Mydriasis: Difference between revisions
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
===Mydriatic drops=== |
===Mydriatic drops=== |
||
[[Image:Dilated_pupil.gk.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Pupil dilated using [[ |
[[Image:Dilated_pupil.gk.jpg|thumb|200px|right|Pupil dilated using the [[anti-cholinergic]] drug [[tropicamide]].]] |
||
A '''mydriatic''' is an agent which induces [[dilation]] of the [[pupil]]. Drugs such as [[tropicamide]] are used in [[medicine]] to permit examination of the [[retina]] and other deep structures of the eye, and also to reduce painful [[ciliary muscle]] [[muscle spasm|spasm]] (see [[cycloplegia]]). One effect of administration of a mydriatic is intolerance to bright light. |
A '''mydriatic''' is an agent which induces [[dilation]] of the [[pupil]]. Drugs such as [[tropicamide]] are used in [[medicine]] to permit examination of the [[retina]] and other deep structures of the eye, and also to reduce painful [[ciliary muscle]] [[muscle spasm|spasm]] (see [[cycloplegia]]). One effect of administration of a mydriatic is intolerance to bright light. |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 05:43, 8 October 2008
- "Dilated pupil" redirects here. An eye examination sometimes requires the dilation of the pupil.
| Mydriasis |
|---|
Mydriasis is an excessive dilation of the pupil due to disease, trauma or drugs. Normally, the pupil dilates in the dark and constricts in the light. A mydriatic pupil will remain excessively large, even in a bright environment. Sometimes colloquially referred to as a "blown pupil."
The opposite, constriction of the pupil, is called miosis.
Mechanism
There are two types of muscle that control the size of the iris: circular muscle and radial muscle. The former is innervated by the parasympathetic nervous system, the latter by the sympathetic nervous system. Sympathetic stimulation of α1 adrenergic receptors causes the contraction of the radial muscle, and subsequent dilation of the pupil. Conversely, parasympathetic stimulation cause contraction of the circular muscle and constriction of the iris.
The mechanism of mydriasis depends on the agent being used. It usually involves either a disruption of the parasympathetic nerve supply to the eye (which causes contraction of the pupil), or over activity of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS).
Causes
Physiological
Endorphin release as found in strong sexual arousal can lead to temporal mydriasis, rather than the minor dilation found during sexual affection. Orgasm has been reported to lead to pupillary block [1] in a single case in combination with an ocular precondition. Here the parasympathetic and sympathetic stimulation lead to sphincter muscle stimulation during pupillary dilation in the dark, while ciliary contraction caused zonular relaxation leading to pupillary block and angle-closure in combination with pre-existing narrow chamber angle.
Pathological
The parasympathetic nervous supply which causes constriction of the pupil, or miosis, is supplied by cranial nerve III, the oculomotor nerve. Damage to this nerve typically manifests itself as mydriasis, because the sympathetic supply to the pupil which causes mydriasis remains unaffected, and therefore unopposed. Multiple central nervous system disorders e.g. epilepsy, stroke are known to lead to temporal mydriasis as well.
Traumatic
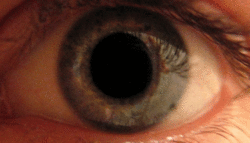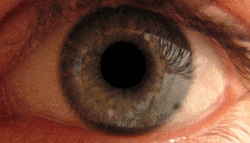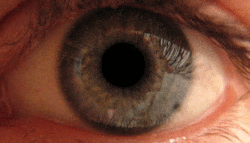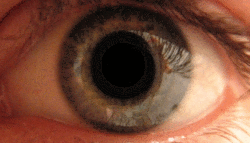
In cases of head injury or orbit trauma (eye injury), the iris sphincter (the muscle responsible for closing the pupil) or the nerves controlling it can be damaged, reducing or eliminating reactivity to light.
Drugs
Cyclomydril is an ophthalmic medication intended to cause mydriasis[2], usually to allow an optometrist or ophthalmologist to perform a better visual inspection of the inside of an eye.
Atropine blocks muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system and blocking its action means the pupil cannot constrict.
Cocaine inhibits the reuptake of noradrenaline (norepinephrine) within a nerve synapse. When a solution of cocaine is dropped into the eye, noradrenaline is no longer reabsorbed by neurons, and its levels increase. Noradrenaline, the neurotransmitter for the SNS, causes dilation of the pupil. Mydriasis is used as a diagnostic test for Horner's Syndrome, in which it is initiated using a similar mechanism, though cocaine is not usually used in this procedure. Many other drugs such as amphetamines and psychedelic drugs (LSD, psychedelic mushrooms, mescaline, and MDMA) are also known to cause mydriasis.
Opiate withdrawal can cause dilated pupils in some people. [3] Opiates normally lead to miosis or the constriction of the pupils.
Antihistamines and tricyclic antidepressants may cause mydriasis.
Mydriatic drops

A mydriatic is an agent which induces dilation of the pupil. Drugs such as tropicamide are used in medicine to permit examination of the retina and other deep structures of the eye, and also to reduce painful ciliary muscle spasm (see cycloplegia). One effect of administration of a mydriatic is intolerance to bright light.
References
- ^ Ritch, R.; Dorairaj, J. M.; Liebmann (16 February 2007), "Angle-closure triggered by orgasm: a new provocative test?", Eye, 21: 872–874, doi:10.1038/sj.eye.6702744
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|link=ignored (help)CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Cyclomydril
- ^ http://www.nd.gov.hk/chapter_4b2_eng.pdf
