QR code: Difference between revisions
m Reverted 1 edit by 98.231.88.15 identified as vandalism to last revision by Dancter. using TW |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
== Use as artwork == |
== Use as artwork == |
||
[[Image:WalrusAndCarpenter.png|thumb|left|Colorized QR-code version of a Lewis Carroll poem.]] |
|||
The design of QR makes it possible to incorporate eye-catching images of logos, characters, or photos into QR code, without losing any information of the code. |
|||
The colorized image represents the first 12 stanzas of [[Lewis Carroll]]'s "[[The Walrus and the Carpenter]]". Encoded in binary mode with "Level M" error correction it contains approximately 2300 characters, but, due to the density of the information, decoding it would require a high resolution image that is unavailable to many QR Code readers (particularly mobile phones). |
|||
British popgroup [[Pet Shop Boys]] used QR-code for the artwork of their download-only single [[Integral (song)|Integral]] in 2007. The videoclip for the song also features QR-code. When the codes are scanned correctly, users are directed to the Pet Shop Boys website, and web pages about the [[British national identity card]] plans, respectively. |
British popgroup [[Pet Shop Boys]] used QR-code for the artwork of their download-only single [[Integral (song)|Integral]] in 2007. The videoclip for the song also features QR-code. When the codes are scanned correctly, users are directed to the Pet Shop Boys website, and web pages about the [[British national identity card]] plans, respectively. |
||
In 2009, QR-code was used for the marketing campaign of the Movie [[9 (2009 film)|9]] at the [[San Diego Comic Con]]. Cards with QR-codes integrated into the artwork were handed out to patrons. These limited edition cards could be read with QR-capable cellphone or presented to the Focus Features both for prizes and access to exclusive stories about each character in the movie. |
|||
== See also == |
== See also == |
||
Revision as of 22:00, 7 October 2009
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2008) |
A QR Code is a matrix code (or two-dimensional bar code) created by Japanese corporation Denso-Wave in 1994. The "QR" is derived from "Quick Response", as the creator intended the code to allow its contents to be decoded at high speed.
QR Codes are common in Japan, where they are currently the most popular type of two dimensional codes. Moreover, most current Japanese mobile phones can read this code with their camera.
Overview
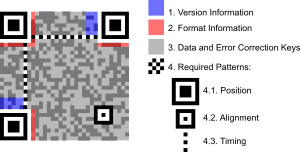
Although initially used for tracking parts in vehicle manufacturing, QR Codes are now used in a much broader context, including both commercial tracking applications and convenience-oriented applications aimed at mobile phone users (known as mobile tagging).
QR Codes storing addresses and URLs may appear in magazines, on signs, buses, business cards or just about any object that users might need information about. Users with a camera phone equipped with the correct reader software can scan the image of the QR Code causing the phone's browser to launch and redirect to the programmed URL. This act of linking from physical world objects is known as a hardlink or physical world hyperlinks.
Users can also generate and print their own QR Code for others to scan and use by visiting one of several free QR Code generating sites.
Standards

There are several standards documents covering the physical encoding of QR Code:[1]
- October 1997 — AIM International[2]
- January 1999 — JIS X 0510
- June 2000 — ISO/IEC 18004:2000 Information technology — Automatic identification and data capture techniques — Bar code symbology — QR Code (now withdrawn)
Defines QR Code Model 1 and QR Code Model 2 symbols. - 1 September 2006 — ISO/IEC 18004:2006 Information technology — Automatic identification and data capture techniques — QR Code 2005 bar code symbology specification
Defines QR Code 2005 symbols, an extension of QR Code Model 2. Does not specify how to read QR Code Model 1 symbols, or require this for compliance.
At the application layer, there is some variation between implementations. NTT docomo has established de facto standards for the encoding of URLs, contact information, and several other data types.[3] Google's open-source "zxing" project maintains a list of QR Code data types.[4]
License
QR Code is an open format - the format's specification is available royalty-free from its owner, who has promised not to exert patent rights on it.[1] The term QR Code itself is a registered trademark of Denso Wave Incorporated.[5]
Storage
| QR Code data capacity[6] | |
|---|---|
| Numeric only | Max. 7,089 characters |
| Alphanumeric | Max. 4,296 characters |
| Binary (8 bits) | Max. 2,953 bytes |
| Kanji/Kana | Max. 1,817 characters |
| Error correction capacity | |
|---|---|
| Level L | 7% of codewords can be restored. |
| Level M | 15% of codewords can be restored. |
| Level Q | 25% of codewords can be restored. |
| Level H | 30% of codewords can be restored. |
QR codes use the Reed–Solomon error correction.
Variants
Micro QR Code is a smaller version of the QR Code standard for applications with less ability to handle large scans.
There are different forms of Micro QR Code as well. The highest of these can hold 35 characters.
Use as artwork
British popgroup Pet Shop Boys used QR-code for the artwork of their download-only single Integral in 2007. The videoclip for the song also features QR-code. When the codes are scanned correctly, users are directed to the Pet Shop Boys website, and web pages about the British national identity card plans, respectively.
See also
- Aztec Code
- Barcode
- Data Matrix
- CueCat
- High Capacity Color Barcode
- PDF417
- Semacode
- ShotCode
- Object hyperlinking
- touchatag
References
- ^ a b "QR Code Standardization | QR Code.com". Denso-wave.com. Retrieved 2009-04-23.
- ^ "AIM GLOBAL Online Store". Aimglobal.org. Retrieved 2009-04-23.
- ^ "Synchronization with Native Applications". NTT docomo. Retrieved 17 February 2009.
- ^ "Barcode Contents". zxing – A rough guide to standard encoding of information in barcodes. Retrieved 17 February 2009.
- ^ "QR Code.com". Denso-wave.com. 2003-11-06. Retrieved 2009-04-23.
- ^ "About 2D Code | QR Code.com". Denso-wave.com. Retrieved 2009-04-23.


