Religion in Lebanon

Lebanon is an eastern Mediterranean country that is composed of mostly Muslims and Christians.[2] The main two religions are Islam with (61.1% of the citizens (Sunni, Shia, and a small number of Alawites and Ismailis) and Christianity with 33.7% of the citizens (the Maronite Church, the Greek Orthodox Church, the Melkite Greek Catholic Church, Protestantism, the Armenian Apostolic Church). The Druze are about 5.2% of the citizens.[2] The country has the most religiously diverse society of all states within the Middle East, comprising 18 recognized religious sects.[3][4] But outside of Lebanon, Lebanese people (including diaspora) are mostly Christians.[5][6] It is also estimated that a large proportion of its population are refugees (1.5 million out of a bit over 6 million in 2017) which affects statistics.[3] The refugees mostly Syrian or Palestinian are predominately Sunni but also includes Christians and Shia.[3]
Lebanon thus differs from other Middle East countries where Muslims are the overwhelming majority and more resembles Bosnia-Herzegovina and Albania, both in Southeastern Europe, in having a diverse mix of Muslims and Christians that each make up approximately half the country's population. Christians were once a majority inside Lebanon and are still a majority in the diaspora of the nearly 14 million Lebanese people living outside of Lebanon. The president of the country is traditionally a Maronite Christian, the prime minister a Sunni Muslim, and the speaker of parliament a Shia Muslim.
Population by religious affiliation
No official census has been taken since 1932, reflecting the political sensitivity in Lebanon over confessional (i.e. religious) balance.[7] As a result, the religious affiliation of the Lebanese population is very difficult to establish with certainty and various sources are used to get the possible estimate of the population by religious affiliation.
The following are different sources that do not pretend to be fully representative of the religious affiliation of the people of Lebanon.
A 2012 study conducted by Statistics Lebanon, a Beirut-based research firm, found that Lebanon's population is estimated to be 59.8% Muslim (28.4% Shia; 31.4% Sunni), 5.72% Druze, 33.2% Christian (22.52% Maronite, 8.15% Greek Orthodox, Melkite, 3.62% ).[8]
The CIA World Factbook estimates (2020) the following (data do not include Lebanon's sizable Syrian and Palestinian refugee populations): Muslim 61.1% (30.6% Sunni, 30.5% Shia, smaller percentages of Alawites and Ismailis), Christian 33.7% (Maronite Catholics are the largest Christian group), Druze 5.2%, and very small numbers of Jews, Baha'is, Buddhists, and Hindus.[2]
The International Foundation for Electoral Systems provides source for the registered voters in Lebanon for 2018 (it has to be noted that voter registration does not include people under 18 and unregistered voters) that puts the numbers as following: Sunni Islam 20.40%, Shia Islam 27.40%, Maronite Catholic 25.52%, Greek Orthodox 8.15%, Druze 5.72%, Melkite Catholic 5.62%, Armenian Apostolic 2.64%, other Christian Minorities 1.28%, Alawite Shia Islam 0.88%, Armenian Catholic 0.62%, Evangelical Protestant 0.53%, and other 0.18% of the population.[citation needed]
There is also a very small and ancient community of Zoroastrians numbering between 100-500 individuals.[9][10] Lebanon also has a Jewish population, estimated at less than 100.[3]
Demographics
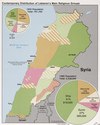
Geographical distribution of sects in Lebanon
Lebanese Muslims
Lebanese Muslims are divided into many sects like Sunnis, Shias, Alawites, and Ismailis.
Lebanese Sunnis are mainly residents of the major cities: west Beirut, Tripoli, and Sidon. Sunnis are also present in rural areas including Akkar, Ikleem al Kharoub, and the western Beqaa Valley.
Lebanese Shias are concentrated in Southern Lebanon, Baalbek District, Hermel District and the south Beirut (southern parts of Greater Beirut).
Lebanese Druze
Under the Lebanese political division (Parliament of Lebanon Seat Allocation) the Druze community goes along with Lebanon's Muslim community to make 50% of the parliament, despite the Druze and Muslims having very different beliefs. Most Druze do not identify as Muslims,[11][12][13][14][15] and they do not accept the five pillars of Islam.[16]
The Druze are located in the areas known as the Metn, Gharb, Chouf, Wadi-al Taym, Beirut and its suburbs, which are the modern day districts of Metn, Baabda, Aley, Chouf, Rashaya, Hasbaya and Beirut. The Druze make the majority in cities like Aley, Choueifat, Rashaya, Ras el-Matn and Baakline, while the rest of the city population is made up with different Christian sects.
Lebanese Christians
Lebanese Christians are divided into many groups, several types of Catholics for instance the Maronites and Greek Catholics (Melkites), Greek Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox (among which are Syriacs, Armenians and Copts), Church of the East (Assyrians) and Protestants.
Lebanese Maronites are concentrated in the north Beirut (northern parts of Greater Beirut), northern part of Mount Lebanon Governorate, southern part of North Governorate, parts of Beqaa Governorate and South Governorate.[17]
Greek Catholics are found everywhere but in particular in districts on the eastern slopes of the Lebanese mountain range and in Zahle where they are a majority.
Lebanese Greek Orthodox are concentrated in the north Beirut (northern parts of Greater Beirut), Lebanese North areas including Zgharta, Bsharre, Koura, and Batroun.
Lebanese Protestants are concentrated mainly within the area of Beirut and Greater Beirut.
The other Lebanese Christians are concentrated also in similar areas like in east Beirut (northern parts of Greater Beirut), Mount Lebanon, Zahlé, and Jezzine.
Lebanese Jews
As of 2018, the Jews in Lebanon make up the smallest religious group, with merely 29 persons or 0.08% of the population.
Religion and society
Religion and politics
Religion plays a big role in politics; some researchers describe the political system in Lebanon as "coming out of the womb of religion and politics".[18] After the independence from France in 1943, the leaders of Lebanon agreed on the distribution of the political positions in the country according to religious affiliation, known as the national pact. Since then, the President is always a Maronite Christian, the Prime Minister is always a Sunni Muslim and the Speaker of the Parliament is always a Shia Muslim.
Most parties have a sectarian identity as well, and represent the interests of their religion. A lot of clergies are involved in politics, and some are members and leaders of those parties.[19]
Current political and religious issues
Under the terms of an agreement known as the National Pact between the various political and religious leaders of Lebanon, the president of the country must be a Maronite, the Prime Minister must be a Sunni, and the Speaker of Parliament must be a Shia.[20][21]
Although Lebanon is a secular country, family matters such as marriage, divorce and inheritance are still handled by the religious authorities representing a person's faith. Calls for civil marriage are unanimously rejected by the religious authorities but civil marriages conducted in another country are recognized by Lebanese civil authorities.
Non-religion is not recognized by the state. However, in 2009, the Minister of the Interior Ziad Baroud made it possible to have a citizen's religious sect removed from his identity card.[22][23]
In April 2010, Laïque Pride, a secular group co-founded by feminist Yalda Younes, called for "an end to the country's deep-rooted sectarian system" and for a "secular Lebanon". Laïque Pride supports the enacting of a unified Civil Code for the Personal Status Law.[24]
On April 26, 2010, in response to Hizb ut-Tahrir's growing appeal in Beirut and demands to re-establish an Islamic caliphate, a Laïque Pride march was held in Beirut. Three days later, 70,000 gathered in Martyrs' Square, Beirut for a march organized by Laïque Pride.
In 2011, hundreds of protesters rallied in Beirut on 27 February in a Laïque Pride march, calling for reform of the country's confessional political system. At the same time, a peaceful sit-in took place in Saida.[25]
At a march in May 2012 in which 600 participated, Laïque Pride issued six demands, four concerning women's rights and two concerning media freedom. Secular student clubs from Saint Joseph University (USJ), the Lebanese Academy of Fine Arts (ALBA), as the American University of Beirut (AUB) also participated in the march.
In October 2019, and until August 2020, a series of civil protests ensued in Lebanon, now known as the October Revolution condemning sectarian rule amongst a myriad of other issues plaguing their country.[26] Lina Khatib, a journalist for Al-Jazeera, has labelled these protests as "cross-sectarian". She notes: "They are taking place across Lebanon, rather than only in Beirut. And they are demanding the fall of the government from the outset, while criticising political leaders from every sect."[27]
Gallery
-
Detail of the dome of the Khatem al-Anbiyaa Mosque in downtown Beirut
-
Saint George Eastern Orthodox Cathedral in downtown Beirut
-
Saint George Greek Orthodox Cathedral on Nejme Square
-
Druze Prophet of Job Shrine
-
Listing the largest community in the Lebanese electorate, per qada and/or "minor district".
Green = Sunni
Purple = Shia
Blue = Druze
Yellow = Maronite
Orange = Greek Orthodox
Red = Armenian Orthodox
See also
- Christianity in Lebanon
- Islam in Lebanon
- History of the Jews in Lebanon
- Secularism in Lebanon
- Irreligion in Lebanon
- Freedom of religion in Lebanon
- Freemasonry in Lebanon
- Demographics of Lebanon
References
- ^ "Lebanon - the World Factbook".
- ^ a b c "Lebanon — The World Factbook". Central Intelligence Agency, United States. Retrieved 10 January 2021.
- ^ a b c d "International Religious Freedom Report for 2017". www.state.gov. United States Department of State. Retrieved 30 March 2019. Cites Statistics Lebanon for most Lebanon statistics
- ^ Alfred B. Prados (June 8, 2006). "CRS Issue Brief for Congress: Lebanon". The Library of Congress. Retrieved June 11, 2012.
- ^ "Bassil promises to ease citizenship for expatriates". The Daily Star. 1 May 2014. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- ^ Writer, Joseph A. Kechichian, Senior (17 November 2015). "Lebanon contemplates a new citizenship law". gulfnews.com. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Population (Lebanon)". Country Studies. Federal Research Division of the Library of Congress. Retrieved 30 December 2019.
- ^ "International Religious Freedom Report for 2012: Lebanon". United States Department of State. Retrieved 30 March 2019.
- ^ "Seif And The "Fire Worshipers" Of Beirut?". Seif and his Beiruti Adventures. 9 October 2010.
- ^ Chebaro, Mohamed (18 November 2014). "Lebanon's Zoroastrians want a civil state". NOw (mmedia.me). Archived from the original on 3 May 2016.
- ^ Pintak, Lawrence (2019). America & Islam: Soundbites, Suicide Bombs and the Road to Donald Trump. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 86. ISBN 9781788315593.
- ^ Jonas, Margaret (2011). The Templar Spirit: The Esoteric Inspiration, Rituals and Beliefs of the Knights Templar. Temple Lodge Publishing. p. 83. ISBN 9781906999254.
[Druze] often they are not regarded as being Muslim at all, nor do all the Druze consider themselves as Muslim
- ^ "Are the Druze People Arabs or Muslims? Deciphering Who They Are". Arab America. Arab America. 8 August 2018. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
- ^ J. Stewart, Dona (2008). The Middle East Today: Political, Geographical and Cultural Perspectives. Routledge. p. 33. ISBN 9781135980795.
Most Druze do not consider themselves Muslim. Historically they faced much persecution and keep their religious beliefs secrets.
- ^ Yazbeck Haddad, Yvonne (2014). The Oxford Handbook of American Islam. Oxford University Press. p. 142. ISBN 9780199862634.
While they appear parallel to those of normative Islam, in the Druze religion they are different in meaning and interpretation. The religion is consider distinct from the Ismaili as well as from other Muslims belief and practice... Most Druze consider themselves fully assimilated in American society and do not necessarily identify as Muslims..
- ^ De McLaurin, Ronald (1979). The Political Role of Minority Groups in the Middle East. Michigan University Press. p. 114. ISBN 9780030525964.
Theologically, one would have to conclude that the Druze are not Muslims. They do not accept the five pillars of Islam. In place of these principles the Druze have instituted the seven precepts noted above..
- ^ Lebanon Maronites Overview World Directory of Minorities. June 2008. Retrieved 28 December 2013.
- ^ "الإصلاح والسلطة في لبنان بين الديني والسياسي". 2020-10-24. Archived from the original on 2020-10-24. Retrieved 2020-10-31.
- ^ Limited, Elaph Publishing (7 February 2008). "رجال الدين في لبنان: يوم للرب وآخر للسياسة". @Elaph (in Arabic). Retrieved 2020-10-31.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "AUB: The Lebanese Civil War and the Taif Agreement". 2018-10-15. Archived from the original on 2018-10-15. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- ^ "Politics and the Airlines". International Affairs. 42 (2): 276. April 1966. doi:10.1093/ia/42.2.276a. ISSN 1468-2346.
- ^ "Religious affiliation to disappear from Lebanese documents". www.asianews.it. 13 February 2009. Retrieved 30 March 2019.
- ^ Religious Affiliation Can Be Removed From Lebanese ID Cards. Barcode Nation (2009-02-25). Retrieved on 2013-09-26.
- ^ adonis49. "Lebanese Laïque Pride activist group". Adonis Diaries. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Reuters Staff (2011-02-27). "Lebanese protest against sectarian political system". Reuters. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
{{cite news}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ Network, Readables (2019-10-27). "Lebanon Protesters Found Strength in Unity, Ditched Sectarianism". Report Syndication. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- ^ Khatib, Lina. "Lebanon is experiencing a social revolution". www.aljazeera.com. Retrieved 2020-10-08.
- ^ "Religion in Lebanon | Arabic Pages". 8 February 2017.