Irkutsk
Irkutsk
Иркутск | |
|---|---|
| Irkutsk at night Irkutsk at night | |
| Coordinates: 52°17′N 104°18′E / 52.283°N 104.300°E | |
| Country | Russia |
| Federal subject | Irkutsk Oblast |
| Founded | 1661[1] |
| Government | |
| • Body | Duma |
| • Mayor | Viktor Kondrashov |
| Elevation | 440 m (1,440 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 587,225 |
| • Rank | 24th in 2010 |
| • Subordinated to | City of Irkutsk[3] |
| • Capital of | City of Irkutsk,[3] Irkutsky District,[3] Irkutsk Oblast[3] |
| • Urban okrug | Irkutsk Urban Okrug[4] |
| • Capital of | Irkutsk Urban Okrug[4] |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (MSK+5 |
| Postal code(s)[6] | 664xxx |
| Dialing code(s) | +7 3952[7] |
| OKTMO ID | 25701000001 |
| City Day | First Sunday of June |
| Website | www1 |
Irkutsk (Russian: Ирку́тск, IPA: [ɪrˈkutsk]) is a city and the administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia, one of the largest cities in Siberia. Population: 593,604 (2002 Census);[9] 622,301 (1989 Soviet census).[10].
History
In 1652, Ivan Pokhabov built a zimovye (winter quarters) near the site of Irkutsk for gold trading and for the collection of fur taxes from the Buryats. In 1661, Yakov Pokhabov built an ostrog nearby.[1] The ostrog gained official town rights from the government in 1686. The first road connection between Moscow and Irkutsk, the Siberian Road, was built in 1760. The town benefited economically from this new road. Many new products, often imported from China via Kyakhta, became widely available in Irkutsk for the first time, including gold, diamonds, fur, wood, silk and tea. In 1821, as part of the Speransky reforms, Siberia was administratively divided at the Yenisei River and Irkutsk became the seat of the Governor-General of East Siberia.

In the early 19th century, many Russian artists, officers and nobles were sent into exile in Siberia for their part in the Decembrist revolt against Tsar Nicholas I. Irkutsk became the major center of intellectual and social life for these exiles, and much of the city's cultural heritage comes from them; many of their wooden houses, adorned with ornate, hand-carved decorations, survive today in stark contrast with the standard Soviet apartment blocks that surround them.
By the end of the 19th century, there was one exiled man for every two locals. People of varying backgrounds, from members of the Decembrist uprising to Bolsheviks, have been in Irkutsk for many years and have greatly influenced the culture and development of the city. As a result, Irkutsk eventually became a prosperous cultural and educational center for Eastern Siberia.
In 1879, on July 4 and 6, the palace of the (then) Governor General, the principal administrative and municipal offices and many of the other public buildings were destroyed by fire, and the government archives, the library and the museum of the Siberian section of the Russian Geographical Society were completely ruined. Three-quarters of the city was destroyed, including approximately four thousand houses. However, the city quickly rebounded, with electricity arriving in 1896, the first theater being built in 1897 and a major train station opened in 1898. The first train arrived in Irkutsk on August 16 of that year. By 1900, the city had earned the nickname of "The Paris of Siberia."
During the Russian Civil War that broke out after the Bolshevik Revolution, Irkutsk became the site of many furious, bloody clashes between the "Whites" and the "Reds". In 1920, Aleksandr Kolchak, the once-feared commander of the largest contingent of anti-Bolshevik forces, was executed in Irkutsk, effectively destroying the anti-Bolshevik resistance.
Irkutsk was the administrative center of the short-lived East Siberian Oblast, which existed from 1936 to 1937. Irkutsk subsequently became the administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast after East Siberian Oblast was divided into Chita Oblast and Irkutsk Oblast.
During the Communist years, the industrialization of Irkutsk and Siberia in general was heavily encouraged. The large Irkutsk Reservoir was built on the Angara River between 1950 and 1959 in order to facilitate industrial development.

The Epiphany Cathedral (left), the governor's palace, a school of medicine, a museum, a military hospital and the crown factories are among the public institutions and buildings. The Aleksandr Kolchak monument, designed by Vyacheslav Klykov, was unveiled in 2004. On July 27, 2004, the Irkutsk Synagogue (1881) was gutted by a conflagration.
Geography
The city proper lies on the Angara River, a tributary of the Yenisei, 72 kilometers (45 mi) below its outflow from Lake Baikal and on the bank opposite the suburb of Glaskovsk. The river, 580 meters (1,900 ft) wide, is crossed by the Irkutsk Hydroelectric Dam and three other bridges downstream.
The Irkut River, from which the town takes its name, is a smaller river that joins the Angara directly opposite the city. The main portion of the city is separated from several landmarks—the monastery, the fort and the port, as well as its suburbs—by another tributary, the Ida (or Ushakovka) River. The two main parts of Irkutsk are customarily referred to as the "left bank" and the "right bank", with respect to the flow of the Angara river.
Irkutsk is situated in a landscape of rolling hills within the thick taiga that is typical of eastern Siberia.
According to the regional plan, Irkutsk city will be combined with its neighboring industrial towns of Shelekhov and Angarsk to form a metropolitan area with a total population of over a million.
Climate
Irkutsk originally has a borderline subarctic climate (Köppen climate classification Dwc), but since 2000 the city warmed to a humid continental climate (Köppen climate classification Dwb). Snow cover disappeared earlier from late April in 1930s to late March in 1980s. Discontinuous permafrost depth had decreased from 200m to 100m. Irkutsk is characterized by extreme variation of temperatures between seasons; temperatures can be very warm in the summer, and very cold in the winter. However, Lake Baikal takes its effect, such that temperatures in Irkutsk are not as extreme as elsewhere in Siberia. The warmest month of the year in Irkutsk is July, when the mean temperature is +18 °C (64 °F), the highest temperature recorded being +37 °C (99 °F). The coldest month of the year is January, when the mean temperature is −18 °C (0 °F). Precipitation also varies widely throughout the year, with the wettest month also being July, when precipitation averages 113 millimeters (4.4 in). The driest month is February, when precipitation averages only 7.6 millimeters (0.30 in). Almost all precipitation during the Siberian winter falls as fluffy, low moisture content snow.
| Climate data for Irkutsk (normals 1981-2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 2.3 (36.1) |
10.2 (50.4) |
20.0 (68.0) |
29.2 (84.6) |
34.5 (94.1) |
35.6 (96.1) |
37.2 (99.0) |
34.1 (93.4) |
29.5 (85.1) |
24.5 (76.1) |
14.1 (57.4) |
4.6 (40.3) |
37.2 (99.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −12.9 (8.8) |
−7.9 (17.8) |
0.3 (32.5) |
9.4 (48.9) |
18.0 (64.4) |
22.7 (72.9) |
24.8 (76.6) |
22.1 (71.8) |
15.7 (60.3) |
7.7 (45.9) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
−10.6 (12.9) |
7.2 (45.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −17.9 (−0.2) |
−14.6 (5.7) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
2.5 (36.5) |
10.2 (50.4) |
15.4 (59.7) |
18.2 (64.8) |
15.8 (60.4) |
9.1 (48.4) |
1.7 (35.1) |
−7.7 (18.1) |
−15.4 (4.3) |
0.9 (33.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −22 (−8) |
−19.8 (−3.6) |
−12.3 (9.9) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
3.4 (38.1) |
9.2 (48.6) |
12.9 (55.2) |
10.8 (51.4) |
4.2 (39.6) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
−11.8 (10.8) |
−19.3 (−2.7) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −49.7 (−57.5) |
−44.7 (−48.5) |
−37.3 (−35.1) |
−31.8 (−25.2) |
−14.3 (6.3) |
−6 (21) |
0.4 (32.7) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
−11.9 (10.6) |
−30.5 (−22.9) |
−40.4 (−40.7) |
−46.3 (−51.3) |
−49.7 (−57.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 14 (0.6) |
7 (0.3) |
12 (0.5) |
18 (0.7) |
35 (1.4) |
75 (3.0) |
113 (4.4) |
93 (3.7) |
51 (2.0) |
22 (0.9) |
20 (0.8) |
17 (0.7) |
477 (18.8) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 82 | 75 | 65 | 57 | 55 | 67 | 75 | 78 | 77 | 73 | 79 | 84 | 72 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 93.0 | 140.0 | 207.7 | 222.0 | 266.6 | 264.0 | 241.8 | 217.0 | 183.0 | 151.9 | 93.0 | 62.0 | 2,142 |
| Source 1: Pogoda.ru.net[11] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: HKO | |||||||||||||
Administrative and municipal status
Administratively, it is incorporated as the City of Irkutsk—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts.[3] Municipally, the City of Irkutsk is incorporated as Irkutsk Urban Okrug.[4]
Coat of arms
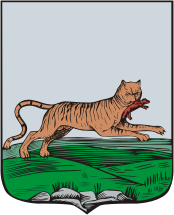
The coat of arms of Irkutsk features an old symbol of Dauria: a Siberian tiger with a sable in his mouth. When the coat of arms was devised in 1690, the animal was described as a tiger ("babr", a bookish word of Persian derivation) with a sable in his mouth. This image had been used by the Yakutsk customs office from about 1642. It has its origin in a seal of the Siberia Khanate representing a sable and showcasing the fact that Siberia (or rather Yugra) was the main source of sable fur throughout the Middle Ages. (Actually, the English word "sable" is derived from the Russian "sobol").
By the mid-19th century, the word "babr" had fallen out of common usage, but it was still recorded in the Armorial of the Russian Empire. Furthermore, the tigers became extinct in this part of Siberia. In the 1870s, a high-placed French heraldist with a limited command of Russian assumed that "babr" was a misspelling of "bobr", the Russian word for "beaver", and changed the wording accordingly. This modification engendered a long dispute between the local authorities, who were so confused by the revised description that they started to depict the "babr" as a fabulous animal, half-tiger and half-beaver.
The Soviets abolished the image altogether, but it was restored following the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Economy
Energy
The 662.4 MW Irkutsk Hydroelectric Power Station was the first cascade hydroelectric power station in the Irkutsk region. The construction of the dam started in 1950 and finished in 1958.[12]
Industry
The largest industry in Irkutsk is Irkut, the Irkutsk Aviation Industrial Association,[13] which was set up in 1932 in the Transbaykal region of the Soviet Union. It is best known as being the manufacturer of the Su-30 family of interceptor/ground-attack aircraft. The Russian government is planning to merge Irkut with Ilyushin, Mikoyan, Sukhoi, Tupolev, and Yakovlev as a new company named United Aircraft Building Corporation.[14]
There is Irkutsk Aluminium Smelter which belongs to the Rusal Company.[1]
Transport

Important roads and railways like the Trans-Siberian Highway (Federal M53 and M55 Highways) and Trans-Siberian Railway connect Irkutsk to other regions in Russia and Mongolia. Also, the city is served by the Irkutsk International Airport and the smaller Irkutsk Northwest Airport.
The Federal road and railway to Moscow and Vladivostok pass through the other side of the Angara River from downtown Irkutsk.
Culture
Television and mass media
There are many state and privately owned television stations in Irkutsk, including state IGTRK company http://irkutsk.rfn.ru and private ones http://as.baikal.tv AS Baikal TV, TV company AIST http://www.aisttv.ru, TV company Gorod http://www.gorodtv.ru, and e.g. http://www.vsp.ru VSP newspaper agency. Irkutsk live webcamera inlc. life temperature in city center: http://as.baikal.tv/webcam/
Education
Irkutsk is home to East Siberian Education Academy (since 1909), Irkutsk State University (1918), Irkutsk State Medical University (1918), Baykalsky State University of Economics and Law (since 1932), Irkutsk State Technical University (since 1939), Irkutsk State Academy of Agriculture, Irkutsk State Linguistic University (1948), Irkutsk State Railway Transport University (since 1975), and a number of private colleges: Siberian Institute of Law, Economics and Management (since 1993), Institute of Economics of ISTU (since 1996), and others.
Science
As part of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences there are nine research institutes located in the Irkutsk Academgorodok suburb: Institute of Geography, Energy Systems Institute, Institute of Geochemistry, Institute of Systems Dynamics and Control Theory, Earth's Crust Institute, solar-terrestrial physics institute, Institute of Chemistry, Institute of Limnology (located on lake Baikal's shore), Institute of Plants Physics, Laser Physics Institute (Branch of the Novosibirsk-based Institute). A number of institutes conduct research within Irkutsk State University: Institute of Biology, Institute of Oil and Coal Chemistry and Synthesis, Laboratory of Quantum Chemistry, Institute of Applied Physics, Interregional Institute of Social Studies, Astronomical Observatory, and Botanical Gardens. The East-Siberian Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences is also located in Irkutsk and is represented by the following research organizations: Scientific Center for medical Ecology, Institute for Paediatrics and Human Reproduction, Institute for Microbiology and Epidemiology, Institute for Medicine of the Workplace and Human Ecology, Institute of Reconstructive and Restorative Surgery, Institute of Surgery, and Institute of Traumatology and Orthopaedics. Also, the Fyodorov Eye Microsurgery Scientific and Technical Center has a branch in Irkutsk. Additionally, there are R&D institutes including GAZPROM R&D Institute (Branch of Moscow-based Institute), Irkutsk Institute of Rare and Precious Metals and Diamonds.
Literature
Irkutsk has long been home to the well-known Russian writer Valentin Rasputin; many of his novels and stories take place in the Angara Valley. An essay on the cultural history of Irkutsk (and another one about the nearby Lake Baikal) is included in Rasputin's non-fiction collection Siberia, Siberia, which is also available in English translation.
Museums
The Taltsy Museum (Russian: Тальцы), located on the Angara 47 kilometers (29 mi) south of Irkutsk, is an open-air museum of Siberian traditional architecture. Numerous old wooden buildings from villages in the Angara valley which have been flooded after the construction of the Bratsk Dam and Ust-Ilimsk Dam have been transported to the museum and reassembled there. One of the centerpieces of the collection is a partial recreation of the 17th-century ostrog (fortress) of Ilimsk, which consists of the original Spasskaya Tower and the Church of Our Lady of Kazan transported from the flooded ostrog in the mid-1970s, to which an exact modern copy of another tower of the ostrog and the southern wall of the fortress were added in the early 2000s.[15] The Botanic Garden of the Irkutsk State University known as the "Irkutsk Botanic Garden" is the only botanic garden as a living museum in Irkutsk Oblast and Baikalian Siberia. Its mission is "to protect and enrich the flora of the Lake Baikal area and the world for people through public education, collection, propagation, research, and conservation of plants". The garden is principally an educational and scientific tool for the Irkutsk State University and maintains largest plant collection of living plants in Eastern Siberia (more than 5000 plant taxa), a herbarium, and a seed bank. It occupies 27 hectares within Irkutsk city, 70 kilometers west of Lake Baikal. It has a status of the federal strictly protected land and a nature memorial of Irkutsk.
Sports
Bandy is a very big sport in the city. There are several clubs, and the best one, Baykal-Energiya[16] in the highest division of Russian Bandy League, can draw spectator crowds of 30 000.[2] It's also the centre of women's bandy in Russia with the club Rekord, [3] which provides most players to the national team.[4] The Bandy World Championships for women 2012[17] was hosted in Irkutsk and received praise from Federation of International Bandy.[18]
Sister cities/twin Cities
Irkutsk has the following sister/twin city relationships:[19]
 Ulan Bator, Mongolia
Ulan Bator, Mongolia Shenyang, China
Shenyang, China Kanazawa, Japan
Kanazawa, Japan Eugene, United States
Eugene, United States Novi Sad, Serbia
Novi Sad, Serbia Pforzheim, Germany
Pforzheim, Germany Évian-les-Bains, France
Évian-les-Bains, France Strömsund, Sweden
Strömsund, Sweden Pordenone, Italy
Pordenone, Italy Grenoble, France
Grenoble, France Dijon, France
Dijon, France
Images gallery
-
A Decembrist house with distinctive hand-carved trim
-
Kazansky Church
-
Irkutsk railway station on the Trans-Siberian Railway
-
Crossing the Angara at Irkutsk (1886)
References
Notes
- ^ a b Lantzeff, George V., and Richard A. Pierce (1973). Eastward to Empire: Exploration and Conquest on the Russian Open Frontier, to 1750. Montreal eduacadtion: McGill-Queen's U.P.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Invalid reference parameter
- ^ a b c d e Law #49-OZ
- ^ a b c Law #88-oz
- ^ "Об исчислении времени". Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации (in Russian). June 3, 2011. Retrieved January 19, 2019.
- ^ Почта России. Информационно-вычислительный центр ОАСУ РПО. (Russian Post). Поиск объектов почтовой связи (Postal Objects Search) (in Russian)
- ^ http://www.the-acr.com/codes/cntrycd2.htm#q
- ^ Federal State Statistics Service (May 21, 2004). Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек [Population of Russia, Its Federal Districts, Federal Subjects, Districts, Urban Localities, Rural Localities—Administrative Centers, and Rural Localities with Population of Over 3,000] (XLS). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года [All-Russia Population Census of 2002] (in Russian).
- ^ Federal State Statistics Service (May 21, 2004). Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек [Population of Russia, Its Federal Districts, Federal Subjects, Districts, Urban Localities, Rural Localities—Administrative Centers, and Rural Localities with Population of Over 3,000] (XLS). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года [All-Russia Population Census of 2002] (in Russian).
- ^ Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 г. Численность наличного населения союзных и автономных республик, автономных областей и округов, краёв, областей, районов, городских поселений и сёл-райцентров [All Union Population Census of 1989: Present Population of Union and Autonomous Republics, Autonomous Oblasts and Okrugs, Krais, Oblasts, Districts, Urban Settlements, and Villages Serving as District Administrative Centers]. Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года [All-Union Population Census of 1989] (in Russian). Институт демографии Национального исследовательского университета: Высшая школа экономики [Institute of Demography at the National Research University: Higher School of Economics]. 1989 – via Demoscope Weekly.
- ^ "Pogoda.ru.net- Climate Data for Irkutsk 1981-2010" (in Russian). Retrieved April 26,2012.
{{cite web}}: Check date values in:|accessdate=(help) - ^ "Irkutsk Hydroelectric Power Station History". Irkutskenergo. Retrieved September 7, 2010.
- ^ globalsecurity.org entry
- ^ "Russian Aircraft Industry Seeks Revival Through Merger." The New York Times. February 22, 2006
- ^ В «Тальцах» завершается реконструкция южной стены Илимского острога (Re-creation of the southern wall of the Ilimsk ostrog in the Taltsy Museum is approaching its completion) Template:Ru icon
- ^ http://www.baikal-energy.ru/
- ^ WCS 2012 home page
- ^ A very well organized World Championship for Women in Irkutsk made a great success
- ^ Irkutsk sister cities
Sources
- Законодательное Собрание Иркутской области. Закон №49-ОЗ от 21 июня 2010 г. «Об административно-территориальном устройстве Иркутской области», в ред. Закона №12-ОЗ от 23 марта 2017 г. «О внесении изменений в статьи 25 и 33 Закона Иркутской области "Об административно-территориальном устройстве Иркутской области" и Закон Иркутской области "О порядке рассмотрения Законодательным Собранием Иркутской области предложений о присвоении наименований географическим объектам и (или) о переименовании географических объектов"». Вступил в силу после дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Областная", №71, 25 июня 2010 г. (Legislative Assembly of Irkutsk Oblast. Law #49-OZ of June 21, 2010 On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Irkutsk Oblast, as amended by the Law #12-OZ of March 23, 2017 On Amending Articles 25 and 33 of the Law of Irkutsk Oblast "On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Irkutsk Oblast" and the Law of Irkutsk Oblast "On the Procedures for Consideration of Assignments of Names to Geographical Objects and (or) Renaming of Geographical Objects". Effective as of after the day of the official publication.).
- Законодательное Собрание Иркутской области. Закон №88-оз от 16 декабря 2004 г. «О статусе и границах муниципального образования "город Иркутск" Иркутской области». Вступил в силу с 31 декабря 2004 г., но не ранее чем через 10 дней со дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Восточно-Сибирская правда", №254–255, 20 декабря 2004 г. (Legislative Assembly of Irkutsk Oblast. Law #88-oz of December 16, 2004 On the Status and Borders of the Municipal Formation of the "City of Irkutsk" of Irkutsk Oblast. Effective as of December 31, 2004, but not earlier than 10 days after the official publication date.).
- This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - Template:German
- Brumfield, William. Irkutsk: Architectural Heritage in Photographs // Moscow: Tri Kvadrata Publishing, 2006. ISBN 978-5-94607-061-4
- Polunina N.M., Korobov S.A., Sutton J.M., Korobova G.W. Her Majesty — Queen of Siberia // Publishers Korobov. — Irkutsk, 2008.
External links
- Official website of Irkutsk Template:Ru icon
- Template:Wikitravel
- Flickr photos tagged Irkutsk
- Irkutsk in old and modern photos
- Irkutsk city architecture views
- Bandy video
- Irkutsk: cultural crossroads in Russian Asia
- Russia - Siberia - Irkutsk - photo galleries
- Irkutsk Webcam Live









