P: Difference between revisions
m Reverted 1 edit by Neosporinsucks identified as test/vandalism using STiki |
|||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
*𐤐 : [[Phoenician alphabet|Semitic]] letter [[Pe (letter)|Pe]], from which the following symbols originally derive |
*𐤐 : [[Phoenician alphabet|Semitic]] letter [[Pe (letter)|Pe]], from which the following symbols originally derive |
||
**Π π : [[Greek alphabet|Greek]] letter [[Pi (letter)|Pi]] |
**Π π : [[Greek alphabet|Greek]] letter [[Pi (letter)|Pi]] |
||
***𐌐 : [[Old Italic script|Old Italic]] P, which derives from Greek Pi, and is the ancestor of modern Latin P |
***𐌐 : [[Old Italic script|Old Italic]] and [[Old Latin]] P, which derives from Greek Pi, and is the ancestor of modern Latin P. The Roman P had this form (𐌐) on coins and inscriptions until the reign of [[Claudius]], ca. 50 AD (See also [[Claudian letters]]). |
||
***{{Script|Goth|𐍀}} : [[Gothic alphabet|Gothic]] letter pertra/pairþa, which derives from Greek Pi |
***{{Script|Goth|𐍀}} : [[Gothic alphabet|Gothic]] letter pertra/pairþa, which derives from Greek Pi |
||
***П п : [[Cyrillic]] letter [[Pe (Cyrillic)|Pe]], which also derives from Pi |
***П п : [[Cyrillic]] letter [[Pe (Cyrillic)|Pe]], which also derives from Pi |
||
Revision as of 22:22, 19 November 2016
| ISO basic Latin alphabet |
|---|
| AaBbCcDdEeFfGgHhIiJjKkLlMmNnOoPpQqRrSsTtUuVvWwXxYyZz |

P (named pee /ˈpiː/[1] ) is the 16th letter of the modern English alphabet and the ISO basic Latin alphabet.
History
| Phoenician P |
Archaic Greek Pi |
Greek Pi |
Etruscan P |
Latin P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Use in writing systems
In English orthography and most other European languages, ⟨p⟩ represents the sound /p/.
A common digraph in English is ⟨ph⟩, which represents the sound /f/, and can be used to transliterate ⟨φ⟩ phi in loanwords from Greek. In German, the digraph ⟨pf⟩ is common, representing a labial affricate /pf/.
Most English words beginning with ⟨p⟩ are of foreign origin, primarily French, Latin, Greek, and Slavic;[citation needed] these languages preserve Proto-Indo-European initial *p. Native English cognates of such words often start with ⟨f⟩, since English is a Germanic language and thus has undergone Grimm's law; a native English word with initial /p/ would reflect Proto-Indo-European initial *b, which is so rare that its existence as a phoneme is disputed.
However, native English words with non-initial ⟨p⟩ are quite common; such words can come from either Kluge's law or the consonant cluster /sp/ (PIE *p has been preserved after s).
In the International Phonetic Alphabet, /p/ is used to represent the voiceless bilabial plosive.
Related characters
Ancestors, descendants and siblings
The Latin letter P represents the same sound as the Greek letter Pi, but it looks like the Greek letter Rho.
- 𐤐 : Semitic letter Pe, from which the following symbols originally derive
- Π π : Greek letter Pi
- 𐌐 : Old Italic and Old Latin P, which derives from Greek Pi, and is the ancestor of modern Latin P. The Roman P had this form (𐌐) on coins and inscriptions until the reign of Claudius, ca. 50 AD (See also Claudian letters).
- 𐍀 : Gothic letter pertra/pairþa, which derives from Greek Pi
- П п : Cyrillic letter Pe, which also derives from Pi
- Ⲡ ⲡ : Coptic letter Pi
- Π π : Greek letter Pi
- P with diacritics: Ṕ ṕ Ṗ ṗ Ᵽ ᵽ Ƥ ƥ ᵱ
Derived ligatures, abbreviations, signs and symbols
- ₱ : Philippine peso sign
- ℘ : script letter P, see Weierstrass p
- ℗ : sound recording copyright symbol
- ♇ : Pluto symbol
Computing codes
| Preview | P | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unicode name | LATIN CAPITAL LETTER P | LATIN SMALL LETTER P | ||
| Encodings | decimal | hex | dec | hex |
| Unicode | 80 | U+0050 | 112 | U+0070 |
| UTF-8 | 80 | 50 | 112 | 70 |
| Numeric character reference | P |
P |
p |
p |
| EBCDIC family | 215 | D7 | 151 | 97 |
| ASCII 1 | 80 | 50 | 112 | 70 |
- 1 Also for encodings based on ASCII, including the DOS, Windows, ISO-8859 and Macintosh families of encodings.
Other representations
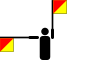
| NATO phonetic | Morse code |
| Papa |

|
File:Sign language .svg | File:BSL letter .svg | 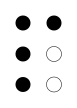
| |
| Signal flag | Flag semaphore | American manual alphabet (ASL fingerspelling) | British manual alphabet (BSL fingerspelling) | Unified English Braille |
See also
- Mind your Ps and Qs
- Pence or "penny," the English slang for which is p (e.g. "20p" = 20 pence)
References
- ^ "P", Oxford English Dictionary, 2nd edition (1989); Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged (1993); "pee," op. cit.