Renton Municipal Airport
Renton Municipal Airport | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Airport during a runway resurfacing project, August 2009 | |||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||
| Owner | City of Renton | ||||||||||
| Serves | Renton, Washington | ||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 32 ft / 10 m | ||||||||||
| Coordinates | 47°29′35″N 122°12′57″W / 47.49306°N 122.21583°W | ||||||||||
| Website | Official website | ||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||
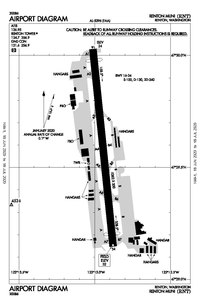 FAA airport diagram | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Statistics | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Renton Municipal Airport (IATA: RNT, ICAO: KRNT, FAA LID: RNT) is a public use airport located in Renton, a city in King County, Washington, United States.[1] The airport was renamed Clayton Scott Field in 2005 to celebrate the 100th birthday of Clayton Scott.[2] The airport's northern boundary is Lake Washington and the Will Rogers–Wiley Post Memorial Seaplane Base. Renton Airport has a floating dock and a launching ramp for conversion from wheeled landings to water takeoffs and landings.

The airport is owned by the City of Renton and is a general aviation airport which serves Renton and other nearby communities. It provides regional aviation services for air charter, air taxi, corporate, business and recreational flyers. It is included in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2017–2021, in which it is categorized as a regional reliever facility.[3]
The airport is located approximately 12 miles southeast of downtown Seattle near the south end of Lake Washington. US Customs service is available for both floatplane and wheeled aircraft arriving by water or by land.[4]
Renton Airport is adjacent to the Boeing Renton Factory that manufactures 737s and formerly 757s, and is the initial point of departure for airplanes produced in that facility.[5]

Facilities and aircraft
[edit]Renton Municipal Airport covers an area of 170 acres (69 ha) at an elevation of 32 feet (9.8 m) above mean sea level. It has one runway designated 16/34 with an asphalt and concrete surface measuring 5,382 by 200 feet (1,640 m × 61 m).[1] The runway was resurfaced and realigned in August 2009; prior to this time, it was designated 15/33.[6]
In 2016, the airport had 122,908 aircraft operations, an average of 337 per day: 98% general aviation, 1% air taxi, <1% scheduled commercial, and <1% military. In July 2017, there were 337 aircraft based at this airport: 243 single-engine, 13 multi-engine, 4 jet, and 8 helicopter.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d FAA Airport Form 5010 for RNT PDF. Federal Aviation Administration. effective May 23, 2019. Retrieved June 1, 2019
- ^ Wallace, James (September 29, 2006). "Clayton Scott, 1905–2006: Longtime aviator, Bill Boeing's personal pilot". Seattle Post-Intelligencer. Retrieved June 1, 2019.
- ^ "Appendix A: List of NPIAS Airports with 5-Year Forecast Activity and Development Estimate" (PDF). National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems. Federal Aviation Administration. October 3, 2018. Retrieved June 1, 2019 – via www.faa.gov.
- ^ "Renton Municipal Airport, Clayton Scott Field". City of Renton. Archived from the original on June 10, 2017. Retrieved January 4, 2016.
- ^ Gates, Dominic (September 6, 2018). "737 problems have grown in Renton despite Boeing's reassurances". The Seattle Times. Retrieved June 1, 2019.
- ^ Radford, Dean (July 30, 2009). "Runway repaving to ground most flights at Renton Municipal Airport". Renton Reporter. Retrieved June 1, 2019.
External links
[edit]- Official website

- Boeing Employees Flying Association
- KRNT listing at FlightCentral.Net
- Aerial image as of July 1990[permanent dead link] from USGS The National Map
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective October 31, 2024
- FAA Terminal Procedures for RNT, effective October 31, 2024
- FAA Airport Form 5010 for RNT PDF
- Resources for this airport:
- FAA airport information for RNT
- AirNav airport information for KRNT
- ASN accident history for RNT
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS weather observations: current, past three days
- SkyVector aeronautical chart, Terminal Procedures


