Hurricane Barry (2019): Difference between revisions
Destroyeraa (talk | contribs) |
No edit summary Tag: Reverted |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| Hurricane season=[[2019 Atlantic hurricane season]] |
| Hurricane season=[[2019 Atlantic hurricane season]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
'''Hurricane Barry''' was an asymmetrical [[Saffir-Simpson hurricane scale|Category 1 hurricane]] that was the wettest [[tropical cyclone]] on record in Arkansas and the fourth-wettest in Louisiana. The second tropical or [[subtropical cyclone|subtropical]] storm and first hurricane of the [[2019 Atlantic hurricane season]], Barry originated as a [[mesoscale convective vortex]] over southwestern [[Kansas]] on July 2. The system eventually emerged into the [[Gulf of Mexico]] from the [[Florida Panhandle]] on July 10, whereupon the [[National Hurricane Center]] (NHC) designated it as a potential tropical cyclone. Early on July 11, the system [[tropical cyclogenesis|developed]] into a tropical depression and later into the second tropical storm on the same day. On July 13, Barry attained its peak intensity with 1-minute sustained winds of 75 mph (120 km/h), with a minimum central pressure of {{convert|993|mbar|inHg}}. Subsequently, Barry made its first landfall at [[Marsh Island (Louisiana)|Marsh Island]], and another landfall in [[Intracoastal City, Louisiana|Intracoastal City]], [[Louisiana]], both times as a Category 1 hurricane. Barry quickly weakened after landfall, falling to tropical depression status on July 15. The storm finally degenerated into a remnant low over northern [[Arkansas]] on the same day, before merging with a trough on July 16. |
'''Hurricane Barry''' was an asymmetrical<!--and rather ugly--> [[Saffir-Simpson hurricane scale|Category 1 hurricane]] that was the wettest [[tropical cyclone]] on record in Arkansas and the fourth-wettest in Louisiana. The second tropical or [[subtropical cyclone|subtropical]] storm and first hurricane of the [[2019 Atlantic hurricane season]], Barry originated as a [[mesoscale convective vortex]] over southwestern [[Kansas]] on July 2. The system eventually emerged into the [[Gulf of Mexico]] from the [[Florida Panhandle]] on July 10, whereupon the [[National Hurricane Center]] (NHC) designated it as a potential tropical cyclone. Early on July 11, the system [[tropical cyclogenesis|developed]] into a tropical depression and later into the second tropical storm on the same day. On July 13, Barry attained its peak intensity with 1-minute sustained winds of 75 mph (120 km/h), with a minimum central pressure of {{convert|993|mbar|inHg}}. Subsequently, Barry made its first landfall at [[Marsh Island (Louisiana)|Marsh Island]], and another landfall in [[Intracoastal City, Louisiana|Intracoastal City]], [[Louisiana]], both times as a Category 1 hurricane. Barry quickly weakened after landfall, falling to tropical depression status on July 15. The storm finally degenerated into a remnant low over northern [[Arkansas]] on the same day, before merging with a trough on July 16. |
||
Barry was one of four hurricanes to hit Louisiana as a Category 1 hurricane in the month of July, the others being [[Hurricane Bob (1979)|Bob]] in [[1979 Atlantic hurricane season|1979]], [[Hurricane Danny (1997)|Danny]] in [[1997 Atlantic hurricane season|1997]], and [[Hurricane Cindy (2005)|Cindy]] in [[2005 Atlantic hurricane season|2005]].<ref name="fourth hurricane landfall">{{Cite news|url=https://www.accuweather.com/en/weather-news/live-barry-strengthens-into-category-1-hurricane-gulf-coast-braces-for-impact/70008799|title=First Hurricane Landfall of the Season Leaves Louisiana, Mississippi waterlogged|last1=Mitchell|first1=Chaffin|last2=Navarro|first2=Adriana|publisher=Accuweather|date=July 14, 2019|access-date=July 15, 2019}}</ref> Numerous [[Tropical cyclone warnings and watches|tropical storm watches and warnings]] were issued for [[Mississippi]] and [[Louisiana]] ahead of the storm. Several states declared state of emergencies ahead of the storm. Though Barry only produced hurricane-force winds in a small area of Louisiana, more than 153,000 customers lost power in the state. The storm’s large circulation produced heavy rainfall over a large area, reaching {{convert|23.43|in|mm|abbr=on}} near [[Ragley, Louisiana]], and {{convert|16.59|in|mm|abbr=}} near [[Dierks, Arkansas]]. The latter value was the highest amount of rainfall recorded in Arkansas related to a tropical cyclone. Many roads, including [[Interstate Highway System|Interstate highways]], were flooded. Dozens of water rescues were carried out in Louisiana and Arkansas, where flooding was the severest. One fatality was attributed to Barry in Florida due to rip currents. In parts of the [[Northeastern United States]] and [[Ontario, Canada]], severe thunderstorms from Barry's remnants caused an additional 160,000 power outages and spawned a few weak tornadoes. Damage from Barry was estimated to be about $600 million (2019 USD). |
Barry was one of four hurricanes to hit Louisiana as a Category 1 hurricane in the month of July, the others being [[Hurricane Bob (1979)|Bob]] in [[1979 Atlantic hurricane season|1979]], [[Hurricane Danny (1997)|Danny]] in [[1997 Atlantic hurricane season|1997]], and [[Hurricane Cindy (2005)|Cindy]] in [[2005 Atlantic hurricane season|2005]].<ref name="fourth hurricane landfall">{{Cite news|url=https://www.accuweather.com/en/weather-news/live-barry-strengthens-into-category-1-hurricane-gulf-coast-braces-for-impact/70008799|title=First Hurricane Landfall of the Season Leaves Louisiana, Mississippi waterlogged|last1=Mitchell|first1=Chaffin|last2=Navarro|first2=Adriana|publisher=Accuweather|date=July 14, 2019|access-date=July 15, 2019}}</ref> Numerous [[Tropical cyclone warnings and watches|tropical storm watches and warnings]] were issued for [[Mississippi]] and [[Louisiana]] ahead of the storm. Several states declared state of emergencies ahead of the storm. Though Barry only produced hurricane-force winds in a small area of Louisiana, more than 153,000 customers lost power in the state. The storm’s large circulation produced heavy rainfall over a large area, reaching {{convert|23.43|in|mm|abbr=on}} near [[Ragley, Louisiana]], and {{convert|16.59|in|mm|abbr=}} near [[Dierks, Arkansas]]. The latter value was the highest amount of rainfall recorded in Arkansas related to a tropical cyclone. Many roads, including [[Interstate Highway System|Interstate highways]], were flooded. Dozens of water rescues were carried out in Louisiana and Arkansas, where flooding was the severest. One fatality was attributed to Barry in Florida due to rip currents. In parts of the [[Northeastern United States]] and [[Ontario, Canada]], severe thunderstorms from Barry's remnants caused an additional 160,000 power outages and spawned a few weak tornadoes. Damage from Barry was estimated to be about $600 million (2019 USD). |
||
Revision as of 14:41, 23 October 2020
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS/NWS) | |
 Hurricane Barry shortly after making landfall in Louisiana on July 13 | |
| Formed | July 11, 2019 |
|---|---|
| Dissipated | July 16, 2019 |
| (Remnant low after July 15) | |
| Highest winds | 1-minute sustained: 75 mph (120 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 993 mbar (hPa); 29.32 inHg |
| Fatalities | 1 total |
| Damage | $600 million (2019 USD) |
| Areas affected | Gulf Coast of the United States, Arkansas, Midwestern United States, Northeastern United States, Ontario, Canada |
| Part of the 2019 Atlantic hurricane season | |
Hurricane Barry was an asymmetrical Category 1 hurricane that was the wettest tropical cyclone on record in Arkansas and the fourth-wettest in Louisiana. The second tropical or subtropical storm and first hurricane of the 2019 Atlantic hurricane season, Barry originated as a mesoscale convective vortex over southwestern Kansas on July 2. The system eventually emerged into the Gulf of Mexico from the Florida Panhandle on July 10, whereupon the National Hurricane Center (NHC) designated it as a potential tropical cyclone. Early on July 11, the system developed into a tropical depression and later into the second tropical storm on the same day. On July 13, Barry attained its peak intensity with 1-minute sustained winds of 75 mph (120 km/h), with a minimum central pressure of 993 millibars (29.3 inHg). Subsequently, Barry made its first landfall at Marsh Island, and another landfall in Intracoastal City, Louisiana, both times as a Category 1 hurricane. Barry quickly weakened after landfall, falling to tropical depression status on July 15. The storm finally degenerated into a remnant low over northern Arkansas on the same day, before merging with a trough on July 16.
Barry was one of four hurricanes to hit Louisiana as a Category 1 hurricane in the month of July, the others being Bob in 1979, Danny in 1997, and Cindy in 2005.[1] Numerous tropical storm watches and warnings were issued for Mississippi and Louisiana ahead of the storm. Several states declared state of emergencies ahead of the storm. Though Barry only produced hurricane-force winds in a small area of Louisiana, more than 153,000 customers lost power in the state. The storm’s large circulation produced heavy rainfall over a large area, reaching 23.43 in (595 mm) near Ragley, Louisiana, and 16.59 inches (421 mm) near Dierks, Arkansas. The latter value was the highest amount of rainfall recorded in Arkansas related to a tropical cyclone. Many roads, including Interstate highways, were flooded. Dozens of water rescues were carried out in Louisiana and Arkansas, where flooding was the severest. One fatality was attributed to Barry in Florida due to rip currents. In parts of the Northeastern United States and Ontario, Canada, severe thunderstorms from Barry's remnants caused an additional 160,000 power outages and spawned a few weak tornadoes. Damage from Barry was estimated to be about $600 million (2019 USD).
Meteorological history
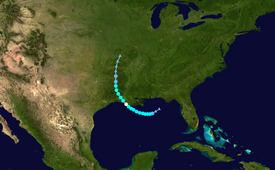
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
The origins of Barry can be traced to a mesoscale convective vortex that formed over southwestern Kansas on July 2.[2] On July 5, the Climate Prediction Center noted the possibility for this disturbance to interact with a trough of low pressure over the Southeastern United States, eventually triggering a low pressure area over the Gulf of Mexico.[3] The following day, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) highlighted a low likelihood of tropical cyclogenesis while the disturbance was still centered well-inland over Tennessee, anticipating that the weather system would track into the northern Gulf of Mexico.[4] Over the next few days, the system drifted southeastward towards Georgia, steered by a ridge to its west.[2] By July 8, the NHC assessed a high probability of a tropical cyclone developing due to favorable conditions in the Gulf.[5] On July 9, a broad low pressure area exited the Florida Panhandle and tracked into the northeastern Gulf of Mexico, accompanied by scattered convection, or thunderstorms. It moved southwestward and curved to the west on the east side of a mid-level ridge.[2] On July 10, the NHC initiated advisories on the system as Potential Tropical Cyclone Two, due to its threat it posed to the United States within a few days. At that time, the low pressure area was experiencing some northerly wind shear, which was expected to decrease. Sea surface temperatures of 86–88 °F (30–31 °C) allowed the system to gradually organize.[6]

At 00:00 UTC on July 11, the system developed into a tropical depression about 200 mi (320 km) south of Mobile, Alabama. The depression intensified into Tropical Storm Barry six hours later as the convection had increased to the south of the system's circulation.[2] The storm's convection organized into a large rainband south of an elongated circulation,[7] though mid-level dry air and northerly wind shear restricted thunderstorms near the center.[8][2] On July 12, data from two hurricane hunter reconnaisance aircraft found that Barry quickly intensified, with its central pressure dropping, despite a marginally favorable environment.[9] Due to a slight decrease in shear on the morning of July 13, the storm's outflow expanded and the banding increased.[10] Barry attained Category 1 hurricane status by 12:00 UTC that day, with a small area of hurricane-force winds occurring east of the center.[11] Simultaneously, the storm reached its peak intensity, with a minimum central pressure of 993 millibars (29.3 inHg).[2] At 15:00 UTC that day, Barry made landfall as a Category 1 hurricane on Marsh Island, Louisiana.[12] Barry was one of four hurricanes to hit Louisiana at Category 1 intensity in the month of July, the others being Bob in 1979, Danny in 1997, and Cindy in 2005.[1]
The storm quickly weakened after landfall, falling to tropical storm status late on July 13.[13] Barry further weakened to a tropical depression at 00:00 UTC on July 15 just south of the Louisiana-Arkansas border.[2] At 12:00 UTC that same day, Barry degenerated into a remnant low over northern Arkansas. The remnant low continue to spin down, and degenerated into a trough at 12:00 UTC a day later over southern Missouri.[2] Barry brought a hot, tropical airmass along its path, continuing a heat wave along the East Coast of the United States.[14]
Preparations

On July 10, the NHC began issuing various warnings and watches, including a hurricane watch for the Louisiana coast from Cameron to the Mississippi River Delta, a tropical storm watch from the Mississippi Delta to the mouth of the Pearl River, and a storm surge watch from the mouth of the Pearl River to Morgan City, Louisiana. After the disturbance became a tropical storm on July 11, the NHC issued a tropical storm warning from the mouth of the Pearl River to Morgan City, and a tropical storm watch eastward to the Mississippi/Alabama border, including the New Orleans metro area, Lake Pontchartrain, and Lake Maurepas. The agency also issued a storm surge warning from the mouth of the Atchafalaya River to Shell Beach, Louisiana.[2]

The United States Army Corps of Engineers feared that levees would be overtopped in Plaquemines Parish by storm surge and historically high river levels. Thus, a mandatory evacuation was ordered for the parish effective on the morning of July 11, affecting approximately 8,000–10,000 residents.[15] An evacuation order was also issued for low-lying areas of Jefferson Parish;[16] the mayor of Grand Isle also issued a mandatory evacuation. Due to the storm threat, the Carnival Valor changed its disembarking point from New Orleans to Mobile, Alabama.[17] Royal Dutch Shell evacuated non-essential personnel from its offshore oil platforms in the Gulf of Mexico.[18] On the afternoon of July 11, the National Hurricane Center issued a hurricane warning for coastal Louisiana between Intracoastal City to Grand Isle, Louisiana.[19] Curfews were enacted in several Louisiana communities across five parishes on July 12.[20] New Orleans Mayor LaToya Cantrell urged residents to "shelter in place" but did not order evacuations, citing Category 3 status as the threshold.[21]
In a 24-hour span between July 10 and 11, 28 parishes issued emergency declarations. After declaring a state of emergency and deploying search and rescue assets,[22] Louisiana Governor John Bel Edwards requested a federal disaster declaration for the entire state on July 11, citing the potential for widespread flooding;[23] the request was granted by President Donald Trump later that day.[24] On July 12, Health and Human Services Secretary Alex Azar declared a public health emergency in Louisiana to prepare for Barry's potential impacts. In addition to making this declaration, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) worked with FEMA and positioned approximately 100 medical and public health personnel from various agencies, and provided medical equipment for medical teams.[25] On July 12, Mississippi Governor Phil Bryant declared a state of emergency, allocating state resources for storm relief and activating the state's emergency operations center.[26] The Mississippi Urban Search and Rescue Task Force dispatched two 12-person water rescue crews to Pike County and Camp Shelby to assist local emergency units.[27]
Impact
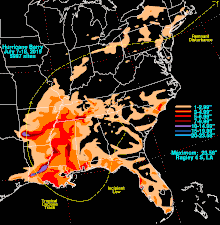
High water levels occurred from the Florida Panandle to the upper Texas Coast.[2] Total economic losses from Barry are estimated at $600 million (2019 USD), with public and private insurers paying out nearly $300 million. More than 50,000 buildings were damaged or destroyed. Most of these losses were due to flooding along the Gulf Coast and in Arkansas.[28]
Louisiana
While Barry was in its formative stages, it dropped 6 to 9 in (150 to 230 mm) of rainfall across the New Orleans area, causing flooding.[29] An expansive thunderstorm inundated streets and businesses over a six-hour period on the morning of July 10.[30] Portions of the French Quarter were flooded and public transportation was disrupted. The impacts were exacerbated by an elevated Mississippi River amid a prolonged period exceeding flood stage.[31] Officials declared a flash flood emergency in New Orleans, as flooded streets forced businesses and government buildings to close.[32][31]

When Barry made landfall, it produced hurricane-force winds in a small area near the Louisiana coast.[33] The strongest recorded winds on land was 66 mph (106 km/h) at Acadiana Regional Airport in New Iberia. For several days, Barry's intense rainbands affected the same portion of south-central and southwestern Louisiana. The highest rainfall total recorded along Barry's path was 23.43 in (595 mm) near Ragley.[2] Waterspouts were reported on Lake Pontchartrain.[32] A possible tornado damaged two homes when it struck the Gentilly neighborhood in New Orleans.[21] The highest storm surge in Louisiana was 6.13 ft (1.87 m) above normal tide levels at Eugene Island in Atchafalaya Bay. A tide station in Amerada Pass recorded a 6.93 ft (2.11 m) high tide, but the station had been recording higher than normal tides due to high runoff from the Mississippi River. On the southern shore of Lake Pontchartrain, the storm surge reached 4.3 ft (1.3 m).[2] Flooding also occurred on the banks of the Atchafalaya River in Morgan City.[34] The Lower Dularge East Levee in Terrebonne Parish was overtopped, prompting a mandatory evacuation for nearby areas.[35] On the afternoon of July 12, Louisiana Highway 1 south of Golden Meadow was closed after seawater began to inundate portions of the road, cutting off access to Grand Isle and Port Fourchon.[36]

A total of 153,000 customers lost power in Louisiana.[37] Power lines knocked down by fallen trees in the Metairie area cut power to 5,140 electricity customers in the New Orleans metropolitan area. The most widespread power outages occurred where wind speeds were highest in Lafourche Parish and Terrebonne Parish, as well as eastern Baton Rouge; over 39,000 lost power in these areas.[38] All electricity customers in Grand Isle lost power, and a total of 4,300 customers were affected by power outages as Barry's initial rainbands swept across coastal Louisiana.[39] The storm also caused The Rolling Stones to postpone their July 14 show at the Superdome to July 15 due to heavy rain.[40]
Mississippi
Five people were rescued 23 mi (37 km) southwest of Gulfport, Mississippi, after their ship ran aground.[41] On July 14, a brief EF0 tornado in Forrest County damaged a few tree limbs on its 0.48 mi (0.77 km) path.[42] In addition, a tornado warning was issued for Jackson County, though no tornadoes were reported in the county.[43]Heavy rain occurred in southwestern Mississippi, and a rainfall amount of 13.30 inches (338 mm) near Pass Christian.[44] The rains flooded roads near the coast, in conjunction with higher tides. Hurricane Barry produced a 3 ft (0.91 m) storm surge in Bay St. Louis, Mississippi.[2] Floodwaters inundated parts of Beach Boulevard in Pascagoula,[45] and closed roads in the Biloxi area. High winds and saturated soils led to fallen trees.[46]
Alabama and Florida
The outer rainbands of Barry dropped heavy rainfall in southern Alabama, reaching 8.36 in (212 mm) near Fairhope.[2]Torrential rainfall overwhelmed sewer systems in Alabama, with over 80,000 gallons (300,000 L) of water spilling into the streets of Mobile County. The storm caused in the closure of popular beaches, including those in Orange Beach and Gulf Shores.[47] In southern Alabama, wind gusts reached 72 mph (116 km/h) on Pinto Island.[2] Around 2.8 feet (850 mm) of storm surge was reported in coastal Alabama.[48] Floodwaters from coastal flooding reached several feet deep in some locations, causing beach erosion and leaving behind 3 ft (0.91 m) of sand on Bienville Boulevard on Dauphin Island. Floodwaters closed lanes of the Cochrane–Africatown USA Bridge in Mobile.[2][48]
Along the Florida Panhandle, beaches issued warnings to the public to stay out of the water in order to avoid rip currents and dangerous swimming conditions; however, there were still many calls of swimmers in distress. In Panama City Beach, multiple people formed a human chain in an effort to save swimmers who had gotten caught in a rip current caused by the storm. Authorities performed 38 water rescues. A 67-year-old man drowned in the waters.[49] Barry's large circulation produced gale-force wind gusts along the Gulf Coast as far east Panama City Beach, which recorded gusts of 41 mph (67 km/h).[2]
Arkansas

Following up to 8 inches (200 mm) of rainfall, the National Weather Service issued a rare flash flood emergency at 5 a.m. CDT on July 16, for southern Pike and southern Clark counties.[50] Later, water rescues and washed-out roads were reported in Hempstead, Howard, and Nevada counties,[44] prompting a flash flood emergency to be issued for those counties as well.[50] A portion of Interstate 30 was closed in Clark County due to flooding.[44] The Clark County Humane Society in Arkadelphia was drenched by floodwaters, killing a puppy. Later, the remaining animals were rescued.[51] A woman was rescued from fast-moving floodwaters in the same area.[52] In Nashville, the police department building and the county jail were damaged by flash flooding, and inmates had to be evacuated.[50] A rainfall total of 16.59 inches (421 mm) was recorded near Dierks, making Barry the wettest tropical cyclone in state history.[53]
Elsewhere
In Texas, wind gusts reached 56 mph (91 km/h) at Sabine Pass.[2] In addition, a peak rainfall amount of 4.61 inches (117 mm) was recorded in Beaumont. In Missouri, a peak rainfall amount of 5.35 inches (136 mm) was recorded in Poplar Bluff, and in Tennessee, a peak amount of 6.09 inches (155 mm) was recorded near Cookeville.[44] More than 60 mm (2.4 in) of rain fell in Toronto, Canada on July 17, as the post-tropical cyclone moved just south of the area, resulting in street-level flash flooding and the blockage of a ramp to Ontario Highway 401, where several cars were submerged.[54] The city recorded its highest daily rainfall total in the month of July since 2013.[55] The storm also produced a funnel cloud in Oro-Medonte.[54] In Indianapolis, Indiana, over an inch of rainfall was recorded.[56] In the Northeastern United States, Barry worsened a heat wave due to the tropical airmass it brought along with it.[14] In addition, Barry's remnant moisture brought severe thunderstorms to the region from July 16-17, causing downed trees and power outages. Trees were reported down and power outages occurred in Ewing, New Jersey.[57] A portion of the Garden State Parkway was closed briefly due to flooding. Rome, New York received more than 3 inches (76 mm) of rain. On July 17, two people were injured in Lancaster, Pennsylvania due to strong winds. Overall, 160,000 customers lost power due to the storms in the Mid-Atlantic and New England.[58]
Aftermath
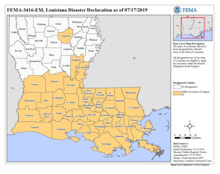
Governor of Louisiana John Bel Edwards traveled to coastal Louisiana on July 15 to inspect damage from the storm. He visited Myrtle Grove, near Port Sulphur, where roads were damaged by floods. The governor later said in a news conference that the storm was not as bad as originally anticipated, but urged residents to prepare for later storms.[49] Mayor of Houston Sylvester Turner called New Orleans Mayor LaToya Cantrell and offered to provide donations to affected areas through the Houston Relief Hub.[59] However, Cantrell said that her city of New Orleans was "beyond lucky" and was ready to help other parishes that got hit harder.[60] Many oil platforms and drilling companies were also affected by the storm. The Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement asserted that Barry caused nearly 73% of crude oil production in the Gulf to shut on July 15, two days after the storm made landfall. About 62% of natural gas production was also ceased.[37]
From July 25 to August 8, FEMA, along with state and local governments conducted Preliminary Damage Assessments in Louisiana.[61][62] On August 14, Governor John Bel Edwards requested a post-storm major disaster declaration for seven parishes,[61] which President Donald Trump granted on August 27.[63] The same day, Governor John Bel Edwards announced that the Governor's Office of Homeland Security and Emergency Preparedness and FEMA had recently completed damage assessments in the impacted areas.[62] Total cost for public assistance cost a little more than $16 million in Louisiana.[61]
See also
- Other storms named Barry
- 1940 Louisiana hurricane – produced flooding rainfall over southern Louisiana due to its slow movement
- 1943 Surprise Hurricane – the first hurricane to be observed by Hurricane Hunters, taking a similar westward path
- Hurricane Bonnie (1986) – a Category 1 hurricane that also took a similar track to Barry's
- Hurricane Danny (1997) – storm with similar origins that struck the Gulf Coast
- Hurricane Isaac (2012) – a Category 1 hurricane that made landfall in a similar location along the Gulf Coast
- Tropical Storm Cindy (2017) – a tropical storm that took a similar track to Barry's
References
- ^ a b Mitchell, Chaffin; Navarro, Adriana (July 14, 2019). "First Hurricane Landfall of the Season Leaves Louisiana, Mississippi waterlogged". Accuweather. Retrieved July 15, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r John P. Cangialosi; Andrew B. Hagen; Robbie Berg (November 18, 2019). Hurricane Barry Tropical Cyclone Report (PDF) (Report). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved November 20, 2019.
- ^ Morgan, Leigh (July 5, 2019). "Could Midwest storms help spawn a tropical storm in the Gulf next week?". Birmingham, Alabama: Alabama Media Group. Retrieved July 8, 2019.
- ^ Blake, Eric S. (July 6, 2019). Two-Day Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook. NHC Graphical Outlook Archive (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 8, 2019.
- ^ Latto, Andrew S.; Pasch, Richard J. (July 8, 2019). Two-Day Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook. NHC Graphical Outlook Archive (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 8, 2019.
- ^ Stewart, Stacy R. (July 10, 2019). Potential Tropical Cyclone Two Discussion Number 1 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 10, 2019.
- ^ Beven, Jack (July 11, 2019). Tropical Storm Barry Discussion Number 5 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 11, 2019.
- ^ Lixion, Avila (July 12, 2019). Tropical Storm Barry Discussion Number 8 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 12, 2019.
- ^ Beven, Jack (July 12, 2019). Tropical Storm Barry Discussion Number 9 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 12, 2019.
- ^ Daniel P., Brown (July 13, 2019). Tropical Storm Barry Discussion Number 11 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 13, 2019.
- ^ Beven, Jack (July 13, 2019). Hurricane Barry Discussion Number 13 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 13, 2019.
- ^ Beven, Jack (July 13, 2019). Tropical Storm Barry Discussion Number 13 (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 14, 2019.
- ^ Beven, Jack (July 13, 2019). Tropical Storm Barry Intermediate Advisory Number 13A (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 14, 2019.
- ^ a b NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information, State of the Climate: Hurricanes and Tropical Storms for July 2019, published online August 2019, retrieved on October 19, 2020 from https://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/sotc/tropical-cyclones/201907.
- ^ Roberts III, Faimon A. (July 10, 2019). "Mandatory evacuation in Plaquemines: Order to leave East Bank goes into effect Thursday". The Times-Picayune/The New Orleans Advocate. New Orleans, Louisiana. Retrieved July 10, 2019.
- ^ Williams, Jessica (July 11, 2019). "Mandatory evacuation for lower-lying areas of Jefferson Parish: 'People's lives are more important'". The Times-Picayune/The New Orleans Advocate. New Orleans, Louisiana. Retrieved July 11, 2019.
- ^ "The Latest: Tropical Storm Barry Forms in the Gulf". The Minneapolis Star-Tribune. Associated Press. July 11, 2019. Retrieved July 11, 2019.
- ^ Mcauley, Anthony (July 9, 2019). "Shell evacuates non-essential staff from Gulf of Mexico platforms as Invest 92L storm brews". The Times-Picayune/The New Orleans Advocate. New Orleans, Louisiana. Retrieved July 10, 2019.
- ^ Beven, Jack (July 11, 2019). Tropical Storm Barry Advisory Number 6 (Report). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 11, 2019.
- ^ "Curfews Set for Acadiana". KATC News. Acadiana, Louisiana: The E.W. Scripps Co. July 12, 2019. Retrieved July 12, 2019.
- ^ a b Williams, Jessica (July 11, 2019). "New Orleans officials give updates, warnings on Tropical Storm Barry prep; issue no evacuation orders". The Times-Picayune/The New Orleans Advocate. New Orleans, Louisiana. Retrieved July 12, 2019.
- ^ McWhriter, Cameron; Calfas, Jennifer (July 11, 2019). "Tropical Storm Barry Brews, Forcing Evacuations". The Wall Street Journal. New York, New York: Dow Jones & Company, Inc. Retrieved July 11, 2019. (subscription required)
- ^ Edwards, John Bel (July 11, 2019). "Gov. Edwards Request Federal Emergency Declaration in Advance of Tropical Storm Barry" (PDF). Office of the Governor. Letter to Trump, Donald J. Baton Rouge, Louisiana: Office of the Governor of Louisiana. Retrieved July 11, 2019.
- ^ Mumphrey, Nicole (July 12, 2019). "President Trump Approves Emergency Declaration for Louisiana Ahead TS Barry". New Orleans, Louisiana: FOX 8. Retrieved July 12, 2019.
- ^ "HHS Secretary Azar Declares Public Health Emergency in Louisiana Due to Tropical Storm Barry" (Press release). United States Department of Health and Human Services. July 12, 2020. Retrieved October 13, 2020.
- ^ Foxx, Keegan (July 12, 2019). "Mississippi Governor Declares State of Emergency Ahead of Barry". WAPT-TV. Jackson, Mississippi: Hearst Television Inc. Retrieved July 12, 2019.
- ^ Jackson, Ann (July 12, 2019). "State Agencies are Positioning Resources Ahead of Tropical Storm Barry's Arrival". WLBT. Jackson, Mississippi. Retrieved July 12, 2019.
- ^ Global Catastrophe Recap July 2019 (PDF) (Report). AON. August 8, 2019. Retrieved October 14, 2020.
- ^ Stewart, Stacy R. (July 10, 2019). Potential Tropical Cyclone Two Intermediate Advisory Number 1A (Report). National Hurricane Center. Retrieved July 10, 2019.
- ^ "New Orleans flooding caused by sudden rain in what might be 'a taste of what could occur'". New Orleans, Louisiana: NOLA.com. July 9, 2019. Retrieved July 10, 2019.
- ^ a b Breslin, Sam (July 10, 2019). "New Orleans Flash Flood Emergency: Streets Inundated, City Offices Closed". Atlanta, Georgia: The Weather Channel. Retrieved July 10, 2019.
- ^ a b Livingston, Ian (July 10, 2019). "New Orleans Just Faced a Flash Flood Emergency, and Barry Could Bring More Severe Flooding Saturday, Testing Levees". The Washington Post. Retrieved July 10, 2019. (subscription required)
- ^ Alex Lamers (July 16, 2019). Post-Tropical Cyclone Barry Advisory Number 25 (Report). Weather Prediction Center. Retrieved July 16, 2019.
- ^ "Barry Making Landfall as Hurricane, Poised to Dump up to 2 Feet of Rain Inland". Accuweather. Archived from the original on July 13, 2019. Retrieved July 19, 2019.
- ^ Sledge, Matt (July 13, 2019). "Overtopped Levee in Terrebonne Prompts Partial Evacuation; people, Cat Rescued from Cut Off Island". The Times-Picayune/The New Orleans Advocate. New Orleans, Louisiana. Retrieved July 13, 2019.
- ^ "La. 1 Closed South of Golden Meadow". Houma Today. July 12, 2019. Retrieved July 12, 2019.
- ^ a b Ling, Danielle (July 15, 2019). "Cleanup Begins After Barry, First Hurricane of the Season, Hits Louisiana". PropertyCasualty360. Retrieved October 12, 2020.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Mcauley, Anthony; Haselle, Della (July 13, 2019). "As Hurricane Barry rolls in, over 114,000 Louisiana customers without power, some areas inaccessible". New Orleans, Louisiana: NOLA.com. Retrieved July 13, 2019.
- ^ Brennan, Sean (July 12, 2019). "Outages: Grand Isle Power Knocked as Storm Nears, Thousands Without Power in Jefferson, Terrebonne Parishes". New Orleans, Louisiana: WWL-TV. Retrieved July 12, 2019.
- ^ Holcombe, Madeline (July 13, 2019). "Rolling Stones' concert postponed as Tropical Storm Barry nears landfall". CNN. Retrieved September 15, 2020.
- ^ Beveridge, Lici (July 12, 2019). "Coast Guard Aircrew Rescues 5 People in Gulf as Tropical Storm Barry Gathers Steam". Jackson, Mississippi: Clarion Ledger. Mississippi Clarion Ledger. Retrieved July 12, 2019. (subscription required)
- ^ Event: Tornado in Forrest, MS [2019-07-14 05:25 CST-6] (Report). Storm Events Database. National Climatic Data Center. 2019. Retrieved November 25, 2019.
- ^ {{cite news|title=
- ^ a b c d "Hurricane Barry Struck the Gulf Coast and Caused Flooding From Louisiana Into Arkansas (RECAP)". The Weather Channel. July 18, 2019. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ Event: Storm Surge/Tide in Jackson, Mississippi [2019-07-11 21:00 CST-6] (Report). Storm Events Database. National Climatic Data Center. 2019. Retrieved November 25, 2019.
- ^ Johnson, Annie (July 13, 2019). "Areas of South Mississippi Seeing Impacts of Hurricane Barry". WLOX. Retrieved July 17, 2019.
- ^ Vollers, Anna Claire (July 14, 2019). "Hurricane Barry Leaves Flooding, Sewer Overflows, Closed Beaches in its Wake". Advance Local. Retrieved July 17, 2019.
- ^ a b Barry, Morgan; Maniscalco, Joe (2019). Hurricane Barry - July 13, 2019 (Report). Mobile-Pensacola National Weather Service. Retrieved November 23, 2019.
- ^ a b Adams, Char (July 15, 2019). "Good Samaritans Form Human Chain to Rescue Swimmers from Rip Current in Florida". People Magazine. Retrieved July 17, 2019.
{{cite magazine}}: Cite magazine requires|magazine=(help) - ^ a b c Heavy Rain/Flooding with Barry on July 14-17, 2019. National Weather Service Little Rock, Arkansas (Report). July 18, 2019. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ Bacon, John (July 16, 2019). "Humane Society SOS: Dogs Swim For Their Lives as Ark. Shelter Floods. Community Comes To The Rescue". USA Today. Retrieved October 12, 2020.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Brackett, Ron (July 16, 2019). "Barry Impacts: Flooding Swamps Arkansas Police Station and Animal Shelter; Washes Out Highways". The Weather Company. Retrieved July 17, 2019.
- ^ Jeromin, Kerrin (July 16, 2020). "Arkansas 5th State Since 2017 to Get Record Tropical Rain". WeatherNation TV. Retrieved October 16, 2020.
- ^ a b Sonnenbury, Kelly (July 17, 2019). "IN PHOTOS: Funnel clouds, flash flooding, more storms ahead". Pelmorex Media. The Weather Network. Retrieved July 17, 2019.
- ^ Hamilton, Tyler (July 17, 2019). "Toronto just had its rainiest July day in over half a decade". Pelmorex Media. The Weather Network. Retrieved July 17, 2019.
- ^ History of Tropical Cyclone Remnants for Central Indiana (Report). National Weather Service Indianapolis, Indiana. 2019. Retrieved October 22, 2020.
- ^ "Barry Remnants Leave Power Out, Trees Down in New Jersey". NBC 10 Philadelphia. July 18, 2019. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ Sosnowski, Alex (July 17, 2019). "Barry Still Packing a Punch with Heavy Thunderstorms, Flooding Downpours". Accuweather. Retrieved October 19, 2020.
- ^ Kirk, Bryan (July 13, 2020). "Hurricane Barry: Houston Taking Donations For Storm Victims". Patch Media. Retrieved October 12, 2020.
- ^ "Barry Spares New Orleans but Fuels Fears of Floods and Tornadoes". The Guardian. July 14, 2019. Retrieved October 16, 2020.
- ^ a b c Preliminary Damage Assessment Report Louisiana–Hurricane Barry FEMA-4458-DR (PDF) (Report). August 27, 2019. Retrieved October 23, 2020.
{{cite report}}: Unknown parameter|agency=ignored (help) - ^ a b Jacobs, David (August 27, 2020). "Federal Government Agrees to Help Pay for Louisiana's Recovery from Hurricane Barry". The Center Square. Retrieved October 12, 2020.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "President Donald J. Trump Approves Louisiana Disaster Declaration" (Press release). Federal government of the United States. August 27, 2020. Retrieved October 12, 2020.
External links
- The National Hurricane Center's advisory archive on Hurricane Barry
- The Weather Prediction Center's advisory archive on Hurricane Barry
- The Weather Prediction Center's storm summaries on Barry