Schistosomiasis vaccine
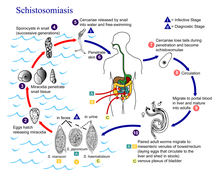
A Schistosomiasis vaccine is a vaccine against Schistosomiasis (also known as bilharzia, bilharziosis or snail fever), a parasitic disease caused by several species of fluke of the genus Schistosoma. No effective vaccine for the disease exists yet. Schistosomiasis affects over 200 million people worldwide, mainly in rural agricultural and peri-urban areas of developing countries, and approximately 10% suffer severe health complications from the infection.[1] While chemotherepeutic drugs, such as praziquantel, oxamniquine and metrifonate both no longer on the market, are currently considered safe and effective for the treatment of schistosomiasis, reinfection occurs frequently following drug treatment, thus a vaccine is sought to provide long-term treatment.[1][2] Additionally, experimental vaccination efforts have been successful in animal models of schistosomiasis.[1]
Paramyosin has been proposed as a vaccine candidate.[3][4]
At present Sm-p80 (calpain) is the sole schistosome vaccine candidate that has been tested for its prophylactic and antifecundity efficacy in different vaccine formulations and approaches (e.g., DNA alone, recombinant protein and prime boost) in two very different experimental animal models (mouse and baboon) of infection and disease. Sm-p80-based vaccine formulation(s) have four effects: Reduction in adult worm numbers; Reduction in egg production (complete elimination of egg induced pathology both in baboons and mice); Protection against acute schistosomiasis; Therapeutic effect on adult worms. This vaccine is now ready for human clinical trials.[5][6][7]
Another target is Sm14.[8]
Research support
Schistosomiasis has been considered a "neglected disease" that disproportionately affects poorer localities and has received little attention from pharmaceutical companies. Support for current research efforts to develop hookworm vaccines has come from the Schistosomiasis Vaccine Initiative, a program of the Sabin Vaccine Institute in collaboration with George Washington University, the Oswaldo Cruz Foundation, the Chinese Institute of Parasitic Diseases, the Queensland Institute of Medical Research, and the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine.[9]
References
- ^ a b c McManus DP, Loukas A (January 2008). "Current status of vaccines for schistosomiasis". Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 21 (1): 225–42. doi:10.1128/CMR.00046-07. PMC 2223839. PMID 18202444.
- ^ Oliveira SC, Fonseca CT, Cardoso FC, Farias LP, Leite LC (2008). "Recent advances in vaccine research against schistosomiasis in Brazil". Acta Tropica. 108 (2–3): 256–62. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2008.05.023. PMID 18577363.
- ^ Jiz M, Wu HW, Meng R, Pond-Tor S, Reynolds M, Friedman JF, et al. (July 2008). "Pilot-scale production and characterization of paramyosin, a vaccine candidate for schistosomiasis japonica". Infection and Immunity. 76 (7): 3164–9. doi:10.1128/IAI.00409-08. PMC 2446706. PMID 18426875.
- ^ Nara T, Iizumi K, Ohmae H, Sy OS, Tsubota S, Inaba Y, et al. (February 2007). "Antibody isotype responses to paramyosin, a vaccine candidate for schistosomiasis, and their correlations with resistance and fibrosis in patients infected with Schistosoma japonicum in Leyte, The Philippines". The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene. 76 (2): 384–91. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.2007.76.384. PMID 17297052.
- ^ Ahmad G, Zhang W, Torben W, Ahrorov A, Damian RT, Wolf RF, et al. (November 2011). "Preclinical prophylactic efficacy testing of Sm-p80-based vaccine in a nonhuman primate model of Schistosoma mansoni infection and immunoglobulin G and E responses to Sm-p80 in human serum samples from an area where schistosomiasis is endemic". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 204 (9): 1437–49. doi:10.1093/infdis/jir545. PMC 3182311. PMID 21921206.
- ^ Ahmad G, Zhang W, Torben W, Haskins C, Diggs S, Noor Z, et al. (November 2009). "Prime-boost and recombinant protein vaccination strategies using Sm-p80 protects against Schistosoma mansoni infection in the mouse model to levels previously attainable only by the irradiated cercarial vaccine". Parasitology Research. 105 (6): 1767–77. doi:10.1007/s00436-009-1646-z. PMC 2813907. PMID 19809833.
- ^ Siddiqui AA, Siddiqui BA, Ganley-Leal L (November 2011). "Schistosomiasis vaccines". Human Vaccines. 7 (11): 1192–7. doi:10.4161/hv.7.11.17017. PMC 3323497. PMID 22048120.
- ^ Tendler M, Simpson AJ (2008). "The biotechnology-value chain: development of Sm14 as a schistosomiasis vaccine". Acta Tropica. 108 (2–3): 263–6. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2008.09.002. PMID 18834847.
- ^ Schistosomiasis Overview, Sabin Vaccine Institute
External links
- Clinical trial number NCT00870649 for "Efficacy of Vaccine Sh28GST in Association With Praziquantel (PZQ) for Prevention of Clinical Recurrences of Schistosoma Haematobium Pathology (Bilhvax)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
