Sodium metaborate
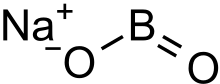
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.028.992 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| NaBO2 | |
| Molar mass | 65.80 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless crystals |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.46 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 966 °C (1,771 °F; 1,239 K) |
| Boiling point | 1,434 °C (2,613 °F; 1,707 K) |
| 16.4 g/100 mL (0 °C) 28.2 g/100 mL (25 °C) 125.2 g/100 mL (100 °C) | |
| Solubility | insoluble in ether, ethanol |
| Structure | |
| trigonal | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
65.94 J/mol K |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
73.39 J/mol K |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-1059 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
2330 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sodium metaborate (NaBO2) is a colorless solid chemical compound. [1]
Preparation
Sodium metaborate is prepared by the fusion of sodium carbonate and borax. Another way to create the compound is by the fusion of sodium tetraborate with sodium hydroxide at 700° C.
Uses
Sodium metaborate is used in the manufacturing of borosilicate glasses. It is also a component of herbicides and antifreeze.
