Cnut: Difference between revisions
name in infobox should match the title of the article |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox royalty |
{{Infobox royalty |
||
|name=Cnut the Great |
|name=Cnut the Great |
||
|title=King of |
|title=King of Denmark, England, Norway and parts of Sweden. |
||
|image=Cnut_the_Great_Obverse.jpg |
|image=Cnut_the_Great_Obverse.jpg |
||
|caption=Coin of Cnut the Great from the [[British Museum]] |
|caption=Coin of Cnut the Great from the [[British Museum]] |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Cnut the Great''' ({{lang-ang|Cnūt}}; [[Old Norse]]: ''Knūtr inn rīki'';<ref>Modern languages: {{lang-no|Knut den mektige}}, {{lang-sv|Knut den Store}}, {{lang-da|Knud den Store}}, {{lang-pl|Kanut Wielki}}</ref> [[circa|c.]] 985 or 995 – 12 November 1035), also known as '''Canute''' or '''Knut''' or '''Cnut Sweynsson''', was a [[Viking]] king of [[ |
'''Cnut the Great''' ({{lang-ang|Cnūt}}; [[Old Norse]]: ''Knūtr inn rīki'';<ref>Modern languages: {{lang-no|Knut den mektige}}, {{lang-sv|Knut den Store}}, {{lang-da|Knud den Store}}, {{lang-pl|Kanut Wielki}}</ref> [[circa|c.]] 985 or 995 – 12 November 1035), also known as '''Canute''' or '''Knut''' or '''Cnut Sweynsson''', was a [[Viking]] king of [[Denmark]], [[England]], [[Norway]] and parts of [[Sweden]]. As a [[statesman]], with notable successes in [[politics]] and the [[military]], and the importance of his legacy - if now obscure - Cnut seems to have been one of the greatest figures of [[History of Europe#Middle Ages|medieval Europe]]. Until recently though his achievements were largely lost to history, after the death of his heirs within a decade of his own and the [[Norman conquest of England]] in 1066. |
||
As a [[prince]] of Denmark, Cnut won the throne of England in 1016 in the wake of [[Viking Age#Northwestern Europe|centuries of Viking activity]] throughout the [[British Isles]]. His accession to the [[Daner|Danish]] throne within a couple of years in 1018 brought the crowns of England and Denmark together. Cnut held this power-base together by uniting Danes and Englishmen under cultural bonds of wealth and custom, rather than sheer brutality. After a decade of conflict with opponents in [[Scandinavia]], Cnut claimed the crown of Norway in [[Trondheim]] in 1028. Sweden's capital at [[Sigtuna]] was held by Cnut.<ref>Graslund, B.,'Knut den store och sveariket: Slaget vid Helgea i ny belysning', ''Scandia'', vol. 52 (1986), pp. 211–238.</ref> He had coins struck which called him king there, but no record of a coronation survives. |
As a [[prince]] of Denmark, Cnut won the throne of England in 1016 in the wake of [[Viking Age#Northwestern Europe|centuries of Viking activity]] throughout the [[British Isles]]. His accession to the [[Daner|Danish]] throne within a couple of years in 1018 brought the crowns of England and Denmark together. Cnut held this power-base together by uniting Danes and Englishmen under cultural bonds of wealth and custom, rather than sheer brutality. After a decade of conflict with opponents in [[Scandinavia]], Cnut claimed the crown of Norway in [[Trondheim]] in 1028. Sweden's capital at [[Sigtuna]] was held by Cnut.<ref>Graslund, B.,'Knut den store och sveariket: Slaget vid Helgea i ny belysning', ''Scandia'', vol. 52 (1986), pp. 211–238.</ref> He had coins struck which called him king there, but no record of a coronation survives. |
||
Revision as of 22:51, 7 November 2009
| Cnut the Great | |
|---|---|
| King of Denmark, England, Norway and parts of Sweden. | |
 Coin of Cnut the Great from the British Museum | |
| King of Denmark | |
| Reign | 1018–1035 (18 years) |
| Predecessor | Harald II |
| Successor | Harthacnut |
| King of England | |
| Reign | 1016–1035 (20 years) |
| Predecessor | Edmund Ironside |
| Successor | Harold Harefoot |
| King of Norway | |
| Reign | 1028–1035 (7 years) |
| Predecessor | Olaf Haraldsson |
| Successor | Magnus Olafsson |
| King of parts of Sweden | |
| Reign | 1026-1030 (4 years) |
| Predecessor | Anund Jacob |
| Successor | Anund Jacob |
| Burial | Old Minster, Winchester. Bones now in Winchester Cathedral |
| Spouse | Ælfgifu of Northampton Emma of Normandy |
| Issue | Sweyn Knutsson Harold Harefoot Harthacnut Gunhilda of Denmark |
| Father | Sweyn Forkbeard |
| Mother | Sigrid the Haughty also known as Gunnhilda |
Cnut the Great (Old English: Cnūt; Old Norse: Knūtr inn rīki;[1] c. 985 or 995 – 12 November 1035), also known as Canute or Knut or Cnut Sweynsson, was a Viking king of Denmark, England, Norway and parts of Sweden. As a statesman, with notable successes in politics and the military, and the importance of his legacy - if now obscure - Cnut seems to have been one of the greatest figures of medieval Europe. Until recently though his achievements were largely lost to history, after the death of his heirs within a decade of his own and the Norman conquest of England in 1066.
As a prince of Denmark, Cnut won the throne of England in 1016 in the wake of centuries of Viking activity throughout the British Isles. His accession to the Danish throne within a couple of years in 1018 brought the crowns of England and Denmark together. Cnut held this power-base together by uniting Danes and Englishmen under cultural bonds of wealth and custom, rather than sheer brutality. After a decade of conflict with opponents in Scandinavia, Cnut claimed the crown of Norway in Trondheim in 1028. Sweden's capital at Sigtuna was held by Cnut.[2] He had coins struck which called him king there, but no record of a coronation survives.
Cnut extended his authority into the Irish Sea, keeping the rival powers around its coasts in check.[3]. In light of the struggles of the Danes for preeminence within Scandinavia, Cnut's rule was definitely felt by the sea-kingdoms of the Viking settlers among the Celtic nations; known as the Gall Gaidel. These were the Kingdom of the Isles (probably under direct overlordship through one of his lieutenants[4]) in the Sea of the Hebrides, and the Kingdom of Dublin (probably on the terms of vassal and suzerain),[5] in the Irish Sea. His chief goal was to control the western seaways to and from Scandinavia, and to check the might of the Earls of Orkney.[6] At the height of his power, Cnut held certain Gaelic kingdoms[7] and the Ui Imhair sea-kingdom of Echmarcach mac Ragnaill[8] as client vassals, too.
Cnut's possession of England's archdioceses and the continental diocese of Denmark – with a claim lain upon it by the Holy Roman Empire's Hamburg-Bremen archdiocese – gave him leverage within the Church to gain concessions on the tolls his people had to pay on the way to Rome. He also gained concessions on the price of the pallium of his bishops, from the Pope, and other magnates of medieval Christendom, at the coronation of the Holy Roman Emperor. After his 1026 victory against Norway and Sweden and on his way to Rome for the coronation, Cnut proclaimed himself in a letter, king of all England and Denmark and the Norwegians and of some of the Swedes.[9]
Birth and kingship
Cnut was a son of the Danish king Sweyn Forkbeard, and an heir to a line of Scandinavian rulers central to the unification of Denmark.[10] Its origins were in the figure of Harthacnut, founder of the royal house, and the father to Gorm the Old, its official progenitor. His mother's name is unknown, although the Slavic princess, Saum-Aesa, daughter to Mieszko I of Poland (in accord with the Monk of St Omer's, Encomium Emmae[11] and Thietmar of Merseburg's contemporary Chronicon[12]), is a possibility.[13] His brother Harald was the first born and crown prince.
Some hint at Cnut's childhood can be found in the Flateyjarbók, a 13th-century source, stating at one point that Cnut was taught his soldiery by the chieftain Thorkell the Tall,[14] brother to Sigurd, Jarl of mythical Jomsborg, and the legendary Joms, at their Viking stronghold on the Island of Wollin, off the coast of Pomerania. Although his date of birth, like his mother's name, is unknown. Contemporary works such as the Chronicon and the Encomium Emmae, do not mention it. Even so, in a Knútsdrápa by the skald Óttarr svarti, there is a statement that Cnut was "of no great age" when he first went to war.[15] It also mentions a battle identifiable with Forkbeard's invasion of England, and attack on the city of Norwich, in 1003/04, after the St. Brice's Day massacre of Danes by the English, in 1002. If it is the case that Cnut was part of this, his birthdate may be near 990, or even 980. If not, and the skald's poetic verse envisages another assault, with Forkbeard's conquest of England in 1013/14, it may even suggest a birth date nearer 1000.[16] There is a passage of the Encomiast's (as the author of the Encomium Emmae is known) with a reference to the force Cnut led in his English conquest of 1015/16. Here (see below) it says all the Vikings were of "mature age" under Cnut "the king".
A description of Cnut can be found within the 13th-century Knýtlinga saga:
Knutr was exceptionally tall and strong, and the handsomest of men, all except for his nose, that was thin, high-set, and rather hooked. He had a fair complexion none-the-less, and a fine, thick head of hair. His eyes were better than those of other men, both the handsomer and the keener of their sight.
Hardly anything is known for sure of Cnut's life until the year he was part of a Scandinavian force under his father, king Sweyn; with his invasion of England in summer 1013. It was the climax to a succession of Viking raids spread over a number of decades. The kingdom fell quickly, and near the end of the year King Aethelred fled to Normandy, leaving Sweyn in possession of England. In the following weeks, Forkbeard was in the process of consolidating his kingship, with Cnut left in charge of the fleet, and the base of the army at Gainsborough.
On the death of Forkbeard after 5 weeks as king, in February 1014, Harald succeeded him as King of Denmark, while Cnut was acclaimed king by the Danish army in England.[19] However, the English nobility took a different view, and the Witenagemot recalled Aethelred from Normandy. The restored king swiftly led an army against Cnut, who fled with his army to Denmark, along the way mutilating the hostages they had taken and abandoning them on the beach at Sandwich.[20] Cnut went to Harald and supposedly made the suggestion they might have a joint kingship, although this found no favour with his brother.[19] Harald is thought to have offered Cnut command of his forces for another invasion of England, on the condition he did not continue to press his claim.[19] In any case, Cnut was able to assemble a large fleet with which to launch another invasion.[20]
Conquest of England


In the summer of 1015, Cnut's fleet set sail for England with a Danish army of perhaps 10,000 in 200 longships.[21] Among the allies of Denmark was Boleslaw the Brave, the Duke of Poland and a relative to the Danish royal house. He lent some Slav troops,[22] likely to have been a pledge made to Cnut and Harald when, in the winter, they "went amongst the Wends" to fetch their mother back to the Danish court. She had been sent away by their father after the death of the Swedish king Eric the Victorious in 995, and his marriage to Sigrid the Haughty, the Swedish queen mother. With this wed-lock there was a strong alliance between the successor to the throne of Sweden, Olof Skotkonung, and the rulers of Denmark, his in-laws.[22] And the Swedes were certainly among the allies in the English conquest.
Eiríkr Hákonarson, was another a relative to the Danish royal house, and Trondejarl, the Earl of Lade, and the co-ruler of Norway, with his brother Svein Hakonarson, under Danish sovereignty - Norway was won by the Danes, with the Swedes in alliance, as well as Norwegians, at the Battle of Svolder, in 999. Eiríkr's participation in the invasion left his son Hakon to rule Norway, with Svein. At the Battle of Nesjar, in 1016, Olaf Haraldsson won the kingdom for himself. With this defeat, and the death of Svein while retreating to Sweden, intent on returning to Norway with reinforcements, Hakon went to join his father and support Cnut in England too.
Cnut was at the head of an array of Vikings from all over Scandinavia. The invasion force was to be in often close and grisly warfare with the English for the next fourteen months. Practically all of the battles were fought against Ethelred the Unready's son, Edmund Ironside.
Landing in Wessex
According to the Peterborough manuscript of the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, early in September 1015 [Cnut] came into Sandwich, and straightway sailed round Kent to Wessex, until he came to the mouth of the Frome, and harried in Dorset and Wiltshire and Somerset.[23] A passage from Emma's Encomium paints a colourful picture of Cnut's fleet:
[T]here were so many kinds of shields, that you could have believed that troops of all nations were present. ... Gold shone on the prows, silver also flashed on the variously shaped ships. ... For who could look upon the lions of the foe, terrible with the brightness of gold, who upon the men of metal, menacing with golden face, ... who upon the bulls on the ships threatening death, their horns shining with gold, without feeling any fear for the king of such a force? Furthermore, in this great expedition there was present no slave, no man freed from slavery, no low-born man, no man weakened by age; for all were noble, all strong with the might of mature age, all sufficiently fit for any type of fighting, all of such great fleetness, that they scorned the speed of horsemen.
— Encomium Emmae Reginae[24]
At this point Eadric Streona, the Ealdorman of Mercia, deserted Aethelred together with 40 ships and their crews and joined forces with Cnut.[25] Another defector was Thorkell the Tall, a Jomsviking chief who had fought against the Viking invasion of Sweyn Forkbeard, with a pledge of allegiance to the English in 1012.[26] Some explanation for this shift of allegiance may be found in a stanza of the Jómsvíkinga saga which mentions two attacks against Jomsborg's mercenaries while they were in England, with a man known as Henninge among their casualties, a brother of Thorkell's.[27] If the Flateyjarbók is correct in its statement this man was Cnut's childhood mentor, it explains his acceptance of his allegiance - with Jomvikings ultimately in the service of Jomsborg. The 40 ships Eadric brought with him, often thought to be of the Danelaw[27] were probably Thorkell's.[28]
Advance into the north
Cnut went across the Thames at mid-winter and devastated his way northwards across eastern Mercia. Meanwhile Uhtred, Earl of Northumbria and Aethelred's eldest son Edmund Ironside were advancing south into western Mercia, attacking the estates of Eadric Streona. As Cnut advanced into Northumbria, Uhtred abandoned Edmund and returned home to submit to Cnut.[29] He was betrayed by Cnut, who sent a Northumbrian rival, Thurbrand the Hold, to massacre Uhtred and his retinue at the agreed meeting-place. Eiríkr Hákonarson, most likely with another force of Scandinavians, came to support Cnut at this point.[30] and the veteran Norwegian jarl was left in control of Northumbria, while Cnut returned southward towards his ships.
Edmund Ironside's counter-offensive
Edmund now withdrew to London, where he was chosen as king following the death of Aethelred on 23 April 1016. Cnut re-embarked his army on their ships and brought them to London, where they arrived in May and began a siege. He saw to the construction of dikes on the northern and southern flanks; a channel was even dug across the banks of the Thames to the south of the city, for the longships to cut off communications up-river. Edmund, however, had broken out of London before Cnut's encirclement was complete and went to gather an army in Wessex, the traditional heartland of the English monarchy. The Danes pursued him, but were defeated at Penselwood, in Somerset; with a hill in Selwood Forest as the likely location. A subsequent battle at Sherston, in Wiltshire, was fought over two days but left neither side victorious.[31]
Edmund followed the retreating Danes to London and raised the siege, again defeating Cnut in battle near Brentford, but having taken heavy losses he withdrew to Wessex to gather fresh troops. Cnut again placed London under siege, but after unsuccessful attempts to take the city by storm the Danes sailed to Essex, apparently preferring to revert to classic Viking raiding tactics rather than directly confront Edmund in battle again. They landed in the River Orwell and advanced inland, raiding across Mercia and continuing into the south. Edmund, returning eastward with his reinforced army, defeated Cnut at Otford in Kent and drove his army in flight onto the Isle of Sheppey. At this point Eadric Streona, apparently in response to the turning tide of the war, again changed sides and came over to Edmund.[32]
The Danish Conquest of England Completed.

The Danes were again able to escape across the Thames estuary on their ships and from Essex they again mounted a raid into Mercia. In October, as they returned towards their ships they were intercepted by Edmund's army, leading to the Battle of Assandun, the site of which may have been either Ashingdon or Ashdon, both being in Essex. As the two armies clashed Edmund was betrayed by Eadric Streona, whose return to the English side had perhaps only been a ruse, and who now withdrew his forces from the fray, bringing about a decisive English defeat.[33] Edmund, his army shattered, fled westwards. Cnut, with Eadric now back by his side, pursued him into Gloucestershire. Through intermediaries Edmund and Cnut agreed to come to a negotiated settlement, and on an island near Deerhurst they met and concluded a peace treaty, dividing the kingdom between them. All of England north of the Thames was to be the domain of the Danish prince, while all to the south was kept by Edmund, along with London. Edmund died on 30 November, within weeks of the agreement. The circumstances of his death are unknown.[34] As a result, Cnut was left as king of all England. His coronation was at Christmas, with recognition by the nobility in January the next year.
King of England

Cnut, a Viking, was to be one of England's most successful kings. The protection he lent against Viking raiders - with many of them under his command - restored the prosperity that had been increasingly impaired since the resumption of Viking attacks in the 980s before As well as England itself, he was able to restore the overlordship of earlier English kings over much of the British Isles, while the resources he commanded in England helped him to establish control of the majority of Scandinavia.[35]
The government of England
In July 1017, Cnut wed Emma of Normandy, the widow of Aethelred, and daughter of Richard the Fearless, the first Duke of Normandy. With Edmund dead, Cnut was quick to eliminate any prospective challenge from the survivors of the legitimate dynasty. The first year of his reign was marked by the executions of a number English noblemen whom he considered suspect. Aethelred's son Eadwig fled from England but was killed on Cnut's orders.[36] Edmund Ironside's sons Edward and Edmund likewise fled abroad, Edward eventually to Hungary. Emma's sons by Aethelred, Edward the Confessor and Alfred Atheling went into exile among their relatives in Normandy. Cnut put forward Harthacnut, his son by Emma, to be his heir; Svein Knutsson and Harold Harefoot, his two sons from his marriage to Ælfgifu of Northampton, his handfast wife, were kept on the sidelines.
In 1018, having collected a Danegeld amounting to the colossal sum of £72,000 levied nationwide, with an additional £10,500 extracted from London, Cnut paid off his army and sent most of them home. He retained 40 ships and their crews as a standing force in England, financed by an annual tax called heregeld, raised through the same system that had been introduced by Aethelred to gather Danegeld.
Cnut extended the existing trend for multiple shires to be grouped together under a single ealdorman, dividing the country into four large administrative units whose geographical extent was based on the largest and most durable of the separate kingdoms which had preceded the unification of England. The officials responsible for these provinces were designated earls, a title of Scandinavian origin already in localised use in England which now everywhere replaced that of ealdorman. Wessex was initially kept under Cnut's personal control, while Northumbria went to Erik of Hlathir, East Anglia to Thorkel the Tall, and Mercia remained in the hands of Eadric Streona.
This initial distribution of power was short-lived. The chronically treacherous Eadric was executed within a year of Cnut's accession.[36] Mercia passed to one of the leading families of the region, probably first to Leofwine, ealdorman of the Hwicce under Aethelred, but certainly soon to his son Leofric.[37] In 1021 Thorkel the Tall also fell from favour and was outlawed. Following the death of Erik in the 1020s, he was succeeded as Earl of Northumbria by Siward, a lord of unknown origin. Bernicia, the northern part of Northumbria, was theoretically part of Erik and Siward's earldom but throughout Cnut's reign it effectively remained under the control of the English dynasty based at Bamburgh who had dominated the area at least since the early tenth century. They served as junior Earls of Bernicia under the titular authority of the Earl of Northumbria. By the 1030s Cnut's direct administration of Wessex had come to an end, with the establishment of an earldom under Godwin, an Englishman from a powerful Sussex family. In general, after an attempt to govern through his Scandinavian followers in the first few years of his reign, Cnut reverted to reliance on the leading families of the existing English aristocracy.
Affairs to the East
Cnut's brother Harald was possibly at Cnut's coronation, in 1016, maybe even for the conquest, with his return to Denmark, as its king, with part of the fleet, at some point thereafter.It is only certain, though, there was an entry of his name, alongside Cnut's, in a confraternity with Christ Church, Canterbury,[38] in 1018. This, though, is not conclusive, for the entry may have been made in Harald's absence, by the hand of Cnut himself even, which means, while it is usually thought that Harald died in 1018, it is unsure if he was even alive to do this. Entry of his brother's name in the Canterbury codex may have been Cnut's attempt to make his vengeance for Harald's murder good with the Church. Of course, this was maybe just a gesture for a soul to be under God's protection. There is evidence Cnut was in battle with pirates in 1018, with his destruction of the crews of thirty ships,[39] although it is unknown if this was off the English or Danish shores. He himself mentions troubles in his 1019 letter (to England, from Denmark), written as the King of England and Denmark. These events can be seen, with plausibility, to be in connection with the death of Harald. Cnut says he dealt with dissenters to ensure Denmark was free to assist England.[40] His words tell us some of what it is that the situation was:

King Cnut greets in friendship his archbishop and his diocesan bishops and Earl Thurkil and all his earls... ecclesiatic and lay, in England... I inform you that I will be a gracious lord and a faithfull observer of God's rights and just secular law. (He exhorts his ealdormen to assist the bishops in the maintenance of) God's rights... and the benefit of the people.
If anyone, ecclesiastic or layman, Dane or Englishman, is so presumptuous as to defy God's law and my royal authority or the secular laws, and he will not make amends and desist according to the direction of my bishops, I then pray, and also command, Earl Thurkil, if he can, to cause the evil-doer to do right. And if he cannot, then it is my will that with the power of us both he shall destroy him in the land or drive him out of the land, whether he be of high or low rank. And it is my will that all the nation, ecclesiatical and lay, shall steadfastly observe Edgar's laws, which all men have chosen and sworn at Oxford.
Since I did not spare my money, as long as hostility was threatening you, I with God's help have put an end to it. Then I was informed that greater danger was approaching us than we liked at all; and then I went myself with the men who accompanied me to Denmark, from where the greatest injury had come to us, and with God's help I have made it so that never henceforth shall hostility reach you from there as long as you support me rightly and my life lasts. Now I thank Almighty God for his help and his mercy, that I have settled the great dangers which were approaching us that we need fear no danger to us from there; but we may rekon on full help and deliverance, if we need it
— Cnut's letter of 1019[41]
Statesmanship
Cnut was generally remembered as a wise and successful king of England, although this view may in part be attributable to his good treatment of the Church, keeper of the historic record. The medieval Church was adept to success, and put itself at the back of any strong and efficient sovereign, if the circumstances were right for it. Accordingly we hear of him, even today, as a religious man (see below), despite the fact that he was in an arguably sinful relationship, with two wives, and the harsh treatment he dealt his fellow Christian opponents.

Under his reign, Cnut brought together the English and Danish kingdoms, and the people saw a golden age of dominance across Scandinavia, as well as within the British Isles.[42] His campaigns abroad meant the tables of Viking supremacy were stacked in favour of the English, turning the prows of the longships towards Scandinavia. He reinstated the Laws of King Edgar to allow for the constitution of a Danelaw, and the activity of Scandinavians at large. He also reinstituted the extant laws with a series of proclamations to assuage common grievances brought to his attention. Two significant ones were: On Inheritance in case of Intestacy, and, On Heriots and Reliefs. He strengthened the currency, initiating a series of coins of equal weight to those being used in Denmark and other parts of Scandinavia. This meant the markets grew, and the economy of England was able to spread itself, as well as widen the scope of goods to be bought and sold.
King of Denmark
In 1018, Harald II died and Cnut went to Denmark to affirm his succession to the Danish crown as Cnut II. In the 1019 letter (see above) he states his intentions to avert attacks against England. It seems there were Danes in opposition to him, while an attack on the Wends of Pomerania, in which Godwin apparently earned the king's trust with a night-time raid he personally led, may have had something to do with it. Thorkell the Tall, said to be a chieftain of the Jomsvikings, was a former associate of the now Norwegian king, and the difficulties Cnut found in Denmark, as well as with Thorkell, may perhaps beseen in relation to Norwegian pressure on the Danish lands too.
In 1020 Cnut was back in England, his hold on the Danish throne presumably stable. Ulf Jarl, his brother-in-law, was his appointee as regent of Denmark. He left his young son, Harthacnut, in his care. By the time of Olof Skötkonung's death in 1022, and the succession to the Swedish throne of his son, Anund Jacob, another opponent of Cnut, there was cause for a demonstration of Danish strength in the Baltic. Jomsborg, the legendary stronghold of the Jomsvikings, thought to be on an island off the coast of Pomerania, was probably the target of Cnut's expedition.[43] After his banishment from England in 1021, and the clear display of the intentions of the king of England and Denmark to dominate Scandinavian affairs, it seems Thorkell was wont to reconcile himself with Cnut in 1023. The alliance between the kings of Norway and Sweden, against Cnut, though, meant there was soon to be war.
When the Norwegian King Olaf Haraldsson and his ally the Swedish King Anund Jakob took advantage of Cnut's absence and began to launch attacks against Denmark, Ulf gave the discontented freemen cause to accept Harthacnut, still a child, as king. This was a ruse on Ulf's part that amounted to a coup, since the role he had as the caretaker of Harthacnut consequently gave him the reign of the kingdom. When news of these events got to Cnut, he brought together his fleet at set sail for Denmark, to restore himself and deal with Ulf, who got back in line. In a battle known as the Holy River, Cnut and his men fought the Norwegians and Swedes at the mouth of the river Helgea. 1026 is the likely date, and the apparent victory left Cnut as the dominant leader in Scandinavia. Ulfs realignment and participation in the battle did not, in the end, earn the usurper Cnut's forgiveness. Some sources state, at a banquet in Roskilde, the brothers-in-law were playing chess when an argument arose between them, and the next day, Christmas of 1026, one of Cnut's housecarls, with his blessing, killed the jarl, in Trinity Church, the predecessor to Roskilde Cathedral.
Journey to Rome
Cnut was able to accept an invitation to witness the accession of the Holy Roman Emperor, his enemies in Scandinavia apparently at his leisure. He left his affairs in the north, and went from Denmark to the coronation of the King of the Romans, at Easter 1027, in Rome - a pilgrimage of considerable prestige for rulers of Europe in the Middle-Ages; to the heart of Christendom.
On the return journey his letter of 1027, like his letter of 1019, was written to inform his subjects in England of his intentions.[44] It is in this letter he proclaims himself ‘king of all England and Denmark and the Norwegians and of some of the Swedes’.[9] In his letter Cnut says he went to Rome to repent for his sins, pray for redemption, and the security of his subjects, as well as negotiate with the Pope for a reduction in the costs of the pallium for English archbishops,[45] and for a resolution to the competition of the archdioceses of Canterbury, and Hamburg-Bremen, for superiority over the Danish dioceses. He also sought to improve the conditions for pilgrims, as well as merchants, on the road to Rome. In his own words:
... I spoke with the Emperor himself and the Lord Pope and the princes there about the needs of all people of my entire realm, both English and Danes, that a juster law and securer peace might be granted to them on the road to Rome and that they should not be straitened by so many barriers along the road, and harassed by unjust tolls; and the Emperor agreed and likewise King Robert who governs most of these same toll gates. And all the merchants confirmed by edict that my people, both merchants, and the others who travel to make their devotions, might go to Rome and return without being afflicted by barriers and toll collectors, in firm peace and secure in a just law.
— Cnut's letter of 1027[46]
"Robert" in Cnut's text is probably a clerical error for Rudolph, the last ruler of an independent Kingdom of Burgundy. Hence, the solemn word of the Pope, the Emperor, and Rudolph, was by the witness of four archbishops, twenty bishops, and 'innumerable multitudes of dukes and nobles'.[46] This suggests it was before the ceremonies were at an end.[46] It is without doubt he threw himself into his role with zest.[47] His image as the just Christian king, statesman and diplomat, and crusader against unjustness, seems to be one with its roots in reality, as well as one he sought to project.
A good illustration of his status within Europe is the fact Cnut, and the King of Burgundy went alongside the emperor in the imperial procession,[48] and stood shoulder to shoulder with him on the same pedestal.[49] Cnut and the successor of Charlemagne, in accord with various sources,[49] took one another's company like brothers, for they were of a similar age. Conrad gave his guest the sovereignty to lands in the Mark of Schleswig—the land-bridge between the Scandinavian kingdoms and the continent—as a token of their treaty of friendship.[50] Conflict in this area over past centuries was the cause for the construction of the Danevirke, from Schleswig, on the Schlei, and the Baltic Sea coast, to the marches of west Jutland, on the North Sea coast.
His visit to Rome was a triumph. In the verse of Knútsdrápa, Sigvatr Þórðarson praises Cnut, his king, to be "dear to the Emperor, close to Peter".[51] In the days of Christendom, a king seen to be in favour with God could expect to be ruler over a happy kingdom.[51] He was surely in a stronger position, not only with the Church, and the people, but with the alliance of his southern rivals he was able to conclude his conflicts with his rivals in the north. His letter not only tells his countrymen of his achievements in Rome, but also of his ambitions within the Scandinavian world at his arrival home:
... I, as I wish to be made known to you, returning by the same route that I took out, am going to Denmark to arrange peace and a firm treaty, in the counsel of all the Danes, with those races and people who would have deprived us of life and rule if they could, but they could not, God destroying their strength. May he preserve us by his bounteous compassion in rule and honour and henceforth scatter and bring to nothing the power and might of all our enemies! And finally, when peace has been arranged with our surrounding peoples and all our kingdom here in the east has been properly ordered and pacified, so that we have no war to fear on any side or the hostility of individuals, I intend to come to England as early this summer as I can to attend to the equipping of a fleet.
— Cnut's letter of 1027[46]
Cnut was to return to Denmark from Rome, by the road he had set out, make arrangements for some kind of pact with the peoples of Scandinavia - though it is not known precisely what it is that this was, his 1019 letter says he went to Denmark to secure support for his English kingdom, and this was probably the purpose[citation needed] of the endeavours he alludes to through his 1027 letter - and return to England. We can only be sure there were important events on the horizon, and the fleet was probably the one he went to Norway with.
King of Norway and part of Sweden

In the 1027 letter (see above), he considers himself King of all England and Denmark, and the Norwegians, and of some of the Swedes[52] (victory over Swedes suggests Helgea to be a river near Sigtuna, while Sweden's king appears to have been made a renegade, with a hold on the parts of Sweden which were too remote to threaten Cnut, or even for Cnut to threaten him). He also stated his intention proceeding to Denmark, for the secureing of a peace between the kingdoms of Scandinavia.
In 1028, after his return from Rome, through Denmark, Cnut set off from England with a fleet of fifty ships,[53] to Norway, and the city of Trondheim. Olaf Haraldsson stood down, unable to put up any fight, as his nobles were against him, with offers of gold from Cnut, and the apparent resentment for their king's tendency to flay their wives for sorcery.[54] Cnut was crowned king, now of England and Denmark, and Norway (he was not King of Sweden, only some of the Swedes).[22] He entrusted the Earldom of Lade to the former line of earls, in Håkon Eiriksson, with Earl Eiríkr Hákonarson probably dead at this date.[55] Hakon was possibly the Earl of Northumbria after Erik too.[56]
Hakon, a member of a family with a long tradition of hostility towards the independent Norwegian kings, and a relative of Cnut's, was already in lordship over the Isles, with the earldom of Worcester, possibly from 1016–17. The sea-lanes through the Irish Sea and Hebrides, led to Orkney and Norway, and were central to Cnut's ambitions for dominance of Scandinavia, as well as the British Isles. Hakon was meant to be Cnut's lieutenant of this strategic chain. And the final component was his installation as the king's deputy in Norway, after the expulsion of Olaf Haraldsson in 1028. Hakon, though, died in a shipwreck in the Pentland Firth, between the Orkneys and the Scottish mainland, either late 1029 or early 1030.[57]
Upon the death of Hakon, Olaf Haraldsson was to return to Norway, with Swedes in his army. He, though, was to meet his death at the hands of his own people, at the Battle of Stiklestad, in 1030. Cnut's subsequent attempt to rule Norway without the key support of the Trondejarls, through Ælfgifu of Northampton, and his eldest son by her, Sweyn Knutsson, was not a success. It is known as Aelfgifu's Time in Norway, with heavy taxation, a rebellion, and the restoration of the former Norwegian dynasty under Saint Olaf's illegitimate son Magnus the Good.
Overlordship outside his kingdoms

In one of his verses, Cnut's court poet Sigvatr Þórðarson recounts that famous princes brought their heads to Cnut and bought peace. This verse mentions Olaf Haraldsson in the past tense, with his death at the Battle of Stiklestad, in 1030. It was therefore at some point after this, and the consolidation of Norway, Cnut went to Scotland, with an army,[58] and the navy in the Irish Sea,[59] in 1031, to receive, without bloodshed, the submission of three Scottish kings; Maelcolm, Maelbeth, and Iehmarc.[60] One of these kings, Iehmarc, is Echmarcach mac Ragnaill, an Ui Imhair chieftain, and the ruler of a sea-kingdom thought to extend throughout the Irish Sea,[48] with Galloway and the Isle of Man among his domains. In 1036 he was to be king of Dublin.[61]
There is reason to believe Vikings of Ireland were in relations with Cnut already, as they were with Sweyn Forkbeard.[62] A Lausavísa attributable to the skald Óttarr svarti, suggests these relations were on the level of overlordship, when he greets the ruler of the Danes, Irish, English and Island-dwellers.[63] It is a possibility, though, his use of Irish here was meant to mean the Gall Ghaedil kingdoms, rather than the Gaelic kingdoms too. After Brian Boru's victories over Sigtrygg Silkbeard, and the Battle of Clontarf, in 1014, the Vikings were wont to opt for a commercial life in Ireland, rather than one of conquest.[64] Still, when the misinformation-prone Encomiast names among Cnut's domains, not only England, Denmark and Norway, but also Scotia and Britannia,[65] there may be just enough evidence to suggest there is no exaggeration, here, of his lordship over the British Isles.[62]
Relations with the Church
Cnut's actions as a Viking conqueror had made him uneasy with the Church, and the secular people of England. He was already a Christian before he was king, although the Christianization of Scandinavia was not at all complete in his day. His ruthless treatment of the overthrown dynasty, as well as his open relationship with a concubine—Ælfgifu of Northampton, his handfast wife, whom he kept as his northern queen when he wed Emma of Normandy, kept in the south, with an estate in Exeter—did not fit with the emergent ideals of Christendom we now know as courtly love at court, and chivalry between the nobles. It was important for him to reconcile himself with his churchmen, the noblemen and commoners alike. He certainly made an effort in England; more or less with success.
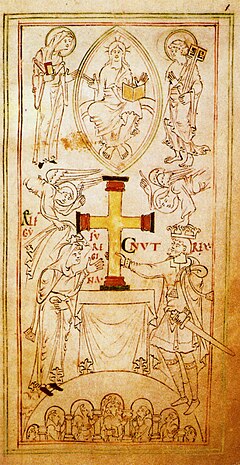
It is hard to conclude if Cnut's attitude towards the Church came out of deep religious devotion, or merely as a means to reinforce his regime's hold on the people. It was probably a bit of a mix. We find evidence of a respect for the Viking religion in his praise poetry, which he was happy enough for his skalds to embellish in Norse mythology, while other Viking leaders were insistent on the rigid observation of the Christian line, like St Olaf.[66] We see too the desire for a respectable Christian nationhood within Europe. In 1018, some sources suggest he was at Canterbury on the return of its Archbishop Lyfing from Rome, to receive letters of exhortation from the Pope.[67] If this chronology is correct, he probably went from Canturbury to the Witan at Oxford, with Archbishop Wulfstan of York in attendance to record the event.[68] Cnut surely saw he was in a potentially useful state of affairs, as far as the Church could be held. With its status as the keeper of the people's health, and the state's general welfare, it was a win-win situation.
His treatment of the Church could not have been kinder. Cnut not only repaired all the English churches and monasteries that were victims of the Viking love for plunder, and refilled their coffers, but he also built new churches, and was a patron of monastic communities. His homeland of Denmark was after all a Christian nation on the rise, and the desire to enhance the religion still fresh. His gifts were widespread, and often exuberant.[69] Commonly land was given, exemption from taxes, as well as relics. Christ Church, was probably given rights at the important port of Sandwich, as well as tax exemption, with confirmation in the placement of their charters on the altar.[68] while it got the relics of St Ælfheah,[70] which was at the displeasure of the people of London. Another see in the king's favour was Winchester, second only to the Canturbury see in terms of its wealth.[71] New Minster's Liber Vitae records Cnut as a benefactor of the monastery,[71] and the Winchester Cross (see image), with 500 marks of silver and 30 marks of gold in, as well as relics of various saints[72] was given to it. Old Minster was the recipient of a shrine for the relics of St Birinus, and the probable confirmation of its privileges.[71] The monastery at Evesham, with its Abbot Ælfweard purportedly a relative of the king, through Ælfgifu the Lady (probably Ælfgifu of Northampton, rather than Queen Emma, also known as Ælfgifu), the ruler of the monastery, got the relics of St Wigstan.[73] Cnut's generosity towards his subjects, a thing his skalds called destroying treasure,[74] was of course popular with the English. Still, it is important to remember, not all Englishmen were in his favour, and the burden of taxation was widely felt.[75] His attitude towards London's see was clearly not benign. The monasteries at Ely and Glastonbury were not it seems on good terms either. Other gifts were also given to his neighbours. Among these were a gift to Chartres, of which its bishiop wrote; "When we saw the gift that you sent us, we were amazed at your knowledge as well as your faith ... since you, whom we had heard to be a pagan prince, we now know to be not only a Christian, but also a most generous donor to God's churches and servants."[71] He is known to have sent a psalter and sacramentary made in Peterborough, famous for its illustrations to Cologne,[76] and a book written in gold, among other gifts, to William the Great of Aquitaine.[76] This golden book was apparently to support Aquitanian claims St Martial, patron saint of Aquitaine was an apostle.[77] Of some consequnce, its recipient was an avid artisan, scholar, and devout Christian, and the Abbey of Saint-Martial was a great library and scriptorium, second only to the one at Cluny. It is probable Cnut's gifts were well beyond anything we can now prove.[76]
Cnut’s journey to Rome in 1027 is another sign of his dedication to the Christian religion. It may be he went to attend Emperor Conrad II’s coronation in order to improve relations between the two powers, yet he had made a vow previously to seek the favour of St Peter, the keeper of the keys to the heavenly kingdom.[78] While in Rome, Cnut got an agreement from the Pope to reduce the fees paid by the English archbishops to receive their pallium. He also arranged for the travelers of his realm that they should pay reduced or no tolls, and that they should be safeguarded on their way to and from Rome. Some evidence exists for a second journey in 1030.[79]
Death & Succession
Cnut died in 1035, at the Abbey in Shaftesbury, Dorset. His burial was in Winchester, the English capital, and stronghold of the house of Wessex the Danes overthrew more or less two decades since. In Denmark he was succeeded by Harthacnut, reigning as Cnut III, although with a war in Scandinavia against Magnus I of Norway, Harthacnut was "forsaken (by the English) because he was too long in Denmark",[80] and his mother Queen Emma, previously resident at Winchester with some of her son's housecarls, was made to flee to Bruges, in Flanders. Harold Harefoot - regent in England 1035–37 - succeeded to claim the throne, in 1037, reigning until his death in 1040. Eventual peace in Scandinavia left Harthacnut free to claim the throne himself, in 1040, and regain his mother her place. He brought the crowns of Denmark and England together again, until his death, in 1042.
The house of Wessex was to reign again in Edward the Confessor, whom Harthacnut had brought out of exile in Normandy and made a treaty. Like in his treaty with Magnus, it was decreed the throne was to go to Edward if Harthacnut died with no legitimate male heir. In 1042, Harthacnut died, and Edward was king. His reign meant Norman influence at Court was on the rise thereafter, and the ambitions of its dukes finally found fruition in 1066, with William the Conqueror's invasion of England, and crowning, fifty years after Cnut was crowned in 1016.
Cnut's sons did not long outlive him, and his (only known) daughter Cunigund was set to marry Conrad II's son Henry III eight months after his death, although she died in Italy before she became empress.[81] The line of Danish rulers in England came to an end within a decade, although its legacy did not.
Bones at Winchester
The new regime of Normandy was keen to signal its arrival with an ambitious programme of grandiose cathedrals and castles throughout the Middle Ages. Winchester Cathedral was built on the old Anglo-Saxon site (Old Minster) and the previous burials were set in mortuary chests there. Then, during the English Civil War, in the 17th century, plundering Roundhead soldiers scattered the bones on the floor, and the bones of Cnut were spread amongst the various other chests of rulers: notably William Rufus.[82]
Marriages and issue
- 1 - Ælfgifu of Northampton
- Sweyn Knutsson, Viceroy of Norway
- Harold Harefoot, King of England
- 2 - Emma of Normandy
- Harthacnut, King of Denmark and England
- Gunhilda of Denmark, wed Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor.
Family tree
Ancestry
| 16. Harthacnut of Denmark | |||||||||||||||||||
| 8. Gorm the Old | |||||||||||||||||||
| 4. Harald I of Denmark | |||||||||||||||||||
| 18. Harald Klak | |||||||||||||||||||
| 9. Thyra | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2. Sweyn Forkbeard | |||||||||||||||||||
| 20. Björn III Eriksson | |||||||||||||||||||
| 10. Olof II Björnsson | |||||||||||||||||||
| 5. Gyrid Olafsdottir | |||||||||||||||||||
| 22. Thrand | |||||||||||||||||||
| 11. Ingeborg Thrandsdotter | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1. Cnut | |||||||||||||||||||
| 24. Lestko | |||||||||||||||||||
| 12. Siemomysł | |||||||||||||||||||
| 6. Mieszko I of Poland | |||||||||||||||||||
| 13. Gorka? | |||||||||||||||||||
| 3. Sigrid the Haughty | |||||||||||||||||||
| 28. Vratislaus I, Duke of Bohemia | |||||||||||||||||||
| 14. Boleslaus I, Duke of Bohemia | |||||||||||||||||||
| 29. Drahomíra | |||||||||||||||||||
| 7. Dubrawka of Bohemia | |||||||||||||||||||
| 15. Biagota | |||||||||||||||||||
Ruler of the waves
Henry of Huntingdon, the 12th-century chronicler, tells how Cnut set his throne by the sea shore and commanded the tide to halt and not wet his feet and robes; but the tide failed to stop. According to Henry, Cnut leapt backwards and said "Let all men know how empty and worthless is the power of kings, for there is none worthy of the name, but He whom heaven, earth, and sea obey by eternal laws." He then hung his gold crown on a crucifix, and never wore it again.[84]
This story may be apocryphal. While the contemporary Encomium Emmae has no mention of it, it would seem that so pious a dedication might have been recorded there, since the same source gives an "eye-witness account of his lavish gifts to the monasteries and poor of St Omer when on the way to Rome, and of the tears and breast-beating which accompanied them".[85] Goscelin, writing later in the 11th century, instead has Cnut place his crown on a crucifix at Winchester one Easter, with no mention of the sea, and 'with the explanation that the king of kings was more worthy of it than he'.[86] However there may be a "basis of fact, in a planned act of piety" behind this story, and Henry of Huntingdon cites it as an example of the king's "nobleness and greatness of mind".[87] Later historians repeated the story, most of them adjusting it to have Cnut more clearly aware that the tides would not obey him, and staging the scene to rebuke the flattery of his courtiers; and there are earlier Celtic parallels in stories of men who commanded the tides, namely Saint Illtud, Maelgwn, king of Gwynedd, and Tuirbe, of Tuirbe's Strand, in Brittany.[88]
The encounter with the waves is said to have taken place at Bosham in West Sussex, or Southampton in Hampshire.
According to the House of Commons Information Office (The Palace of Westminster Factsheet G11, General Series Revised March 2008), Cnut set up a Royal palace during his reign on Thorney Island (later to become known as Westminster) as the area was sufficiently far away from the busy settlement to the east known as London. It is believed that, on this site, Cnut tried to command the tide of the river to prove to his courtiers that they were fools to think that he could command the waves.
Skaldic poetry
The Old Norse catalogue of skalds known as Skáldatal lists as many as eight skalds who have been active at Cnut's court. Four of them, namely Sigvatr Þórðarson, Óttarr svarti, Þórarinn loftunga and Hallvarðr háreksblesi, composed verses in honour of Cnut which have survived in some form, while no such thing is apparent from the four other skalds Bersi Torfuson, Arnórr Þórðarson jarlaskáld (known from other works), Steinn Skaptason and Óðarkeptr (unknown). The principal works for Cnut are the three Knútsdrápur by Sigvatr Þórðarson, Óttarr svarti and Hallvarðr háreksblesi, and the Höfuðlausn and Tøgdrápa by Þórarinn loftunga.
Cnut also features in two other contemporary skaldic poems, namely Þórðr Kolbeinsson's Eiríksdrápa and the anonymous Liðsmannaflokkr.
See also
- The Viking Age
- The Raven banner
Notes on the text
- ^ Modern languages: Norwegian: Knut den mektige, Swedish: Knut den Store, Danish: Knud den Store, Polish: Kanut Wielki
- ^ Graslund, B.,'Knut den store och sveariket: Slaget vid Helgea i ny belysning', Scandia, vol. 52 (1986), pp. 211–238.
- ^ Forte, et al., Viking Empires, p. 196.
- ^ Forte, et al., Viking Empires, pp. 197–198
- ^ Forte, et al., Viking Empires, pp. 202 & 206.
- ^ Forte, et al., Viking Empires, pp.196–197, 201–202 & 272
- ^ Forte, et al., Viking Empires, pp. 197–198 & 202.
- ^ Forte, et al., Viking Empires, pp. 197-198 & 202.
- ^ a b Lawson, Cnut, p. 97. The Anglo-Saxon kings used the title "king of the English". Canute was ealles Engla landes cyning -- "king of all England."
- ^ Trow, Cnut, pp. 30–31.
- ^ Encomiast, Encomium Emmae, ii. 2, pg. 18
- ^ Thietmar, Chronicon, vii. 39, pgs. 446-447
- ^ Trow, Cnut, p. 40.
- ^ Trow, Cnut, p. 44.
- ^ Douglas, English Historical Documents, pp. 335–336
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p. 160.
- ^ Trow, Cnut, p. 92.
- ^ John, H., The Penguin Historical Atlas of the Vikings, Penguin (1995), p. 122.
- ^ a b c Sawyer, History of the Vikings, pp. 171
- ^ a b Lawson, Cnut, p. 27
- ^ Trow, Cnut, p. ???.
- ^ a b c Lawson, Cnut, p. ???.
- ^ Garmonsway, G.N. (ed. & trans.), The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, Dent Dutton, 1972 & 1975, Peterborough (E) text, s.a. 1015, p. 146.
- ^ Campbell, A. (ed. & trans.), Encomium Emmae Reginae, Camden 3rd Series vol.LXXII, 1949, pp. 19–21.
- ^ G. Jones, Vikings, p. 370
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p. 27.
- ^ a b Trow, Cnut, p. 57.
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p. 161
- ^ Anglo-Saxon Chronicles, pp. 146-9.
- ^ Trow, Cnut, p. 59.
- ^ Anglo-Saxon Chronicles, pp. 148-50
- ^ Anglo-Saxon Chronicles, pp. 150-1
- ^ Anglo-Saxon Chronicles, pp. 151-3
- ^ Anglo-Saxon Chronicles, pp. 152-3; Williams, A., Æthelred the Unready The Ill-Counselled King, Hambledon & London, 2003, pp. 146–7.
- ^ Forte, Oram & Pedersen, Viking Empires, pp. 198
- ^ a b Anglo-Saxon Chronicles, p. 154
- ^ Lawson, cnut, p.162
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p. 89.
- ^ Thietmar, Chronicon, vii. 7, pp.502–03
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p. 90.
- ^ Trow, Cnut, pp.168–69.
- ^ Forte, et al., Viking Empires, pp. 198
- ^ Jones, Vikings, p.373
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, pp. 65–66.
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, pp. 124–125.
- ^ a b c d Trow, Cnut, p. 193.
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p. 125
- ^ a b Forte, et al., Viking Empires, pp. 198.
- ^ a b Trow, Cnut, p. 189.
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p. 104.
- ^ a b Trow, Cnut, p. 191.
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, pp. 95–98.
- ^ Trow, Cnut, p.197.
- ^ Adam of Bremen, Gesta Daenorum, ii.61, p. 120.
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, pp. ??
- ^ Trow, Cnut, pp. 197.
- ^ Forte, et al., Viking Empires, pp. 196–197
- ^ Forte, et al., Viking Empires, pp.197–198.
- ^ Lawson, Cnut. pp. 102.
- ^ Trow, Cnut, pp. 197–198.
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p. 102.
- ^ a b Lawson, Cnut, p. 103.
- ^ Lausavisur, ed. Johson Al, pgs. 269–270
- ^ Ranelagh, A Short History of Ireland, p.31
- ^ Encomiast, Encomium Emmae, ii. 19, pg 34
- ^ Trow, Cnut, p.129
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, P.86
- ^ a b Lawson, Cnut, P.87
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, pp.139–147
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p.141
- ^ a b c d Lawson, Cnut, p.142
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p.126
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p.143
- ^ Trow, Cnut, p.128
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p.147
- ^ a b c Lawson, Cnut, p.146
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p.144
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p.145
- ^ Trow, Cnut, p.186
- ^ The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p. 98 & pp. 104–105
- ^ "Photo of a sign posted in Winchester Cathedral marking Cnut's mortuary chest, posted at the astoft.co.uk web site, retrieved 2009-07-25".
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p "Kings of Wessex and England 802–1066" (PDF). The official website of The British Monarchy. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-08-24. Retrieved 2015-07-05.
- ^ Forester, T. (ed. & trans.), The Chronicle of Henry of Huntingdon, Bohn, 1853 (reprinted Llanerch, 1991), p. 199.
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p. 133.
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p. 134.
- ^ Lawson, Cnut, p. 133; Forester, , pp. 198–9.
- ^ Lord Raglan: "Cnut and the Waves": Man, Vol. 60, (Jan., 1960), pp. 7–8. The legend of Canute's attempt to rule the waves has long persisted in the lore of western civilization, being cited, for example, by Stacy Head as typifying the New Orleans City Council's response to Hurricane Katrina.
References
- Campbell, Alistair (ed.) (1949) Encomium Emmae Reginae. (Camden third series; no. 72.) London: Royal Historical Society (Reissued by Cambridge University Press with a supplementary introduction by Simon Keynes, 1988.)
- Forte, A. (2005), Viking Empires (1st ed.), Cambridge, New York: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-82992-5
- Godsell, Andrew "King Canute and the Advancing Tide", History For All magazine 2002, republished in Legends of British History 2008 ISBN 978-0951557334
- Jones, G (1984), A History of the Vikings (2nd ed.), Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-285139-X
- Lawson, M. K. (2004), Cnut: England's Viking King (2nd ed.), Stroud: Tempus, ISBN 0-7524-2964-7
- Ranelagh, John O'Beirne (2001). A Short History of Ireland. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521469449.
- Sawyer, P. (1997), The Oxford Illustrated History of the Vikings (1st ed.), Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-820526-0
- Swanton, Michael, ed. (1996), The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, New York: Routledge, ISBN 0-415-92129-5
- Thietmar (1962) Chronik: Chronicon; Neu übertragen und erläutert von Werner Trillmich.
Darmstadt: Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft
- Trow, M. J. (2005), Cnut: Emperor of the North, Stroud: Sutton, ISBN 0-7509-3387-9
External links
- Canute the Great
- Canute (Knud) The Great - From Viking warrior to English king
- Vikingworld (Danish) - Canute the Great (Knud den Store)
- Cnut the Great: Emperor of the North
- Time Team - Who was King Cnut?
- Canute the Great At Find A Grave
- Northvegr (Scandinavian) - A History of the Vikings (Search)
- Canute Or Cnut from the Online Encyclopedia
- Monarchies of Britain: Danish Kings of England
- Images from the British Library's collections

