Cervix: Difference between revisions
→Childbirth: not really a main as the article is not about how childbirth relates to the cervix |
separated into two sentences like it was before, the lead should be kept as simple as possible, part of writing in simple English is keeping sentences short |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
| DorlandsID = cervix uteri |
| DorlandsID = cervix uteri |
||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''cervix''' (''{{lang-la|neck}}'') or '''cervix uteri''' is the lower part of the [[uterus]] |
The '''cervix''' (''{{lang-la|neck}}'') or '''cervix uteri''' is the lower part of the [[uterus]]. It is part of the [[female reproductive system]]. In a non-pregnant woman, the cervix is usually between 2 and 3 cm long. Roughly cylindrical in shape, it has a narrow central canal called the [[cervical canal]] running along its entire length, connecting the [[cavity of the body of the uterus]] and the [[lumen (biology)|lumen]] of the [[vagina]]. The opening into the uterus is called the [[internal os]] and the opening into the vagina is called the [[external os]]. The lower part of the cervix, known as the [[vaginal portion of the cervix]] (or ectocervix), bulges into the top of the vagina. The cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of [[Hippocrates]], over 2,000 years ago. |
||
The cervical canal is a passage through which [[sperm]] must travel to fertilise an [[egg cell]] after sexual intercourse. Several methods of contraception, including [[cervical cap]]s and [[Diaphragm (contraceptive)|cervical diaphragm]]s aim to block or prevent the passage of sperm through the cervical canal. Cervical mucus is used in several methods of fertility awareness, such as the [[Creighton model]] and [[Billings method]], due to its changes in consistency throughout the [[menstrual period]]. During vaginal [[childbirth]], the cervix must flatten and [[Cervical dilation|dilate]] to allow the [[fetus]] to progress along the birth canal. Midwives and doctors use the extent of the dilation of the cervix to assist decision making during childbirth. |
The cervical canal is a passage through which [[sperm]] must travel to fertilise an [[egg cell]] after sexual intercourse. Several methods of contraception, including [[cervical cap]]s and [[Diaphragm (contraceptive)|cervical diaphragm]]s aim to block or prevent the passage of sperm through the cervical canal. Cervical mucus is used in several methods of fertility awareness, such as the [[Creighton model]] and [[Billings method]], due to its changes in consistency throughout the [[menstrual period]]. During vaginal [[childbirth]], the cervix must flatten and [[Cervical dilation|dilate]] to allow the [[fetus]] to progress along the birth canal. Midwives and doctors use the extent of the dilation of the cervix to assist decision making during childbirth. |
||
Revision as of 05:21, 17 June 2014
| Cervix | |
|---|---|
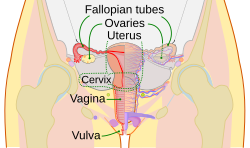 The female reproductive system. The cervix is part of the uterus. The cervical canal connects the interiors of the uterus and vagina. | |
| File:Female reproductive system lateral nolabel.png 1: Fallopian tube, 2: bladder, 3: pubic bone, 4: vagina–G-Spot, 5: clitoris, 6: urethra, 7: vagina, 8: ovary, 9: sigmoid colon, 10: uterus, 11: fornix, 12: cervix, 13: rectum, 14: anus | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Müllerian duct |
| Artery | Vaginal artery and uterine artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Cervix uteri |
| MeSH | D002584 |
| TA98 | A09.1.03.010 |
| TA2 | 3508 |
| FMA | 17740 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The cervix (Latin: neck) or cervix uteri is the lower part of the uterus. It is part of the female reproductive system. In a non-pregnant woman, the cervix is usually between 2 and 3 cm long. Roughly cylindrical in shape, it has a narrow central canal called the cervical canal running along its entire length, connecting the cavity of the body of the uterus and the lumen of the vagina. The opening into the uterus is called the internal os and the opening into the vagina is called the external os. The lower part of the cervix, known as the vaginal portion of the cervix (or ectocervix), bulges into the top of the vagina. The cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago.
The cervical canal is a passage through which sperm must travel to fertilise an egg cell after sexual intercourse. Several methods of contraception, including cervical caps and cervical diaphragms aim to block or prevent the passage of sperm through the cervical canal. Cervical mucus is used in several methods of fertility awareness, such as the Creighton model and Billings method, due to its changes in consistency throughout the menstrual period. During vaginal childbirth, the cervix must flatten and dilate to allow the fetus to progress along the birth canal. Midwives and doctors use the extent of the dilation of the cervix to assist decision making during childbirth.
The endocervical canal is lined with a layer of column-shaped cells and the ectocervix is covered with multiple layers of cells topped with flat cells. The two types of epithelia meet the squamocolumnar junction. Infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV) can cause changes in the epithelium, which can lead to cancer of the cervix. Cervical cytology tests can often detect precursors of cervical cancer and enable early successful treatment. HPV vaccines, developed in the early 21st century, can be given to prevent HPV infection.
Structure
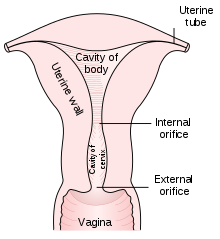
The cervix is part of the female reproductive system. Around 2–3 centimetres (0.8–1.2 in) in length,[1] it is the lower narrower part of the uterus continuous above with the broader upper part—or body—of the uterus.[2] The lower end of the cervix bulges into the anterior wall of the vagina, and is referred to as the vaginal portion of cervix (or ectocervix); the rest of the cervix above the vagina is called the supravaginal portion of cervix.[2] A central canal, known at the cervical canal, runs along its length and connects the cavity of the body of the uterus with the lumen of the vagina.[2] The openings are known as the internal os and external orifice of the uterus (or external os) respectively.[2] The mucosal lining of the cervical canal is known as the endocervix[3] and the mucosa covering the ectocervix is known as the exocervix.[4] The cervix has an inner mucosal layer, a thick layer of smooth muscle, and posteriorly the supravaginal portion has a serosal covering consisting of connective tissue and overlying peritoneum.[2]
In front of the upper part of the cervix lies the bladder, separated from it by cellular connective tissue known as parametrium, which also extends over the sides of the cervix.[2] To the rear, the supravaginal cervix is covered by peritoneum, which runs onto the back of the vaginal wall and then turns upwards and onto the rectum forming the recto-uterine pouch.[2] The cervix is more tightly connected to surrounding structures than the rest of the uterus.[5]
The cervical canal varies greatly in length and width between women and over the course of a woman's life,[1] and can measure 8 mm (0.3 in) at its widest diameter in premenopausal adults. The ectocervix has a convex, elliptical surface and is divided into anterior and posterior lips. The size and shape of the external opening and the ectocervix can vary according to age, hormonal state, and whether natural or normal childbirth has taken place. In women who have not had a vaginal delivery, the external os is a small circular opening, and in women who have had a vaginal delivery, the external os is slit-like.[6] On average, the ectocervix is 3 cm (1.2 in) long and 2.5 cm (1 in) wide.[1]
The cervix is supplied blood by the descending branch of the uterine artery[7] and drains into the uterine vein.[8] The pelvic splanchnic nerves, emerging as S2–S3, transmit the sensation of pain from the cervix to the brain.[3] These nerves travel along the uterosacral ligaments, which pass from the uterus to the anterior sacrum.[7]
Three channels act to facilitate lymphatic drainage to the cervix.[9] The anterior and lateral cervix drains to nodes along the uterine arteries, travelling along the cardinal ligaments at the base of the broad ligament to the external iliac lymph nodes and ultimately the paraaortic lymph nodes. The posterior and lateral cervix drains along the uterine arteries to the internal iliac lymph nodes and ultimately the paraaortic lymph nodes, and the posterior section of the cervix drains to the obturator and presacral lymph nodes.[1][8][9]
After menstruation and directly under the influence of estrogen, the cervix undergoes a series of changes in position and texture. During most of the menstrual cycle, the cervix remains firm, and is positioned low and closed. However, as ovulation approaches, the cervix becomes softer and rises to open in response to the higher levels of estrogen present.[10] These changes are also accompanied by changes in cervical mucus,[11] described below.
Development
As a component of the female reproductive system, the cervix is derived from the two paramesonephric ducts (also called Mullarian ducts), which develop around the sixth week of embryogenesis. During development, the outer parts of the two ducts fuse, forming a single urogenital canal that will become the vagina, cervix and uterus.[12] The cervix grows in size at a smaller rate than the body of the uterus, so the relative size of the cervix over time decreases, decreasing from being much larger than the body of the uterus in fetal life, twice as large during childhood, and decreasing to its adult size, smaller than the uterus, after puberty.[8] In fetal development, the original squamous epithelium of the cervix is derived from the urogenital sinus and the original columnar epithelium is derived from the paramesonephric duct. The point at which these two original epithelia meet is called the original squamocolumnar junction.[13]: 15–16
Histology

The endocervical canal is lined with a single layer of columnar cells and the exocervix is covered with non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.[2] The junction between these two types of epithlia is called the squamocolumnar junction.[14]: 408–11 The squamous epithelium of the ectocervix resembles the vaginal epithelium.[14]: 41 Underlying both types of epithelium is a tough layer of collagen.[15] The cervix has more fibrous tissue, including collagen and elastin than the rest of the uterus.[2]
In pre-pubertal girls the functional squamocolumnar junction is just within the entocervical canal.[14]: 411 At puberty, under hormonal influence, and during pregnancy, the columnar epithelium extends outwards over the ectocervix as the cervix everts.[13]: 106 Hence, this also causes the squamocolumnar junction to move outwards onto the vaginal portion of the cervix, where it is exposed to the acidic vaginal environment.[13]: 106 [14]: 411 The exposed columnar epithelium can undergo physiological metaplasia and change to tougher metaplastic squamous epithelium in days or weeks,[14]: 25 which when mature is similar to the original squamous epithelium.[14]: 411 The new squamocolumnar junction is therefore internal to the original squamocolumnar junction, and the zone of unstable epithelium between the two junctions is called the transformation zone of the cervix.[14]: 411 After the menopause the uterine structures involute and the functional squamocolumnar junction moves into the endocervical canal.[14]: 41
Function
Fertility
The cervical canal is a pathway through which sperm enter the uterus after sexual intercourse.[16] Some sperm remains in cervical crypts, infoldings of the endocervix, which act as a reservoir, releasing sperm over several hours and maximising the changes of fertilisation.[17] There is a theory the cervical and uterine contractions during orgasm draw semen into the uterus.[16] Although the "upsuck theory" has been generally accepted for some years, it has been disputed due to lack of evidence, small sample size, and methodological errors.[18][19]
Some methods of fertility awareness such as the Creighton model and the Billings method involve estimating a woman's periods of fertility and infertility by observing physiological changes in her body. Among these changes are several involving the quality of her cervical mucus: the sensation it causes at the vulva, its elasticity (Spinnbarkeit), its transparency, and the presence of ferning.[10]
Childbirth
The cervix plays a major role in childbirth. As the foetus descends within the uterus in preparation for birth, the presenting part, usually the head, rests on and is supported by the cervix.[20] As labour progresses, the cervix becomes softer and shorter, begins to dilate, and rotates to face anteriorly.[21] The support the cervix provides to the foetal head starts to give way when the uterus begins its contractions. During childbirth, the cervix must dilate to a diameter of more than 10 cm (4 in) to accommodate the head of the foetus as it descends from the uterus to the vagina. In becoming wider, the cervix also becomes shorter, a phenomenon known as effacement.[20]
Along with other factors, midwifes and doctors use the extent of cervical dilation to assist decision making during childbirth.[22][23] Generally, the active first stage of labour, when the uterine contractions become strong and regular,[24] begins when the cervical dilation is more than 3–5 cm (1.2–2.0 in).[25][26] The second phase of labor begins when the cervix has dilated to 10 cm (4 in), which is regarded as its fullest dilation,[20] and is when active pushing and contractions push the baby along the birth canal leading to the birth of the baby.[27] The number of past vaginal deliveries is a strong factor in influencing how rapidly the cervix is able to dilate in labour.[20] The time taken for the cervix to dilate and efface is one factor used in reporting systems such as the Bishop score, used to recommend whether interventions such as a forceps delivery, induction, or Caesarean section should be used in childbirth.[20]
Cervical incompetence is a condition in which shortening of the cervix due to dilation and thinning occurs, before term pregnancy. Short cervical length is the strongest predictor of preterm birth.[21]
Cervical mucus
Several hundred glands in the endocervix produce 20-60 mg of cervical mucus a day, increasing to 600 mg around the time of ovulation. It is viscous as it contains large proteins known as mucins. The viscosity and water content varies during the menstrual cycle; mucus is composed of around 93% water, reaching 98% at midcycle. These changes allow it to function either as a barrier or a transport medium to spermatozoa. It contains electrolytes such as calcium, sodium, and potassium; organic components such as glucose, amino acids, and soluble proteins; trace elements including zinc, copper, iron, manganese, and selenium; free fatty acids; enzymes such as amylase; and prostaglandins.[11] Its consistency is determined by the influence of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. At midcycle around the time of ovulation—a period of high estrogen levels— the mucus is thin and serous to allow sperm to enter the uterus, and is more alkaline and hence more hospitable to sperm.[17] It is also higher in electrolytes, which results in the "ferning" pattern that can be observed in drying mucus under low magnification; as the mucus dries, the salts crystallize, resembling the leaves of a fern.[10] The mucus has stretchy character described as Spinnbarkeit most prominent around the time of ovulation.[28]
At other times in the cycle, the mucus is thick and more acidic due to the effects of progesterone.[17] This "infertile" mucus acts as a barrier to sperm from entering the uterus.[29] Women taking an oral contraceptive pill also have thick mucus from the effects of progesterone.[17] Thick mucus also prevents pathogens from interfering with a nascent pregnancy.[30]
A cervical mucus plug, called the operculum, forms inside the cervical canal during pregnancy. This provides a protective seal for the uterus against the entry of pathogens and against leakage of uterine fluids. The mucus plug is also known to have antibacterial properties. This plug is released as the cervix dilates, either during the first stage of childbirth or shortly before.[31] It is visible as a blood-tinged mucous discharge.[32]
Contraception
Several methods of contraception involve the cervix. Cervical diaphragms are small, reusable, firm-rimmed plastic devices inserted by a woman prior to intercourse that cover the cervix. Pressure against the walls of the vagina maintain the position of the diaphragm, and it acts as a physical barrier to prevent the entry of sperm into the uterus, preventing fertilisation. Cervical caps are a similar method, although they are smaller and adhere to the cervix by suction. Diaphragms and caps are often used in conjunction with spermicides.[33] In one year, 12% of women using the diaphragm will undergo an unintended pregnancy, and with optimal use this falls to 6%.[34] Efficacy rates are lower for the cap, with 18% of women undergoing an unintended pregnancy, and 10–13% with optimal use.[35] Most methods of hormonal contraception, such as the oral contraceptive pill, work primarily by preventing ovulation, but their effectiveness is increased because they prevent the production of the types of cervical mucus that are conducive to fertilisation.[10]
Clinical significance
Cancer

In 2008, cervical cancer was the third-most common cancer in women worldwide, with rates varying geographically from less than one to more than 50 cases per 100,000 women.[36] Cervical cancer nearly always involves human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, and generally involves the ectocervix at the transformation zone.[37][38] HPV is a virus with numerous strains, several of which predispose to dysplasia of cervical tissue, particularly in the transformation zone. This dysplasia increases the risk of cancer forming in the transformation zone, which is the most common area for cervical cancer to occur.[39]
The colposcope, used in a colposcopy to visualise the cervix, was invented in 1925. The Pap smear was developed by Georgios Papanikolaou in 1928.[40] A LEEP procedure using a heated loop of platinum to excise a patch of cervical tissue was developed by Aurel Babes in 1927.[41]
Potentially precancerous changes in the cervix can be detected by a Pap smear (also called a cervical smear), in which epithelial cells are scraped from the surface of the cervix and examined under a microscope.[42] In some parts of the developed world including the UK, the Pap test has been superseded with liquid-based cytology.[43] A result of dysplasia is usually further investigated, such as by taking a cone biopsy, which may also remove the cancerous lesion.[42] Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia is a possible result of the biopsy, and represents dysplastic changes that may eventually progress to invasive cancer.[44] Most cases of cervical cancer are detected in this way, without having caused any symptoms. When symptoms occur, they may include vaginal bleeding, discharge, or discomfort.[45] The introduction of routine screening has resulted in fewer cases of (and deaths from) cervical cancer, however this has mainly taken place in developed countries. Most developing countries have limited or no screening, and 85% of the global burden occurring there.[46] Most women who develop cervical cancer have never had a Pap smear, or have not had one within the last 10 years.[47] Vaccines against HPV, such as Gardasil and Cervarix, also reduce the incidence of cervical cancer, by inoculating against the viral strains involved in cancer development.[42]
Inflammation
Inflammation of the cervix is referred to as cervicitis. This inflammation may be of the endocervix or ectocervix.[48] When associated with the endocervix, it is associated with a mucous vaginal discharge and the sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia and gonorrhoea.[49] Other causes include overgrowth of the commensal flora of the vagina.[38] When associated with the ectocervix, inflammation may be caused by the herpes simplex virus. Inflammation is often investigated through directly visualising the cervix using a speculum, which may appear whiteish due to exudate, and by taking a Pap smear and examining for causal bacteria. Special tests may be used to identify particular bacteria. If the inflammation is due to a bacterium, then antibiotics may be given as treatment.[49]
Anatomical abnormalities
Cervical stenosis refers to an abnormally narrow cervical canal, typically associated with trauma caused by removal of tissue for investigation or treatment of cancer, or cervical cancer itself.[38][50] Diethylstilbestrol, used from 1938 to 1971 to prevent preterm labour and miscarriage, is also strongly associated with the development of cervical stenosis and other abnormalities in the daughters of the exposed women. Other abnormalities include vaginal adenosis, in which the squamous epithelium of the ectocervix becomes columnar, cancers such as clear cell adenocarcinomas, cervical ridges and hoods, and development of a "cockscomb" cervical appearance.[51]
Cervical agenesis is a rare congenital condition in which the cervix completely fails to develop, often associated with the concurrent failure of the vagina to develop.[52] Other congenital cervical abnormalities exist, often associated with abnormalities of the vagina and uterus. The cervix may be duplicated in situations such as bicornuate uterus and uterine didelphys.[53]
Other
Nabothian cysts may develop from metaplasia, which often takes place in the transformation zone, and can cause the glands underlying the columnar epithelium to become blocked.[10] Cervical polyps, which are benign overgrowths of endocervical tissue, if present, may cause bleeding, or a benign overgrowth may be present in the endocervical canal.[38] Cervical ectropion refers to the horizontal overgrowth of the endocervical columnar lining in a one-cell-thick layer over the ectocervix.[49]
History
The name of the cervix comes from Latin: cervix (neck) from the Proto-Indo-European root ker-, referring to a "structure that projects". Thus, the word cervix is linguistically related to the English words "horn", "head" (Sanskrit: sar), "head" (Greek: koryphe), and "deer" (Welsh: carw).[54][55]
The cervix was documented in anatomical literature in at least the time of Hippocrates, although there was some variation in early writers, who used the term to refer to both the cervix and the internal uterine orifice.[56] The first attested use of the word to refer to the cervix of the uterus was in 1702.[54]
Cervical cancer has been described for over 2,000 years, with descriptions provided by both Hippocrates and Aretaeus,[40] although the causal role played by HPV for cervical cancer was only elucidated in the late 20th century by Harald zur Hausen, who published a hypothesis in 1976, and whose hypothesis was confirmed in 1983 and 1984.[57] Based on work done by Jian Zhou and Ian Fraser, a vaccine for four strains of HPV was released in 2006.[58]
References
- ^ a b c d Kurman, edited by Robert J. (1994). Blaustein's Pathology of the Female Genital Tract (4th ed.). New York, NY: Springer New York. pp. 185–201. ISBN 978-1-4757-3889-6.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h i Gray, Henry (1995). Williams, Peter L (ed.). Gray's Anatomy (38th ed.). Churchill Livingstone. p. 1870-73. ISBN 0-443-04560-7.
- ^ a b Drake, Richard L. (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. pp. 415, 423. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Ovalle, William K.; Nahirney, Patrick C. ; illustrations by Frank H. Netter, contributing illustrators, Joe Chovan ... ; et al. (2013). "Female Reproductive System". Netter's Essential Histology (2nd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders. p. 416. ISBN 978-1-4557-0631-0.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Gardner, Ernest (1969) [1960]. Anatomy: A Regional Study of Human Structure (3rd ed.). Philadelphia, PA: W.B.Saunders. pp. 495–98.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Kurman, R. J, ed. (2002). Blaustein's Pathology of the Female Genital Tract (5th ed.). Spinger. p. 207.
- ^ a b Daftary (2011). Manual of Obstretics, 3/e. Elsevier. pp. 1–16. ISBN 81-312-2556-9.
- ^ a b c Ellis, Harold (2011). "Anatomy of the uterus". Anaesthesia & Intensive Care Medicine. 12 (3): 99–101. doi:10.1016/j.mpaic.2010.11.005.
- ^ a b The cervix (2nd ed.). Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. 2005. pp. Chapter 3. The Vascular, Neural and Lymphatic Anatomy of the Cervix. ISBN 9781405131377.
{{cite book}}:|first1=has generic name (help);|first1=missing|last1=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|first1=(help) - ^ a b c d e Weschler, Toni (2006). Taking charge of your fertility : the definitive guide to natural birth control, pregnancy achievement, and reproductive health (Revised ed.). New York, NY: Collins. pp. 59, 64. ISBN 978-0-06-088190-0. Cite error: The named reference "Weschler" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ a b Sharif, Khaldoun (2006). "The structure chemistry and physics of human cervical mucus". In Jordan, Joseph; Singer, Albert; Jones, Howard; Shafi, Mahmood (ed.). The Cervix (2nd ed.). Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishing. pp. 157–68. ISBN 978-1-4051-3137-7.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ Larsen's human embryology (4th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. 2009. pp. "Development of the Urogenital system". ISBN 978-0-443-06811-9.
{{cite book}}:|first=missing|last=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|first=(help) - ^ a b c McLean, John M (2006). "Morphogenesis and Differentiation of the cervicovaginal epithelium". In Jordan, Joseph; Singer, Albert; Jones, Howard; Shafi, Mahmood (eds.). The Cervix (2nd ed.). Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-3137-7.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h Beckmann, Charles R B A; Herbert, William; Laube, Douglas; Ling, Frank; Smith, Roger (2013). Obstetrics and Gynecology (7th ed.). pp. 408–11. ISBN 9781451144314.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Deakin, Barbara Young ... ; drawings by Philip J.; et al. (2006). Wheater's functional histology : a text and colour atlas (5th ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. p. 376. ISBN 978-0-443-06850-8.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|first=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Guyton, Arthur C.; Hall, John Edward (2005). Textbook of Medical Physiology (11th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: W.B. Saunders. p. 1027. ISBN 978-0-7216-0240-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b c d Brannigan, Robert E. (2008). "Sperm Transport and Capacitation". The Global Library of Women's Medicine. doi:10.3843/GLOWM.10316.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Levin, Roy J. (November 2011). "The human female orgasm: a critical evaluation of its proposed reproductive functions". Sexual and Relationship Therapy. 26 (4): 301–14. doi:10.1080/14681994.2011.649692.
- ^ Borrow, Amanda P. "The role of oxytocin in mating and pregnancy". Hormones and Behavior. 61 (3): 266–76. doi:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2011.11.001.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e Williams obstetrics (22nd ed.). New York ; Toronto: McGraw-Hill Professional. 2005. pp. 157–60, 537–39. ISBN 0-07-141315-4.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help);|first=missing|last=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|first=(help) - ^ a b Goldenberg, Robert L. "Epidemiology and causes of preterm birth". The Lancet. 371 (9606): 75–84. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60074-4.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ NICE (2007). Section 1.6, Normal labour: first stage
- ^ NICE (2007). Section 1.7, Normal labour: second stage
- ^ NICE (2007). Section 1.6, Normal labour: first stage
- ^ "Obstetric Data Definitions Issues and Rationale for Change" (PDF). 2012.
{{cite news}}:|first=missing|last=(help); Check|first=value (help) - ^ Su, Min. "Planned caesarean section decreases the risk of adverse perinatal outcome due to both labour and delivery complications in the Term Breech Trial". BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 111 (10): 1065–74. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00266.x.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ NICE (2007). Section 1.7, Normal labour: second stage
- ^ Anderson, Matthew; Karasz, Alison (2004). "Are Vaginal Symptoms Ever Normal? A Review of the Literature". Medscape General Medicine. 6 (4): 49.
- ^ Westinore, Ann; Evelyn, Billings (1998). The Billings Method: Controlling Fertility Without Drugs or Devices. Toronto: Life Cycle Books. p. 37. ISBN 0-919225-17-9.
- ^ Wagner, G.; Levin, R. J. "Electrolytes in vaginal fluid during the menstrual cycle of coitally active and inactive women" (PDF).
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Becher, Naja (2009). "The cervical mucus plug: Structured review of the literature". Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica. 88 (5): 502–13. doi:10.1080/00016340902852898.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Maternity nursing (7th ed.). Edinburgh: Elsevier Mosby. 2006. p. 394. ISBN 978-0-323-03366-4.
{{cite book}}:|first=missing|last=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ NSW, Family Planning (2009). Contraception : healthy choices : a contraceptive clinic in a book (2nd ed.). Sydney: UNSW Press. pp. 27–37. ISBN 978-1-74223-136-5.
- ^ Trussell, James (2011). "Contraceptive failure in the United States". Contraception. 83 (5): 397–404. doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2011.01.021.
- ^ Trussell, J (May–Jun 1993). "Contraceptive efficacy of the diaphragm, the sponge and the cervical cap". Family planning perspectives. 25 (3): 100–05, 135. PMID 8354373.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Arbyn, M. (6 April 2011). "Worldwide burden of cervical cancer in 2008". Annals of Oncology. 22 (12): 2675–86. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdr015.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Wahl, Carter E. (2007). Hardcore pathology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 72. ISBN 9781405104982.
- ^ a b c d Mitchell, Richard Sheppard; Kumar, Vinay; Robbins, Stanley L.; Abbas, Abul K.; Fausto, Nelson (2007). Robbins basic pathology (8th ed.). Saunders/Elsevier. pp. 716–21. ISBN 1-4160-2973-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lowe, Alan Stevens, James S. (2005). Human histology (3rd ed.). Philadelphia, Toronto: Elsevier Mosby. pp. 350–51. ISBN 0-323-03663-5.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Gasparini, R; Panatto, D (May 29, 2009). "Cervical cancer: from Hippocrates through Rigoni-Stern to zur Hausen". Vaccine. 27 Suppl 1: A4-5. PMID 19480961.
- ^ Diamantis, Aristidis (November 2010). "Different strokes: Pap-test and Babes method are not one and the same". Diagnostic Cytopathology. 38 (11): 857–59. doi:10.1002/dc.21347.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine (17th ed.). New York [etc.]: McGraw-Hill Medical. 2008. pp. 608–09. ISBN 978-0-07-147692-8.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help);|first=missing|last=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|first=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Gray, Winifred; Kocjan, Gabrijela, eds. (2010). Diagnostic Cytopathology. Churchill Livingstone. p. 613.
- ^ Cannistra, Stephen A. (1996). "Cancer of the Uterine Cervix". New England Journal of Medicine. 334 (16): 1030–37. doi:10.1056/NEJM199604183341606.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Davidson's principles and practice of medicine (21st ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. 2010. p. 276. ISBN 978-0-7020-3084-0.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help);|first=missing|last=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Vaccarella, Salvatore; Lortet-Tieulent, Joannie; Plummer, Martyn; Franceschi, Silvia; Bray, Freddie (2013). "Worldwide Trends in Cervical Cancer Incidence: Impact of Screening against Changes in Disease Risk Factors". European Journal of Cancer. 49 (15): 3262–73.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ World Health Organization (February 2006). "Fact sheet No. 297: Cancer". Retrieved 1 December 2007.
- ^ Stamm, Walter (2013). The Practitioner's Handbook for the Management of Sexually Transmitted Diseases. Seattle STD/HIV Prevention Training Center. pp. Chapter 7: Cervicitis.
- ^ a b c Harrison's principles of internal medicine (17th ed.). New York [etc.]: McGraw-Hill Medical. 2008. pp. 828–29. ISBN 978-0-07-147692-8.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help);|first=missing|last=(help); Explicit use of et al. in:|first=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Valle, Rafael F. "Cervical Stenosis: A Challenging Clinical Entity". Journal of Gynecologic Surgery. 18 (4): 129–43. doi:10.1089/104240602762555939.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Casey, Petra M. "Abnormal Cervical Appearance: What to Do, When to Worry?". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 86 (2): 147–51. doi:10.4065/mcp.2010.0512.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Fujimoto, Victor Y. "Congenital cervical atresia: Report of seven cases and review of the literature". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 177 (6): 1419–25. doi:10.1016/S0002-9378(97)70085-1.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ Patton, PE (Jun 2004). "The diagnosis and reproductive outcome after surgical treatment of the complete septate uterus, duplicated cervix and vaginal septum". American journal of obstetrics and gynecology. 190 (6): 1669–75, discussion 1675-78. PMID 15284765.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Harper, Douglas. "Cervix". Etymology Online. Retrieved 19 March 2014.
- ^ Harper, Douglas. "Horn". Etymology Online. Retrieved 19 March 2014.
- ^ Galen/Johnston (2011). Galen: On Diseases and Symptoms. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 247. ISBN 978-1-139-46084-2.
- ^ McIntyre, Peter (July–August 2006). "Finding the viral link: the story of Harald zur Hausen" (PDF). Cancer World: 32–37.
- ^ McLemore, Monica R. (1 October 2006). "Gardasil®: Introducing the New Human Papillomavirus Vaccine". Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing. 10 (5): 559–60. doi:10.1188/06.CJON.559-560.
- Cited texts
- "Intrapartum care: Care of healthy women and their babies during childbirth". NICE. 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)
External links
 Media related to Cervix uteri at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Cervix uteri at Wikimedia Commons
