Papaya
| Papaya | |
|---|---|
| |
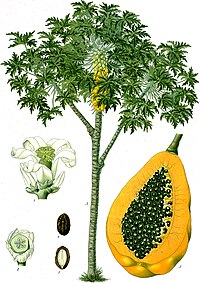
| Papaya tree and fruit, from Koehler's Medicinal-Plants (1887) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | C. papaya
|
| Binomial name | |
| Carica papaya | |
The papaya (from Carib via Spanish), is the fruit of the plant Carica papaya, in the genus Carica. It is native to the tropics of the Americas, and was cultivated in Mexico several centuries before the emergence of the Mesoamerican classic cultures. It is sometimes called "tree melon" or "pawpaw," but the North American pawpaw is a different species, in the genus Asimina.
It is a large tree-like plant, the single stem growing from 5 to 10 meters tall, with spirally arranged leaves confined to the top of the trunk; the lower trunk is conspicuously scarred where leaves and fruit were borne. The leaves are large, 50-70 cm diameter, deeply palmately lobed with 7 lobes. The tree is usually unbranched if unlopped. The flowers are similar in shape to the flowers of the Plumeria but are much smaller and wax like. They appear on the axils of the leaves, maturing into the large 15-45 cm long, 10-30 cm diameter fruit. The fruit is ripe when it feels soft (like a ripe avocado or a bit softer) and its skin has attained an amber to orange hue. The fruit's taste is vaguely similar to pineapple and peach, although much milder without the tartness.
It is the first fruit tree to have its genome deciphered.[1]
Cultivation and uses of papaya
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | 163 kJ (39 kcal) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
9.81 g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sugars | 5.90 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dietary fibre | 1.8 g | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0.14 g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
0.61 g | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| †Percentages estimated using US recommendations for adults,[2] except for potassium, which is estimated based on expert recommendation from the National Academies.[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Originally from southern Mexico, Central America and northern South America, the papaya is now cultivated in most countries with a tropical climate, such as Brazil, India, South Africa, Sri Lanka, and the Philippines.
In Hawaii, two varieties of genetically-modified papayas: SunUp and Rainbow, have been grown by several growers since their development in the 1990s.[1] By 2004, non-genetically modified and organic papayas throughout Hawaii had experienced widespread contamination from the genetically-modified varieties.[2]
The ripe fruit is usually eaten raw, without the skin or seeds. The unripe green fruit of papaya can be eaten cooked, usually in curries, salads and stews.
Green papaya fruit and the tree's latex are both rich in an enzyme called papain, a protease which is useful in tenderizing meat and other proteins. Its ability to break down tough meat fibers was utilized for thousands of years by indigenous Americans. It is included as a component in powdered meat tenderizers, and is also marketed in tablet form to remedy digestive problems. Green papaya is used in Thai cuisine, both raw and cooked.[4] Papain is also popular (in countries where it grows) as a topical application in the treatment of cuts, rashes, stings and burns. Papain ointment is commonly made from fermented papaya flesh, and is applied as a gel-like paste. Harrison Ford was treated for a ruptured disc incurred during filming of Indiana Jones and the Temple of Doom by having papain injected into his back.[5]
Women in India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and other parts of the world have long used papaya as a folk remedy for contraception and abortion.[citation needed] Medical research in animals has confirmed the contraceptive and abortifacient capability of papaya, and also found that papaya seeds have contraceptive effects in adult male langur monkeys, possibly in adult male humans as well.[6] Unripe papaya is especially effective in large amounts or high doses. Papaya is not teratogenic and will not cause miscarriage in small, ripe amounts. Phytochemicals in papaya may suppress the effects of progesterone.[7]
The black seeds are edible and have a sharp, spicy taste. They are sometimes ground up and used as a substitute for black pepper. In some parts of Asia the young leaves of papaya are steamed and eaten like spinach.
The papaya fruit is susceptible to the Papaya Fruit Fly. This wasp-like fly lays its eggs in young fruit.
Allergies and side-effects
Caution should be taken when harvesting, as papaya is known to release a latex fluid when not quite ripe, which can cause irritation and provoke allergic reaction in some people. The papaya fruit, seeds, latex, and leaves also contains carpaine, an anthelmintic alkaloid which could be dangerous in high doses.
Excessive consumption of papaya, as of carrots, can cause carotenemia, the yellowing of soles and palms which is otherwise harmless.[citation needed]
Ethnomedical uses

- The mature (ripe) fruit treats ringworm, green fruits treat high blood pressure, and are used as an aphrodisiac.
- The fruit can be directly applied topically to skin sores [1].
- The juice of the fruit (specifically the enzymes within it) are used to reduce gastrointestinal gas, useful to sufferers of IBS.
- The seeds are anti-inflammatory, anthelmintic, and analgesic, and they are used to treat stomachache and fungal infections[1].
- The leaves are used as a heart tonic, analgesic, and to treat stomachache[1].
- The roots are used as an analgesic[2].
Diseases
Names in other languages
- Assamese - Amita
- Bengali - PEnPe (Bengali: পেঁপে),
- Chinese - mugua (木瓜; literally "tree melon")
- Ewe - pawpo[citation needed]
- Filipino - Papaya
- Indonesian - pepaya (the word papaya originated from this word)
- Javanese - kates
- Malay- betik
- Portuguese - mamão (Brazil/Angola), papaia (Portugal/Angola)
- Sinhala - papol', guslabu (literally "tree melon")
- Spanish - papaya
- Cuba - fruta bomba
- Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico, and Venezuela - Lechosa
- Swahili -Papai
- Sri Lankan English - papaw
- Thai - malakau (มะละกอ)
- Vietnamese - đu đủ
- Hindi - papita
- Marathi - papai
- Tamil - papaali
- Telugu - Boppayi
- Gujarati - Pappayu
- Malayalam - papaya, omakai
- Swahili - papayu
oriya- Amrut Bhanda..
See also
- Papaya Coconut, a 1986 hit song by Swedish pop and country singer Kikki Danielsson.
-
Papaya tree
-
Papaya leaf
-
female flowers
-
Papaya
-
Papaya trunk with immature fruit
-
tree and flowers, from Koehler's Medicinal-Plants (1887)
-
Hawaiian papaya (with lilies and ginger)
-
Tanzanian Papaya tree
-
An Indian papaya tree
References
- ^ University of Granada
- ^ United States Food and Drug Administration (2024). "Daily Value on the Nutrition and Supplement Facts Labels". FDA. Archived from the original on 2024-03-27. Retrieved 2024-03-28.
- ^ National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Health and Medicine Division; Food and Nutrition Board; Committee to Review the Dietary Reference Intakes for Sodium and Potassium (2019). Oria, Maria; Harrison, Meghan; Stallings, Virginia A. (eds.). Dietary Reference Intakes for Sodium and Potassium. The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health. Washington, DC: National Academies Press (US). ISBN 978-0-309-48834-1. PMID 30844154. Archived from the original on 2024-05-09. Retrieved 2024-06-21.
- ^ Green Papaya Salad Recipe - ThaiTable.com
- ^ Entry on Harrison Ford's back treatment.
- ^ Lohiya, N. K. (2002). "Chloroform extract of Carica papaya seeds induces long-term reversible azoospermia in langur monkey" ([dead link] – Scholar search). Asian Journal of Andrology. 4: 17–26. Retrieved 2006-11-18.
{{cite journal}}: External link in|format=|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Oderinde, O. "Abortifacient properties of Carica papaya (Linn) seeds in female Sprague-Dawley rats". Niger Postgrad Medical Journal. PMID 12163882.
- ^ Berrin, Katherine & Larco Museum. The Spirit of Ancient Peru:Treasures from the Museo Arqueológico Rafael Larco Herrera. New York: Thames and Hudson, 1997.








