Lithuania: Difference between revisions
| [pending revision] | [pending revision] |
back to the shorter table (what's wrong with it? Do you plan to change the name of the country soon or what?) |
Gzornenplatz (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| border=1 align=right cellpadding=4 cellspacing=0 width=300 style="margin: 0 0 1em 1em; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1px #aaaaaa solid; border-collapse: collapse; font-size: 95%;" |
|||
|+<big><big>'''Lietuvos Respublika'''</big></big> |
|||
|- |
|||
| style="background:#efefef;" align="center" colspan=2 | |
|||
{| border="0" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" |
|||
| align="center" width="140px" | [[image:Lithuania flag large.png|125px|Flag of Lithuania]] |
|||
| align="center" width="140px" | [[Image:Vytis.gif|111px|Lithuania: Coat of Arms]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center" width="140px" | ([[Flag of Lithuania|In Detail]]) |
|||
| align="center" width="140px" | ([[Coat of Arms of Lithuania|Full size]]) |
|||
|} |
|||
|- |
|||
| align="center" colspan=2 | <small">''National [[motto]]: None''</small> |
|||
|- |
|||
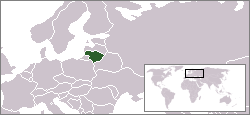
| align=center colspan=2 | [[image:LocationLithuania.png]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[Official language]]''' |
|||
| [[Lithuanian language|Lithuanian]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[Capital]]''' |
|||
| [[Vilnius]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[List of Presidents of Lithuania|President]]''' |
|||
| [[Valdas Adamkus]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[Prime Minister of Lithuania|Prime Minister]]''' |
|||
| [[Algirdas Brazauskas]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[Area]]'''<br> - Total <br> - % water |
|||
| [[List of countries by area|Ranked 128th]] <br> [[1 E10 m²|65,200 km²]] <br> Negligible |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[Population]]'''<br> - Total ([[July 2003]])<br> - [[Population density|Density]] |
|||
| [[List of countries by population|Ranked 125th]]<br> 3,436,561<br> 55.1/km² |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[Gross Domestic Product|GDP]]''' (PPP)<br> - Total ([[Year]])<br> - GDP/head |
|||
| [[List of countries by GDP|Ranked 85th]]<br>$30,080 million<br>$8,400 |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[Independence]]'''<br> - Declared<br> - Recognised<br> - Lost<br>[[Collapse of the Soviet Union|Independence]]<br> - Declared<br> - Recognised |
|||
| From [[Imperial Russia]]<br>[[16 February]] [[1918]]<br>[[12 July]] [[1920]]<br>[[1940]]<br>From [[Soviet Union]]<br>[[11 March]] [[1990]]<br>[[4 February]] [[1991]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[Currency]]''' |
|||
| [[Litas]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[Time zone]]''' |
|||
| [[East European Time|EET]] ([[UTC]]+2; [[UTC]]+3 in [[European Summer Time|summer]]) |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[National anthem]]''' |
|||
| ''[[Tautiska Giesme]]'' |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[Top-level domain|Internet TLD]]''' |
|||
| [[.lt]] |
|||
|- |
|||
| '''[[List_of_country_calling_codes|Calling Code]]''' |
|||
| 370 |
|||
|} |
|||
The '''Republic of Lithuania''' ([[Lithuanian language|Lithuanian]] - '''Lietuva''', [[Polish language|Polish]] - Litwa, [[German language|German]] - Litauen, [[French language|French]] - Lituanie, [[Spanish language|Spanish]] - Lituania, [[Estonian language|Estonian]] - Leedu, [[Finnish language|Finnish]] - Liettua) is a [[republic]] in [[Northeastern Europe]]. One of the three [[Baltic States]] along the [[Baltic Sea]], it shares borders with fellow Baltic State [[Latvia]] to the north, [[Belarus]] to the southeast, [[Poland]] to the south and the [[Kaliningrad Oblast]] of [[Russia]] to the southwest. |
The '''Republic of Lithuania''' ([[Lithuanian language|Lithuanian]] - '''Lietuva''', [[Polish language|Polish]] - Litwa, [[German language|German]] - Litauen, [[French language|French]] - Lituanie, [[Spanish language|Spanish]] - Lituania, [[Estonian language|Estonian]] - Leedu, [[Finnish language|Finnish]] - Liettua) is a [[republic]] in [[Northeastern Europe]]. One of the three [[Baltic States]] along the [[Baltic Sea]], it shares borders with fellow Baltic State [[Latvia]] to the north, [[Belarus]] to the southeast, [[Poland]] to the south and the [[Kaliningrad Oblast]] of [[Russia]] to the southwest. |
||
Capital city - [[Vilnius]] (from [[1323]] till [[1919]] and from [[1940]] till now). From [[1919]] till [[1940]] [[Kaunas]] was capital city of Lithuania. |
Capital city - [[Vilnius]] (from [[1323]] till [[1919]] and from [[1940]] till now). From [[1919]] till [[1940]] [[Kaunas]] was capital city of Lithuania. |
||
{{Lithuania infobox}} |
|||
== History == |
== History == |
||
''Main article: [[History of Lithuania]]'' |
''Main article: [[History of Lithuania]]'' |
||
Revision as of 04:56, 10 January 2005
| |||||
| <small">National motto: None | |||||
| |||||
| Official language | Lithuanian | ||||
| Capital | Vilnius | ||||
| President | Valdas Adamkus | ||||
| Prime Minister | Algirdas Brazauskas | ||||
| Area - Total - % water |
Ranked 128th 65,200 km² Negligible | ||||
| Population - Total (July 2003) - Density |
Ranked 125th 3,436,561 55.1/km² | ||||
| GDP (PPP) - Total (Year) - GDP/head |
Ranked 85th $30,080 million $8,400 | ||||
| Independence - Declared - Recognised - Lost Independence - Declared - Recognised |
From Imperial Russia 16 February 1918 12 July 1920 1940 From Soviet Union 11 March 1990 4 February 1991 | ||||
| Currency | Litas | ||||
| Time zone | EET (UTC+2; UTC+3 in summer) | ||||
| National anthem | Tautiska Giesme | ||||
| Internet TLD | .lt | ||||
| Calling Code | 370 | ||||
The Republic of Lithuania (Lithuanian - Lietuva, Polish - Litwa, German - Litauen, French - Lituanie, Spanish - Lituania, Estonian - Leedu, Finnish - Liettua) is a republic in Northeastern Europe. One of the three Baltic States along the Baltic Sea, it shares borders with fellow Baltic State Latvia to the north, Belarus to the southeast, Poland to the south and the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia to the southwest.
Capital city - Vilnius (from 1323 till 1919 and from 1940 till now). From 1919 till 1940 Kaunas was capital city of Lithuania.
History
Main article: History of Lithuania
First mentioned in 1009, Lithuania grew to be a significant nation in the Middle Ages. Lithuania became an independent multi-ethnic Grand Duchy that eventually stretched across much of Eastern Europe. In the 16th century, it joined with Poland in a personal union under one monarch as the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. This union remained until the partitions of Poland in 1795 when Lithuania was itself annexed by Imperial Russia.
Under the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, a smaller Lithuania established its independence in February 1918 as a part of German planned Mitteleuropa, in the aftermath of the Russian Revolution, and then as a republic in November, after Germany's defeat in World War I. The republic intended to consolidate territories where Lithuanians lived and turned down the idea to re-establish union with Poland. It subsequently was plagued by territorial disputes with Poland (over Central Lithuania and Suvalkija/Suwalki) and Germany (over Klaipėda), and it became a dictatorship in 1926. It was annexed by the Soviet Union in 1940 during World War II.
Communist rule ended after the advent of glasnost and Lithuania proclaimed its renewed independence on 11 March 1990, the first Soviet republic to do so, though Soviet forces unsuccessfully tried to suppress this until September 1991.
On February 4, 1991 Iceland became the first country to recognise Lithuanian independence. Moldova did the same thing on May 31, 1991. These countries were followed by Russian Federation on July 29, 1991 (while the central government of the USSR didn't recognise Lithuanian independence till the beginning of September 1991) and Croatia on August 3, 1991.
Lithuania was admitted into the United Nations on September 17, 1991. Lithuania has since sought closer ties with the West and so became a member of NATO on 29 March 2004 and of the European Union on 1 May 2004.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Lithuania
The Lithuanian head of state is the president, elected directly for a five-year term, who also functions as commander in chief overseeing foreign and security policy. The president, on the approval of the parliament, also appoints the prime minister and on the latter's nomination the rest of the cabinet, as well as a number of other top civil servants and the judges for all courts, including the Constitutional Court (Konstitucinis Teismas).
The unicameral Lithuanian parliament, the Seimas, has 141 members that are elected for a four-year term. About half of the members of this legislative body are elected in single constituencies (71), and the other half (70) are elected in the nationwide vote by proportional representation. A party must receive at least 5% of the national vote to be represented in the Seimas.
Counties
Main article: Counties of Lithuania
Lithuania consists of 10 counties (apskritys, singular - apskritis), each named after their principal city. The counties are subdivided into 56 municipalities, both cities and districts (see: List of municipalities in Lithuania). This administrative division was created in 1994.

- Alytus County (Alytaus apskritis)
- Kaunas County (Kauno apskritis)
- Klaipėda County (Klaipėdos apskritis)
- Marijampolė County (Marijampolės apskritis)
- Panevėžys County (Panevėžio apskritis)
- Šiauliai County (Šiaulių apskritis)
- Tauragė County (Tauragės apskritis)
- Telšiai County (Telšių apskritis)
- Utena County (Utenos apskritis)
- Vilnius County (Vilniaus apskritis)
Geography
Main article: Geography of Lithuania
The largest and most populous of the Baltic states, Lithuania is a partly maritime country with about 100 km of sandy coastline, of which only 38 km face the open Baltic Sea. Lithuania's major warm-water port of Klaipėda lies at the narrow mouth of Kuršių Marios (Curonian Lagoon), a shallow lagoon extending south to Kaliningrad. The main river Nemunas and some of its tributaries are used for internal shipping.
The Lithuanian landscape is glacially flat, except for morainic hills in the western uplands and eastern highlands no higher than 300 m, with the highest point being the Juozapinės at 292 m. The terrain is marked by numerous lakes (e.g. Lake Vištytis) and swamps, and a mixed forest zone covers 30% of the country. The climate lies between maritime and continental, with wet, moderate winters and summers. According to some geographers, Lithuania's capital, Vilnius, lies a few kilometres south of the geographical centre of Europe.
Lithuania consists of historical and cultural regions:
- Aukštaitija (literally the Highlands).
- Samogitia, (also known as Žemaitija, or literally the Lowlands).
- Lithuania Minor (Mažoji Lietuva) also known as Prussian Lithuania (Prūsų Lietuva).
- Dzūkija (Dzūkija or Dainava).
- Sudovia (Sūduva or Suvalkija).
Economy
Main article: Economy of Lithuania
In 2003 Lithuania had the highest economic growth ratio among all European Union candidates, reaching 8,8% in third quarter. In the first quarter of 2004, GDP growth rate of 7.7% reflects impressive economic development in Lithuania. Before 1998 Lithuania, the Baltic state that has conducted the most trade with Russia, however the 1998 Russian financial crisis forced country to orient toward the West. Lithuania has gained membership of the World Trade Organization and joined the European Union on 1 May 2004. Accession to EU reduced previously high unemployment, to 7.0% in 2004. Lithuania has almost finished privatization of the large, state-owned utilities, with one of two power distribution networks and railways left. The litas, the national currency, has been pegged to the euro since 2 February 2002 at a rate of EUR 1.00 = LTL 3.4528 and country is expected to switch to euro one of the first among new accession countries in 2006.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Lithuania
Over 80% of the Lithuanian population is ethnically Lithuanian and speaks the Lithuanian language, one of the two remaining living members of the Baltic language group, which is also the only official state language. Several sizable minorities exist, such as Russians (8%), Poles (7%) and Belarusians (1.5%), and each respective language is also spoken in Lithuania.
The predominant religion is Roman Catholicism, but Eastern Orthodoxy, Protestantism (especially Calvinism) and Judaism also exist as minority religions.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Lithuania
Lithuanians Abroad
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Lithuania
- Transportation in Lithuania
- Military of Lithuania
- Foreign relations of Lithuania
- Tourism in the Baltics
- Holidays in Lithuania
- List of cities in Lithuania
- Sports in Lithuania
- List of Lithuanian rulers
External links
- Lithuanian Central Internet Gates - Main Lithuanian portal
- Vyriausybe - Official governmental site
- Prezidentas - Official presidential site
- Seimas - Official parliamentary site
- Lithuania Online - Wide collection of Lithuanian links
- Istorija.net - Pages and forum on the history of Lithuania (in Lithuanian, English, Russian)