Foramen magnum: Difference between revisions
m Bot: removing deprecated anatomy infobox parameters (Task 11) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{more footnotes|date=January 2013}} |
{{more footnotes|date=January 2013}} |
||
{{Infobox bone |
{{Infobox bone |
||
| Name = Foramen magnum |
| Name = ''Foramen magnum'' |
||
| Latin = Foramen magnum |
| Latin = ''Foramen magnum'' |
||
| Image = Crane4 Foramen magnum.png |
| Image = Crane4 Foramen magnum.png |
||
| Caption = Upper surface of [[base of the skull]]. The hole indicated by an arrow is the foramen magnum |
| Caption = Upper surface of [[base of the skull]]. The hole indicated by an arrow is the ''foramen magnum'' |
||
| Image2 = Gray130.png |
| Image2 = Gray130.png |
||
| Caption2 = Occipital bone. Inner surface. |
| Caption2 = Occipital bone. Inner surface. |
||
}} |
}} |
||
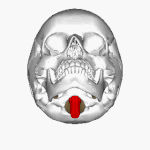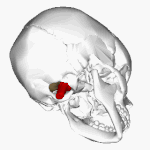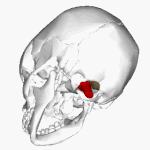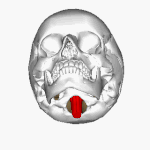
The '''foramen magnum''' ({{lang-la|great hole}}) is a large oval opening ([[foramen]]) in the [[occipital bone]] of the [[skull]] in humans and various other [[animal]]s. It is one of [[list of foramina of the human body|the several oval or circular openings (foramina)]] in the [[base of skull|base of the skull]]. The [[spinal cord]], an extension of the [[medulla oblongata|medulla]], passes through the foramen magnum as it exits the [[cranial cavity]]. |
The '''''foramen magnum''''' ({{lang-la|great hole}}) is a large oval opening (''[[foramen]]'') in the [[occipital bone]] of the [[skull]] in humans and various other [[animal]]s. It is one of [[list of foramina of the human body|the several oval or circular openings (''foramina'')]] in the [[base of skull|base of the skull]]. The [[spinal cord]], an extension of the [[medulla oblongata|''medulla'']], passes through the ''foramen magnum'' as it exits the [[cranial cavity]]. |
||
Apart from the transmission of the ''medulla oblongata'' and its membranes, the ''foramen magnum'' transmits the [[Vertebral artery|vertebral arteries]], the [[Anterior spinal artery|anterior]] and [[Posterior spinal artery|posterior spinal arteries]], the [[Tectorial membrane of atlanto-axial joint|tectorial membranes]] and [[alar ligament]]s. It also transmits the spinal component of the [[accessory nerve]] into the skull. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | The foramen magnum is a very important feature in bipedal mammals. One of the attributes of a bipedal animal’s foramen magnum is a forward shift of the anterior border; this is caused by the shortening of the cranial base. Studies on the foramen magnum position have shown a connection to the functional influences of both posture and locomotion. The forward shift of the foramen magnum is apparent in bipedal hominins, including modern humans, ''Australopithecus africanus'', and ''Paranthropus boisei''. This common feature of bipedal [[hominini|hominins]] is the driving argument used by [[Michel Brunet (paleontologist)|Michel Brunet]] that ''[[Sahelanthropus tchadensis]]'' was also bipedal, and may be the earliest known bipedal ape. The discovery of this feature has given scientists another form of identifying bipedal mammals. |
||
<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Russo|first1=Gabrielle A.|last2=Kirk|first2=Christopher E.|title=Foramen magnum position in bipedal mammals|journal=Journal of Human Evolution|date=November 2013|volume=65|issue=5|pages=656–670|doi=10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.07.007|url=http://www.sciencedirect.com.prox.lib.ncsu.edu/science/article/pii/S0047248413001681|accessdate=12 March 2015|pmid=24055116}}</ref> |
|||
| ⚫ | The ''foramen magnum'' is a very important feature in bipedal mammals. One of the attributes of a bipedal animal’s ''foramen magnum'' is a forward shift of the anterior border; this is caused by the shortening of the cranial base. Studies on the foramen magnum position have shown a connection to the functional influences of both posture and locomotion. The forward shift of the foramen magnum is apparent in bipedal hominins, including modern humans, ''Australopithecus africanus'', and ''Paranthropus boisei''. This common feature of bipedal [[hominini|hominins]] is the driving argument used by [[Michel Brunet (paleontologist)|Michel Brunet]] that ''[[Sahelanthropus tchadensis]]'' was also bipedal, and may be the earliest known bipedal ape. The discovery of this feature has given scientists another form of identifying bipedal mammals.<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Russo |first1=Gabrielle A. |last2=Kirk |first2=Christopher E. |title=Foramen magnum position in bipedal mammals |journal=Journal of Human Evolution |date=November 2013 |volume=65 |issue=5 |pages=656–670 |doi=10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.07.007 |url=http://www.sciencedirect.com.prox.lib.ncsu.edu/science/article/pii/S0047248413001681 |accessdate=12 March 2015 |pmid=24055116}}</ref> |
||
==Compartments== |
==Compartments== |
||
The [[alar ligament]] which is attached on each side to the tubercle of [[occipital condyle]] on each side of |
The [[alar ligament]] which is attached on each side to the tubercle of [[occipital condyle]] on each side of the ''foramen magnum'' divides it into anterior smaller compartment and posterior larger compartment;<ref name="A.K. DUTTA 2013">{{cite book|last=Dutta|first=Asim Kumar|title=Essentials of Human Anatomy Head & Neck |year=2013|publisher=Current books international|location=kolkata|isbn=81-86793-79-8|pages=56–57}}</ref> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
Structures passing through neuro-vascular (posterior) compartment are: |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
==Other animals== |
==Other animals== |
||
In humans, the foramen magnum is farther underneath the head than in the other [[great apes]]. Thus, in humans, the neck muscles (including the [[occipitofrontalis muscle]]) do not need to be as robust in order to hold the head upright. Comparisons of the position of the foramen magnum in early hominid species are useful to determine how comfortable a particular species was when walking on two limbs ([[bipedalism]]) rather than four ([[quadrupedalism]]). |
In humans, the ''foramen magnum'' is farther underneath the head than in the other [[great apes]]. Thus, in humans, the neck muscles (including the [[occipitofrontalis muscle]]) do not need to be as robust in order to hold the head upright. Comparisons of the position of the ''foramen magnum'' in early hominid species are useful to determine how comfortable a particular species was when walking on two limbs ([[bipedalism]]) rather than four ([[quadrupedalism]]). |
||
==Additional images== |
==Additional images== |
||
| Line 38: | Line 40: | ||
| height = 170 |
| height = 170 |
||
| lines = 4 |
| lines = 4 |
||
|File:Medulla oblongata and foramen magnum animation small.gif|Skull seen from below. The hole through which the |
|File:Medulla oblongata and foramen magnum animation small.gif|Skull seen from below. The hole through which the ''medulla'' (shown in red) is passing is ''foramen magnum''. |
||
|File:Foramen magnum - close-up - superior view animation.gif|[[Occipital bone]]. Foramen magnum shown in red. |
|File:Foramen magnum - close-up - superior view animation.gif|[[Occipital bone]]. ''Foramen magnum'' shown in red. |
||
|File:Human brain dura mater (reflections) description.JPG|Human brain with [[dura mater]] intact. The foramen magnum is visible as the large hole in the centre. |
|File:Human brain dura mater (reflections) description.JPG|Human brain with ''[[dura mater]]'' intact. The ''foramen magnum'' is visible as the large hole in the centre. |
||
|File:Occipital bone Opisthion01.png|Opisthion shown in red |
|File:Occipital bone Opisthion01.png|''Opisthion'' shown in red |
||
|File:Occipital bone Basion05.png|Occipital bone inner surface (basion shown in red) |
|File:Occipital bone Basion05.png|Occipital bone inner surface (''basion'' shown in red) |
||
}} |
}} |
||
Revision as of 19:56, 21 March 2018
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (January 2013) |
| Foramen magnum | |
|---|---|
 Upper surface of base of the skull. The hole indicated by an arrow is the foramen magnum | |
 Occipital bone. Inner surface. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | 'Foramen magnum' |
| MeSH | D005539 |
| TA98 | A02.1.04.002 |
| TA2 | 553 |
| FMA | 75306 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The foramen magnum (Template:Lang-la) is a large oval opening (foramen) in the occipital bone of the skull in humans and various other animals. It is one of the several oval or circular openings (foramina) in the base of the skull. The spinal cord, an extension of the medulla, passes through the foramen magnum as it exits the cranial cavity.
Apart from the transmission of the medulla oblongata and its membranes, the foramen magnum transmits the vertebral arteries, the anterior and posterior spinal arteries, the tectorial membranes and alar ligaments. It also transmits the spinal component of the accessory nerve into the skull.
The opisthion is the midpoint on the posterior margin of the foramen magnum and is a cephalometric landmark. Another landmark is the basion located at the midpoint on the anterior margin of the foramen magnum.
The foramen magnum is a very important feature in bipedal mammals. One of the attributes of a bipedal animal’s foramen magnum is a forward shift of the anterior border; this is caused by the shortening of the cranial base. Studies on the foramen magnum position have shown a connection to the functional influences of both posture and locomotion. The forward shift of the foramen magnum is apparent in bipedal hominins, including modern humans, Australopithecus africanus, and Paranthropus boisei. This common feature of bipedal hominins is the driving argument used by Michel Brunet that Sahelanthropus tchadensis was also bipedal, and may be the earliest known bipedal ape. The discovery of this feature has given scientists another form of identifying bipedal mammals.[1]
Compartments
The alar ligament which is attached on each side to the tubercle of occipital condyle on each side of the foramen magnum divides it into anterior smaller compartment and posterior larger compartment;[2]
Structures passing through the osseo-ligamentous (anterior) compartment are:
- Apical ligament and tip of dens
- Upper band of Cruciate ligament
- Membrana tectoria
Structures passing through neuro-vascular (posterior) compartment are:
- Lower end of the medulla oblongata with meninges
- Fourth part of vertebral artery surrounded by sympathetic plexus of nerves
- Spinal roots of accessory nerves
- Anterior and posterior spinal arteries
- Tonsil of cerebellum (occasionally)
Other animals
In humans, the foramen magnum is farther underneath the head than in the other great apes. Thus, in humans, the neck muscles (including the occipitofrontalis muscle) do not need to be as robust in order to hold the head upright. Comparisons of the position of the foramen magnum in early hominid species are useful to determine how comfortable a particular species was when walking on two limbs (bipedalism) rather than four (quadrupedalism).
Additional images
-
Skull seen from below. The hole through which the medulla (shown in red) is passing is foramen magnum.
-
Occipital bone. Foramen magnum shown in red.
-
Human brain with dura mater intact. The foramen magnum is visible as the large hole in the centre.
-
Opisthion shown in red
-
Occipital bone inner surface (basion shown in red)
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 129 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 129 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Russo, Gabrielle A.; Kirk, Christopher E. (November 2013). "Foramen magnum position in bipedal mammals". Journal of Human Evolution. 65 (5): 656–670. doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2013.07.007. PMID 24055116. Retrieved 12 March 2015.
- ^ Dutta, Asim Kumar (2013). Essentials of Human Anatomy Head & Neck. kolkata: Current books international. pp. 56–57. ISBN 81-86793-79-8.
External links
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
- Diagram 1
- Diagram 2
- 3D animation showing position of basion on YouTube