oxytocin has peripheral (hormonal) actions, and also has actions in the brain. Its actions are mediated by specific, oxytocin receptors. The oxytocin receptor is a G-protein-coupled receptor that requires magnesium and cholesterol. It belongs to the rhodopsin-type (class I) group of G-protein-coupled receptors.
Studies have looked at oxytocin's role in various behaviors, including orgasm, social recognition, pair bonding, anxiety, and maternal behaviors.[12]
The peripheral actions of oxytocin mainly reflect secretion from the pituitary gland. The behavioral effects of oxytocin are thought to reflect release from centrally projecting oxytocin neurons, different from those that project to the pituitary gland, or that are collaterals from them.[13] Oxytocin receptors are expressed by neurons in many parts of the brain and spinal cord, including the amygdala, ventromedial hypothalamus, septum, nucleus accumbens, and brainstem.
- Letdown reflex: In lactating (breastfeeding) mothers, oxytocin acts at the mammary glands, causing milk to be 'let down' into subareolar sinuses, from where it can be excreted via the nipple.[14] Suckling by the infant at the nipple is relayed by spinal nerves to the hypothalamus. The stimulation causes neurons that make oxytocin to fire action potentials in intermittent bursts; these bursts result in the secretion of pulses of oxytocin from the neurosecretory nerve terminals of the pituitary gland.
- Uterine contraction: Important for cervical dilation before birth, oxytocin causes contractions during the second and third stages of labor. Oxytocin release during breastfeeding causes mild but often painful contractions during the first few weeks of lactation. This also serves to assist the uterus in clotting the placental attachment point postpartum. However, in knockout mice lacking the oxytocin receptor, reproductive behavior and parturition are normal.[15]
- Social behavior[16][17] and wound healing: Oxytocin is also thought to modulate inflammation by decreasing certain cytokines. Thus, the increased release in oxytocin following positive social interactions has the potential to improve wound healing. A study by Marazziti and colleagues used heterosexual couples to investigate this possibility. They found increases in plasma oxytocin following a social interaction were correlated with faster wound healing. They hypothesized this was due to oxytocin reducing inflammation, thus allowing the wound to heal more quickly. This study provides preliminary evidence that positive social interactions may directly influence aspects of health.[18] According to a study published in 2014, silencing of oxytocin receptor interneurons in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) of female mice resulted in loss of social interest in male mice during the sexually receptive phase of the estrous cycle.[19]
- Oxytocin evokes feelings of contentment, reductions in anxiety, and feelings of calmness and security when in the company of the mate.[20] This suggests oxytocin may be important for the inhibition of the brain regions associated with behavioral control, fear, and anxiety, thus allowing orgasm to occur. Research has also demonstrated that oxytocin can decrease anxiety and protect against stress, particularly in combination with social support.[21]
- Due to its similarity to vasopressin, it can reduce the excretion of urine slightly. In several species, oxytocin can stimulate sodium excretion from the kidneys (natriuresis), and, in humans, high doses can result in hyponatremia.
- Oxytocin and oxytocin receptors are also found in the heart in some rodents, and the hormone may play a role in the embryonal development of the heart by promoting cardiomyocyte differentiation.[22][23] However, the absence of either oxytocin or its receptor in knockout mice has not been reported to produce cardiac insufficiencies.[15]
- Modulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity: Oxytocin, under certain circumstances, indirectly inhibits release of adrenocorticotropic hormone and cortisol and, in those situations, may be considered an antagonist of vasopressin.[24]
- Autism: Oxytocin may play a role in autism and may be an effective treatment for autism's repetitive and affiliative behaviors.[25] Oxytocin treatments also resulted in an increased retention of affective speech in adults with autism.[26] Two related studies in adults, in 2003 and 2007, found oxytocin decreased repetitive behaviors and improved interpretation of emotions. More recently, intranasal administration of oxytocin was found to increase emotion recognition in children as young as 12 who are diagnosed with autism spectrum disorders.[27] Oxytocin has also been implicated in the etiology of autism, with one report suggesting autism is correlated with genomic deletion of the gene containing the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR). Studies involving Caucasian and Finnish samples and Chinese Han families provide support for the relationship of OXTR with autism.[26][28] Autism may also be associated with an aberrant methylation of OXTR.[26] After treatment with inhaled oxytocin, autistic patients exhibit more appropriate social behavior.[29] While this research suggests some promise, further clinical trials of oxytocin are required to demonstrate potential benefit and side effects in the treatment of autism. As such, researchers do not recommend use of oxytocin as a treatment for autism outside of clinical trials.[30]
- Nasally administered oxytocin has also been reported to reduce fear, possibly by inhibiting the amygdala (which is thought to be responsible for fear responses).[31] Indeed, studies in rodents have shown oxytocin can efficiently inhibit fear responses by activating an inhibitory circuit within the amygdala.[32][33] Some researchers have argued oxytocin has a general enhancing effect on all social emotions, since intranasal administration of oxytocin also increases envy and Schadenfreude.[34]
- Trust is increased by oxytocin.[35][36][37] Disclosure of emotional events is a sign of trust in humans. When recounting a negative event, humans who receive intranasal oxytocin share more emotional details and stories with more emotional significance.[36] Humans also find faces more trustworthy after receiving intranasal oxytocin. In a study, participants who received intranasal oxytocin viewed photographs of human faces with neutral expressions and found them to be more trustworthy than those who did not receive oxytocin.[35] This may be because oxytocin reduces the fear of social betrayal in humans.[38] Even after experiencing social alienation by being excluded from a conversation, humans who received oxytocin scored higher in trust on the Revised NEO Personality Inventory.[37] Moreover, in a risky investment game, experimental subjects given nasally administered oxytocin displayed "the highest level of trust" twice as often as the control group. Subjects who were told they were interacting with a computer showed no such reaction, leading to the conclusion that oxytocin was not merely affecting risk aversion.[39] When there is a reason to be distrustful, such as experiencing betrayal, differing reactions are associated with oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) differences. Those with the CT haplotype experience a stronger reaction, in the form of anger, to betrayal.[40]
- Oxytocin affects social distance between adult males and females, and may be responsible at least in part for romantic attraction and subsequent monogamous pair bonding. An oxytocin nasal spray caused men in a monogamous relationship, but not single men, to increase the distance between themselves and an attractive woman during a first encounter by 10 to 15 centimeters. The researchers suggested that oxytocin may help promote fidelity within monogamous relationships.[41] For this reason, it is sometimes referred to as the "bonding hormone". There is some evidence that oxytocin promotes ethnocentric behavior, incorporating the trust and empathy of in-groups with their suspicion and rejection of outsiders.[16] Furthermore, genetic differences in the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) have been associated with maladaptive social traits such as aggressive behaviour.[42]
- Affecting generosity by increasing empathy during perspective taking: In a neuroeconomics experiment, intranasal oxytocin increased generosity in the Ultimatum Game by 80%, but had no effect in the Dictator Game that measures altruism. Perspective-taking is not required in the Dictator Game, but the researchers in this experiment explicitly induced perspective-taking in the Ultimatum Game by not identifying to participants into which role they would be placed.[43] Serious methodological questions have arisen, however, with regard to the role of oxytocin in trust and generosity.[44]
- Empathy in healthy males has been shown to be increased after intranasal oxytocin[45][46] This is most likely due to the effect of oxytocin in enhancing eye gaze.[47] There is some discussion about which aspect of empathy oxytocin might alter – for example, cognitive vs. emotional empathy.[48]
- Certain learning and memory functions are impaired by centrally administered oxytocin.[49] Also, systemic oxytocin administration can impair memory retrieval in certain aversive memory tasks.[50] Interestingly, oxytocin does seem to facilitate learning and memory specifically for social information. Healthy males administered intranasal oxytocin show improved memory for human faces, in particular happy faces.[51][52] They also show improved recognition for positive social cues over threatening social cues [53][54] and improved recognition of fear.[55]
- Sexual activity: The relationship between oxytocin and human sexual response is unclear. At least two uncontrolled studies have found increases in plasma oxytocin at orgasm – in both men and women.[56][57] Plasma oxytocin levels are notably increased around the time of self-stimulated orgasm and are still higher than baseline when measured five minutes after self arousal.[56] The authors of one of these studies speculated that oxytocin's effects on muscle contractibility may facilitate sperm and egg transport.[56]
- In a study measuring oxytocin serum levels in women before and after sexual stimulation, the author suggests it serves an important role in sexual arousal. This study found genital tract stimulation resulted in increased oxytocin immediately after orgasm.[58] Another study reported increases of oxytocin during sexual arousal could be in response to nipple/areola, genital, and/or genital tract stimulation as confirmed in other mammals.[59] Murphy et al. (1987), studying men, found oxytocin levels were raised throughout sexual arousal with no acute increase at orgasm.[60] A more recent study of men found an increase in plasma oxytocin immediately after orgasm, but only in a portion of their sample that did not reach statistical significance. The authors noted these changes "may simply reflect contractile properties on reproductive tissue".[61]
- Bonding: In the prairie vole, oxytocin released into the brain of the female during sexual activity is important for forming a monogamous pair bond with her sexual partner. Vasopressin appears to have a similar effect in males.[62] Oxytocin has a role in social behaviors in many species, so it likely also does in humans. In a 2003 study, both humans and dog oxytocin levels in the blood rose after five to 24 minutes of a petting session. This possibly plays a role in the emotional bonding between humans and dogs.[63]
- Maternal behavior: Female rats given oxytocin antagonists after giving birth do not exhibit typical maternal behavior.[64] By contrast, virgin female sheep show maternal behavior toward foreign lambs upon cerebrospinal fluid infusion of oxytocin, which they would not do otherwise.[65] Oxytocin is involved in the initiation of maternal behavior, not its maintenance; for example, it is higher in mothers after they interact with unfamiliar children rather than their own.[66]
- Drug interactions: According to some studies in animals, oxytocin inhibits the development of tolerance to various addictive drugs (opiates, cocaine, alcohol), and reduces withdrawal symptoms.[67] MDMA (ecstasy) may increase feelings of love, empathy, and connection to others by stimulating oxytocin activity primarily via activation of serotonin 5-HT1A receptors, if initial studies in animals apply to humans.[68] The anxiolytic Buspar (buspirone) may produce some of its effects via 5-HT1A receptor-induced oxytocin stimulation as well.[69][70]
- Preparing fetal neurons for delivery: Crossing the placenta, maternal oxytocin reaches the fetal brain and induces a switch in the action of neurotransmitter GABA from excitatory to inhibitory on fetal cortical neurons. This silences the fetal brain for the period of delivery and reduces its vulnerability to hypoxic damage.[71]
- Romantic attachment: In some studies, high levels of plasma oxytocin have been correlated with romantic attachment. For example, if a couple is separated for a long period of time, anxiety can increase due to the lack of physical affection. Oxytocin may aid romantically attached couples by decreasing their feelings of anxiety when they are separated.[20]
- Feeding: Recent evidence has suggested that oxytocin neurons in the para-ventricular hypothalamus in the brain may play a key role in suppressing appetite under normal conditions and that other hypothalamic neurons may trigger eating via inhibition of these oxytocin neurons. This population of oxytocin neurons are absent in Prader-Willi syndrome, a genetic disorder that leads to uncontrollable feeding and obesity, and may play a key role in its pathophysiology.[72]
- Group-serving dishonesty/deception: In a carefully controlled study exploring the biological roots of immoral behavior, oxytocin was shown to promote dishonesty when the outcome favored the group to which an individual belonged instead of just the individual.[73]
- Intergroup bonding: Oxytocin can increase positive attitudes, such as bonding, toward individuals with similar characteristics, who then become classified as “in-group” members, whereas individuals who are dissimilar become classified as “out-group” members. Race can be used as an example of in-group and out-group tendencies because society often categorizes individuals into groups based on race (Caucasian, African American, Latino, etc.). One study that examined race and empathy found that participants receiving nasally administered oxytocin had stronger reactions to pictures of in-group members making pained faces than to pictures of out-group members with the same expression.[74] This shows that oxytocin may be implicated in our ability to empathize with individuals of different races and could potentially translate into willingness to help individuals in pain or stressful situations. Moreover, individuals of one race may be more inclined to help individuals of the same race than individuals of another race when they are experiencing pain. Oxytocin has also been implicated in lying when lying would prove beneficial to other in-group members. In a study where such a relationship was examined, it was found that when individuals were administered oxytocin, rates of dishonesty in the participants’ responses increased for their in-group members when a beneficial outcome for their group was expected.[75] Both of these examples show the tendency to act in ways that benefit people with which one feels is part of their social group, or in-group. Oxytocin is not only correlated with the preferences of individuals to associate with members of their own group, but it is also evident during conflicts between members of different groups. During conflict, individuals receiving nasally administered oxytocin demonstrate more frequent defense-motivated responses toward in-group members than out-group members. Further, oxytocin was correlated with participant desire to protect vulnerable in-group members, despite that individual’s attachment to the conflict.[76] Similarly, it has been demonstrated that when oxytocin is administered, individuals alter their subjective preferences in order to align with in-group ideals over out-group ideals.[77] These studies demonstrate that oxytocin is associated with intergroup dynamics. Further, oxytocin influences the responses of individuals in a particular group to those of another group. The in-group bias is evident in smaller groups; however, it can also be extended to groups as large as one’s entire country leading toward a tendency of strong national zeal. A study done in the Netherlands showed that oxytocin increased the in-group favoritism of their nation while decreasing acceptance of members of other ethnicities and foreigners.[16] People also show more affection for their country’s flag while remaining indifferent to other cultural objects when exposed to oxytocin.[78] It has thus been hypothesized that this hormone may be a factor in xenophobic tendencies secondary to this effect. Thus, oxytocin appears to affect individuals at an international level where the in-group becomes a specific "home" country and the out-group grows to include all other countries.
Fear and anxiety
Oxytocin is typically remembered for the effect it has on prosocial behaviors, such as its role in facilitating trust and attachment between individuals. Consequently, oxytocin is often referred to as the “love hormone".[79] However, oxytocin has a more complex role than solely enhancing prosocial behaviors. There is consensus that oxytocin modulates fear and anxiety; that is, it does not directly elicit fear or anxiety.[80] Two dominant theories explain the role of oxytocin in fear and anxiety. One theory states that oxytocin increases approach/avoidance to certain social stimuli and the second theory states that oxytocin increases the salience of certain social stimuli, causing the animal or human to pay closer attention to socially relevant stimuli.[81]
Individuals who receive an intranasal dose of oxytocin identify facial expressions of disgust faster than individuals who do not receive oxytocin.[81] Facial expressions of disgust are evolutionarily linked to the idea of contagion. Thus, oxytocin increases the salience of cues that imply contamination, which leads to a faster response because these cues are especially relevant for survival. In another study, after administration of oxytocin, individuals displayed an enhanced ability to recognize expressions of fear compared to the individuals who received the placebo.[55] Oxytocin modulates fear responses by enhancing the maintenance of social memories. Rats that are genetically modified to have a surplus of oxytocin receptors display a greater fear response to a previously conditioned stressor. Oxytocin enhances the aversive social memory, leading the rat to display a greater fear response when the aversive stimulus is encountered again.[80]
Sex differences
It has been shown that oxytocin differentially affects males and females. Females who are administered oxytocin are overall faster in responding to socially relevant stimuli than males who received oxytocin.[81][82] Additionally, after the administration of oxytocin, females show increased amygdala activity in response to threatening scenes; however, males do not show increased amygdala activation. This phenomenon can be explained by looking at the role of gonadal hormones, specifically estrogen, which modulate the enhanced threat processing seen in females. Estrogen has been shown to stimulate the release of oxytocin from the hypothalamus and promote receptor binding in the amygdala.[82]
It has also been shown that testosterone directly suppresses oxytocin. [83] This has been hypothesized to have evolutionary significance. With oxytocin suppressed, activities such as hunting and attacking invaders would be less mentally difficult as oxytocin is strongly associated with empathy. [84]
Mood and depression
Oxytocin produces antidepressant-like effects in animal models of depression,[85] and a deficit of it may be involved in the pathophysiology of depression in humans.[86] The antidepressant-like effects of oxytocin are not blocked by a selective antagonist of the oxytocin receptor, suggesting that these effects are not mediated by the oxytocin receptor.[87] In accordance, unlike oxytocin, the selective non-peptide oxytocin receptor agonist WAY-267,464 does not produce antidepressant-like effects, at least in the tail suspension test.[88] (In contrast to WAY-267,464, carbetocin, a close analogue of oxytocin and peptide oxytocin receptor agonist, notably does produce antidepressant-like effects in animals.)[88] As such, the antidepressant-like effects of oxytocin may be mediated by modulation of a different target, perhaps the vasopressin V1A receptor where oxytocin is known to weakly bind as an agonist.[89][90]
Sildenafil has been found to enhance electrically evoked oxytocin release from the pituitary gland.[85] In accordance, the drug shows oxytocin-dependent antidepressant-like effects in animals, and it has proposed that sildenafil may hold promise as a potential antidepressant in humans.[85]
Medical uses
An intravenous infusion of oxytocin is used to induce labor and to support labor in case of slow childbirth. It is unclear whether a high dose is better than a standard dose for labor induction. It has largely replaced ergometrine as the principal agent to increase uterine tone in acute postpartum hemorrhage. Oxytocin is also used in veterinary medicine to facilitate birth and to stimulate milk release. The tocolytic agent atosiban (Tractocile) acts as an antagonist of oxytocin receptors; this drug is registered in many countries to suppress premature labor between 24 and 33 weeks of gestation. It has fewer side effects than drugs previously used for this purpose (ritodrine, salbutamol, and terbutaline).[91]
Side effects
Oxytocin is relatively safe when used at recommended doses, and side effects are uncommon.[92] The following maternal events have been reported:[92]
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Increased heart rate
- Decreased blood pressure
- Cardiac arrhythmia and premature ventricular contraction
- Impaired uterine blood flow
- Pelvic hematoma
- Afibrinogenemia
- Anaphylaxis
- Nausea and vomiting
- Increase fetal blood flow
Excessive dosage or long-term administration (over a period of 24 hours or longer) have been known to result in tetanic uterine contractions, uterine rupture, postpartum hemorrhage, and water intoxication, sometimes fatal.
During pregnancy, increased uterine motility has led to decreased heart rate, cardiac arrhythmia, seizures, brain damage, death in the fetus/neonate:[92]
Administration
Oxytocin is destroyed in the gastrointestinal tract, so it is not active orally and must be administered by injection or as nasal spray. The compound has a half-life of typically about three minutes in the blood when given intravenously. Peripherally administered (e.g., intravenous) peptides like oxytocin cross the blood-brain-barrier very poorly, although very small amounts (< 1%) do appear to enter the central nervous system in humans when given via this route.[93] In contrast to peripheral administration, when administered intranasally via a nasal spray, oxytocin reliably crosses the blood–brain barrier and exhibits psychoactive effects in humans.[94][95] In addition, also unlike the case of peripheral administration, intranasal oxytocin has a central duration of at least 2.25 hours and as long as 4 hours.[2][3] In likely relation to this fact, endogenous oxytocin concentrations in the brain have been found to be as much as 1000-fold higher than peripheral levels.[93]
Structure

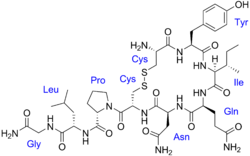
Oxytocin is a peptide of nine amino acids (a nonapeptide). Its systematic name is cysteine-tyrosine-isoleucine-glutamine-asparagine-cysteine-proline-leucine-glycine-amide (cys – tyr – ile – gln – asn – cys – pro – leu – gly – NH2, or CYIQNCPLG-NH2). Oxytocin has a molecular mass of 1007 daltons. One international unit (IU) of oxytocin is the equivalent of about 2 micrograms of pure peptide. While the structure of oxytocin is highly conserved in placental mammals, a novel structure of oxytocin was recently reported in marmosets, tamarins, and other new world primates. Genomic sequencing of the gene for oxytocin revealed a single in-frame mutation (thymine for cytosine) which results in a single amino acid substitution at the 8-position (proline for leucine).[96]
The biologically active form of oxytocin, commonly measured by RIA and/or HPLC techniques, is also known as the octapeptide "oxytocin disulfide" (oxidized form), but oxytocin also exists as a reduced dithiol nonapeptide called oxytoceine.[97] It has been theorized that open chain oxytoceine (the reduced form of oxytocin) may also act as a free radical scavenger (by donating an electron to a free radical); oxytoceine may then be oxidized back to oxytocin via the dehydroascorbate <---> ascorbate redox couple.[98]
The structure of oxytocin is very similar to that of vasopressin (cys – tyr – phe – gln – asn – cys – pro – arg – gly – NH2), also a nonapeptide with a sulfur bridge, whose sequence differs from oxytocin by two amino acids. A table showing the sequences of members of the vasopressin/oxytocin superfamily and the species expressing them is present in the vasopressin article. Oxytocin and vasopressin were isolated and synthesized by Vincent du Vigneaud in 1953, work for which he received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1955.
Oxytocin and vasopressin are the only known hormones released by the human posterior pituitary gland to act at a distance. However, oxytocin neurons make other peptides, including corticotropin-releasing hormone and dynorphin, for example, that act locally. The magnocellular neurosecretory cells that make oxytocin are adjacent to magnocellular neurosecretory cells that make vasopressin. These are large neuroendocrine neurons which are excitable and can generate action potentials.
Synthesis, storage, release, and metabolism
The oxytocin peptide is synthesized as an inactive precursor protein from the OXT gene.[99][100][101] This precursor protein also includes the oxytocin carrier protein neurophysin I.[102] The inactive precursor protein is progressively hydrolyzed into smaller fragments (one of which is neurophysin I) via a series of enzymes. The last hydrolysis that releases the active oxytocin nonapeptide is catalyzed by peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (PAM).[103]
The activity of the PAM enzyme system is dependent upon vitamin C (ascorbate), which is a necessary vitamin cofactor. By chance, sodium ascorbate by itself was found to stimulate the production of oxytocin from ovarian tissue over a range of concentrations in a dose-dependent manner.[104] Many of the same tissues (e.g. ovaries, testes, eyes, adrenals, placenta, thymus, pancreas) where PAM (and oxytocin by default) is found are also known to store higher concentrations of vitamin C.[105]
Oxytocin is known to be metabolized by the oxytocinase, leucyl/cystinyl aminopeptidase.[106][107] Other oxytocinases are also known to exist.[106][108] Amastatin, bestatin (ubenimex), leupeptin, and puromycin have been found to inhibit the enzymatic degradation of oxytocin, though they also inhibit the degradation of various other peptides, such as vasopressin, met-enkephalin, and dynorphin A.[108][109][110][111]
Neural sources
In the hypothalamus, oxytocin is made in magnocellular neurosecretory cells of the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei, and is stored in Herring bodies at the axon terminals in the posterior pituitary. It is then released into the blood from the posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) of the pituitary gland. These axons (likely, but dendrites have not been ruled out) have collaterals that innervate oxytocin receptors in the nucleus accumbens.[13] The peripheral hormonal and behavioral brain effects of oxytocin are thought to be coordinated through its common release through these collaterals.[13] Oxytocin is also made by some neurons in the paraventricular nucleus that project to other parts of the brain and to the spinal cord.[112] Depending on the species, oxytocin receptor-expressing cells are located in other areas, including the amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis.
In the pituitary gland, oxytocin is packaged in large, dense-core vesicles, where it is bound to neurophysin I as shown in the inset of the figure; neurophysin is a large peptide fragment of the larger precursor protein molecule from which oxytocin is derived by enzymatic cleavage.
Secretion of oxytocin from the neurosecretory nerve endings is regulated by the electrical activity of the oxytocin cells in the hypothalamus. These cells generate action potentials that propagate down axons to the nerve endings in the pituitary; the endings contain large numbers of oxytocin-containing vesicles, which are released by exocytosis when the nerve terminals are depolarised.
Non-neural sources
Outside the brain, oxytocin-containing cells have been identified in several diverse tissues, including in females in the corpus luteum [113][114] and the placenta,[115] in males in the testicles' interstitial cells of Leydig,[116] the retina,[117] the adrenal medulla,[118] the thymus[119] and the pancreas.[120] The finding of significant amounts of this classically "neurohypophysial" hormone outside the central nervous system raises many questions regarding its possible importance in these different tissues.
Male
The Leydig cells in some species have been shown to possess the biosynthetic machinery to manufacture testicular oxytocin de novo, to be specific, in rats (which can synthesize vitamin C endogenously), and in guinea pigs, which, like humans, require an exogenous source of vitamin C (ascorbate) in their diets.[121]
Female
Oxytocin is synthesized by corpora lutea of several species, including ruminants and primates. Along with estrogen, it is involved in inducing the endometrial synthesis of prostaglandin F2α to cause regression of the corpus luteum.
Miscellaneous
Estrogen has been found to increase the secretion of oxytocin and to increase the expression of its receptor, the oxytocin receptor, in the brain.[122] In women, a single dose of estradiol has been found to be sufficient to increase circulating oxytocin concentrations.[87]
Evolution
Virtually all vertebrates have an oxytocin-like nonapeptide hormone that supports reproductive functions and a vasopressin-like nonapeptide hormone involved in water regulation. The two genes are usually located close to each other (less than 15,000 bases apart) on the same chromosome, and are transcribed in opposite directions (however, in fugu,[123] the homologs are further apart and transcribed in the same direction).
The two genes are believed to result from a gene duplication event; the ancestral gene is estimated to be about 500 million years old and is found in cyclostomata (modern members of the Agnatha).[49]
History
The word oxytocin was coined from the term oxytocic. Greek ὀξύς, oxys, and τόκος, tokos, meaning "quick birth")
Its uterine-contracting properties were discovered by British pharmacologist Sir Henry Hallett Dale in 1906.[124] And its milk ejection property was described by Ott and Scott in 1910[125] and by Schafer and Mackenzie in 1911.[126]
Oxytocin became the first polypeptide hormone to be sequenced[127] or synthesized.[128][129][130] Du Vigneaud was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1955 for his work.[131]
Research
Oxytocin nasal sprays have been used to stimulate breastfeeding, but the efficacy of this approach is doubtful.[132]
The trust-inducing property of oxytocin might help those with social anxiety and depression,[45] but with the potential for abuse with confidence tricks[133][134] and military applications.[135] The use of oxytocin in relationship counseling is being investigated, as research has shown the hormone could both enhance trust and improve people's ability to interpret the emotions of others correctly.[136]
A nasal spray formulation of oxytocin branded Syntocinon is under development by Retrophin for the treatment of lactation deficiency and as a novel treatment for autism and schizophrenia.[137] As of October 2014[update], it has reached phase III, phase II, and phase II clinical trials for these indications, respectively.[138] In October 2014, Retrophin divested Syntocinon to Turing Pharmaceuticals.[139]
Society and culture
Brand names
Synthetic oxytocin is sold as proprietary medication under the trade names Pitocin and Syntocinon, and as generic oxytocin.
References
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ^ a b Weisman O, Zagoory-Sharon O, Feldman R (September 2012). "Intranasal oxytocin administration is reflected in human saliva". Psychoneuroendocrinology. 37 (9): 1582–6. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.02.014. PMID 22436536.
- ^ a b Huffmeijer R, Alink LR, Tops M, et al. (2012). "Salivary levels of oxytocin remain elevated for more than two hours after intranasal oxytocin administration". Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 33 (1): 21–5. PMID 22467107.
- ^ a b c d "Oxytocin". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved June 2015.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ The Oxford Handbook of Prosocial Behavior. Oxford University Press. 2015. p. 354. ISBN 9780195399813.
- ^ a b c Chiras, Daniel D. (2012). Human biology (7th ed.). Sudbury, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 262. ISBN 9780763783457.
- ^ Yang, HP; Wang, L; Han, L; Wang, SC (2013). "Nonsocial functions of hypothalamic oxytocin". ISRN neuroscience. 2013: 179272. doi:10.1155/2013/179272. PMC 4045544. PMID 24967304.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Human Evolutionary Biology. Cambridge University Press. 2010. p. 282. ISBN 9781139789004.
- ^ Corey, E.J. (2012). "Oxytocin". Molecules and Medicine. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118361733.
- ^ "WHO Model List of EssentialMedicines" (PDF). World Health Organization. October 2013. Retrieved 22 April 2014.
- ^ "Oxytocin". International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Retrieved 20 December 2015.
- ^ Lee HJ, Macbeth AH, Pagani JH, Young WS (Jun 2009). "Oxytocin: the great facilitator of life". Progress in Neurobiology. 88 (2): 127–51. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.04.001. PMC 2689929. PMID 19482229.
- ^ a b c Ross HE, Cole CD, Smith Y, Neumann ID, Landgraf R, Murphy AZ, Young LJ (Sep 2009). "Characterization of the oxytocin system regulating affiliative behavior in female prairie voles". Neuroscience. 162 (4): 892–903. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.05.055. PMC 2744157. PMID 19482070.
- ^ Human Milk and Lactation at eMedicine
- ^ a b Takayanagi Y, Yoshida M, Bielsky IF, Ross HE, Kawamata M, Onaka T, Yanagisawa T, Kimura T, Matzuk MM, Young LJ, Nishimori K (Nov 2005). "Pervasive social deficits, but normal parturition, in oxytocin receptor-deficient mice". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 102 (44): 16096–101. doi:10.1073/pnas.0505312102. PMC 1276060. PMID 16249339.
- ^ a b c De Dreu CK, Greer LL, Van Kleef GA, Shalvi S, Handgraaf MJ (Jan 2011). "Oxytocin promotes human ethnocentrism". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 108 (4): 1262–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.1015316108. PMC 3029708. PMID 21220339.
- ^ Zak PJ, Kurzban R, Matzner WT (Dec 2004). "The neurobiology of trust". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1032 (1): 224–7. doi:10.1196/annals.1314.025. PMID 15677415.
- ^ Gouin JP, Carter CS, Pournajafi-Nazarloo H, Glaser R, Malarkey WB, Loving TJ, Stowell J, Kiecolt-Glaser JK (Aug 2010). "Marital behavior, oxytocin, vasopressin, and wound healing". Psychoneuroendocrinology. 35 (7): 1082–90. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2010.01.009. PMC 2888874. PMID 20144509.
- ^ Nakajima M, Görlich A, Heintz N (2014). "Oxytocin modulates female sociosexual behavior through a specific class of prefrontal cortical interneurons". Cell. 159 (2): 295–305. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.020. PMC 4206218. PMID 25303526.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|laysource=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysummary=ignored (help) - ^ a b Marazziti D, Dell'Osso B, Baroni S, Mungai F, Catena M, Rucci P, Albanese F, Giannaccini G, Betti L, Fabbrini L, Italiani P, Del Debbio A, Lucacchini A, Dell'Osso L (2006). "A relationship between oxytocin and anxiety of romantic attachment". Clinical Practice and Epidemiology in Mental Health. 2 (1): 28. doi:10.1186/1745-0179-2-28. PMC 1621060. PMID 17034623.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Heinrichs M, Baumgartner T, Kirschbaum C, Ehlert U (2003). "Social support and oxytocin interact to suppress cortisol and subjective responses to psychosocial stress". Biol. Psychiatry. 54 (12): 1389–98. doi:10.1016/S0006-3223(03)00465-7. PMID 14675803.
- ^ Paquin J, Danalache BA, Jankowski M, McCann SM, Gutkowska J (Jul 2002). "Oxytocin induces differentiation of P19 embryonic stem cells to cardiomyocytes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 99 (14): 9550–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.152302499. PMC 123178. PMID 12093924.
- ^ Jankowski M, Danalache B, Wang D, Bhat P, Hajjar F, Marcinkiewicz M, Paquin J, McCann SM, Gutkowska J (Aug 2004). "Oxytocin in cardiac ontogeny". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (35): 13074–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.0405324101. PMC 516519. PMID 15316117.
- ^ Hartwig W (1989). Endokrynologia praktyczna. Warsaw: Państwowy Zakład Wydawnictw Lekarskich. ISBN 83-200-1415-8.[page needed]
- ^ Bartz JA, Hollander E (2008). "Oxytocin and experimental therapeutics in autism spectrum disorders". Progress in Brain Research. Progress in Brain Research. 170: 451–62. doi:10.1016/S0079-6123(08)00435-4. ISBN 978-0-444-53201-5. PMID 18655901.
- ^ a b c Jacob S, Brune CW, Carter CS, Leventhal BL, Lord C, Cook EH (Apr 2007). "Association of the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) in Caucasian children and adolescents with autism". Neuroscience Letters. 417 (1): 6–9. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.02.001. PMC 2705963. PMID 17383819.
- ^ Guastella AJ, Einfeld SL, Gray KM, Rinehart NJ, Tonge BJ, Lambert TJ, Hickie IB (Apr 2010). "Intranasal oxytocin improves emotion recognition for youth with autism spectrum disorders". Biological Psychiatry. 67 (7): 692–4. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.09.020. PMID 19897177.
- ^ Wermter AK, Kamp-Becker I, Hesse P, Schulte-Körne G, Strauch K, Remschmidt H (Mar 2010). "Evidence for the involvement of genetic variation in the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) in the etiology of autistic disorders on high-functioning level". American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics. 153B (2): 629–39. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.31032. PMID 19777562.
- ^ Andari E, Duhamel JR, Zalla T, Herbrecht E, Leboyer M, Sirigu A (Mar 2010). "Promoting social behavior with oxytocin in high-functioning autism spectrum disorders". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 107 (9): 4389–94. doi:10.1073/pnas.0910249107. PMC 2840168. PMID 20160081.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|laysource=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysummary=ignored (help) - ^ Gordon I, Vander Wyk BC, Bennett RH, Cordeaux C, Lucas MV, Eilbott JA, Zagoory-Sharon O, Leckman JF, Feldman R, Pelphrey KA (Dec 2013). "Oxytocin enhances brain function in children with autism". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 110 (52): 20953–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.1312857110.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|laysource=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysummary=ignored (help) - ^ Kirsch P, Esslinger C, Chen Q, Mier D, Lis S, Siddhanti S, Gruppe H, Mattay VS, Gallhofer B, Meyer-Lindenberg A (Dec 2005). "Oxytocin modulates neural circuitry for social cognition and fear in humans". The Journal of Neuroscience. 25 (49): 11489–93. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3984-05.2005. PMID 16339042.
- ^ Huber D, Veinante P, Stoop R (Apr 2005). "Vasopressin and oxytocin excite distinct neuronal populations in the central amygdala". Science. 308 (5719): 245–8. doi:10.1126/SCIENCE.1105636. PMID 15821089.
- ^ Viviani D, Charlet A, van den Burg E, Robinet C, Hurni N, Abatis M, Magara F, Stoop R (Jul 2011). "Oxytocin selectively gates fear responses through distinct outputs from the central amygdala". Science. 333 (6038): 104–7. doi:10.1126/SCIENCE.1201043. PMID 21719680.
- ^ Shamay-Tsoory SG, Fischer M, Dvash J, Harari H, Perach-Bloom N, Levkovitz Y (Nov 2009). "Intranasal administration of oxytocin increases envy and schadenfreude (gloating)". Biological Psychiatry. 66 (9): 864–70. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.06.009. PMID 19640508.
- ^ a b Theodoridou A, Rowe AC, Penton-Voak IS, Rogers PJ (Jun 2009). "Oxytocin and social perception: oxytocin increases perceived facial trustworthiness and attractiveness". Hormones and Behavior. 56 (1): 128–32. doi:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2009.03.019. PMID 19344725.
- ^ a b Lane A, Luminet O, Rimé B, Gross JJ, de Timary P, Mikolajczak M (2013). "Oxytocin increases willingness to socially share one's emotions". International Journal of Psychology. 48 (4): 676–81. doi:10.1080/00207594.2012.677540. PMID 22554106.
- ^ a b Cardoso C, Ellenbogen MA, Serravalle L, Linnen AM (Nov 2013). "Stress-induced negative mood moderates the relation between oxytocin administration and trust: evidence for the tend-and-befriend response to stress?". Psychoneuroendocrinology. 38 (11): 2800–4. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.05.006. PMID 23768973.
- ^ Baumgartner T, Heinrichs M, Vonlanthen A, Fischbacher U, Fehr E (May 2008). "Oxytocin shapes the neural circuitry of trust and trust adaptation in humans". Neuron. 58 (4): 639–50. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2008.04.009. PMID 18498743.
- ^ Kosfeld M, Heinrichs M, Zak PJ, Fischbacher U, Fehr E (Jun 2005). "Oxytocin increases trust in humans". Nature. 435 (7042): 673–6. doi:10.1038/nature03701. PMID 15931222.
- ^ Tabak BA, McCullough ME, Carver CS, Pedersen EJ, Cuccaro ML (Jun 2014). "Variation in oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) polymorphisms is associated with emotional and behavioral reactions to betrayal". Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience. 9 (6): 810–6. doi:10.1093/scan/nst042. PMID 23547247.
- ^ Scheele D, Striepens N, Güntürkün O, Deutschländer S, Maier W, Kendrick KM, Hurlemann R (Nov 2012). "Oxytocin modulates social distance between males and females". The Journal of Neuroscience. 32 (46): 16074–9. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2755-12.2012. PMID 23152592.
- ^ Malik AI, Zai CC, Abu Z, Nowrouzi B, Beitchman JH (Jul 2012). "The role of oxytocin and oxytocin receptor gene variants in childhood-onset aggression". Genes, Brain, and Behavior. 11 (5): 545–51. doi:10.1111/j.1601-183X.2012.00776.x. PMID 22372486.
- ^ Zak PJ, Stanton AA, Ahmadi S (2007). Brosnan S (ed.). "Oxytocin increases generosity in humans". PLOS ONE. 2 (11): e1128. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0001128. PMC 2040517. PMID 17987115.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Conlisk J (2011). "Professor Zak's empirical studies on trust and oxytocin". J Econ Behav Organizat. 78 (1–2): 160–166. doi:10.1016/j.jebo.2011.01.002.
- ^ a b Hurlemann R, Patin A, Onur OA, Cohen MX, Baumgartner T, Metzler S, Dziobek I, Gallinat J, Wagner M, Maier W, Kendrick KM (Apr 2010). "Oxytocin enhances amygdala-dependent, socially reinforced learning and emotional empathy in humans". The Journal of Neuroscience. 30 (14): 4999–5007. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5538-09.2010. PMID 20371820.
- ^ Domes G, Heinrichs M, Michel A, Berger C, Herpertz SC (Mar 2007). "Oxytocin improves "mind-reading" in humans". Biological Psychiatry. 61 (6): 731–3. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.07.015. PMID 17137561.
- ^ Guastella AJ, Mitchell PB, Dadds MR (Jan 2008). "Oxytocin increases gaze to the eye region of human faces". Biological Psychiatry. 63 (1): 3–5. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.06.026. PMID 17888410.
- ^ Singer T, Snozzi R, Bird G, Petrovic P, Silani G, Heinrichs M, Dolan RJ (Dec 2008). "Effects of oxytocin and prosocial behavior on brain responses to direct and vicariously experienced pain". Emotion. 8 (6): 781–91. doi:10.1037/a0014195. PMC 2672051. PMID 19102589.
- ^ a b Gimpl G, Fahrenholz F (Apr 2001). "The oxytocin receptor system: structure, function, and regulation". Physiological Reviews. 81 (2): 629–83. PMID 11274341.
- ^ de Oliveira LF, Camboim C, Diehl F, Consiglio AR, Quillfeldt JA (Jan 2007). "Glucocorticoid-mediated effects of systemic oxytocin upon memory retrieval". Neurobiology of Learning and Memory. 87 (1): 67–71. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2006.05.006. PMID 16997585.
- ^ Guastella AJ, Mitchell PB, Mathews F (Aug 2008). "Oxytocin enhances the encoding of positive social memories in humans". Biological Psychiatry. 64 (3): 256–8. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.02.008. PMID 18343353.
- ^ Rimmele U, Hediger K, Heinrichs M, Klaver P (Jan 2009). "Oxytocin makes a face in memory familiar". The Journal of Neuroscience. 29 (1): 38–42. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4260-08.2009. PMID 19129382.
- ^ Unkelbach C, Guastella AJ, Forgas JP (Nov 2008). "Oxytocin selectively facilitates recognition of positive sex and relationship words". Psychological Science. 19 (11): 1092–4. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02206.x. PMID 19076479.
- ^ Marsh AA, Yu HH, Pine DS, Blair RJ (Apr 2010). "Oxytocin improves specific recognition of positive facial expressions". Psychopharmacology. 209 (3): 225–32. doi:10.1007/s00213-010-1780-4. PMID 20186397.
- ^ a b Fischer-Shofty M, Shamay-Tsoory SG, Harari H, Levkovitz Y (Jan 2010). "The effect of intranasal administration of oxytocin on fear recognition". Neuropsychologia. 48 (1): 179–84. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2009.09.003. PMID 19747930.
- ^ a b c Carmichael MS, Humbert R, Dixen J, Palmisano G, Greenleaf W, Davidson JM (Jan 1987). "Plasma oxytocin increases in the human sexual response". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 64 (1): 27–31. doi:10.1210/jcem-64-1-27. PMID 3782434.
- ^ Carmichael MS, Warburton VL, Dixen J, Davidson JM (Feb 1994). "Relationships among cardiovascular, muscular, and oxytocin responses during human sexual activity". Archives of Sexual Behavior. 23 (1): 59–79. doi:10.1007/BF01541618. PMID 8135652.
- ^ Blaicher W, Gruber D, Bieglmayer C, Blaicher AM, Knogler W, Huber JC (1999). "The role of oxytocin in relation to female sexual arousal". Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation. 47 (2): 125–6. doi:10.1159/000010075. PMID 9949283.
- ^ Anderson-Hunt M, Dennerstein L (1995). "Oxytocin and female sexuality". Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation. 40 (4): 217–21. doi:10.1159/000292340. PMID 8586300.
- ^ Murphy MR, Seckl JR, Burton S, Checkley SA, Lightman SL (Oct 1987). "Changes in oxytocin and vasopressin secretion during sexual activity in men". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 65 (4): 738–41. doi:10.1210/jcem-65-4-738. PMID 3654918.
- ^ Krüger TH, Haake P, Chereath D, Knapp W, Janssen OE, Exton MS, Schedlowski M, Hartmann U (Apr 2003). "Specificity of the neuroendocrine response to orgasm during sexual arousal in men". The Journal of Endocrinology. 177 (1): 57–64. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1770057. PMID 12697037.
- ^ Vacek M, High on Fidelity. What can voles teach us about monogamy?
- ^ Kuchinskas Susan, The Chemistry of Connection: How the Oxytocin Response Can Help You Find Trust, Intimacy, and Love p65
- ^ van Leengoed E, Kerker E, Swanson HH (Feb 1987). "Inhibition of post-partum maternal behaviour in the rat by injecting an oxytocin antagonist into the cerebral ventricles". The Journal of Endocrinology. 112 (2): 275–82. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1120275. PMID 3819639.
- ^ Kendrick KM (2004-01-01). "The Neurobiology of Social Bonds". British Society for Neuroendocrinology. Retrieved 2009-04-13.
- ^ Bick J, Dozier M (Jan 2010). "Mothers' and Children's Concentrations of Oxytocin Following Close, Physical Interactions with Biological and Non-biological Children". Developmental Psychobiology. 52 (1): 100–107. doi:10.1002/dev.20411. PMC 2953948. PMID 20953313.
- ^ Kovács GL, Sarnyai Z, Szabó G (Nov 1998). "Oxytocin and addiction: a review". Psychoneuroendocrinology. 23 (8): 945–62. doi:10.1016/S0306-4530(98)00064-X. PMID 9924746.
- ^ Thompson MR, Callaghan PD, Hunt GE, Cornish JL, McGregor IS (May 2007). "A role for oxytocin and 5-HT(1A) receptors in the prosocial effects of 3,4 methylenedioxymethamphetamine ("ecstasy")". Neuroscience. 146 (2): 509–14. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.02.032. PMID 17383105.
- ^ Uvnäs-Moberg K, Hillegaart V, Alster P, Ahlenius S (1996). "Effects of 5-HT agonists, selective for different receptor subtypes, on oxytocin, CCK, gastrin and somatostatin plasma levels in the rat". Neuropharmacology. 35 (11): 1635–40. doi:10.1016/S0028-3908(96)00078-0. PMID 9025112.
- ^ Chiodera P, Volpi R, Capretti L, Caffarri G, Magotti MG, Coiro V (Apr 1996). "Different effects of the serotonergic agonists buspirone and sumatriptan on the posterior pituitary hormonal responses to hypoglycemia in humans". Neuropeptides. 30 (2): 187–92. doi:10.1016/S0143-4179(96)90086-4. PMID 8771561.
- ^ Tyzio R, Cossart R, Khalilov I, Minlebaev M, Hübner CA, Represa A, Ben-Ari Y, Khazipov R (Dec 2006). "Maternal oxytocin triggers a transient inhibitory switch in GABA signaling in the fetal brain during delivery". Science. 314 (5806): 1788–92. doi:10.1126/science.1133212. PMID 17170309.
- ^ Atasoy D, Betley JN, Su HH, Sternson SM (Aug 2012). "Deconstruction of a neural circuit for hunger". Nature. 488 (7410): 172–7. doi:10.1038/nature11270. PMID 22801496.
- ^ Shalvi S, De Dreu CK (Apr 2014). "Oxytocin promotes group-serving dishonesty". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 111 (15): 5503–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.1400724111. PMID 24706799.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|laydate=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysource=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|layurl=ignored (help) - ^ Sheng F, Liu Y, Zhou B, Zhou W, Han S (2013). "Oxytocin modulates the racial bias in neural responses to others' suffering". Biol Psychol. 92 (2): 380–6. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2012.11.018. PMID 23246533.
- ^ Shalvi S, De Dreu CK (Apr 2014). "Oxytocin promotes group-serving dishonesty". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 111 (15): 5503–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.1400724111. PMID 24706799.
- ^ De Dreu CK, Shalvi S, Greer LL, Van Kleef GA, Handgraaf MJ (2012). "Oxytocin motivates non-cooperation in intergroup conflict to protect vulnerable in-group members". PLOS ONE. 7 (11): e46751. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046751. PMC 3492361. PMID 23144787.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Stallen M, De Dreu CK, Shalvi S, Smidts A, Sanfey AG (2012). "The herding hormone: oxytocin stimulates in-group conformity". Psychological Science. 23 (11): 1288–92. doi:10.1177/0956797612446026. PMID 22991128.
- ^ Ma X, Luo L, Geng Y, Zhao W, Zhang Q, Kendrick KM (2014). "Oxytocin increases liking for a country's people and national flag but not for other cultural symbols or consumer products". Front Behav Neurosci. 8: 266. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00266. PMC 4122242. PMID 25140135.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Grillon C, Krimsky M, Charney DR, Vytal K, Ernst M, Cornwell B (Sep 2013). "Oxytocin increases anxiety to unpredictable threat". Molecular Psychiatry. 18 (9): 958–60. doi:10.1038/mp.2012.156. PMC 3930442. PMID 23147382.
- ^ a b Guzmán YF, Tronson NC, Jovasevic V, Sato K, Guedea AL, Mizukami H, Nishimori K, Radulovic J (Sep 2013). "Fear-enhancing effects of septal oxytocin receptors". Nature Neuroscience. 16 (9): 1185–7. doi:10.1038/nn.3465. PMC 3758455. PMID 23872596.
- ^ a b c Theodoridou A, Penton-Voak IS, Rowe AC (2013). "A direct examination of the effect of intranasal administration of oxytocin on approach-avoidance motor responses to emotional stimuli". PLOS ONE. 8 (2): e58113. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058113. PMC 3585234. PMID 23469148.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Lischke A, Gamer M, Berger C, Grossmann A, Hauenstein K, Heinrichs M, Herpertz SC, Domes G (September 2012). "Oxytocin increases amygdala reactivity to threatening scenes in females". Psychoneuroendocrinology. 37 (9): 1431–8. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.01.011. PMID 22365820.
- ^ Okabe S, Kitano K, Nagasawa M, Mogi K, Kikusui T (June 2013). "Testosterone inhibits facilitating effects of parenting experience on parental behavior and the oxytocin neural system in mice". Physiology & Behavior. 118: 159–64. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2013.05.017. PMID 23685236.
- ^ Hurlemann R, Patin A, Onur OA, Cohen MX, Baumgartner T, Metzler S, Dziobek I, Gallinat J, Wagner M, Maier W, Kendrick KM (April 2010). "Oxytocin enhances amygdala-dependent, socially reinforced learning and emotional empathy in humans". The Journal of Neuroscience. 30 (14): 4999–5007. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5538-09.2010. PMID 20371820.
- ^ a b c Matsuzaki M, Matsushita H, Tomizawa K, Matsui H (Nov 2012). "Oxytocin: a therapeutic target for mental disorders". The Journal of Physiological Sciences. 62 (6): 441–4. doi:10.1007/s12576-012-0232-9. PMID 23007624.
- ^ McQuaid RJ, McInnis OA, Abizaid A, Anisman H (Sep 2014). "Making room for oxytocin in understanding depression". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews. 45: 305–22. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.07.005. PMID 25025656.
- ^ a b Acevedo-Rodriguez A, Mani SK, Handa RJ (2015). "Oxytocin and Estrogen Receptor β in the Brain: An Overview". Frontiers in Endocrinology. 6: 160. doi:10.3389/fendo.2015.00160. PMID 26528239.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Shalev, Idan; Ebstein, Richard Paul (11 February 2015). Social Hormones and Human Behavior: What Do We Know and Where Do We Go from Here. Frontiers Media SA. pp. 51–. ISBN 978-2-88919-407-0.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Hicks C, Ramos L, Reekie T, Misagh GH, Narlawar R, Kassiou M, McGregor IS (Jun 2014). "Body temperature and cardiac changes induced by peripherally administered oxytocin, vasopressin and the non-peptide oxytocin receptor agonist WAY 267,464: a biotelemetry study in rats". British Journal of Pharmacology. 171 (11): 2868–87. doi:10.1111/bph.12613. PMID 24641248.
- ^ Manning M, Misicka A, Olma A, Bankowski K, Stoev S, Chini B, Durroux T, Mouillac B, Corbani M, Guillon G (Apr 2012). "Oxytocin and vasopressin agonists and antagonists as research tools and potential therapeutics". Journal of Neuroendocrinology. 24 (4): 609–28. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2826.2012.02303.x. PMID 22375852.
- ^ Budden A, Chen LJ, Henry A (Oct 9, 2014). "High-dose versus low-dose oxytocin infusion regimens for induction of labour at term". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 10: CD009701. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009701.pub2. PMID 25300173.
- ^ a b c "Pitocin (drug label for professionals)". Rx List. WebMD. Retrieved 2010-09-09.
- ^ a b Baribeau, Danielle A.; Anagnostou, Evdokia (2015). "Oxytocin and vasopressin: linking pituitary neuropeptides and their receptors to social neurocircuits". Frontiers in Neuroscience. 9. doi:10.3389/fnins.2015.00335. ISSN 1662-453X.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2009). "Chapter 7: Neuropeptides". In Sydor A, Brown RY (eds.). Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical. p. 195. ISBN 9780071481274.
Oxytocin can be delivered to humans via nasal spray following which it crosses the blood–brain barrier. ... In a double-blind experiment, oxytocin spray increased trusting behavior compared to a placebo spray in a monetary game with real money at stake.
- ^ McGregor IS, Callaghan PD, Hunt GE (May 2008). "From ultrasocial to antisocial: a role for oxytocin in the acute reinforcing effects and long-term adverse consequences of drug use?". British Journal of Pharmacology. 154 (2): 358–68. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.132. PMC 2442436. PMID 18475254.
Recent studies also highlight remarkable anxiolytic and prosocial effects of intranasally administered OT in humans, including increased 'trust', decreased amygdala activation towards fear-inducing stimuli, improved recognition of social cues and increased gaze directed towards the eye regions of others (Kirsch et al., 2005; Kosfeld et al., 2005; Domes et al., 2006; Guastella et al., 2008).
- ^ Lee AG, Cool DR, Grunwald WC, Neal DE, Buckmaster CL, Cheng MY, Hyde SA, Lyons DM, Parker KJ (Aug 2011). "A novel form of oxytocin in New World monkeys". Biology Letters. 7 (4): 584–7. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2011.0107. PMC 3130245. PMID 21411453.
- ^ du Vigneaud V. (1960). "Experiences in the Polypeptide Field: Insulin to Oxytocin". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 88 (3): 537–48. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1960.tb20052.x.
- ^ Kukucka MA (1993-04-18). "Mechanisms by which hypoxia augments Leydig cell viability and differentiated cell function in vitro". Digital Library and Archives. Retrieved 2010-02-21.
- ^ Sausville E, Carney D, Battey J (Aug 1985). "The human vasopressin gene is linked to the oxytocin gene and is selectively expressed in a cultured lung cancer cell line". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 260 (18): 10236–41. PMID 2991279.
- ^ Repaske DR, Phillips JA, Kirby LT, Tze WJ, D'Ercole AJ, Battey J (Mar 1990). "Molecular analysis of autosomal dominant neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 70 (3): 752–7. doi:10.1210/jcem-70-3-752. PMID 1968469.
- ^ Summar ML, Phillips JA, Battey J, Castiglione CM, Kidd KK, Maness KJ, Weiffenbach B, Gravius TC (Jun 1990). "Linkage relationships of human arginine vasopressin-neurophysin-II and oxytocin-neurophysin-I to prodynorphin and other loci on chromosome 20". Molecular Endocrinology. 4 (6): 947–50. doi:10.1210/mend-4-6-947. PMID 1978246.
- ^ Brownstein MJ, Russell JT, Gainer H (Jan 1980). "Synthesis, transport, and release of posterior pituitary hormones". Science. 207 (4429): 373–8. doi:10.1126/science.6153132. PMID 6153132.
- ^ Sheldrick EL, Flint AP (Jul 1989). "Post-translational processing of oxytocin-neurophysin prohormone in the ovine corpus luteum: activity of peptidyl glycine alpha-amidating mono-oxygenase and concentrations of its cofactor, ascorbic acid". The Journal of Endocrinology. 122 (1): 313–22. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1220313. PMID 2769155.
- ^ Luck MR, Jungclas B (Sep 1987). "Catecholamines and ascorbic acid as stimulators of bovine ovarian oxytocin secretion". The Journal of Endocrinology. 114 (3): 423–30. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1140423. PMID 3668432.
- ^ Hornig D (Sep 1975). "Distribution of ascorbic acid, metabolites and analogues in man and animals". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 258: 103–18. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29271.x. PMID 1106295.
- ^ a b Tsujimoto M, Hattori A (2005). "The oxytocinase subfamily of M1 aminopeptidases". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1751 (1): 9–18. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2004.09.011. PMID 16054015.
- ^ Nomura S, Ito T, Yamamoto E, Sumigama S, Iwase A, Okada M, Shibata K, Ando H, Ino K, Kikkawa F, Mizutani S (2005). "Gene regulation and physiological function of placental leucine aminopeptidase/oxytocinase during pregnancy". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1751 (1): 19–25. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2005.04.006. PMID 15894523.
- ^ a b Mizutani S, Yokosawa H, Tomoda Y (1992). "Degradation of oxytocin by the human placenta: effect of selective inhibitors". Acta Endocrinol. 127 (1): 76–80. doi:10.1530/acta.0.1270076. PMID 1355623.
- ^ Meisenberg G, Simmons WH (1984). "Amastatin potentiates the behavioral effects of vasopressin and oxytocin in mice". Peptides. 5 (3): 535–9. doi:10.1016/0196-9781(84)90083-4. PMID 6540873.
- ^ Stancampiano R, Melis MR, Argiolas A (1991). "Proteolytic conversion of oxytocin by brain synaptic membranes: role of aminopeptidases and endopeptidases". Peptides. 12 (5): 1119–25. doi:10.1016/0196-9781(91)90068-z. PMID 1800950.
- ^ Itoh C, Watanabe M, Nagamatsu A, Soeda S, Kawarabayashi T, Shimeno H (1997). "Two molecular species of oxytocinase (L-cystine aminopeptidase) in human placenta: purification and characterization". Biol. Pharm. Bull. 20 (1): 20–4. doi:10.1248/bpb.20.20. PMID 9013800.
- ^ Landgraf R, Neumann ID (2004). "Vasopressin and oxytocin release within the brain: a dynamic concept of multiple and variable modes of neuropeptide communication". Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology. 25 (3–4): 150–76. doi:10.1016/j.yfrne.2004.05.001. PMID 15589267.
- ^ Wathes DC, Swann RW (May 1982). "Is oxytocin an ovarian hormone?". Nature. 297 (5863): 225–7. doi:10.1038/297225a0. PMID 7078636.
- ^ Wathes DC, Swann RW, Pickering BT, Porter DG, Hull MG, Drife JO (Aug 1982). "Neurohypophysial hormones in the human ovary". Lancet. 2 (8295): 410–2. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(82)90441-X. PMID 6124806.
- ^ Fields PA, Eldridge RK, Fuchs AR, Roberts RF, Fields MJ (Apr 1983). "Human placental and bovine corpora luteal oxytocin". Endocrinology. 112 (4): 1544–6. doi:10.1210/endo-112-4-1544. PMID 6832059.
- ^ Guldenaar SE, Pickering BT (1985). "Immunocytochemical evidence for the presence of oxytocin in rat testis". Cell and Tissue Research. 240 (2): 485–7. doi:10.1007/BF00222364. PMID 3995564.
- ^ Gauquelin G, Geelen G, Louis F, Allevard AM, Meunier C, Cuisinaud G, Benjanet S, Seidah NG, Chretien M, Legros JJ (1983). "Presence of vasopressin, oxytocin and neurophysin in the retina of mammals, effect of light and darkness, comparison with the neuropeptide content of the neurohypophysis and the pineal gland". Peptides. 4 (4): 509–15. doi:10.1016/0196-9781(83)90056-6. PMID 6647119.
- ^ Ang VT, Jenkins JS (Apr 1984). "Neurohypophysial hormones in the adrenal medulla". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 58 (4): 688–91. doi:10.1210/jcem-58-4-688. PMID 6699132.
- ^ Geenen V, Legros JJ, Franchimont P, Baudrihaye M, Defresne MP, Boniver J (Apr 1986). "The neuroendocrine thymus: coexistence of oxytocin and neurophysin in the human thymus". Science. 232 (4749): 508–11. doi:10.1126/science.3961493. PMID 3961493.
- ^ Amico JA, Finn FM, Haldar J (Nov 1988). "Oxytocin and vasopressin are present in human and rat pancreas". The American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 296 (5): 303–7. doi:10.1097/00000441-198811000-00003. PMID 3195625.
- ^ Kukucka MA, Misra HP (1992). "HPLC determination of an oxytocin-like peptide produced by isolated guinea pig Leydig cells: stimulation by ascorbate". Archives of Andrology. 29 (2): 185–90. doi:10.3109/01485019208987723. PMID 1456839.
- ^ Goldstein, Irwin; Meston, Cindy M.; Davis, Susan; Traish, Abdulmaged (17 November 2005). Women's Sexual Function and Dysfunction: Study, Diagnosis and Treatment. CRC Press. pp. 205–. ISBN 978-1-84214-263-9.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Venkatesh B, Si-Hoe SL, Murphy D, Brenner S (Nov 1997). "Transgenic rats reveal functional conservation of regulatory controls between the Fugu isotocin and rat oxytocin genes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 94 (23): 12462–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.23.12462. PMC 25001. PMID 9356472.
- ^ Dale HH (May 1906). "On some physiological actions of ergot". The Journal of Physiology. 34 (3): 163–206. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.1906.sp001148. PMC 1465771. PMID 16992821.
- ^ Ott, I; Scott, JC (1910). "The Action of Infundibulum upon Mammary Secretion". Proc Soc Exp Biol. 8: 48–49.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Schafer EA, Mackenzie K (July 1911). "The Action of Animal Extracts on Milk Secretion". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 84 (568): 16–22. doi:10.1098/rspb.1911.0042.
- ^ Du Vigneaud V, Ressler C, Trippett S (Dec 1953). "The sequence of amino acids in oxytocin, with a proposal for the structure of oxytocin". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 205 (2): 949–57. PMID 13129273.
- ^ du Vigneaud V, Ressler C, Swan JM, Roberts CW, Katsoyannis PG, Gordon S (1953). "The synthesis of an octapeptide amide with the hormonal activity of oxytocin". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 75 (19): 4879–80. doi:10.1021/ja01115a553.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ du Vigneaud V, Ressler C, Swan JM, Roberts CW, Katsoyannis PG (June 1954). "The synthesis of oxytocin". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 76 (12): 3115–3121. doi:10.1021/ja01641a004.
- ^ du Vigneaud V, Ressler C, Swan JM, Roberts CW, Katsoyannis PG (1954). "The Synthesis of Oxytocin1". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 76 (12): 3115–21. doi:10.1021/ja01641a004.
- ^ Du Vigneaud V (Jun 1956). "Trail of sulfur research: from insulin to oxytocin". Science. 123 (3205): 967–74. doi:10.1126/science.123.3205.967. PMID 13324123.
- ^ Fewtrell MS, Loh KL, Blake A, Ridout DA, Hawdon J (May 2006). "Randomised, double blind trial of oxytocin nasal spray in mothers expressing breast milk for preterm infants". Archives of Disease in Childhood: Fetal and Neonatal Edition. 91 (3): F169-74. doi:10.1136/adc.2005.081265. PMC 2672698. PMID 16223754.
- ^ Petrovic P, Kalisch R, Singer T, Dolan RJ (Jun 2008). "Oxytocin attenuates affective evaluations of conditioned faces and amygdala activity". The Journal of Neuroscience. 28 (26): 6607–15. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4572-07.2008. PMC 2647078. PMID 18579733.
- ^ "To sniff at danger – Mind Matters". Health And Fitness. Boston Globe. 2006-01-12. Retrieved 2009-04-13.
- ^ Dando M (Aug 2009). "Biologists napping while work militarized". Nature. 460 (7258): 950–1. doi:10.1038/460950a. PMID 19693065.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|laysource=ignored (help); Unknown parameter|laysummary=ignored (help) - ^ Smith, D. Clashing couples to get a spray of love. Sydney Morning Herald May 26, 2007.
- ^ Retrophin (December 2013). "Retrophin Signs U.S. License Agreement for Syntocinon™ Nasal Spray (Oxytocin)".
- ^ Retrophin. "Retrophin – Pipeline". Retrieved 2014-10-24.
- ^ Retrophin (October 2014). "Retrophin Announces Divestment of Non-Core Assets to Turing Pharmaceuticals".
Further reading
- Caldwell HK, Young WS (2006). "Oxytocin and Vasopressin: Genetics and Behavioral Implications". In Abel L, Lim R (eds.). Handbook of neurochemistry and molecular neurobiology (PDF). Berlin: Springer. pp. 573–607. ISBN 0-387-30348-0.
- Lee HJ, Macbeth AH, Pagani JH, Young WS (Jun 2009). "Oxytocin: the great facilitator of life". Progress in Neurobiology. 88 (2): 127–51. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.04.001. PMC 2689929. PMID 19482229.
- Yong, Ed (13 November 2015), "The weak science behind the wrongly named moral molecule", The Atlantic.
