Somali Plate: Difference between revisions
Pbsouthwood (talk | contribs) Adding local short description: "Minor tectonic plate including the east coast of Africa and the ajoining seabed" (Shortdesc helper) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
The Somali Plate is bounded on the west by the East African Rift, which stretches south from the [[triple junction]] in the [[Afar Triangle|Afar depression]], with an undersea continuation of the rift extending southward offshore. The northern boundary is the [[Aden Ridge]] along the coast of [[Saudi Arabia]]. The eastern boundary is the [[Central Indian Ridge]], the northern portion of which is also known as the [[Carlsberg Ridge]]. The southern boundary is the [[Southwest Indian Ridge]]. Dating of volcanism in the [[Comoro Islands]] and northern [[Madagascar]] [[volcano]]es indicates a rate of motion to the east over a [[Hotspot (geology)|hotspot]] of approximately 45 mm/yr. |
The Somali Plate is bounded on the west by the East African Rift, which stretches south from the [[triple junction]] in the [[Afar Triangle|Afar depression]], with an undersea continuation of the rift extending southward offshore. The northern boundary is the [[Aden Ridge]] along the coast of [[Saudi Arabia]]. The eastern boundary is the [[Central Indian Ridge]], the northern portion of which is also known as the [[Carlsberg Ridge]]. The southern boundary is the [[Southwest Indian Ridge]]. Dating of volcanism in the [[Comoro Islands]] and northern [[Madagascar]] [[volcano]]es indicates a rate of motion to the east over a [[Hotspot (geology)|hotspot]] of approximately 45 mm/yr. |
||
There is a divergence in the vertical geological movement of India and Africa along the Somali sea.<ref>Geology and the water resource system of the Indus Plains, Alfred J. Tamburi, Colorado State University, 1974, page 57</ref> |
|||
==Notes== |
==Notes== |
||
Revision as of 18:50, 23 October 2018
| Somali Plate | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Minor |
| Approximate area | 16,700,000 km2[1] |
| Movement1 | south-east |
| Speed1 | 6mm/year |
| Features | East Africa, Madagascar, Indian Ocean |
| 1Relative to the African Plate | |
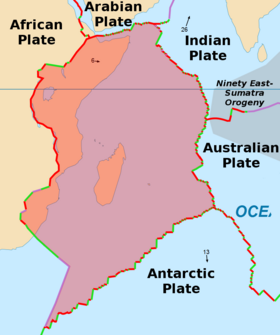
The Somali Plate, or Somalian Plate, is a minor tectonic plate, which straddles the equator in the eastern hemisphere. It is approximately centered on the island of Madagascar and includes about half of the East coast of Africa, from the Gulf of Aden in the North to somewhere near Durban in the South.
Geology

The Somali Plate formed between 60 million years ago and 10 million years ago by the rifting of the African Plate along the East African Rift.[2] Because the East Africa Rift separates the continent into two plates, the African Plate west of the rift is sometimes referred to as the Nubian Plate.[3]
The Somali Plate is bounded on the west by the East African Rift, which stretches south from the triple junction in the Afar depression, with an undersea continuation of the rift extending southward offshore. The northern boundary is the Aden Ridge along the coast of Saudi Arabia. The eastern boundary is the Central Indian Ridge, the northern portion of which is also known as the Carlsberg Ridge. The southern boundary is the Southwest Indian Ridge. Dating of volcanism in the Comoro Islands and northern Madagascar volcanoes indicates a rate of motion to the east over a hotspot of approximately 45 mm/yr.
There is a divergence in the vertical geological movement of India and Africa along the Somali sea.[4]
Notes
- ^ "Here are the Sizes of Tectonic or Lithospheric Plates".
- ^ "Somali Plate".
- ^ Chu, Dezhi; Gordon, Richard G. (4 March 1999). "Evidence for motion between Nubia and Somalia along the Southwest Indian ridge". Nature. 398 (6722): 64–67. Bibcode:1999Natur.398...64C. doi:10.1038/18014 – via www.nature.com.
- ^ Geology and the water resource system of the Indus Plains, Alfred J. Tamburi, Colorado State University, 1974, page 57
References
- Emerick, C. M., 1985, Age progressive volcanism in the Comores Archipelago and Northern Madagascar, Oregon State Univ., Corvallis, PhD Thesis, Abstract
- Chorowicz, Jean (October 2005). "The East African rift system". Journal of African Earth Sciences. 43 (1–3): 379–410. Bibcode:2005JAfES..43..379C. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2005.07.019.