Fursultiamine
Appearance
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.234 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
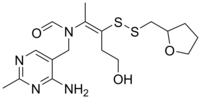
| Formula | C17H26N4O3S2 |
| Molar mass | 398.54 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Fursultiamine (INN; chemical name thiamine tetrahydrofurfuryl disulfide or TTFD; brand names Adventan, Alinamin-F, Benlipoid, Bevitol Lipophil, Judolor, Lipothiamine) is a medication and vitamin used to treat thiamine deficiency. Chemically, it is a disulfide derivative of thiamine and is similar in structure to allithiamine.[1]
It was synthesized in Japan in the 1960s from allithiamine for the purpose of developing forms of thiamine with improved lipophilicity for treating vitamin B1 deficiency (i.e., beriberi),[1] It was subsequently commercialized not only in Japan but also in Spain, Austria, Germany, and the United States.[2]
See also
References
- ^ a b Lonsdale D (September 2004). "Thiamine tetrahydrofurfuryl disulfide: a little known therapeutic agent". Medical Science Monitor. 10 (9): RA199–203. PMID 15328496.
- ^ Swiss Pharmaceutical Society (2000). Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory (Book with CD-ROM). Boca Raton: Medpharm Scientific Publishers. p. 1932. ISBN 3-88763-075-0.
Further reading
- Lonsdale D (September 2004). "Thiamine tetrahydrofurfuryl disulfide: a little known therapeutic agent". Medical Science Monitor. 10 (9): RA199–203. PMID 15328496.
