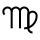Virgo (astrology)
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
| Virgo | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Zodiac symbol | Maiden |
| Duration (tropical, western) | August 22 – September 22 (2024, UT1)[1] |
| Constellation | Virgo |
| Zodiac element | Earth |
| Zodiac quality | Mutable |
| Sign ruler | Mercury |
| Detriment | Jupiter and Neptune |
| Exaltation | Mercury and Pluto |
| Fall | Venus |
| Astrology |
|---|
 |
| Background |
| Traditions |
| Branches |
| Astrological signs |
| Symbols |
Virgo (♍︎) (Greek: Παρθένος, Parthenos) is the sixth astrological sign in the Zodiac. It spans the 150–180th degree of the zodiac. Under the tropical zodiac, the Sun transits this area on average between August 23 and September 22,[2] and the Sun transits the constellation Virgo from approximately September 16 to October 30.[3] Individuals born during these dates, depending on which system of astrology they subscribe to, may be called Virgos or Virgoans;[4] they are also represented in newspaper horoscopes with other astrological signs.[5] The symbol of the maiden is based on Astraea. In Greek mythology, she was the last immortal to abandon Earth at the end of the Silver Age, when the gods fled to Olympus – hence the sign's association with Earth.[6]
Origins
The constellation Virgo has different origins depending on which mythology is being studied. Most myths generally view Virgo as a maiden with heavy association with wheat. In Greek and Roman mythology, they relate the constellation to Demeter, mother of Persephone, or Proserpina, the Roman goddess of the harvest.[7] Another association is with the myth of Parthenos (meaning virgin in Greek), which explains how the actual constellation Virgo came to be.[8]
In the legend, Parthenos is the ded of Staphylus and Chrysothemis, and sister to Rhoeo and Molpadia. Rhoeo had been impregnated by Apollo, but when her father discovered her pregnancy, he assumed it was by a random suitor and was greatly ashamed. As punishment, he locked her in a box and threw her in a river. After the terrible fate of their sister, Parthenos and Molpadia lived in fear of their father's terrible wrath. One evening, Staphylus left his daughters in charge of a very valuable bottle of wine. When they both accidentally fell asleep, one of their swine broke the bottle. Terrified of their father, the sisters fled to a nearby cliff and threw themselves off. But because of his previous relations with Rhoeo, Apollo saved his two sisters and delivered them to the safety of nearby cities in Cherronseos. Molpadia ended up in Castabus where she changed her name to Hemithea and was worshipped as a local goddess for many years. Parthenos settled in Bubastus where she was also worshipped as a local goddess. According to another story, Parthenos was a daughter of Apollo who made the constellation to commemorate her death at a young age.[8]
While this is only one myth of the origin of Virgo, she is seen throughout all manner of myths. In Egyptian mythology, the time when the Sun was in the constellation Virgo marked the beginning of the wheat harvest, thus connecting Virgo back to the wheat grain. In Christianity, Jesus was born to a virgin in the town of Bethlehem ("bread"); the ancient Zodiac ended in the constellation Leo and began with Virgo. Virgo has the equivalent sign in Indian astrology as the Kanya (which also means "maiden"), and has even been connected with the Virgin Mary.[8]
Notes
Works cited
- Allen, Richard Hinckley (1963). Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning. Nineola: Dover Publications.
- Astronomical Applications Department (2011). Multiyear Computer Interactive Almanac. 2.2.2. Washington DC: US Naval Observatory. Longitude of Sun, apparent geocentric ecliptic of date, interpolated to find time of crossing 0°, 30°....
- Atsma, Aaron J. (c. 2015). "ASTRAEA : Greek goddess of justice".
- Rigoglioso, Marguerite (2009). "Artemis's Divine Birth Priestesshood". The Cult of Divine Birth in Ancient Greece. New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Shapiro, Lee (2011). "The Real Constellations of the Zodiac". International Planetarium Society. Retrieved September 9, 2018.
- "Virgo (constellation)". Encyclopedia Britannica. n.d. Retrieved September 20, 2018.
- "Virgo". Oxford Dictionaries. n.d. Retrieved December 23, 2018.
- "Virgoan – Dictionary definition and pronunciation - Yahoo! Education". Education.yahoo.com. Archived from the original on October 8, 2012. Retrieved August 15, 2012.