Thioformaldehyde: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
Category improvement |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
| AutoignitionPt = }} |
| AutoignitionPt = }} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
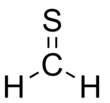
'''Thioformaldehyde''' is the [[organosulfur compound]] with the formula CH<sub>2</sub>S. This compound is very rarely observed because it [[oligomer]]izes to [[1,3,5-trithiane]], which is a stable colorless compound with the same formula. Despite its instability under normal terrestrial conditions, the molecule has been observed in the [[interstellar medium]]<ref>Despois, D., "Radio Line Observations of Molecular and Isotopic Species in Comet C/1995 O1 (Hale-Bopp) Implications on the Interstellar Origin of Cometary Ices", Earth, Moon, Planets 1999, 79, 103-124.</ref> and has attracted much attention for its fundamental nature.<ref>Clouthier, D. J.; Ramsay, D. A., "The Spectroscopy of Formaldehyde and Thioformaldehyde", Annual Review of Physical Chemistry 1983, 34, 31-58. {{DOI|10.1146/annurev.pc.34.100183.000335}}</ref> The tendency of thioformaldehyde to form chains and rings is a manifestation of the [[Double bond rule]]. |
'''Thioformaldehyde''' is the [[organosulfur compound]] with the formula CH<sub>2</sub>S. This compound is very rarely observed because it [[oligomer]]izes to [[1,3,5-trithiane]], which is a stable colorless compound with the same empirical formula. Despite its instability under normal terrestrial conditions, the molecule has been observed in the [[interstellar medium]]<ref>Despois, D., "Radio Line Observations of Molecular and Isotopic Species in Comet C/1995 O1 (Hale-Bopp) Implications on the Interstellar Origin of Cometary Ices", Earth, Moon, Planets 1999, 79, 103-124.</ref> and has attracted much attention for its fundamental nature.<ref>Clouthier, D. J.; Ramsay, D. A., "The Spectroscopy of Formaldehyde and Thioformaldehyde", Annual Review of Physical Chemistry 1983, 34, 31-58. {{DOI|10.1146/annurev.pc.34.100183.000335}}</ref> The tendency of thioformaldehyde to form chains and rings is a manifestation of the [[Double bond rule]]. |
||
==References== |
==References== |
||
Revision as of 10:00, 27 November 2018
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Other names
methanethial
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CH2S | |||
| Molar mass | 46.09 | ||
| Appearance | elusive | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Thioformaldehyde is the organosulfur compound with the formula CH2S. This compound is very rarely observed because it oligomerizes to 1,3,5-trithiane, which is a stable colorless compound with the same empirical formula. Despite its instability under normal terrestrial conditions, the molecule has been observed in the interstellar medium[1] and has attracted much attention for its fundamental nature.[2] The tendency of thioformaldehyde to form chains and rings is a manifestation of the Double bond rule.
References
- ^ Despois, D., "Radio Line Observations of Molecular and Isotopic Species in Comet C/1995 O1 (Hale-Bopp) Implications on the Interstellar Origin of Cometary Ices", Earth, Moon, Planets 1999, 79, 103-124.
- ^ Clouthier, D. J.; Ramsay, D. A., "The Spectroscopy of Formaldehyde and Thioformaldehyde", Annual Review of Physical Chemistry 1983, 34, 31-58. doi:10.1146/annurev.pc.34.100183.000335