Bulldozer (microarchitecture)
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Launched | late 2011 |
| Discontinued | present |
| Common manufacturer | |
| Architecture and classification | |
| Technology node | 32 nm |
| Instruction set | x86-64 |
| Physical specifications | |
| Socket | |
| Products, models, variants | |
| Core names | |
| History | |
| Predecessor | Family 10h (K10) |
| Successor | Piledriver - Family 15h (2nd-gen) |
The AMD Bulldozer Family 15h is a microprocessor microarchitecture for the FX and Opteron line of processors, developed by AMD for the desktop and server markets.[1][2] Bulldozer is the codename for this family of microarchitectures. It was released on October 12, 2011 as the successor to the K10 microarchitecture.
Bulldozer is designed from scratch, not a development of earlier processors.[3] The core is specifically aimed at computing products with TDPs of 10 to 125 watts. AMD claims dramatic performance-per-watt efficiency improvements in high-performance computing (HPC) applications with Bulldozer cores.
The Bulldozer cores support most of the instruction sets implemented by Intel processors available at its introduction (including SSE4.1, SSE4.2, AES, CLMUL, and AVX) as well as new instruction sets proposed by AMD; ABM, XOP, FMA4 and F16C.[4][5]
Overview
According to AMD, Bulldozer-based CPUs are based on GlobalFoundries' 32 nm Silicon on insulator (SOI) process technology and reuses the approach of DEC for multitasking computer performance with the arguments that it, according to press notes, "balances dedicated and shared computer resources to provide a highly compact, high units count design that is easily replicated on a chip for performance scaling."[6] In other words, by eliminating some of the "redundant" elements that naturally creep into multicore designs, AMD has hoped to take better advantage of its hardware capabilities, while using less power.
Bulldozer-based implementations built on 32nm SOI with HKMG arrived in October 2011 for both servers and desktops. The server segment included the dual chip (16-core) Opteron processor codenamed Interlagos (for Socket G34) and single chip (4, 6 or 8 cores) Valencia (for Socket C32), while the Zambezi (4, 6 and 8 cores) targeted desktops on Socket AM3+.[7][8]
Bulldozer is the first major redesign of AMD’s processor architecture since 2003, when the firm launched its K8 processors, and also features two 128-bit FMA-capable FPUs which can be combined into one 256-bit FPU. This design is accompanied by two integer clusters, each with 4 pipelines (the fetch/decode stage is shared). Bulldozer also introduced shared L2 cache in the new architecture. AMD calls this design a "Module". A 16-core processor design would feature eight of these "modules",[9] but the operating system will recognize each "module" as two logical cores.
The modular architecture consists of multithreaded shared L2 cache and FlexFPU, which uses simultaneous multithreading. Each physical integer core, two per module, is single threaded, in contrast with Intel's Hyperthreading, where two virtual simultaneous threads share the resources of a single physical core.[10]
Architecture
Bulldozer core

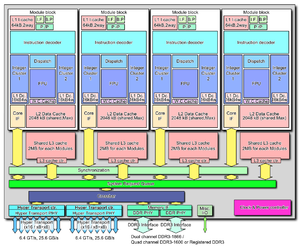
- With the Bulldozer family of processors, AMD re-introduced the "Clustered Integer Core" micro-architecture, an architecture developed by DEC in 1996 with the RISC microprocessor Alpha 21264. This technology is informally called CMT (Clustered Multi-Thread) and formally called "module" by AMD.
In terms of hardware complexity and functionality, the Bulldozer CMT module is equal to a dual-core processor in its integer power, and to either a single-core processor or a dual core its floating-point power, depending on whether the code is saturated in floating point instructions in both threads running on the same CMT module, and whether the FPU is performing 128-bit or 256-bit floating point operations. The reason for this is that for each two integer cores, there is a floating-point unit consisting of a pair of 128-bit FMAC execution units.
CMT is a simpler alternate design philosophy to SMT; both designs try to utilize execution units efficiently; in either method, when two threads compete for some execution pipelines, there is a loss in performance in one or more of the threads. Due to dedicated integer cores, the Bulldozer family modules performed roughly like a dual core dual thread processor during sections of code that were either wholly integer or a mix of integer and floating point; yet, due to the SMT use of the shared floating point pipelines, the module would perform similarly to a single core dual thread SMT processor (SMT2) for a pair of threads saturated with floating point instructions. (Both of these last two comparisons make the assumption that the comparison processor possesses and equally wide and capable execution core, integer-wise and floating-point wise, respectively.)
Both CMT and SMT are at peak effectiveness while running integer and floating point code on a pair of threads. CMT stays at peak effectiveness while working on a pair threads consisting both of integer code, while under SMT, one or both threads will underperform due to competition for integer execution units. The disadvantage for CMT is a greater number of idle integer execution units in a single threaded case. In the single threaded case, CMT is limited to use at most half of the integer execution units in its module, while SMT imposes no such limit. A large SMT core with integer circuitry as wide and fast as two CMT cores could in theory have momentarily up to twice an integer performance in a single thread case. (More realistically for general code as a whole, Pollack's Rule estimates a speedup factor of , or approximately 40% increase in performance.)
CMT processors and a typical SMT processor are similar in their efficient shared use of the L2 cache between a pair of threads.
- A module consists of a coupling of two "conventional" x86 out-of-order processing cores. The processing core shares the early pipeline stages (e.g. L1i, fetch, decode), the FPUs, and the L2 cache with the rest of the module.
- Each module has the following independent hardware resources:[11][12]
- 2 MB of L2 cache per module (shared between the two integer clusters in the core)
- 16 KB 4-way of L1d (way-predicted) per cluster and 2-way 64 KB of L1i per core, one way for each of the two cluster[13][14][15]
- Two dedicated integer clusters
- each one consists of two ALU and two AGU which are capable of a total of four independent arithmetic and memory operations per clock and per cluster
- duplicating integer schedulers and execution pipelines offers dedicated hardware to each of two threads which double performance for multi-threaded integer loads
- the second integer cluster increases the Bulldozer core die by around 12%, which at chip level adds about 5% of total die space[16] - Two symmetrical 128-bit FMAC (fused multiply–add capability) floating-point pipelines per module that can be unified into one large 256-bit-wide unit if one of the integer cores dispatches AVX instruction and two symmetrical x87/MMX/SSE capable FPPs for backward compatibility with SSE2 non-optimized software. Each FMAC unit also also capable of division and square root operations with variable latency.
- All modules present share the L3 cache as well as an Advanced Dual-Channel Memory Sub-System (IMC - Integrated Memory Controller).
- A module has 213 million transistors in an area of 30.9 mm² (including the 2 MB shared L2 cache) on an Orochi die.[17]
- The pipeline depth of Bulldozer (as well as Piledriver and Steamroller) is 18 cycles, compared to 12 cycles of the K10 core.
predecessor.[18] The longer pipeline allowed the Bulldozer family of processors to achieve a much higher clock frequency compared to its K10 predecessors. While this increased frequencies and throughput, the longer pipeline also increased latencies and increased branch misprediction penalties.
- The width of the Bulldozer integer core, four (2 ALU, 2 AGU), is somewhat less than the width of the K10 core, six (3 ALU, 3 AGU). Bobcat and Jaguar also used a four wide integer core, yet with lighter execution units: 1 ALU, 1 simple ALU, 1 load AGU, 1 store AGU.[19]
The issue widths (and peak instruction executions per cycle) of a Jaguar, K10, and Bulldozer core are 2, 3, and 4 respectively. This made Bulldozer a more superscalar design compared to Jaguar/Bobcat. However, due to K10's somewhat wider core (in addition to the lack of refinements and optimizations in a first generation design) the Bulldozer architecture typically performed with somewhat lower IPC compared to its K10 predecessors. It was not until the refinements made in Piledriver and Steamroller, that the IPC of the Bulldozer family distinctly began to exceed that of K10 processors such as Phenom II.
Instruction set extensions
- Support for Intel's Advanced Vector Extensions (AVX) instruction set, which supports 256-Bit floating point operations, and SSE4.1, SSE4.2, AES, CLMUL, as well as future 128-bit instruction sets proposed by AMD (XOP, FMA4 and F16C),[20] which have the same functionality as the SSE5 instruction set formerly proposed by AMD, but with compatibility to the AVX coding scheme.
Process technology and clock frequency
- 11-metal layer 32 nm SOI process with implemented first generation GlobalFoundries's High-K Metal Gate (HKMG)
- Turbo Core 2 performance boost to increase clock frequency up to 500 MHz with all threads active (for most workloads) and up to 1 GHz with the half of the thread active, within the TDP limit.[21]
- The chip operates at 0.775 to 1.425 V, achieving clock frequencies of 3.6 GHz or more[17]
- Min-Max TDP: 25 – 140 watts
Cache and memory interface
- Up to 8 MB of L3 shared among all cores on the same silicon die (8 MB for 4 cores in Desktop segment and 16 MB for 8 cores in the Server segment), divided into four subcaches of 2 MB each, capable of operating at 2.2 GHz at 1.1125 V[17]
- Native DDR3 memory support up to DDR3-1866[22]
- Dual Channel DDR3 integrated memory controller for Desktop and Server/Workstation Opteron 42xx "Valencia";[23] Quad Channel DDR3 Integrated Memory Controller[24] for Server/Workstation Opteron 62xx "Interlagos"
- AMD claims support for two DIMMs of DDR3-1600 per channel. Two DIMMs of DDR3-1866 on a single channel will be down-clocked to 1600.
I/O and socket interface
- HyperTransport Technology rev. 3.1 (3.20 GHz, 6.4 GT/s, 25.6 GB/s & 16-bit wide link) [first implemented into HY-D1 revision "Magny-Cours" on the socket G34 Opteron platform in March 2010 and "Lisbon" on the socket C32 Opteron platform in June 2010]
- Socket AM3+ (AM3r2)
- For the server segment, the existing socket G34 (LGA1974) and socket C32 (LGA1207) will be used.
Processors
The first revenue shipments of Bulldozer-based Opteron processors was announced on September 7, 2011.[28] The FX-4100, FX-6100, FX-8120 and FX-8150 were released in October 2011; with remaining FX series AMD processors released at the end of the first quarter of 2012.
Desktop
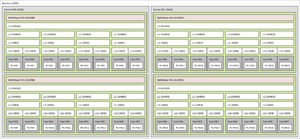
| Model | Modules | Frequency | Max. turbo | L2 cache | L3 cache | TDP | Memory | Turbo Core | Socket | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Half load | Full load | |||||||||
| FX-8150 | 4 | 3.6 GHz | 3.9 GHz | 4.2 GHz | 4 × 2 MB | 8 MB | 125 W | DDR3 1866 MHz |
Yes (2.0) | AM3+ |
| FX-8120 | 3.1 GHz | 3.4 GHz | 4.0 GHz | |||||||
| FX-8100 | 2.8 GHz | 3.1 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 95 W | ||||||
| FX-6200 | 3 | 3.8 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 4.1 GHz | 3 × 2 MB | 125 W | ||||
| FX-6120 | 3.5 GHz | 3.9 GHz | 4.1 GHz | 95 W | ||||||
| FX-6100 | 3.3 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 3.9 GHz | |||||||
| FX-4170 | 2 | 4.2 GHz | 4.3 GHz | 4.3 GHz | 2 x 2 MB | 125 W | ||||
| FX-4130 | 3.8 GHz | 3.9 GHz | 4.0 GHz | 4 MB | ||||||
| FX-4100 | 3.6 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 3.8 GHz | 8 MB | 95 W | |||||
Major Sources: CPU-World[29] and Xbit-Labs[30]
Server
There are two series of Bulldozer-based processors for servers: Opteron 4200 series (Socket C32, code named Valencia, with up to four modules) and Opteron 6200 series (Socket G34, code named Interlagos, with up to 8 modules).[31][32]
False advertising lawsuit
In November 2015, AMD was sued under the California Consumers Legal Remedies Act and Unfair Competition Law for allegedly misrepresenting the specifications of Bulldozer chips. The class-action lawsuit, filed on 26 October in the US District Court for the Northern District of California, claims that the Bulldozer CPU does not have eight cores as advertised, but were effectively quad-core chips due to their module count.[33]
Performance
Performance on Linux
On 24 October 2011, the first generation tests done by Phoronix confirmed that the performance of Bulldozer CPU is somewhat less than expected.[34] In many tests the CPU has performed on same level as older generation Phenom 1060T.
The performance later substantially increased, as various compiler optimizations and CPU driver fixes were released.[35][36]
Performance on Windows
The first Bulldozer CPUs were met with a mixed response. It was discovered that the FX-8150 performed poorly in benchmarks that were not highly threaded, falling behind the second-generation Intel Core i* series processors and being matched or even outperformed by AMD's own Phenom II X6 at lower clock speeds. In highly threaded benchmarks, the FX-8150 performed on par with the Phenom II X6, and the Intel Core i7 2600K, depending on the benchmark. Given the overall more consistent performance of the Intel Core i5 2500K at a lower price, these results left many reviewers underwhelmed. The processor was found to be extremely power-hungry under load, especially when overclocked, compared to Intel's Sandy Bridge.[37][38]
On 13 October 2011, AMD stated on its blog that "there are some in our community who feel the product performance did not meet their expectations", but showed benchmarks on actual applications where it outperformed the Sandy Bridge i7 2600k and AMD X6 1100T.[39]
In January 2012, Microsoft released two hotfixes for Windows 7 and Server 2008 R2 that marginally improve the performance of Bulldozer CPUs by addressing the thread scheduling concerns raised after the release of Bulldozer.[40][41][42]
On 6 March 2012, AMD posted a knowledge base article stating that there was a compatibility problem with FX processors, and certain games on the widely used digital game distribution platform, Steam. AMD stated that they had provided a BIOS update to several motherboard manufacturers (namely: Asus, Gigabyte Technology, MSI, and ASRock) that would fix the problem.[43]
In September 2014, AMD CEO Rory Read conceded the Bulldozer design had not been a "game-changing part", and that AMD had to live with the design for four years.[44]
In July 29, 2015 Microsoft released the Direct X 12 API (DX12) for its Windows 10 operating system. This API allows programmers to achieve greater parallelism, notably in graphics intensive game titles. DX12 titles make better use of the higher core counts and high thread count processor such as the Bulldozer family's FX-6300 and FX-8100 series chips, extending the usability of these systems under Windows 10.[45]
Overclocking
On 31 August 2011, AMD and a group of well-known overclockers including Brian McLachlan, Sami Mäkinen, Aaron Schradin, and Simon Solotko managed to set a new world record for CPU frequency using the unreleased and overclocked FX-8150 Bulldozer processor. Before that day, the record sat at 8.309 GHz, but the Bulldozer combined with liquid helium cooling reached a new high of 8.429 GHz. The record has since been overtaken at 8.58 GHz by Andre Yang using liquid nitrogen.[46][47] On August 22, 2014 and using an FX-8370 (Piledriver), The Stilt from Team Finland achieved a maximum CPU frequency of 8.722 GHz.[48]
Revisions
Piledriver is the AMD codename for its improved second-generation microarchitecture based on Bulldozer. AMD Piledriver cores are found in Socket FM2 Trinity and Richland based series of APUs and CPUs and the Socket AM3+ Vishera based FX-series of CPUs. Piledriver was the last generation in the Bulldozer family to be available for socket AM3+ and to be available with an L3 cache. The Piledriver processors available for FM2 (and its mobile variant) sockets did not come with a L3 cache, as the L2 cache is the last-level cache for all FM2/FM2+ processors.
Steamroller is the AMD codename for its third-generation microarchitecture based on an improved version of Piledriver. Steamroller cores are found in the Socket FM2+ Kaveri based series of APUs and CPUs.
On 12 October 2011, AMD revealed Excavator to be the codename for the fourth-generation Bulldozer core.[49] Excavator will initially be implemented in the 4th Generation A-series Fusion APU line in 2015. Reports indicated that this APU was codenamed Carrizo.[50] A new low latency L2 cache design derived from the Zen design project was used in the Excavator core, and typically, yet not always, improved performance, due the trade-off between low latency with smaller size (inclusive 1MB per module versus non-inclusive 2MB per module).
The last generation of mainstream processors in the Bulldozer family are codenamed Bristol Ridge (BR). These APUs revised the Carrizo design for socket compatibility with AM4 (or FP4), and included numerous improvements, notably in the areas of power efficiency and graphics. The use of DDR4 in BR allows for a more capable iGPU due to higher memory bandwidth over DDR3 systems. Socket compatibility with Zen AM4 CPUs and APUs allows for a smoother transition from the Bulldozer family of processors to the Zen family of processors. This move to a new generation of large-core and highly superscalar architecture was required by the competitive pressure from later generations of the large-core Intel Core series processors. The new Zen architecture's nearly twice as wide core (4 ALU, 2 AGU, and dedicated floating point circuitry consisting of two dual-issue 128-bit FMAC units) allows AMD to address the Bulldozer family's most urgent limitation of its relatively modest single-threaded IPC (and its competitive disadvantage in lightly threaded yet demanding workloads). In contrast to Bulldozer, the Zen design is wide-core and highly superscalar (12-wide: 6-wide integer, 4-wide FPUs, 2-wide AES), is SMT capable, and has a 4-wide pair of dual-issue FPUs per physical core; furthermore, it was designed to target a much newer 14 nm FinFET fabrication process.[51]
See also
- List of AMD CPU microarchitectures
- List of AMD FX microprocessors
- Alpha 21264
- K10 (microarchitecture)
- Bobcat (microarchitecture)
- Opteron
- Piledriver (microarchitecture)
- Steamroller (microarchitecture)
- Excavator (microarchitecture)
- Zen (microarchitecture)
References
- ^ "FX Processors". AMD. 24 February 2016. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ "AMD ships 16 core bulldozer powered Opteron 6200". Engadget. 14 November 2011. Retrieved 24 February 2016.
- ^ Bulldozer 50% Faster than Core i7 and Phenom II, techPowerUp, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ AMD64 Architecture Programmer’s Manual Volume 6: 128-Bit and 256-Bit XOP, and FMA4 Instructions (PDF), AMD, May 1, 2009, retrieved 2009-05-08
- ^ Striking a balance, Dave Christie, AMD Developer blogs, 7 May 2009, retrieved 2009-05-08
- ^ AMD Sets New Mark in x86 Innovation with First Detailed Disclosures of Two New Core Designs, AMD, August 24, 2011, p. 1, retrieved September 18, 2011
- ^ Analyst Day 2009 Summary, AMD, November 11, 2009, retrieved 2009-11-14
- ^ AMD bestätigt: "Zambezi" ist inkompatibel zum Sockel AM3, Planet3dnow.de, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ Analyst Day 2009 Presentations, AMD, November 11, 2009, retrieved 2009-11-14
- ^ http://cdn3.wccftech.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/AMD-Steamroller-vs-Bulldozer.jpg
- ^ Bulldozer microarchitecture block, AnandTech, August 24, 2010
- ^ Bulldozer module functional schematic, AMD, August 24, 2010
- ^ More On Bulldozer, Tomshardware.com, 2010-08-24, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ AMD Reveals Details About Bulldozer Microprocessors, AMD Reveals Details About Bulldozer Microprocessors, Xbitlabs.com, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ Real World Technologies (2010-08-26), AMD's Bulldozer Microarchitecture, Realworldtech.com, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ Bulldozer design power efficiency, AMD, August 24, 2010
- ^ a b c AP (PDF), retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ Jason Robert Carey Patterson, Modern Microprocessors A 90-Minute Guide!
- ^ Anand Lal Shimpi, AMD’s Jaguar Architecture: The CPU Powering Xbox One, PlayStation 4, Kabini & Temash
- ^ XOP and FMA4 Instruction set in SSE5, Techreport.com, 2009-05-06, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ AMD Financial Analyst Day 2010, Server Platforms Presentation, Ir.amd.com, 2010-11-09, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ AMD Roadmap, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ AMD (2012-05-14), AMD Opteron&TM; 4200 Series Processor Quick Reference Guide (PDF), www.amd.com, retrieved 2012-08-15
- ^ AMD (2012-05-14), AMD Opteron&TM; 6200 Series Processor Quick Reference Guide (PDF), www.amd.com, retrieved 2012-08-15
- ^ ASUS confirms AM3+ compatibility on AM3 boards, Event.asus.com, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ MSI confirms AM3+ compatibility on AM3 boards, Event.msi.com, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ AM3 processors will work in the AM3+ socket, but Bulldozer chips will not work in non-AM3+ motherboards Archived 2010-12-10 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ AMD Ships First "Bulldozer" Processors
- ^ AMD FX-Series processor families, Cpu-world.com, 2012-10-02, retrieved 2012-10-21
- ^ Shilov, Anton (2012-09-21). "AMD Sets the FX "Vishera" Launch Date". X-bit laboratories. X-bit labs. Retrieved 2012-09-23.
- ^ What Is Bulldozer?, 2010-08-02, archived from the original on August 6, 2010
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ AMD Opteron 6200 series microprocessor family, cpu-world.com
- ^ "AMD sued over allegedly misleading Bulldozer core count". Ars Technica. Retrieved 8 November 2015.
- ^ AMD FX-8150 Bulldozer On Ubuntu Linux, phoronix.com, 2011-10-24, retrieved 2012-12-13
- ^ AMD Bulldozer Cache Aliasing Issue Fix, phoronix.com
- ^ AMD's FX-8150 Bulldozer Benefits From New Compilers, Tuning, phoronix.com
- ^ Bulldozer Has Arrived: AMD FX-8150 Processor Review, X-bit labs, 2011-10-11, p. 13, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ Bulldozer Has Arrived: AMD FX-8150 Processor Review, X-bit labs, 2011-10-11, p. 14, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ Our Take on AMD FX, community.amd.com, 2013-11-14, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ An update is available for computers that have an AMD FX, AMD Opteron 4200, AMD Opteron 6200, or AMD Bulldozer series processor installed and that are running Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2, support.microsoft.com, January 2012, retrieved 2014-02-11
- ^ An update that selectively disables the Core Parking feature in Windows 7 or in Windows Server 2008 R2 is available, support.microsoft.com, January 2012, retrieved 2014-02-11
- ^ [1]
- ^ STEAM Games on AMD FX platforms, support.amd.com, 2012-06-12, retrieved 2012-10-11
- ^ AMD: next-generation microarchitecture will make up for muted Bulldozer reception (PC Gamer, Oct. 8, 2014)
- ^ Why DirectX 12 is a game-changer for PC enthusiasts, August 2, 2015
- ^ AMD Bulldozer CPU beats world record again achieving 8.461GHz, geek.com, 2011-11-01, retrieved 2012-10-16
- ^ AMD Bulldozer Speed Record Broken Again at 8.58GHz
- ^ Samuel D. "CPU-Z Validator 4.0". Retrieved 23 September 2014.
- ^ The Bulldozer Review: AMD FX-8150 Tested, AnandTech, 2011-10-12, retrieved 2012-01-23
- ^ New confirmed details on AMD's 2014 APU lineup, Kaveri delayed - VR-Zone
- ^ AMD Opens The Lid on Zen Architectural Details at Hot Chips
External links
- David Kanter (August 26, 2010), AMD's Bulldozer Microarchitecture, realworldtech.com, retrieved December 16, 2010
- Gabriel Torres (August 24, 2010), Inside the AMD Bulldozer Architecture, hardwaresecrets.com, retrieved December 16, 2010
- AMD Bulldozer CPU beats world record again achieving 8.461GHz, geek.com, 2011-11-01, retrieved 2012-10-16
- Why AMD's chip is so disappointing, extremetech.com, 2011-10-24, retrieved 2012-10-16
- Agner Fog (January 16, 2016), The microarchitecture of Intel, AMD and VIA CPUs (PDF), Technical University of Denmark, retrieved August 22, 2016

