MATLAB
 | |
| File:MATLAB-R2008a-for-Linux.png MATLAB R2008a screenshot | |
| Developer(s) | MathWorks |
|---|---|
| Stable release | R2011a
/ April 8, 2011 |
| Preview release | R2020a Prerelease [±] |
| Written in | C, Java |
| Operating system | Cross-platform[1] |
| Type | Technical computing |
| License | Proprietary |
| Website | MATLAB product page |
| Paradigm | multi-paradigm: imperative, procedural, object-oriented, array |
|---|---|
| Designed by | Cleve Moler |
| Developer | MathWorks |
| First appeared | late 1970s |
| Preview release | R2020a Prerelease [±] |
| Typing discipline | dynamic, weak |
| OS | Cross-platform |
| Website | www |
MATLAB (matrix laboratory) is a numerical computing environment and fourth-generation programming language. Developed by MathWorks, MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages, including C, C++, Java, and Fortran.
Although MATLAB is intended primarily for numerical computing, an optional toolbox uses the MuPAD symbolic engine, allowing access to symbolic computing capabilities. An additional package, Simulink, adds graphical multi-domain simulation and Model-Based Design for dynamic and embedded systems.
In 2004, MATLAB had around one million users across industry and academia.[2] MATLAB users come from various backgrounds of engineering, science, and economics. MATLAB is widely used in academic and research institutions as well as industrial enterprises.
History
MATLAB was created in the late 1970s by Cleve Moler, the chairman of the computer science department at the University of New Mexico.[3] He designed it to give his students access to LINPACK and EISPACK without having to learn Fortran. It soon spread to other universities and found a strong audience within the applied mathematics community. Jack Little, an engineer, was exposed to it during a visit Moler made to Stanford University in 1983. Recognizing its commercial potential, he joined with Moler and Steve Bangert. They rewrote MATLAB in C and founded MathWorks in 1984 to continue its development. These rewritten libraries were known as JACKPAC.[4] In 2000, MATLAB was rewritten to use a newer set of libraries for matrix manipulation, LAPACK.[5]
MATLAB was first adopted by control design engineers, Little's specialty, but quickly spread to many other domains. It is now also used in education, in particular the teaching of linear algebra and numerical analysis, and is popular amongst scientists involved with image processing.[3]
Syntax
This article is written like a manual or guide. (October 2008) |
The MATLAB application is built around the MATLAB language. The simplest way to execute MATLAB code is to type it in the Command Window, which is one of the elements of the MATLAB Desktop. When code is entered in the Command Window, MATLAB can be used as an interactive mathematical shell. Sequences of commands can be saved in a text file, typically using the MATLAB Editor, as a script or encapsulated into a function, extending the commands available.[6]
Variables
Variables are defined with the assignment operator, =. MATLAB is a weakly dynamically typed programming language. It is a weakly typed language because types are implicitly converted.[7] It is a dynamically typed language because variables can be assigned without declaring their type, except if they are to be treated as symbolic objects,[8] and that their type can change. Values can come from constants, from computation involving values of other variables, or from the output of a function. For example:
>> x = 17
x =
17
>> x = 'hat'
x =
hat
>> y = x + 0
y =
104 97 116
>> x = [3*4, pi/2]
x =
12.0000 1.5708
>> y = 3*sin(x)
y =
-1.6097 3.0000
MATLAB has several functions for rounding fractional values to integers:
round(X): round to nearest integer, trailing 5 rounds to the nearest integer away from zero. For example,round(2.5)returns 3;round(-2.5)returns -3.fix(X): round to nearest integer toward zero (truncate). For example,fix(2.7)returns 2;fix(-2.7)returns -2floor(X): round to the nearest integer toward minus infinity (round to the nearest integer less than or equal to X). For example,floor(2.7)returns 2;floor(-2.3)returns -3.ceil(X): round to the nearest integer toward positive infinity (round to the nearest integer greater than or equal to X); for example,ceil(2.3)returns 3;ceil(-2.7)returns -2
Vectors/matrices
MATLAB is a "Matrix Laboratory", and as such it provides many convenient ways for creating vectors, matrices, and multi-dimensional arrays. In the MATLAB vernacular, a vector refers to a one dimensional (1×N or N×1) matrix, commonly referred to as an array in other programming languages. A matrix generally refers to a 2-dimensional array, i.e. an m×n array where m and n are greater than or equal to 1. Arrays with more than two dimensions are referred to as multidimensional arrays. Arrays are among the fundamental types and several standard functions natively support array operations which are optimized to work without explicit loops. Therefore the MATLAB language is also an example of array programming language.
MATLAB provides a simple way to define simple arrays using the syntax: init:increment:terminator. For instance:
>> array = 1:2:9
array =
1 3 5 7 9
defines a variable named array (or assigns a new value to an existing variable with the name array) which is an array consisting of the values 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9. That is, the array starts at 1 (the init value), increments with each step from the previous value by 2 (the increment value), and stops once it reaches (or to avoid exceeding) 9 (the terminator value).
>> array = 1:3:9
array =
1 4 7
the increment value can actually be left out of this syntax (along with one of the colons), to use a default value of 1.
>> ari = 1:5
ari =
1 2 3 4 5
assigns to the variable named ari an array with the values 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, since the default value of 1 is used as the incrementer.
Indexing is one-based,[9] which is the usual convention for matrices in mathematics, although not for some programming languages.
Matrices can be defined by separating the elements of a row with blank space or comma and using a semicolon to terminate each row. The list of elements should be surrounded by square brackets: []. Parentheses: () are used to access elements and subarrays (they are also used to denote a function argument list).
>> A = [16 3 2 13; 5 10 11 8; 9 6 7 12; 4 15 14 1]
A =
16 3 2 13
5 10 11 8
9 6 7 12
4 15 14 1
>> A(2,3)
ans =
11
Sets of indices can be specified by expressions such as "2:4", which evaluates to [2, 3, 4]. For example, a submatrix taken from rows 2 through 4 and columns 3 through 4 can be written as:
>> A(2:4,3:4)
ans =
11 8
7 12
14 1
A square identity matrix of size n can be generated using the function eye, and matrices of any size with zeros or ones can be generated with the functions zeros and ones, respectively.
>> eye(3)
ans =
1 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 1
>> zeros(2,3)
ans =
0 0 0
0 0 0
>> ones(2,3)
ans =
1 1 1
1 1 1
Most MATLAB functions can accept matrices and will apply themselves to each element. For example, mod(2*J,n) will multiply every element in "J" by 2, and then reduce each element modulo "n". MATLAB does include standard "for" and "while" loops, but using MATLAB's vectorized notation often produces code that is easier to read and faster to execute. This code, excerpted from the function magic.m, creates a magic square M for odd values of n (MATLAB function meshgrid is used here to
generate square matrices I and J containing 1:n).
[J,I] = meshgrid(1:n);
A = mod(I+J-(n+3)/2,n);
B = mod(I+2*J-2,n);
M = n*A + B + 1;
Semicolons
Unlike many other languages, where the semicolon is used to terminate commands, in MATLAB the semicolon serves to suppress the output of the line that it concludes (it serves a similar purpose in Mathematica.)
Graphics
Function plot can be used to produce a graph from two vectors x and y. The code:
x = 0:pi/100:2*pi;
y = sin(x);
plot(x,y)
produces the following figure of the sine function:
Three-dimensional graphics can be produced using the functions surf, plot3 or mesh.
[X,Y] = meshgrid(-10:0.25:10,-10:0.25:10);
f = sinc(sqrt((X/pi).^2+(Y/pi).^2));
mesh(X,Y,f);
axis([-10 10 -10 10 -0.3 1])
xlabel('{\bfx}')
ylabel('{\bfy}')
zlabel('{\bfsinc} ({\bfR})')
hidden off
|
[X,Y] = meshgrid(-10:0.25:10,-10:0.25:10);
f = sinc(sqrt((X/pi).^2+(Y/pi).^2));
surf(X,Y,f);
axis([-10 10 -10 10 -0.3 1])
xlabel('{\bfx}')
ylabel('{\bfy}')
zlabel('{\bfsinc} ({\bfR})')
| |
| This code produces a wireframe 3D plot of the two-dimensional unnormalized sinc function: | This code produces a surface 3D plot of the two-dimensional unnormalized sinc function: | |

|
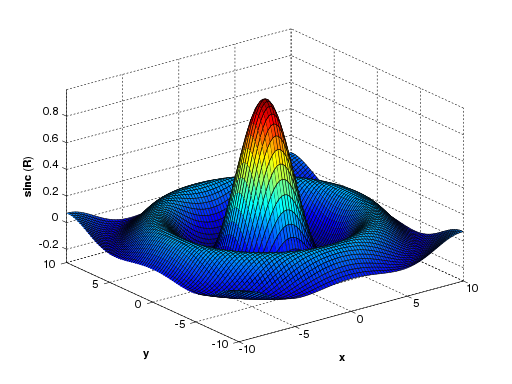
|
Structures
MATLAB supports structure data types. Since all variables in MATLAB are arrays, a more adequate name is "structure array", where each element of the array has the same field names. In addition, MATLAB supports dynamic field names (field look-ups by name, field manipulations etc). Unfortunately, MATLAB JIT does not support MATLAB structures, therefore just a simple bundling of various variables into a structure will come at a cost.[citation needed]
Function handles
MATLAB supports elements of lambda-calculus by introducing function handles, or function references, which are implemented either in .m files or anonymous/nested functions.
Secondary programming
MATLAB also carries secondary programming which incorporates the MATLAB standard code into a more user friendly way to represent a function or system.
Classes
MATLAB supports classes, however the syntax and calling conventions are significantly different than in other languages. MATLAB supports value classes and reference classes, depending if the class has handle as super-class (for reference classes) or not (for value classes).
Depending if a class is declared as value or reference, method call behavior is different. For example, a call to a method
object.method();
can alter any variables of object variable only for reference classes.
Object-oriented programming
MATLAB's support for object-oriented programming includes classes, inheritance, virtual dispatch, packages, pass-by-value semantics, and pass-by-reference semantics.[10]
classdef hello
methods
function doit(this)
disp('Hello!')
end
end
end
When put into a file named hello.m, this can be executed with the following commands:
>> x = hello;
>> x.doit;
Hello!
Interfacing with other languages
MATLAB can call functions and subroutines written in the C programming language or Fortran. A wrapper function is created allowing MATLAB data types to be passed and returned. The dynamically loadable object files created by compiling such functions are termed "MEX-files" (for MATLAB executable).[11][12]
Libraries written in Java, ActiveX or .NET can be directly called from MATLAB and many MATLAB libraries (for example XML or SQL support) are implemented as wrappers around Java or ActiveX libraries. Calling MATLAB from Java is more complicated, but can be done with MATLAB extension,[13] which is sold separately by MathWorks, or using an undocumented mechanism called JMI (Java-to-Matlab Interface),[14] which should not be confused with the unrelated Java Metadata Interface that is also called JMI.
As alternatives to the MuPAD based Symbolic Math Toolbox available from MathWorks, MATLAB can be connected to Maple or Mathematica.[15]
License
MATLAB is a proprietary product of MathWorks, so users are subject to vendor lock-in.[2][16] Although MATLAB Builder can deploy MATLAB functions as library files which can be used with .NET or Java application building environment, future development will still be tied to the MATLAB language.
Alternatives
MATLAB has a number of competitors.[17] Commercial competitors include Mathematica, Maple, IDL by ITT Visual Information Solutions and Metlynx.
There are also free open source alternatives to MATLAB, in particular GNU Octave, FreeMat, and Scilab which are intended to be mostly compatible with the MATLAB language (but not the MATLAB desktop environment).
Among other languages that treat arrays as basic entities (array programming languages) are APL and J, Fortran 95 and 2003, as well as the statistical language S (the main implementations of S are S-PLUS and the popular open source language R).
There are also several libraries to add similar functionality to existing languages, such as Itpp for C++, Perl Data Language for Perl and SciPy together with NumPy and Matplotlib for Python.
Release history
| Version[18] | Release name | Year | Release Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MATLAB 1.0 | 1984 | |||
| MATLAB 2 | 1986 | |||
| MATLAB 3 | 1987 | |||
| MATLAB 3.5 | 1990 | Ran on MS-DOS but required at least a 386 processor. Version 3.5m required math coprocessor | ||
| MATLAB 4 | 1992 | |||
| MATLAB 4.2c | R7 | 1994 | Ran on Windows 3.1. Required a math coprocessor | |
| MATLAB 5.0 | R8 | 1996 | ||
| MATLAB 5.1 | R9 | 1997 | ||
| MATLAB 5.1.1 | R9.1 | |||
| MATLAB 5.2 | R10 | 1998 | ||
| MATLAB 5.2.1 | R10.1 | |||
| MATLAB 5.3 | R11 | 1999 | ||
| MATLAB 5.3.1 | R11.1 | |||
| MATLAB 6.0 | R12 | 2000 | ||
| MATLAB 6.1 | R12.1 | 2001 | ||
| MATLAB 6.5 | R13 | 2002 | ||
| MATLAB 6.5.1 | R13SP1 | 2003 | ||
| MATLAB 6.5.2 | R13SP2 | |||
| MATLAB 7 | R14 | 2004 | ||
| MATLAB 7.0.1 | R14SP1 | |||
| MATLAB 7.0.4 | R14SP2 | 2005 | March 7, 2005 | |
| MATLAB 7.1 | R14SP3 | September 1, 2005 | ||
| MATLAB 7.2 | R2006a | 2006 | March 1, 2006 | |
| MATLAB 7.3 | R2006b | September 1, 2006 | HDF5-based MAT-file support | |
| MATLAB 7.4 | R2007a | 2007 | March 1, 2007 | |
| MATLAB 7.5 | R2007b | September 1, 2007 | Last release for Windows 2000 and PowerPC Mac. License Server support for Windows Vista[19] | |
| MATLAB 7.6 | R2008a | 2008 | March 1, 2008 | |
| MATLAB 7.7 | R2008b | October 9, 2008 | ||
| MATLAB 7.8 | R2009a | 2009 | March 6, 2009 | First release for 32-bit & 64-bit Windows 7. |
| MATLAB 7.9 | R2009b | September 4, 2009 | First release for Intel 64-bit Mac, and last for Solaris SPARC. | |
| MATLAB 7.9.1 | R2009bSP1 | 2010 | April 1, 2010 | |
| MATLAB 7.10 | R2010a | March 5, 2010 | Last release for Intel 32-bit Mac. | |
| MATLAB 7.11 | R2010b | September 3, 2010 | ||
| MATLAB 7.11.1 | R2010bSP1 | 2011 | March 17, 2011 | |
| MATLAB 7.12 | R2011a | April 8, 2011 |
File Extensions
Native
- .fig
- MATLAB Figure
- .m
- MATLAB function, script, or class
- .mat
- MATLAB binary file for storing variables
- .mex...
- MATLAB executable (platform specific, e.g. ".mexmac" for the Mac, ".mexglx" for Linux, etc.)
- .p
- MATLAB content-obscured .m file (result of pcode() )
Third-party
- .jkt
- GPU Cache file generated by Jacket for MATLAB (AccelerEyes)
- .mum
- MATLAB CAPE-OPEN Unit Operation Model File (AmsterCHEM)
See also
- List of numerical analysis software
- Comparison of numerical analysis software
- List of numerical libraries
Notes
- ^ "Requirements". MathWorks. Retrieved 2010-06-07.
- ^ a b Richard Goering, "Matlab edges closer to electronic design automation world," EE Times, 10/04/2004
- ^ a b Cleve Moler, the creator of MATLAB (2004). "The Origins of MATLAB". Retrieved April 15, 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ "MATLAB Programming Language". Retrieved 2010-12-17.
- ^ Note from Cleve Moler in a Mathworks newsletter Cleve Moler, the creator of MATLAB (2000). "MATLAB Incorporates LAPACK". Retrieved December 20, 2008.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|month=(help) - ^ "MATLAB technical documentation". Mathworks.com. Retrieved 2010-06-07.
- ^ [1] Documentation on MATLAB in relation to other languages
- ^ sym function Documentation for the MATLAB Symbolic Toolbox
- ^ "MATLAB Online Documentation". Mathworks.com. Retrieved 2010-06-07.
- ^ "MATLAB Class Overview". Mathworks.com. Retrieved 2010-06-07.
- ^ "MATLAB external interface guide". Retrieved 2008-05-25.
- ^ Spielman, Dan (2004-02-10). "Connecting C and Matlab". Yale University, Computer Science Department. Retrieved 2008-05-20.
- ^ "MATLAB Builder JA". MathWorks. Retrieved 2010-06-07.
- ^ "Java-to-Matlab Interface". Undocumented Matlab. 2010-04-14. Retrieved 2010-06-07.
- ^ Mathsource item #618 for calling MATLAB from Mathematica Roger Germundsson from Wolfram Research
- ^ Jan Stafford, "The Wrong Choice: Locked in by license restrictions," SearchOpenSource.com, 21 May 2003
- ^ Comparison of mathematical programs for data analysis ScientificWeb
- ^ Cleve Moler (2006). "The Growth of MATLAB and The MathWorks over Two Decades" (PDF). Retrieved August 18, 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ "Do MATLAB versions prior to R2007a run under Windows Vista?" (HTML). 2010. Retrieved February 8, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)
References
- Gilat, Amos (2004). MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications 2nd Edition. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-69420-5.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Quarteroni, Alfio (2006). Scientific Computing with MATLAB and Octave. Springer. ISBN 978-3-540-32612-0.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) - Ferreira, A.J.M. (2009). MATLAB Codes for Finite Element Analysis. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4020-9199-5.
- Lynch, Stephen (2004). Dynamical Systems with Applications using MATLAB. Birkhäuser. ISBN 978-0-8176-4321-8.
External links
- MATLAB overview, at the MathWorks website
- System Requirements - Platform Roadmap, at the MathWorks website.
- MATLAB Central File Exchange - library of over 12,000 MATLAB files and toolboxes, mostly distributed under BSD License.
- Template:Dmoz
- comp.soft-sys.matlab
- LiteratePrograms (MATLAB)
- Official blogs
- Examples to remote control R&S instruments from MATLAB
- Comparison of mathematical programs for data analysis ScientificWeb
- Physical Modeling in MATLAB by Allen B. Downey, Green Tea Press, PDF, ISBN 978-0-615-18550-7. An introduction to MATLAB.
- Writing Fast MATLAB Code by P. Getreuer
- Calling Matlab from Java: MatlabControl JMI Wrapper, The MatlabJava Server, MatlabControl
- Calling Matlab from Java: using Java RMI server - JAMAL

