Tisza
| Tisza | |
|---|---|
 | |
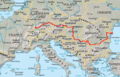
 Map of the Tisza | |
| Native name | |
| Location | |
| Countries | |
| Towns | |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Eastern Carpathians, Ukraine |
| • elevation | 2,020 m (6,630 ft) |
| Mouth | Danube |
• location | Downstream of Novi Sad, Serbia |
• coordinates | 45°8′17″N 20°16′39″E / 45.13806°N 20.27750°E[1] |
| Length | 966 km (600 mi) |
| Basin size | 156,087 km2 (60,266 sq mi)[2] 154,073.1 km2 (59,488.0 sq mi)[3] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Novi Slankamen, Serbia (near mouth) |
| • average | 820 m3/s (29,000 cu ft/s) 920.111 m3/s (32,493.4 cu ft/s)[4] |
| • minimum | 160 m3/s (5,700 cu ft/s) |
| • maximum | 4,500 m3/s (160,000 cu ft/s) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Szeged, Hungary (173.6 km upstream of mouth - Basin size: 138,857.7 km2 (53,613.3 sq mi)[5] |
| • average | 769 m3/s (27,200 cu ft/s) 890.451 m3/s (31,446.0 cu ft/s)[6] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Szolnok, Hungary (334.6 km upstream of mouth - Basin size: 72,889.4 km2 (28,142.8 sq mi)[7] |
| • average | 546 m3/s (19,300 cu ft/s) 578.922 m3/s (20,444.4 cu ft/s) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Tokaj, Hungary (543.079 km upstream of mouth - Basin size: 49,120.9 km2 (18,965.7 sq mi)[8] |
| • average | 465 m3/s (16,400 cu ft/s) 468.77 m3/s (16,554 cu ft/s)[9] |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Vásárosnamény, Hungary (684.45 km upstream of mouth - Basin size: 30,978.9 km2 (11,961.0 sq mi)[10] |
| • average | 340.62 m3/s (12,029 cu ft/s)[11] |
| Basin features | |
| Progression | Danube→ Black Sea |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Someș, Körös, Mureș, Bega |
| • right | Bodrog, Sajó, Eger, Zagyva |
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa, is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. Once, it was called "the most Hungarian river" because it flowed entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national borders.
The Tisza begins near Rakhiv in Ukraine, at the confluence of the White Tisa and Black Tisa, which is at coordinates 48.07465560782065, 24.24443465360461 (the former springs in the Chornohora mountains; the latter in the Gorgany range). From there, the Tisza flows west, roughly following Ukraine's borders with Romania and Hungary, then shortly as border between Slovakia and Hungary, later into Hungary, and finally into Serbia. It enters Hungary at Tiszabecs. It traverses Hungary from north to south. A few kilometers south of the Hungarian city of Szeged, it enters Serbia. Finally, it joins the Danube near the village of Stari Slankamen in Vojvodina, Serbia.
The Tisza drains an area of about 156,087 km2 (60,266 sq mi)[2] and has a length of 966 km (600 mi)[12] Its mean annual discharge is seasonally 792 m3/s (28,000 cu ft/s) to 1,050 m3/s (37,000 cu ft/s). It contributes about 13% of the Danube's total runoff.[2]
Attila the Hun is said to have been buried under a diverted section of the river Tisza.[13]
Names
The river was known as the Tisia in antiquity; other ancient names for it included Pathissus (Πάθισσος in Ancient Greek and later Tissus (in Latin)), (Pliny, Naturalis historia, 4.25). It may be referred to as the Theiss in older English references, after the German name for the river, Theiß. It is known as the Tibisco in Italian, and in older French references (as for instance in relation to the naval battles on the Danube between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg Empire in the 17th and 18th centuries) it is often referred to as the Tibisque.
Modern names for the Tisza in the languages of the countries it flows through include:
- Template:Lang-ro, pronounced [ˈtisa];
- Template:Lang-uk, pronounced [ˈtɪsɐ];
- Template:Lang-sk, pronounced [ˈtisa];
- Template:Lang-hu, pronounced [ˈtisɒ];
- Serbo-Croatian Cyrillic: Тиса / Serbo-Croatian Latin: Tisa, pronounced [tîsa].
Regulation
The length of the Tisza in Hungary used to be 1,419 km (882 mi). It flowed through the Great Hungarian Plain, which is one of the largest flat areas in central Europe. Since plains can cause a river to flow very slowly, the Tisza used to follow a path with many curves and turns, which led to many large floods in the area.
After several small-scale attempts, István Széchenyi organised the "regulation of the Tisza" (Template:Lang-hu) which started on August 27 1846, and substantially ended in 1880. The new length of the river in Hungary was reduced to 966 km (600 mi) in total, with 589 km (366 mi) of dead channels and 136 km (85 mi) of new riverbed.[14]
Lake Tisza
In the 1970s, the building of the Tisza Dam at Kisköre started with the purpose of helping to control floods as well as storing water for drought seasons. However, the resulting Lake Tisza became one of the most popular tourist destinations in Hungary since it had similar features to Lake Balaton at drastically cheaper prices and was not crowded.
Navigation
The Tisza is navigable over much of its course. The river opened up for international navigation only recently; before, Hungary distinguished "national rivers" and "international rivers", indicating whether non-Hungarian vessels were allowed or not. After Hungary joined the European Union, this distinction was lifted and vessels were allowed on the Tisza.[15]
Conditions of navigation differ with the circumstances: when the river is in flood, it is often unnavigable, just as it is at times of extreme drought.[16]
Wildlife
The Tisza has a rich and varied wildlife. Over 200 species of birds reside in the bird reserve of Tiszafüred. The flood plains along the river boast large amounts of diverse plant and animal life. In particular, the yearly "flowering" of the Tisza is considered a local natural wonder. The flowering attracts vast numbers of mayflies which is a well known spectacle.[17][18]
In September 2020, colonies of magnificent bryozoans were discovered in the river.[19]
Pollution
In early 2000, there was a sequence of serious pollution incidents originating from accidental industrial discharges in Romania. The first, in January 2000, occurred when there was a release of sludge containing cyanide from a Romanian mine and killed 2000 tons of fish. The second, from a mine pond at Baia Borsa, northern Romania, resulted in the release of 20,000 m3 (710,000 cu ft) of sludge containing zinc, lead and copper occurred in early March 2000. A week later, the third spill occurred at the same mining site at Baia Borsa, staining the river black, possibly including heavy metals.[20]
This series of incidents were described at the time as the most serious environmental disaster to hit central Europe since the Chernobyl disaster. Usage of river water for any purpose was temporarily banned and the Hungarian government pressed the Romanians and the European Union to close all installations that could lead to further pollution.[20]
Examination of river sediments indicates that pollution incidents from mines have occurred for over a century.[21]
Geography
Tributaries


The following rivers are tributaries to the river Tisza:
- Vișeu (entering at Valea Vișeului)
- Kosivska (entering at Luh)
- Shopurka (entering at Velykyi Bychkiv)
- Iza (entering at Sighetu Marmației)
- Sarasău
- Bic
- Săpânța
- Șaroș
- Teresva (entering near Teresva)
- Baia
- Valea lui Francisc
- Tereblia (entering at Bushtyno)
- Rika (entering near Khust)
- Batar
- Borzhava
- Tur
- Szamos (entering near Vásárosnamény)
- Someșul Mare (in Dej)
- Someșul Mic (in Dej)
- Someșul Cald (in Gilău)
- Someșul Rece (in Gilău)
- Kraszna (entering in Vásárosnamény)
- Bodrog (entering in Tokaj)
- Sajó (entering near Tiszaújváros)
- Hornád (near Kesznyéten)
- Eger (entering in Poroszló)
- Zagyva (entering in Szolnok)
- Körös (entering near Csongrád)
- Sebes-Körös (near Gyoma)
- White-Körös (near Gyula)
- Black-Körös (near Gyula)
- Maros (entering near Szeged)
- Arieș (near Gura Arieșului)
- Târnava (near Teiuș)
- Târnava Mare (in Blaj)
- Târnava Mică (in Blaj)
- Aranca (entering near Padej)
- Čik (entering near Bačko Petrovo Selo)
- Jegrička (entering near Žabalj)
- Bega (entering near Titel)
Cities and towns
The Tisza (Tisa) flows through the following countries and cities (ordered from the source to mouth):
 Ukraine
Ukraine
 Slovakia
Slovakia
 Romania
Romania
 Hungary
Hungary
 Serbia
Serbia
See also
References
- ^ Tisza at GEOnet Names Server
- ^ a b c Tockner, Klement; Uehlinger, Urs; Robinson, Christopher T., eds. (2009). Rivers of Europe (First ed.). London: Academic Press. Sec. 3.9.5. ISBN 978-0-12-369449-2.
- ^ "Rivers Network". 2020.
- ^ "Rivers Network". 2020.
- ^ "Rivers Network". 2020.
- ^ "Rivers Network". 2020.
- ^ "Rivers Network". 2020.
- ^ "Rivers Network". 2020.
- ^ "Rivers Network". 2020.
- ^ "Rivers Network". 2020.
- ^ "Rivers Network". 2020.
- ^ "Analysis of the Tisza River Basin 2007- Initial step toward the Tisza River Basin Management Plan – 2009" (PDF). www.icpdr.or. March 2008. Retrieved 5 February 2021.
- ^ Ildiko Ecsedy, "The Oriental Background to the Hungarian Tradition about 'Attila's Tomb'", Acta Orientalia, 36 (1982), pp. 129-153
- ^ "Danube + Tisza River". danube.panda.org. Retrieved 5 November 2019.
- ^ "Declaration On Co-Operation Concerning The Tisza/Tisa River Basin And Initiative On The Sustainable Spatial Development Of The Tisza/Tisa River | International Environmental Agreements (IEA) Database Project". iea.uoregon.edu. Retrieved 2019-02-03.
- ^ NoorderSoft Waterway Database; accessed 13 March 2016.
- ^ Konyvek, Szalay (2009). Our Beloved Hungaricums. Pannon-Literatura Kft. p. 94. ISBN 978-963-251-145 0.
- ^ Klaushik. "Blooming of the Tisza". amusingplanet.com. Retrieved 25 November 2019.
- ^ Đorđe Đukić (8 September 2020). "Otkriveni organizmi stari 500 miliona godina" [Organisms originating rom 500 million years ago discovered]. Politika (in Serbian). p. 12.
- ^ a b "Third pollution spill hits Hungary". BBC. 15 March 2000. Retrieved 11 October 2010.
- ^ H. L. Nguyen; M. Braun; I. Szaloki; W. Baeyens; R. Van Grieken; M. Leermakers (2009). "Tracing the Metal Pollution History of the Tisza River". Water, Air, and Soil Pollution. 200: 119–132. doi:10.1007/s11270-008-9898-2. S2CID 94627373.
External links
- Backabanat.com, About Tisza
- Historia.hu, the Living Tisza (in Hungarian)
- River Basin Report: Tisza River Ywat.org
- Awarded "EDEN - European Destinations of Excellence" non traditional tourist destination 2010
- Tisza basin
- Bačka
- Banat
- Border rivers
- Braided rivers in Ukraine
- Geography of Bács-Kiskun County
- Geography of Vojvodina
- Hungary–Slovakia border
- Hungary–Serbia border
- Hungary–Ukraine border
- International rivers of Europe
- Ramsar sites in Slovakia
- Rivers of Hungary
- Rivers of Maramureș County
- Rivers of Romania
- Rivers of Serbia
- Rivers of Slovakia
- Rivers of Zakarpattia Oblast
- Tributaries of the Danube