From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Cinaciguat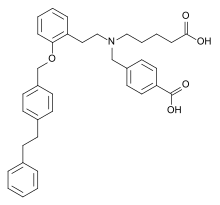 |
|
Routes of
administration | intravenous (?) |
|---|
| ATC code | |
|---|
|
4-({(4-carboxybutyl)[2-(2-{[4-(2-phenylethyl)
phenyl]methoxy}phenyl)ethyl]amino}methyl)
benzoic acid
|
| CAS Number | |
|---|
| PubChem CID | |
|---|
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
|---|
| ChemSpider | |
|---|
| UNII | |
|---|
| ChEBI | |
|---|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
|---|
|
| Formula | C36H39NO5 |
|---|
| Molar mass | 565.710 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
c4ccccc4CCc3ccc(cc3)COc1ccccc1CCN(CCCCC(O)=O)Cc2ccc(C(=O)O)cc2
|
InChI=1S/C36H39NO5/c38-35(39)12-6-7-24-37(26-30-19-21-33(22-20-30)36(40)41)25-23-32-10-4-5-11-34(32)42-27-31-17-15-29(16-18-31)14-13-28-8-2-1-3-9-28/h1-5,8-11,15-22H,6-7,12-14,23-27H2,(H,38,39)(H,40,41)  N NKey:WPYWMXNXEZFMAK-UHFFFAOYSA-N  N N
|
 N N Y (what is this?) (verify) Y (what is this?) (verify) |
Cinaciguat (BAY 58-2667) is an experimental drug for the treatment of acute decompensated heart failure.
Mechanism of action
Cinaciguat activates the soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) which is a receptor for nitric oxide. This increases biosynthesis of cyclic GMP, resulting in vasodilation.[1]
See also
- Riociguat, another drug stimulating sGC, but with a different mechanism
- PDE5 inhibitors act further downstream in the nitric oxide signalling pathway, reducing cyclic GMP degradation.
References
- ^ Schubert-Zsilavecz, M, Wurglics, M, Neue Arzneimittel 2009
|
|---|
| Forms | |
|---|
| Targets | |
|---|
NO donors
(prodrugs) | |
|---|
Enzyme
(inhibitors) | |
|---|
| Others |
- Indirect/downstream NO modulators: ACE inhibitors/AT-II receptor antagonists (e.g., captopril, losartan)
- ETB receptor antagonists (e.g., bosentan)
- L-Type calcium channel blockers (e.g., dihydropyridines: nifedipine)
- Nebivolol (beta blocker)
- PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil)
- non-selective PDE inhibitors (e.g., caffeine)
- PDE9 inhibitors (e.g., paraxanthine)
- cGMP preferring PDE inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil, paraxanthine, tadalafil)
- Statins (e.g., simvastatin)
|
|---|
|

