Gallbladder
| Gallbladder | |
|---|---|
 The gallbladder is located beneath the liver and drains bile into the duodenum via the biliary tree. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Foregut |
| System | Digestive system |
| Artery | Cystic artery |
| Vein | Cystic vein |
| Nerve | Celiac ganglia, Vagus (CN X)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Vesica biliaris, vesica fellea |
| MeSH | D005704 |
| TA98 | A05.8.02.001 |
| TA2 | 3081 |
| FMA | 7202 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In vertebrates the gallbladder (gall bladder, biliary vesicle or cholecyst), is a small organ where bile is stored, before it is released into the small intestine. Humans can live without a gallbladder. The surgical removal of the gallbladder is called a cholecystectomy.
Structure


The gallbladder is a hollow organ that sits just beneath the right lobe of the liver.[2] In adults, the gallbladder measures approximately 8 centimetres (3.1 in) in length and 4 centimetres (1.6 in) in diameter when fully distended.[3] The gallbladder has a capacity of about 100 mL.[4]: 298
The gallbladder is shaped like a tapered sac, with the open end opening into the biliary tree and the cystic duct. Anatomically, the gallbladder is divided into three sections: the fundus, body, and neck:[5] The fundus is a rounded end that faces the front of the body.[5] The body (Latin: corpus) is in contact with the liver, lying in a depression at the bottom of the liver.[5] The neck tapers and is continuous with the cystic duct, part of the biliary tree. The cystic duct unites with the common hepatic duct to become the common bile duct. At the junction of the neck of the gallbladder and the cystic duct, there is an out-pouching of the gallbladder wall forming a mucosal fold known as Hartmann's pouch, where gallstones commonly get stuck.
The angle of the gallbladder is located between the costal margin and the lateral margin of the rectus abdominis muscle. The fundus is at the same level as the transpyloric plane.
Histology

Under the microscope, the layers of the gallbladder wall can be seen. The gallbladder wall's innermost surface is lined by a single layer of columnar cells with an apical brush border of microvilli, very similar to intestinal absorptive cells.[6][7] Underneath the epithelia is an underlying lamina propria, a muscular layer, perimuscular layer and serosa. Unlike elsewhere in the intestinal tract, the gallbladder does not have a muscularis mucosae, and the muscular fibres are not arranged in distinct layers.[4] In greater detail, the layers are:[4][8]
- The epithelium is the innermost layer of the gallbladder, and is of simple columnar type. Underneath the epithelia is a lamina propria: together, these two layers are known as the mucosa.
- The submucosa is a thin layer of loose connective tissue with smaller blood vessels. It contains many elastin fibres, lymphatics, and in the neck of the gallbladder, glands which secrete mucous. The lymphatics of this layer help to drain water when the bile is concentrated, and the mucous glands may create a surface that protects the wall of the biliary tree.
- The muscularis, a layer of smooth muscular tissue. The interspersed muscle fibres lie in longitudinal, oblique and transverse directions, and are not arranged in separate layers. The muscle fibres here contract to expel bile from the gallbladder.
- The perimuscular ("around the muscle") fibrous tissue, another layer of connective tissue
- The serosa is a thick layer that covers the outer gallbladder, and is continuous with peritoneum, which lines the abdominal cavity. The serosa layer contains blood vessels and lymphatics.
Development
The gallbladder develops from an endodermal outpouching of the embryonic gut tube.[9]Early in development, the human embryo has three germ layers and abuts an embryonic yolk sac. During the second week of embryogenesis, as the embryo grows, it begins to surround and envelop portions of this sac. The enveloped portions form the basis for the adult gastrointestinal tract. Sections of this gut begin to differentiate into the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, such as the oesophagus, stomach, and intestines.[9]
During the fourth week of embryological development, the stomach rotates. The stomach, originally lying in the midline of the embryo, rotates so that its body is on the left. This rotation also affects the part of the gastrointestinal tube immediately below the stomach, which will go on to become the duodenum. By the end of the fourth week, the developing duodenum begins to spout a small outpouching on its right side, which will go on to become the liver biliary tree. Just below this is a second outpouching, known as the cystic diverticulum, that will eventually develop into the gallbladder.[9]
Variation
Anatomical variants of the gallbladder occur very rarely, although a range of abnormalities have been documented.
The number and structure of the gallbladder may vary. Occasionally two or even three gallbladders may coexist, either as separate bladders draining into the cystic duct, or sharing a common branch that drains into the cystic duct. Additionally, the gallbladder may fail to form at all. Gallbladders with two lobes separated by a septum may also exist. These abnormalities are not likely to affect function and are generally asymptomatic.[10]
The location of the gallbladder with regard to the liver may also vary, with documented variants including gallbladders found within, above, on the left side of, behind, and detached from the liver. Such variants are very rare: from 1886 to 1998, only 110 cases of left-lying liver, or less than one per year, were reported in scientific literature.[11][12]
An anatomical variation, which is an innocuous fold in the fundus is named after its resemblance to the Phrygian cap.[citation needed]
Function
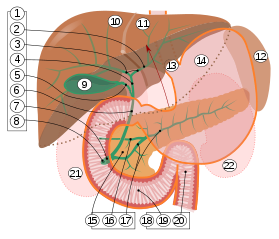
2. Intrahepatic bile ducts
3. Left and right hepatic ducts
4. Common hepatic duct
5. Cystic duct
6. Common bile duct
7. Ampulla of Vater
8. Major duodenal papilla
9. Gallbladder
10–11. Right and left lobes of liver
12. Spleen
13. Esophagus
14. Stomach
15. Pancreas:
16. Accessory pancreatic duct
17. Pancreatic duct
18. Small intestine:
19. Duodenum
20. Jejunum
21–22. Right and left kidneys
The front border of the liver has been lifted up (brown arrow).[13]
The main purpose of the gallbladder is to store bile, also called gall. The gallbladder is part of the biliary system and serves as a reservoir for bile, which is produced by the liver. The liver produces the bile and then it flows through the hepatic ducts into the gallbladder. At any one time, 30 to 60 cubic millimetres (0.0010 to 0.0020 US fl oz) of bile is stored within the gallbladder.[14]
When food containing fat enters the digestive tract, it stimulates the secretion of cholecystokinin (CCK) from I cells of the duodenum and jejunum. In response to cholecystokinin, the gallbladder rhythmically contracts and releases its contents into the common bile duct, eventually draining into the duodenum. The bile, originally produced in the liver, emulsifies fats in partly digested food, thereby assisting their absorption. Bile consists primarily of water and bile salts, and also acts as a means of eliminating bilirubin, a product of hemoglobin metabolism, from the body.[14]
The bile that is secreted by the liver and stored in the gallbladder is not the same as the bile that is secreted by the gallbladder. During gallbladder storage of bile, it is concentrated by removal of some water and electrolytes. This is through the active transport of sodium ions across the epithelia of the gallbladder, which creates an osmotic pressure that also causes water and other electrolytes such as chlorine to be reabsorbed.[14]
Clinical significance
Gallstone
Gallstones are the most common problem to affect the gallbladder.[15] Gallstones generally form because the bile is saturated with either cholesterol or bilirubin. Only the minority of gallstones cause symptoms, and the majority of stones are passed along the biliary tree. When symptoms occur, a person may feel severe pain in the upper right part of their abdomen. If the stone blocks the gallbladder, cholecystitis may occur. If the stone lodges in the biliary tree, jaundice may occur; and if the stone blocks the pancreatic duct, then pancreatitis may occur. Gallstones are often managed by waiting for them to be naturally passed. In people with recurrent gallstones, surgery to remove the gallbladder may be considered. Some medication, such as Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), and ultrasound to break down the stones may also be used.[16]
Inflammation
Inflammation of the gallbladder is known as cholecystitis. Inflammation is most commonly because of obstruction of the duct with gallstones, known as cholelithiasis. Blocked bile accumulates, and pressure on the gallbladder wall may lead to the release of substances that cause inflammation, such as phospholipase. There is also the risk of bacterial infection. An inflamed gallbladder is likely to cause pain and fever, and tenderness in the upper, right corner of the abdomen, and may have a positive Murphy's sign. Cholecystitis is often managed with rest and antibiotics, particularly cephalosporins and, in severe cases, metronidazole.[16]
Cholecystitis may also occur chronically, particularly when a person is prone to getting gallstones.[16]
Gallbladder polyps
Gallbladder polyps are mostly benign growths or lesions resembling growths that form in the gallbladder wall.
Gallbladder removal
A cholecystectomy is a procedure in which the gallbladder is removed. It may be removed because of recurrent gallstones, and is considered an elective procedure. A cholecystectomy may be an open procedure, or one conducted by laparoscopy. In the surgery, the gallbladder is removed from the neck to the fundus,[17] and so bile will drain directly from the liver into the biliary tree. About 30% of patients may experience some degree of indigestion following the procedure, although severe complications are much rarer.[16]
Society and culture
Numerous words in the English language relate to the gallbladder and the bile that it stores. To have 'gall' is associated with bold behaviour, whereas to have 'bile' is associated with bitterness.[18]
In the Chinese language, the gallbladder (Chinese: 膽) is associated with courage and a plethora of related idioms, including using terms such as "a body completely [of] gall" (Chinese: 渾身是膽) to describe a brave person, and "single gallbladder hero" (Chinese: 孤膽英雄) to describe a lone hero.[19]
In the Zangfu theory of Chinese medicine, the gallbladder not only has a digestive role, but is seen as the seat of decision-making.[19]
In other animals
Most vertebrates have gallbladders, whereas invertebrates do not. However, its precise form and the arrangement of the bile ducts may vary considerably. In many species, for example, there are several separate ducts running to the intestine, rather than a single common bile duct, as in humans. Several species of mammals (including horses, deer, rats, and various laminis[20]) and several species of birds lack a gallbladder altogether, as do lampreys.[21]
Additional images
-
Diagram of Stomach
-
Gallbladder and surrounding organs.
-
Gall bladder.Visceral surface of liver.
References
- ^ Ginsburg, Ph.D., J.N. (2005-08-22). "Control of Gastrointestinal Function". In Thomas M. Nosek, Ph.D. (ed.). Gastrointestinal Physiology. Essentials of Human Physiology. Augusta, Georgia, United State: Medical College of Georgia. pp. p. 30. Retrieved 2007-06-29.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|1=(help); External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ "Where is the Gallbladder Located in the Body". Buzzle.com. 2013-02-28. Retrieved 2013-08-18.
- ^ Jon W. Meilstrup (1994). Imaging Atlas of the Normal Gallbladder and Its Variants. Boca Raton: CRC Press. p. 4. ISBN 0-8493-4788-2.
- ^ a b c Deakin, Barbara Young ... ; drawings by Philip J.; et al. (2006). Wheater's functional histology : a text and colour atlas (5th ed. ed.). [Edinburgh?]: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. p. 298. ISBN 978-0-443-06850-8.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help); Explicit use of et al. in:|first=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. p. 287. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- ^ "Gall bladder". Retrieved 15 April 2014.
- ^ Zaki, Mohamed; Al-Refeidi, Abdullah (2009). "Histological Changes in the Human Gallbladder Epithelium associated with Gallstones". OMJ. 24: 269–273. doi:10.5001/omj.2009.55.
- ^ "Staging of Gallbladder Cancer".
- ^ a b c Larsen's human embryology (4th ed., Thoroughly rev. and updated. ed.). Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. 2009. pp. "Development of the Gastrointestinal Tract". ISBN 9780443068119.
{{cite book}}:|first=missing|last=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|first=(help) - ^ Leeuw, Th.G.; Verbeek, P.C.M.; Rauws, E.A.J.; Gouma, D.J. (September 1995). "A double or bilobar gallbladder as a cause of severe complications after (laparoscopic) cholecystectomy". Surgical Endoscopy. 9 (9). doi:10.1007/BF00188459.
- ^ Dhulkotia, A; Kumar, S; Kabra, V; Shukla, HS (1 March 2002). "Aberrant gallbladder situated beneath the left lobe of liver". HPB: Official Journal of The International Hepato Pancreato Biliary Association. 4 (1): 39–42. doi:10.1080/136518202753598726.
- ^ Naganuma, S. (6 March 2014). "Sonographic findings of anomalous position of the gallbladder". Abdominal Imaging. 23 (1): 67–72. doi:10.1007/s002619900287.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Standring S, Borley NR, eds. (2008). Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Brown JL, Moore LA (40th ed.). London: Churchill Livingstone. pp. 1163, 1177, 1185–6. ISBN 978-0-8089-2371-8.
- ^ a b c Hall, Arthur C. Guyton, John E. (2005). Textbook of medical physiology (11th ed. ed.). Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders. pp. 802–804. ISBN 978-0-7216-0240-0.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Rodriguez, D. (2010, Jan. 25). What Is the Gallbladder?. Everyday Health, Retrieved Mar. 20, 2011, from http://www.everydayhealth.com/gallbladder/what-is-the-gallbladder.html
- ^ a b c d Britton, the editors Nicki R. Colledge, Brian R. Walker, Stuart H. Ralston ; illustrated by Robert (2010). Davidson's principles and practice of medicine (21st ed. ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. pp. 977–979. ISBN 978-0-7020-3085-7.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help);|first=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Neri V, Ambrosi A, Fersini A, Tartaglia N, Valentino TP (2007). "Antegrade dissection in laparoscopic cholecystectomy". JSLS : Journal of the Society of Laparoendoscopic Surgeons / Society of Laparoendoscopic Surgeons. 11 (2): 225–8. PMC 3015719. PMID 17761085.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ The Oxford English dictionary (2nd ed. ed.). Oxford: Clarendon Press. 1989. p. gall, bile. ISBN 9780198611868.
{{cite book}}:|edition=has extra text (help);|first=missing|last=(help) - ^ a b Yu, Ning (1 January 2003). "Metaphor, Body, and Culture: The Chinese Understanding of Gallbladder and Courage". Metaphor and Symbol. 18 (1): 13–31. doi:10.1207/S15327868MS1801_2.
- ^ C. Michael Hogan. 2008. Guanaco: Lama guanicoe, GlobalTwitcher.com, ed. N. Strömberg
- ^ Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977). The Vertebrate Body. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. p. 355. ISBN 0-03-910284-X.
External links
- Diagram of Human Stomach and Gallbladder – Human Anatomy Online dd, MyHealthScore.com.
- www.newchronicles.webs.com/f/gastrointestinalphysiology – Gastrointestinal Physiology Review.
- http://www.ece.ncsu.edu/imaging/MedImg/SIMS/GF32.gif
- Anatomy photo:38:14-0100 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Stomach, Spleen and Liver: The Gallbladder and the Bile System"
- http://training.seer.cancer.gov/ss_module13_biliary_tract/unit02_sec02_anatomy.html
- http://anatomy.med.umich.edu/gastrointestinal_system/duodenum_tables.html
- Rodriguez, D. (2010, Jan. 25). What Is the Gallbladder?. Everyday Health, Retrieved Mar. 20, 2011, from http://www.everydayhealth.com/gallbladder/what-is-the-...
- (2009, Jan.). Life Without a Gallbladder. Digestive Disorders, 30–31. Retrieved n.d., from Health Source – Consumer Edition (9780929661674).



