Bond event
Bond events are North Atlantic ice rafting events that are tentatively linked to climate fluctuations in the Holocene. Eight such events have been identified. Bond events were previously believed to exhibit a roughly c. 1,500-year cycle, but the primary period of variability is now put at c. 1,000 years.[1][2]
Gerard C. Bond of the Lamont–Doherty Earth Observatory at Columbia University was the lead author of the 1997 paper that postulated the theory of 1470-year climate cycles in the Late Pleistocene and Holocene, mainly based on petrologic tracers of drift ice in the North Atlantic.[1][3] However, more recent work at a single site suggested that these tracers did not provide sufficient support for 1,500-year intervals of climate change, and suggested that the reported c. 1,500 ± 500-year period was a statistical artifact.[2]
Furthermore, following publication of the Greenland Ice Core Chronology 2005 (GICC05)[4] for the North GRIP ice core, it became clear that Dansgaard–Oeschger events also show no such pattern.[2][5][6] The North Atlantic ice-rafting events happen to correlate with episodes of lowered lake levels in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States,[7] the weakest[clarification needed] events of the Asian monsoon for at least the past 9,000 years,[8][9] and also correlate with most aridification events in the Middle East for the past 55,000 years (both Heinrich and Bond events).[10][11]
List
[edit]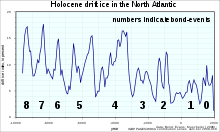
Most Bond events do not have a clear climate signal; some correspond to periods of cooling, but others are coincident with aridification in some regions. Gap between events has been estimated to be 1,000-1,500 years[2][1] with Bond event # 4 as an outlying data point.
| No | Time (BP) |
Time (AD, BC) |
Gap from previous event | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ≈ −0.5 ka | ≈ 1500 AD | 900 years | See Little Ice Age[12] |
| 1 | ≈ −1.4 ka | ≈ 600 AD | 1400 years | See Migration Period[12] and Late Antique Little Ice Age |
| 2 | ≈ −2.8 ka | ≈ 800 BC | 1400 years | See Iron Age Cold Epoch |
| 3 | ≈ −4.2 ka | ≈ 2200 BC | 1700 years | See 4.2-kiloyear event; collapse of the Akkadian Empire and the end of the Egyptian Old Kingdom.[13][14] |
| 4 | ≈ −5.9 ka | ≈ 3900 BC | 2300 years | Sahara desert reforms by 3500–3000 BC, ending Neolithic Subpluvial. Piora Oscillation. Early Bronze Age begins ~3300 BC. |
| 5 | ≈ −8.2 ka | ≈ 6200 BC | 1200 years | See 8.2-kiloyear event |
| 6 | ≈ −9.4 ka | ≈ 7400 BC | 1100 years | Erdalen event of glacier activity in Norway,[15] as well as a cold event in China.[16] |
| 7 | ≈ −10.3 ka | ≈ 8300 BC | 800 years | |
| 8 | ≈ −11.1 ka | ≈ 9100 BC | — | Transition from the Younger Dryas to the Boreal.[17] |
Influence in regional climate
[edit]
Bond events have been detected in remote regions such as the central Andes of South America.[18] Up to six Bond cycles during the upper and middle Holocene have been identified in three ice core records of the tropical Andes. The records were extracted from the summits of Nevado Sajama, Nevado Huascarán and Nevado Illimani. The detected cycles were at 6400 years Before Present, 5500 years B.P., 3700 years B.P., 2700 years B.P., 1300 years B.P. and 200 years B.P. and represented temperature drops.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Bond, G.; et al. (2001). "Persistent Solar Influence on North Atlantic Climate During the Holocene". Science. 294 (5549): 2130–2136. Bibcode:2001Sci...294.2130B. doi:10.1126/science.1065680. PMID 11739949. S2CID 38179371.
- ^ a b c d Obrochta, Stephen P.; Miyahara, Hiroko; Yokoyama, Yusuke; Crowley, Thomas J. (2012-11-08). "A re-examination of evidence for the North Atlantic "1500-year cycle" at Site 609". Quaternary Science Reviews. 55: 23–33. Bibcode:2012QSRv...55...23O. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.08.008.
- ^ Bond, G.; et al. (1997). "A Pervasive Millennial-Scale Cycle in North Atlantic Holocene and Glacial Climates" (PDF). Science. 278 (5341): 1257–1266. Bibcode:1997Sci...278.1257B. doi:10.1126/science.278.5341.1257. S2CID 28963043. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-02-27.
- ^ Svensson, A.; Andersen, K. K.; Bigler, M.; Clausen, H. B.; Dahl-Jensen, D.; Davies, S. M.; Johnsen, S. J.; Muscheler, R.; Parrenin, F. (2008-03-31). "A 60 000 year Greenland stratigraphic ice core chronology" (PDF). Clim. Past. 4 (1): 47–57. Bibcode:2008CliPa...4...47S. doi:10.5194/cp-4-47-2008.
- ^ Ditlevsen, P. D.; Andersen, K. K.; Svensson, A. (2007-02-28). "The DO-climate events are probably noise induced: statistical investigation of the claimed 1470 years cycle". Clim. Past. 3 (1): 129–134. Bibcode:2007CliPa...3..129D. doi:10.5194/cp-3-129-2007.
- ^ Obrochta, Stephen P.; Yokoyama, Yusuke; Morén, Jan; Crowley, Thomas J. (2014-04-01). "Conversion of GISP2-based sediment core age models to the GICC05 extended chronology". Quaternary Geochronology. 20: 1–7. Bibcode:2014QuGeo..20....1O. doi:10.1016/j.quageo.2013.09.001.
- ^ Li, Yong-Xiang; Yu, Zicheng; Kodama, Kenneth P. (2007). "Sensitive moisture response to Holocene millennial-scale climate variations in the Mid-Atlantic region, USA". The Holocene. 17 (1): 3–8. Bibcode:2007Holoc..17....3L. doi:10.1177/0959683606069386. S2CID 2206358.
- ^ Gupta, Anil K.; Anderson, David M.; Overpeck, Jonathan T. (2003). "Abrupt changes in the Asian southwest monsoon during the Holocene and their links to the North Atlantic Ocean". Nature. 421 (6921): 354–357. Bibcode:2003Natur.421..354G. doi:10.1038/nature01340. PMID 12540924. S2CID 4304234.
- ^ Yongjin Wang; et al. (2005). "The Holocene Asian Monsoon: Links to Solar Changes and North Atlantic Climate" (PDF). Science. 308 (5723): 854–857. Bibcode:2005Sci...308..854W. doi:10.1126/science.1106296. PMID 15879216. S2CID 54532439.
- ^ Bartov, Yuval; Goldstein, Steven L.; Stein, Mordechai; Enzel, Yehouda (2003). "Catastrophic arid episodes in the Eastern Mediterranean linked with the North Atlantic Heinrich events". Geology. 31 (5): 439–442. Bibcode:2003Geo....31..439B. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0439:CAEITE>2.0.CO;2.
- ^ Parker, Adrian G.; et al. (2006). "A record of Holocene climate change from lake geochemical analyses in southeastern Arabia". Quaternary Research. 66 (3): 465–476. Bibcode:2006QuRes..66..465P. doi:10.1016/j.yqres.2006.07.001. S2CID 140158532.
- ^ a b Zhao, Keliang; et al. (2012). "Climatic variations over the last 4000 cal yr BP in the western margin of the Tarim Basin, Xinjiang, reconstructed from pollen data". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 321–322: 16–23. Bibcode:2012PPP...321...16Z. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2012.01.012.
- ^ Gibbons, Ann (1993). "How the Akkadian Empire Was Hung Out to Dry". Science. 261 (5124): 985. Bibcode:1993Sci...261..985G. doi:10.1126/science.261.5124.985. PMID 17739611.
- ^ Stanley, Jean-Daniel; et al. (2003). "Nile flow failure at the end of the Old Kingdom, Egypt: Strontium isotopic and petrologic evidence". Geoarchaeology. 18 (3): 395–402. doi:10.1002/gea.10065. S2CID 53571037.
- ^ Dahl, Svein Olaf; et al. (2002). "Timing, equilibrium-line altitudes and climatic implications of two early-Holocene glacier readvances during the Erdalen Event at Jostedalsbreen, western Norway". The Holocene. 12 (1): 17–25. Bibcode:2002Holoc..12...17D. doi:10.1191/0959683602hl516rp. S2CID 128539563.
- ^ Zhou Jing; Wang Sumin; Yang Guishan; Xiao Haifeng (2007). "Younger Dryas Event and Cold Events in Early-Mid Holocene: Record from the sediment of Erhai Lake" (PDF). Advances in Climate Change Research. 3 (Suppl): 1673–1719. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-07-06.
- ^ Allen, Harriet D. (2003). "Response of past and present Mediterranean ecosystems to environmental change". Progress in Physical Geography. 27 (3): 359–377. doi:10.1191/030913303767888482.
- ^ Fernández - Sánchez, Adrián; Martín - Chivelet, Javier (2016). "A Revisión de la estratigrafía del d18O en sondeos de hielo de glaciares en los Andes Centrales: Implicaciones para la variabilidad climática del Holoceno". Geotemas. Journal of the Geological Society of Spain. 16: 565–568.
