Sulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix | |
|---|---|
 Portrait of Sulla on a denarius minted in 54 BC by his grandson Q. Pompeius Rufus[1] | |
| Born | 138 BC[2] |
| Died | 78 BC (aged 60) Puteoli, Italy, Roman Republic |
| Nationality | Roman |
| Notable credit | Constitutional reforms of Sulla |
| Office | Dictator of Rome (82–79 BC)[3] Consul of Rome (88, 80 BC) |
| Political party | Optimates |
| Opponent | Gaius Marius |
| Spouses | |
| Children |
|
| Military career | |
| Service years | 107–82 BC |
| Wars | |
| Awards | Grass Crown |
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix[4] (/ˈsʌlə/; 138–78 BC), commonly known simply as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman who won the first large-scale civil war in Roman history and became the first man of the Republic to seize power through force. He had the distinction of holding the office of consul twice, as well as reviving the dictatorship. Sulla was a gifted and innovative general, achieving numerous successes in wars against different opponents, both foreign and domestic. Sulla rose to prominence during the war against the Numidian king Jugurtha, whom he captured through betrayal, although his superior Gaius Marius took credit for ending the war. He then fought successfully against Germanic tribes during the Cimbrian War, and Italic tribes during the Social War. He was even awarded the Grass Crown for his command in the latter war.
Sulla played an important role in the long political struggle between the Optimates and Populares factions at Rome. He was a leader of the former, which sought to maintain the Senatorial supremacy against the social reforms advocated by the latter, headed by Marius. In a dispute over the command of the war against Mithridates, initially awarded to Sulla by the Senate but withdrawn as a result of Marius's intrigues, Sulla marched on Rome in an unprecedented act and defeated Marius in battle. The Populares nonetheless seized power once he left with his army to Asia. He returned victorious from the East in 82 BC, marched a second time on Rome, and crushed the Populares and their Italian allies at the Battle of the Colline Gate. He then revived the office of dictator, which had been inactive since the Second Punic War over a century before. He used his powers to purge his opponents, and reform Roman constitutional laws, in order to restore the primacy of the Senate and limit the power of the tribunes of the plebs. Resigning his dictatorship in 79 BC, Sulla retired to private life and died the following year.
Sulla's military coup—ironically enabled by Marius' military reforms that bound the army's loyalty with the general rather than to the Republic—permanently destabilized the Roman power structure. Later leaders like Julius Caesar would follow his precedent in attaining political power through force.[5]
Early years
Sulla, the son of Lucius Cornelius Sulla and the grandson of Publius Cornelius Sulla,[6] was born into a branch of the patrician gens Cornelia, but his family had fallen to an impoverished condition at the time of his birth. The reason behind this was because an ancestor, Publius Cornelius Rufinius, was banished from the senate after having been caught possessing more than ten pounds of silver plate.[7][8] As a result of this, Sulla's branch of the gens lost public standing and never retained the position of consul or dictator until Sulla came.[5] A story goes as the following, when he was a baby: his nurse was carrying him around the streets and a strange woman walked up to her and said, "Puer tibi et reipublicae tuae felix". This can be translated: "The boy will be a source of luck to you and your state".[9] Lacking ready money, Sulla spent his youth among Rome’s comics, actors, lute-players, and dancers. During these times on the stage, he, after initially singing, started writing plays, Atellan farces, a kind of crude comedy.[10] He retained an attachment to the debauched nature of his youth until the end of his life; Plutarch mentions that during his last marriage – to Valeria – he still kept company with "actresses, musicians, and dancers, drinking with them on couches night and day".[11]
It seems certain that Sulla received a good education. Sallust declares him well-read and intelligent, and he was fluent in Greek, which was a sign of education in Rome. The means by which Sulla attained the fortune which later would enable him to ascend the ladder of Roman politics, the Cursus honorum, are not clear, although Plutarch refers to two inheritances; one from his stepmother (who loved him dearly, as if he were her own son[12]) and the other from Nicopolis, a (Greek?) low-born woman, but became rich.[13]
Capture of Jugurtha
The Jugurthine War had started in 112 BC when Jugurtha, grandson of Massinissa of Numidia, claimed the entire kingdom of Numidia in defiance of Roman decrees that divided it between several members of the royal family.
Rome declared war on Jugurtha in 111 BC, but for five years the Roman legions were unsuccessful. Several Roman commanders were bribed (Bestia and Spurius), one (Aulus Postimius Albinus) was defeated. In 109 Rome sent Quintus Caecilius Metellus to continue the war. Gaius Marius, a lieutenant of Metellus, saw an opportunity to usurp his commander and fed rumors of incompetence and delay to the publicani (tax gatherers) in the region. These machinations caused calls for Metellus's removal; despite delaying tactics by Metellus, in 107 BC Marius returned to Rome to stand for the consulship. Marius was elected consul and took over the campaign while Sulla was nominated quaestor to him.

Under Marius, the Roman forces followed a very similar plan as under Metellus and ultimately defeated the Numidians in 106 BC, thanks in large part to Sulla's initiative in capturing the Numidian king. He had persuaded Jugurtha's father-in-law, King Bocchus I of Mauretania (a nearby kingdom), to betray Jugurtha who had fled to Mauretania for refuge. It was a dangerous operation from the first, with King Bocchus weighing up the advantages of handing Jugurtha over to Sulla or Sulla over to Jugurtha.[14] The publicity attracted by this feat boosted Sulla's political career. A gilded equestrian statue of Sulla donated by King Bocchus was erected in the Forum to commemorate his accomplishment. Although Sulla had engineered this move, as Sulla was serving under Marius at the time, Marius took credit for this feat.
The Cimbri and the Teutones

In 113 BC a large migrating Germanic-Celtic alliance headed by the Cimbri and the Teutones entered the Roman sphere of influence. They invaded Noricum which was inhabited by the Taurisci people, friends and allies of Rome. The Senate commissioned Gnaeus Papirius Carbo, one of the consuls, to lead a substantial Roman army to Noricum to force the barbarians out. An engagement, later called the battle of Noreia, took place, in which the invaders, to everyone's surprise, completely overwhelmed the Legions and inflicted a devastating loss on them.[15]
After the Noreia victory the Cimbri and Teutones moved westward towards Gaul. They became a problem again in 109 when they moved along the Rhodanus River towards the Roman province in Transalpine Gaul. Another consul, Marcus Junius Silanus was commissioned to take an army against the invaders. Silanus marched against them along the Rhodanus River. He met the Cimbri approximately 100 miles north of Arausio, an engagement took place and the Romans suffered another humiliating defeat. The Germanic tribes then moved to the lands north and east of Tolosa in south-western Gaul.[16]
To the Romans the presence of the Germanic tribes in Gaul posed a serious threat to the stability in the area and so they decided to send another army against them. Lucius Cassius Longinus, one of the consuls of 107, was sent to Gaul with yet another army. They first fought the Cimbri and their Gallic allies the Volcae Tectosages just outside Tolosa, and despite the huge number of tribesmen, the Romans routed them. Unfortunately for the Romans, a few days later they were ambushed while marching on Burdigala. The battle of Burdigala destroyed the Romans’ hope of finishing off the Cimbri, and the Germanic threat continued to exist.[17]
In 106 the Romans sent their largest army yet against the Germans. One of the consuls of 106, Quintus Servilius Caepio, was authorized to use eight legions in an effort to end the Germanic threat once and for all. While the Romans were busy getting their army together the Volcae Tectosages had quarrelled with their German guests, and had asked them to leave the area. When Caepio arrived he only found the local tribes and they sensibly decided not to fight the newly arrived legions. In 105 a further six legions were raised in Rome by Gnaeus Mallius Maximus, one of the consuls of 105, he led them to reinforce Caepio who was near Arausio. Unfortunately for the Romans, Caepio who was a patrician and Mallius Maximus who was a 'new man' did not get along. Caepio refused to take orders from Mallius Maximus who as consul outranked him. All this led to a divided Roman force with the two armies so far apart they could not support each other when the fighting started. Meanwhile, the Germanic tribes had combined their forces and together they first attacked and defeated Caepio's army and then, with great confidence, took on Mallius Maximus' army and defeated them too. The battle of Arausio was considered the greatest Roman defeat since the slaughter suffered at the battle of Cannae during the Punic Wars.[18]
In 104 the Cimbri and the Teutones seemed to be heading for Italy. As Marius was the best general Rome had, the Senate allowed him to lead the campaign against them. Sulla served on Marius' staff as tribunus militum. Sulla helped Marius in recruiting and training legionaries. He also led troops to subdue the Volcae Tectosages successfully and succeeded in capturing their leader Copillus.[19] In 103 Sulla succeeded in persuading the Germanic Marsi tribe to become friends and allies of Rome; they detached themselves from the Germanic confederation and went back to Germania.[20] In 102, when Marius became consul for the fourth time, there came an unusual separation between Marius and Sulla. For reasons unknown Sulla requested a transfer to the army of Quintus Lutatius Catulus Caesar, Marius' consular partner.[19] While Marius marched against the Teutones and Ambrones in Gaul, Catulus was tasked with keeping the Cimbri out of Italy. Catulus tasked Sulla with subduing the tribes in the north of Cisalpine Gaul to keep them from joining the Cimbri.[21] Overconfident Catulus tried to stop the Cimbri in a valley near Lake Benacus but he was severely outnumbered so Sulla convinced him to retreat.[22] Catulus' army suffered some losses when the Cimbri attacked near Tridentum but a disaster was avoided through the swift action of Gnaeus Petreius the Primus Pilus Centurion of the Samnite legion.[23] Sulla is credited with keeping Catulus from losing his army.[22] Meanwhile Marius had completely defeated the Ambrones and the Teutones in a battle near Aquae Sextiae. In 101 the armies of Marius and Catulus joined forces and faced the enemy tribes at the Battle of Vercellae. During the battle Sulla commanded the cavalry on the right and was instrumental in achieving victory.[24] Sulla and his cavalry routed the barbarian cavalry and drove them into the main body of the Cimbri causing chaos.[24] Catulus, seeing an opportunity, threw his men forward and followed up on Sulla's successful action. By noon the warriors of the Cimbri were defeated. Victorious at Vercellae, Marius and Catulus were both granted triumphs as the co-commanding generals. Sulla's role in the Vercellae victory was also hard to ignore and formed the launchpad for his political career.[25]
Cilician governorship

Returning to Rome, Sulla was elected Praetor urbanus for 97 BC.[26] In 96 BC he was appointed propraetor of the province of Cilicia in Asia Minor. There was a serious problem with pirates there and it is commonly assumed that he was sent there to deal with that.[27]
While governing Cilicia, Sulla received orders from the Senate to restore king Ariobarzanes to the throne of Cappadocia. Ariobarzanes had been driven out by Mithridates VI of Pontus who wanted to install one of his own sons (Ariarathes) on the Cappadocian throne. Despite initial difficulties Sulla succeeded in restoring Ariobarzanes to the throne. The Romans among his troops were sufficiently impressed by his leadership they hailed him Imperator on the field.[28]
Sulla's campaign in Cappadocia had led him to the banks of the Euphrates, where he was approached by an embassy from the Parthian Empire. Sulla was the first Roman magistrate to meet a Parthian ambassador. At the meeting he took the seat between the Parthian ambassador, Orobazus, and king Ariobarzanes, hereby, perhaps unintentionally, slighting the Parthian king by portraying the Parthians and the Cappadocians as equals and himself and Rome superior. The Parthian ambassador, Orobazus, was executed upon his return to Parthia for allowing this humiliation. It was at this meeting that Sulla was told by a Chaldean seer that he would die at the height of his fame and fortune. This prophecy was to have a powerful hold on Sulla throughout his lifetime.[29]
In 94 BC Sulla repulsed the forces of Tigranes the Great of Armenia from Cappadocia.[30] In 93 BC Sulla left the East and returned to Rome, where he aligned himself with the optimates in opposition to Gaius Marius. Sulla had done quite well in the East; restoring Ariobarzanes to the throne, being hailed Imperator on the field by his men, and being the first Roman to make a treaty with the Parthians.[31]
Social War

The Social War (91–88 BC) resulted from Rome's intransigence regarding the civil liberties of the Socii, Rome's Italian allies. The Socii were old enemies of Rome that submitted (such as the Samnites) whereas the Latins were confederates of longer standing with Rome; therefore the Latins were given more respect and better treatment.[32] Subjects of the Roman Republic, these Italian provincials might be called to arms in its defence or might be subjected to extraordinary taxes, but they had no say in the expenditure of these taxes or in the uses of the armies that might be raised in their territories. The Social War was, in part, caused by the continued rebuttal of those who sought to extend Roman citizenship to the Socii and to address various injustices inherent in the Roman system. The Gracchi, Tiberius and Gaius, were successively killed by optimate supporters who sought to maintain the status quo. The assassination of Marcus Livius Drusus the Younger, whose reforms were intended not only to strengthen the position of the Senate but also to grant Roman Citizenship to the allies, greatly angered the Socii. In consequence, most allied against Rome, leading to the outbreak of the Social War.
At the beginning of the Social War, the Roman aristocracy and Senate were beginning to fear Gaius Marius's ambition, which had already given him 6 consulships (including 5 in a row, from 104 BC to 100 BC). They were determined that he should not have overall command of the war in Italy. In this last rebellion of the Italian allies, Sulla outshone both Marius and the consul Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo (the father of Pompey).
Serving under Lucius Caesar (90 BC)
Sulla first served under the consul of 90, Lucius Julius Caesar, and fought against the southern group of the Italian rebels; the Samnites and their allies. Sulla and Caesar defeated Gaius Papius Mutilus, one of the leaders of the Samnites, at Acerrae. Then, commanding one of Caesar's divisions and working in tandem with his old commander Marius, Sulla defeated an army of the Marsi and the Marruncini, together they killed 6,000 rebels and the Marruncini general Herius Asinus.[33] When Lucius Caesar returned to Rome he ordered Sulla to reorganize the legions for deployment next year.[34]
In sole command (89 BC)
In 89 BC, a praetor now, Sulla served under the consul Lucius Porcius Cato Licinianus. Cato got himself killed early on while storming a rebel camp.[35] Sulla, being an experienced military man, took command of Rome's southern army and continued the fight against the Samnites and their allies. He besieged the rebel cities of Pompeii and Herculaneum. The admiral in command of the fleet blockading Pompeii, Aulus Postimius Albinus, offended his troops so that they stoned him to death. When news of this reached Sulla he declined to punish the murderers. He needed the men and he figured Albinus had brought it on himself.[36] During the siege of Pompeii rebel reinforcements under the command of a general called Lucius Cleuntius arrived.[37] Sulla drove off Cleuntius and his men and pursued them all the way to the city of Nola, a town to the north east of Pompeii.[37] At Nola a terrible battle ensued; Cleuntius' troops were desperate and fought savagely, but Sulla's army killed them almost to the last man, 20,000 rebels died in front of the city walls.[37] It is said Sulla killed Cleuntius with his own hands. The men who had fought with Sulla at the battle before the walls of Nola hailed him Imperator on the field and also awarded him the Grass Crown, or Corona Graminea.[38] This was the highest Roman military honour, awarded for personal bravery to a commander who saves a Roman legion or army in the field. Unlike other Roman military honours, it was awarded by acclamation of the soldiers of the rescued army, and consequently very few were ever awarded. The crown, by tradition, was woven from grasses and other plants taken from the actual battlefield.[39] Sulla then returned to the siege of Pompeii. After taking Pompeii and Herculaneum Sulla captured Aeclanum, the chief town of the Hirpini (he did this by setting the wooden breastwork on fire).[40]
After forcing the capitulation of all the rebel-held cities in Campania, with the exception of Nola, Sulla launched a dagger-thrust into the heartland of the Samnites. He was able to ambush a Samnite army in a mountain pass (in a reversal of the Battle of the Caudine Forks) and then having routed them, he marched on the rebel capital, storming it in a brutal three hour assault. Although Nola remained defiant, along with a few other pockets of resistance, Sulla had effectively finished the rebellion in the south for good.[41]
Consul of Rome (88 BC)
As a result of his success in bringing the Social War to a successful conclusion, he was elected consul (for the first time) in 88 BC, with Quintus Pompeius Rufus (soon his daughter's father-in-law) as his colleague. Sulla was 50 years old by then (most Roman consuls being in their early forties), he had finally achieved his rise into Rome's ruling class. He also married his third wife, Caecilia Metella, which connected him to the mighty Caecilii Metelli family.[42]
Sulla started his consulship by passing two laws designed to regulate Rome's finances, which were in a very sorry state after all the years of continual warfare. The first of the Leges Corneliae concerned the interest rates, and stipulated that all debtors were to pay simple interest only, rather than the common compound interest which so easily bankrupted the debtors. Also the interest rates were to be agreed between both parties, at the time that the loan was made, and should stand for the whole term of the debt, without further increase.[43]
The second law was concerned with the sponsio, which was the sum in dispute in cases of debt and usually had to be lodged with the praetor before the case was heard. This, of course, meant that many cases were never heard at all, as poorer clients did not have the money for the sponsio. Sulla's law waived the sponsio, allowing such cases to be heard without it. This, of course, made him very popular with the poorer citizens.[43]
After passing his laws Sulla temporarily left Rome to attend to the cleaning-up of the Italian Allies, especially Nola which was still holding out. While Sulla was besieging Nola, his political opponents were moving against him in Rome.[44]
First march on Rome

As senior consul, Sulla had been allocated the command of the First Mithridatic War against king Mithridates VI of Pontus.[45] This war against Mithridates promised to be a very prestigious and also a very lucrative affair.[46] Marius, Sulla's old commander, also ran for the command, but Sulla was fresh from his victories in Campania and Samnium, and almost twenty years younger (50 vs Marius' 69), so Sulla was confirmed in the command against the Pontic king.[45] Before he left Rome Sulla passed two laws (the first of the Leges Corneliae), he then went south into Campania to take care of the last Italian rebels.[47] Before leaving, Sulla and his consular colleague Quintus Pompeius Rufus blocked legislation of the tribune Publius Sulpicius Rufus, meant to ensure the rapid organisation of the Italian Allies into Roman citizenship.[48] Sulpicius found an ally in Marius who said he would support the bill, at which point Sulpicius felt confident enough to tell his supporters to start a riot. Sulla was besieging Nola when he heard that rioting had broken out in Rome; he quickly returned to Rome to meet with Pompeius Rufus; however, Sulpicius' followers attacked the meeting, forcing Sulla to take refuge in Marius' house, who in turn forced him to support Sulpicius' pro-Italian legislation in exchange for protection from the mob.[49] Sulla's son-in-law (Pompeius Rufus' son) was killed in the midst of these violent riots.[49] After leaving Rome again for Nola, Sulpicius (who was given a promise from Marius to wipe out his enormous debts) called an Assembly of the People to reverse the Senate's previous decision to grant Sulla military command, and instead transfer it to Marius.[49] Sulpicius also used the assembly to forcefully eject Senators from the Senate until there weren't enough of them to form a quorum. Violence in the Forum ensued, some nobles tried to lynch Sulpicius (as had been done to the brothers Gracchi, and to Saturninus) but failed in the face of his bodyguard of gladiators.
Sulla received news of this new turmoil while at his camp at Nola, surrounded by his Social War veterans, the men whom he had personally led to victory, the men who had hailed him Imperator and who had awarded him the Grass Crown (Corona Graminea).[50] His soldiers stoned envoys of the assemblies who came to announce that the command of the Mithridatic War had been transferred to Marius. Sulla then took five of the six legions stationed at Nola and marched on Rome. This was an unprecedented event. No general before him had ever crossed the city limits, the pomerium, with his army. It is worth mentioning however, that most of his commanders (with the exception of his kinsman through marriage Lucullus) refused to accompany him. Sulla justified his actions on the grounds that the Senate had been neutered; the mos maiorum ("the way of the elders"/"the traditional way", which amounted to a Roman constitution though none of it was codified as such) had been offended by the Senate's negation of the rights of the year's consuls to fight the year's wars. Even the armed gladiators were unable to resist the organized Roman soldiers; and although Marius offered freedom to any slave that would fight with him against Sulla (an offer which Plutarch says only three slaves accepted)[51] he and his followers were forced to flee the city.[52]
Sulla consolidated his position, declared Marius and his allies hostes (enemies of the state) and addressed the Senate in a harsh tone, portraying himself as a victim, presumably to justify his violent entrance into the city. After restructuring the city's politics and strengthening the Senate's power, Sulla once more returned to his military camp and proceeded with the original plan of fighting Mithridates in Pontus.
Sulpicius was later betrayed and killed by one of his slaves, whom Sulla subsequently freed and then executed (being freed for giving the information leading to Sulpicius, but sentenced to death for betraying his master). Marius, however, fled to safety in Africa until he heard Sulla was once again out of Rome, at which point he began plotting his return. During his period of exile, Marius became determined that he would hold a seventh consulship, as foretold by the Sibyl decades earlier. By the end of 87 BC Marius returned to Rome with the support of Lucius Cornelius Cinna and, in Sulla's absence, took control of the city. Marius declared Sulla's reforms and laws invalid and officially exiled him. Marius and Cinna were elected consuls for the year 86 BC. Marius died a fortnight later and Cinna was left in sole control of Rome.
First Mithridatic War
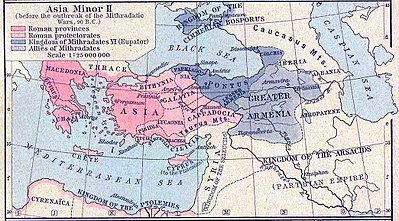
In the spring of 87 BC Sulla landed at Dyrrachium, in Illyria. Asia was occupied by the forces of Mithridates under the command of Archelaus. Sulla’s first target was Athens, ruled by a Mithridatic puppet; the tyrant Aristion. Sulla moved southeast, picking up supplies and reinforcements as he went. Sulla’s chief of staff was Lucullus, who went ahead of him to scout the way and negotiate with Bruttius Sura, the existing Roman commander in Greece. After speaking with Lucullus, Sura handed over the command of his troops to Sulla. At Chaeronea, ambassadors from all the major cities of Greece (except Athens) met with Sulla, who impressed on them Rome's determination to drive Mithridates from Greece and Asia Province. Sulla then advanced on Athens.
Sack of Athens
On arrival, Sulla threw up siege works encompassing not only Athens but also the port of Piraeus. At the time Archelaus had command of the sea, so Sulla sent Lucullus to raise a fleet from the remaining Roman allies in the eastern Mediterranean. His first objective was Piraeus, as without it Athens could not be re-supplied. Huge earthworks were raised, isolating Athens and its port from the land side. Sulla needed wood, so he cut down everything, including the sacred groves of Greece, up to 100 miles from Athens. When more money was needed he took from temples and Sibyls alike. The currency minted from this treasure was to remain in circulation for centuries and was prized for its quality.
Despite the complete encirclement of Athens and its port, and several attempts by Archelaus to raise the siege, a stalemate seemed to have developed. Sulla, however, patiently bided his time. Soon Sulla's camp was to fill with refugees from Rome, fleeing the massacres of Marius and Cinna. These also included his wife and children, as well as those of the optimate faction who had not been killed.
Athens by now was starving, and grain was at famine levels in price. Inside the city, the population was reduced to eating shoe leather and grass. A delegation from Athens was sent to treat with Sulla, but instead of serious negotiations they expounded on the glory of their city. Sulla sent them away saying: “I was sent to Athens, not to take lessons, but to reduce rebels to obedience.”
His spies then informed him that Aristion was neglecting the Heptachalcum (part of the city wall). Sulla immediately sent sappers to undermine the wall. Nine hundred feet of wall was brought down between the Sacred and Piraeic gates on the southwest side of the city. A midnight sack of Athens began, and after the taunts of Aristion, Sulla was not in a mood to be magnanimous. Blood was said to have literally flowed in the streets;[53] it was only after the entreaties of a couple of his Greek friends (Midias and Calliphon) and the pleas of the Roman Senators in his camp that Sulla decided enough was enough.[citation needed] He then concentrated his forces on the Port of Piraeus, and Archelaus, seeing his hopeless situation, withdrew to the citadel and then abandoned the port to join up with his forces under the command of Taxiles. Sulla, as yet not having a fleet, was powerless to prevent Archelaus’ escape. Before leaving Athens, he burnt the port to the ground. Sulla then advanced into Boeotia to take on Archelaus's armies and remove them from Greece.
Battle of Chaeronea
Sulla lost no time in intercepting the Pontic army, occupying a hill called Philoboetus that branched off Mount Parnassus, overlooking the Elatean plain, with plentiful supplies of wood and water. The army of Archelaus, presently commanded by Taxiles, had to approach from the north and proceed along the valley towards Chaeronea. Over 120,000 strong, it outnumbered Sulla's forces by at least 3 to 1. Archelaus was in favour of a policy of attrition with the Roman forces, but Taxiles had orders from Mithridates to attack at once. Sulla got his men digging, and occupied the ruined city of Parapotamii, which was impregnable and commanded the fords on the road to Chaeronea. He then made a move that looked to Archelaus like a retreat. He abandoned the fords and moved in behind an entrenched palisade. Behind the palisade were the field artillery from the siege of Athens.
Archelaus advanced across the fords and tried to outflank Sulla’s men, only to have his right wing hurled back, causing great confusion in the Pontic army. Archelaus’s chariots then charged the Roman centre, only to be destroyed on the palisades. Next came the phalanxes: they too found the palisades impassable, and received withering fire from the Roman field artillery. Then Archelaus flung his right wing at the Roman left; Sulla, seeing the danger of this manoeuvre, raced over from the Roman right wing to help. Sulla stabilized the situation, at which point Archelaus flung in more troops from his right flank. This destabilized the Pontic army, slewing it towards its right flank. Sulla dashed back to his own right wing and ordered the general advance. The legions, supported by cavalry, dashed forward and Archelaus’ army folded in on itself, like closing a pack of cards. The slaughter was terrible, and some reports estimate that only 10,000 men of Mithridates' original army survived. Sulla had defeated a vastly superior force in terms of numbers.
Battle of Orchomenus
The government of Rome (under the de facto rule of Cinna) then sent out Lucius Valerius Flaccus with an army to relieve Sulla of command in the east. Flaccus' second in command was Gaius Flavius Fimbria, who had few virtues. (He was to eventually agitate against his commanding officer and incite the troops to murder Flaccus). The two Roman armies camped next to each other; and Sulla, not for the first time, encouraged his soldiers to spread dissension among Flaccus’ army. Many deserted to Sulla before Flaccus packed up and moved on north to threaten Mithridates’ northern dominions. Meanwhile, Arhelaeus had been reinforced by 80,000 men brought over from Asia Minor by Dorylaeus, another of Mithridates' generals, and was embarking his army from his base on Euboea. The return of a large Mithridatic army caused the revolt of Boeotians from the Romans. Sulla immediately marched his army back south.[54]
He chose the site of the battle to come — Orchomenus, a town in Boeotia that allowed a smaller army to meet a much larger one, due to its natural defences, and was ideal terrain for Sulla's innovative use of entrenchment. This time the Pontic army was in excess of 150,000, and it encamped itself in front of the busy Roman army, next to a large lake. It soon dawned on Archelaus what Sulla was up to. Sulla had not only been digging trenches but also dikes, and before long he had the Pontic army in deep trouble. Desperate sallies by the Pontic forces were repulsed by the Romans and the dikes moved onward.
On the second day, Archelaus made a determined effort to escape Sulla’s web of dikes—the entire Pontic army was hurled at the Romans—but the Roman legionaries were pressed together so tightly that their short swords were like an impenetrable barrier, through which the enemy could not escape. The battle turned into a rout, with slaughter on an immense scale. Plutarch notes that two hundred years later, armour and weapons from the battle were still being found. The battle of Orchomenus was another of the world's decisive battles. It determined that the fate of Asia Minor lay with Rome and her successors for the next millennium.
Sulla's victory and settlement

In 86 BC, after Sulla's victory in Orchomenos, he initially spent some time re-establishing Roman authority. His legate soon arrived with the fleet he was sent to gather, and Sulla was ready to recapture lost Greek islands before crossing into Asia Minor. The second Roman army under the command of Flaccus, meanwhile, moved through Macedonia and into Asia Minor. After the capture of Philippi, the remaining Mithridatic forces crossed the Hellespont to get away from the Romans. Fimbria encouraged his forces to loot and create general havoc as they went. Flaccus was a fairly strict disciplinarian and the behaviour of his lieutenant led to discord between the two.
At some point, as this army crossed the Hellespont to pursue Mithridates' forces, Fimbria seems to have started a rebellion against Flaccus. While seemingly minor enough to not cause immediate repercussions in the field, Fimbria was relieved of his duty and ordered back to Rome. The return trip included a stop at the port city of Byzantium, however, and here Fimbria took command of the garrison, rather than continue home. Flaccus, hearing of this, marched his army to Byzantium to put a stop to the rebellion, but walked right into his own undoing. The army preferred Fimbria (not surprising considering his leniency in regard to plunder) and a general revolt ensued. Flaccus attempted to flee, but was captured shortly after and the consul was executed. With Flaccus out of the way, Fimbria took complete command.
The following year (85 BC) Fimbria took the fight to Mithridates while Sulla continued to operate in the Aegean. Fimbria quickly won a decisive victory over remaining Mithridatic forces and moved on the capital of Pergamum. With all vestige of hope crumbling for Mithridates, he fled Pergamum to the coastal city of Pitane. Fimbria, in pursuit, laid siege to the town, but had no fleet to prevent Mithridates' escape by sea. Fimbria called upon Sulla's legate, Lucullus, to bring his fleet around to blockade Mithridates, but it seems that Sulla had other plans.
Sulla apparently had been in private negotiation with Mithridates to end the war. He wanted to develop easy terms and get the ordeal over as quickly as possible. The quicker it was dealt with, the faster he would be able to settle political matters in Rome. With this in mind, Lucullus and his navy refused to help Fimbria, and Mithridates 'escaped' to Lesbos. Later at Dardanus, Sulla and Mithridates met personally to negotiate terms. With Fimbria re-establishing Roman hegemony over the cities of Asia Minor, Mithridates' position was completely untenable. Yet Sulla, with his eyes on Rome, offered uncharacteristically mild terms. Mithridates was forced to give up all his conquests (which Sulla and Fimbria had already managed to take back by force), surrender any Roman prisoners, provide a 70 ship fleet to Sulla along with supplies, and pay a tribute of 2,000 to 3,000 gold talents. In exchange, Mithridates was able to keep his original kingdom and territory and regain his title of "friend of the Roman people."
But things in the east weren't yet settled. Fimbria was enjoying free rein in the province of Asia and led a cruel oppression of both those who were involved against Romans, and those who were now in support of Sulla. Unable to leave a potentially dangerous army in his rear, Sulla crossed into Asia. He pursued Fimbria to his camp at Thyatira where Fimbria was confident in his ability to repulse an attack. Fimbria, however, soon found that his men wanted nothing to do with opposing Sulla and many deserted or refused to fight in the coming battle. Sensing all was lost, Fimbria took his own life, while his army went over to Sulla.
To ensure the loyalty of both Fimbria's troops and his own veterans, who weren't happy about the easy treatment of their enemy, Mithridates, Sulla now started to penalize the province of Asia. His veterans were scattered throughout the province and allowed to extort the wealth of local communities. Large fines were placed on the province for lost taxes during their rebellion and the cost of the war.
As the year 84 BC began, Cinna, still Consul in Rome, was faced with minor disturbances among Illyrian tribes. Perhaps in an attempt to gain experience for an army to act as a counter to Sulla's forces, or to show Sulla that the Senate also had some strength of its own, Cinna raised an army to deal with this Illyrian problem. Conveniently the source of the disturbance was located directly between Sulla and another march on Rome. Cinna pushed his men hard to move to position in Illyria, and forced marches through snow-covered mountains did little to endear Cinna to his army. A short time after departing Rome, Cinna was stoned to death by his own men. Hearing of Cinna's death, and the ensuing power gap in Rome, Sulla gathered his forces and prepared for a second march on the capital.
Second march on Rome
In 83 BC Sulla prepared his five legions and left the two originally under Fimbria to maintain peace in Asia Minor. In the spring of that year, Sulla crossed the Adriatic with a large fleet from Patrae, west of Corinth, to Brundisium and Tarentum in the heel of Italy.[55] Landing uncontested, he had ample opportunity to prepare for the coming war.
In Rome the newly elected consuls, Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus (Asiagenus) and C. Norbanus levied and prepared armies of their own to stop Sulla and protect the Republican government. Norbanus marched first with the intention of blocking a Sullan advance at Canusium. Seriously defeated, Norbanus was forced to retreat to Capua where there was no respite. Sulla followed his defeated adversary and won another victory in a very short time. Meanwhile, Asiagenus was also on the march south with an army of his own. However, neither Asiagenus nor his army, seemed to have any motivation to fight. At the town of Teanum Sidicinum, Sulla and Asiagenus met face-to-face to negotiate and Asiagenus surrendered without a fight. The army sent to stop Sulla wavered in the face of battle against experienced veterans, and certainly along with the prodding of Sulla's operatives, gave up the cause, going over to Sulla's side as a result. Left without an army, Asiagenus had little choice but to cooperate and later writings of Cicero suggest that the two men actually discussed many matters regarding Roman government and the Constitution.
Sulla let Asiagenus leave the camp, firmly believing him to be a supporter. He was possibly expected to deliver terms to the Senate, but immediately rescinded any thought of supporting Sulla upon being set free. Sulla later made it publicly known that not only would Asiagenus suffer for opposing him, but that any man who continued to oppose him after this betrayal would suffer bitter consequences. With Sulla's three quick victories, though, the situation began to rapidly turn in his favour. Many of those in a position of power, who had not yet taken a clear side, now chose to support Sulla. The first of these was Q. Caecilius Metellus Pius, who governed Africa. The old enemy of Marius, and assuredly of Cinna as well, led an open revolt against the Marian forces in Africa. Additional help came from Picenum and Spain. Two of the three future triumvirs joined Sulla's cause in his bid to take control. Marcus Licinius Crassus marched with an army from Spain, and would later play a pivotal role at the Colline Gates. The young son of Pompeius Strabo (the butcher of Asculum during the Social War), Pompey, raised an army of his own from among his father's veterans and threw his lot in with Sulla. At the age of 23, and never having held a senatorial office, Pompey forced himself into the political scene with an army at his back.
Regardless, the war would continue on with Asiagenus raising another army in defence. This time he moved after Pompey, but once again, his army abandoned him and went over to the enemy. As a result, desperation followed in Rome as the year 83 came to a close. Cinna's old co-consul, Papirius Carbo, and Gaius Marius the Younger, the 26-year-old son of the dead consul, were elected as consuls. Hoping to inspire Marian supporters throughout the Roman world, recruiting began in earnest among the Italian tribes who had always been loyal to Marius. In addition, possible Sullan supporters were murdered. The urban praetor L. Junius Brutus Damasippus led a slaughter of those senators who seemed to lean towards the invading forces—yet one more incident of murder in a growing spiral of violence as a political tool in the late Republic.
As the campaign year of 82 BC opened, Carbo took his forces to the north to oppose Pompey while Marius moved against Sulla in the south. Attempts to defeat Pompey failed and Metellus with his African forces along with Pompey secured northern Italy for Sulla. In the south, young Marius gathered a large host of Samnites, who assuredly would lose influence with the anti-popular Sulla in charge of Rome. Marius met Sulla at Sacriportus and the two forces engaged in a long and desperate battle. In the end, many of Marius' men switched sides over to Sulla and he had no choice but to retreat to Praeneste. Sulla followed the son of his arch-rival and laid siege to the town, leaving a subordinate in command. Sulla himself moved north to push Carbo, who had withdrawn to Etruria to stand between Rome and the forces of Pompey and Metellus.
Indecisive battles were fought between Carbo and Sulla's forces but Carbo knew that his cause was lost. News arrived of a defeat by Norbanus in Gaul, and that he also switched sides to Sulla. Carbo, caught between three enemy armies and with no hope of relief, fled to Africa. It was not yet the end of the resistance, however; those remaining Marian forces gathered together and attempted several times to relieve young Marius at Praeneste. A Samnite force under Pontius Telesinus joined in the relief effort but the combined armies were still unable to break Sulla. Rather than continue trying to rescue Marius, Telesinus moved north to threaten Rome.
On November 1 of 82 BC, the two forces met at the Battle of the Colline Gate, just outside Rome. The battle was a huge and desperate final struggle with both sides certainly believing their own victory would save Rome. Sulla was pushed hard on his left flank with the situation so dangerous that he and his men were pushed right up against the city walls. Crassus' forces, fighting on Sulla's right however, managed to turn the opposition's flank and drive them back. The Samnites and the Marian forces were folded up and broke. In the end, over 50,000 combatants lost their lives and Sulla stood alone as the master of Rome.
Dictatorship and constitutional reforms
At the end of 82 BC or the beginning of 81 BC,[56] the Senate appointed Sulla dictator legibus faciendis et reipublicae constituendae causa ("dictator for the making of laws and for the settling of the constitution"). The "Assembly of the People" subsequently ratified the decision, with no limit set on his time in office. Sulla had total control of the city and republic of Rome, except for Hispania (which Marius's general Quintus Sertorius had established as an independent state). This unusual appointment (used hitherto only in times of extreme danger to the city, such as during the Second Punic War, and then only for 6-month periods) represented an exception to Rome's policy of not giving total power to a single individual. Sulla can be seen as setting the precedent for Julius Caesar's dictatorship, and for the eventual end of the Republic under Augustus.
In total control of the city and its affairs, Sulla instituted a series of proscriptions (a program of executing those whom he perceived as enemies of the state and confiscating their property). Plutarch states in his "Life" of Sulla (XXXI): "Sulla now began to make blood flow, and he filled the city with deaths without number or limit", further alleging that many of the murdered victims had nothing to do with Sulla, though Sulla killed them to "please his adherents".
"Sulla immediately proscribed eighty persons without communicating with any magistrate. As this caused a general murmur, he let one day pass, and then proscribed two hundred and twenty more, and again on the third day as many. In an harangue to the people, he said, with reference to these measures, that he had proscribed all he could think of, and as to those who now escaped his memory, he would proscribe them at some future time." -Plutarch, Life of Sulla (XXXI)
The proscriptions are widely perceived as a response to similar killings which Marius and Cinna had implemented while they controlled the Republic during Sulla's absence. Proscribing or outlawing every one of those whom he perceived to have acted against the best interests of the Republic while he was in the East, Sulla ordered some 1,500 nobles (i.e., senators and equites) executed, although it is estimated that as many as 9,000 people were killed.[57] The purge went on for several months. Helping or sheltering a proscribed person was punishable by death, while killing a proscribed person was rewarded with two talents. Family members of the proscribed were not excluded from punishment, and slaves were not excluded from rewards. As a result, "husbands were butchered in the arms of their wives, sons in the arms of their mothers".[58] The majority of the proscribed had not been enemies of Sulla, but instead were killed for their property, which was confiscated and auctioned off. The proceeds from auctioned property more than made up for the cost of rewarding those who killed the proscribed, filling the treasury. Possibly to protect himself from future political retribution, Sulla had the sons and grandsons of the proscribed banned from running for political office, a restriction not removed for over 30 years.
The young Gaius Julius Caesar, as Cinna's son-in-law, became one of Sulla's targets and fled the city. He was saved through the efforts of his relatives, many of whom were Sulla's supporters, but Sulla noted in his memoirs that he regretted sparing Caesar's life, because of the young man's notorious ambition. The historian Suetonius records that when agreeing to spare Caesar, Sulla warned those who were pleading his case that he would become a danger to them in the future, saying: "In this Caesar there are many Mariuses."[59][60]
Sulla, who opposed the Gracchian popularis reforms, was an optimate; though his coming to the side of the traditional Senate originally could be described as more reactionary when dealing with the Tribunate and legislative bodies, while more visionary when reforming the court system, governorships and membership of the Senate.[61] As such, he sought to strengthen the aristocracy, and thus the Senate.[61] Sulla retained his earlier reforms, which required senatorial approval before any bill could be submitted to the Plebeian Council (the principal popular assembly), and which had also restored the older, more aristocratic "Servian" organization to the Centuriate Assembly (assembly of soldiers).[62] Sulla, himself a patrician and thus ineligible for election to the office of Plebeian Tribune, thoroughly disliked the office. As Sulla viewed the office, the Tribunate was especially dangerous and his intention was to not only deprive the Tribunate of power, but also of prestige. (Sulla himself had been officially deprived of his eastern command through the underhand activities of a tribune.) Over the previous three hundred years, the tribunes had directly challenged the patrician class and attempted to deprive it of power in favor of the plebeian class. Through Sulla's reforms to the Plebeian Council, tribunes lost the power to initiate legislation. Sulla then prohibited ex-tribunes from ever holding any other office, so ambitious individuals would no longer seek election to the Tribunate, since such an election would end their political career.[63] Finally, Sulla revoked the power of the tribunes to veto acts of the Senate, although he left intact the tribunes' power to protect individual Roman citizens.
Sulla then increased the number of magistrates elected in any given year,[61] and required that all newly elected quaestors gain automatic membership in the Senate. These two reforms were enacted primarily to allow Sulla to increase the size of the Senate from 300 to 600 senators. This also removed the need for the censor to draw up a list of senators, since there were always more than enough former magistrates to fill the senate.[61] To further solidify the prestige and authority of the Senate, Sulla transferred the control of the courts from the equites, who had held control since the Gracchi reforms, to the senators. This, along with the increase in the number of courts, further added to the power that was already held by the senators.[63] Sulla also codified, and thus established definitively, the cursus honorum,[63] which required an individual to reach a certain age and level of experience before running for any particular office. Sulla also wanted to reduce the risk that a future general might attempt to seize power, as he himself had done. To this end he reaffirmed the requirement that any individual wait for ten years before being reelected to any office. Sulla then established a system where all consuls and praetors served in Rome during their year in office, and then commanded a provincial army as a governor for the year after they left office.[63]
Finally, in a demonstration of his absolute power, Sulla expanded the "Pomerium", the sacred boundary of Rome, unchanged since the time of the kings.[64] Sulla's reforms both looked to the past (often re-passing former laws) and regulated for the future, particularly in his redefinition of maiestas (treason) laws and in his reform of the Senate.
After a second consulship in 80 BC (with Metellus Pius), Sulla, true to his traditionalist sentiments, resigned his dictatorship in early 79,[3] disbanded his legions and re-established normal consular government. He dismissed his lictors and walked unguarded in the Forum, offering to give account of his actions to any citizen.[65][8] In a manner that the historian Suetonius thought arrogant, Julius Caesar would later mock Sulla for resigning the dictatorship.[66]
Retirement and death
After his second consulship, and as promised when his tasks were complete, Sulla returned his powers and withdrew to his country villa near Puteoli to be with his family. Plutarch states in his "Life of Sulla" that he retired to a life spent in dissolute luxuries: "He consorted with actresses, harpists, and theatrical people, drinking with them on couches all day long". From this distance, Sulla remained out of the day-to-day political activities in Rome, intervening only a few times when his policies were involved (e.g., the execution of Granius shortly before his own death).[67][68]
Sulla's goal now was to write his memoirs, which he finished in 78 BC, just before his death. They are now largely lost, although fragments from them exist as quotations in later writers. Ancient accounts of Sulla's death indicate that he died from liver failure or a ruptured gastric ulcer (symptomised by a sudden haemorrhage from his mouth followed by a fever from which he never recovered) possibly caused by chronic alcohol abuse.[69][70] Accounts were also written that he had an infestation of worms, caused by the ulcers, which led to his death.[71]
His public funeral in Rome (in the Forum, in the presence of the whole city) was on a scale unmatched until that of Augustus in AD 14. Sulla's body was brought into the city on a golden bier, escorted by his veteran soldiers, and orations were delivered by several eminent senators: the main funeral oration was delivered by Lucius Marcius Philippus. Sulla's body was cremated and his ashes placed in his tomb in the Campus Martius.[72] An epitaph, which Sulla composed himself, was inscribed onto the tomb, reading: "No friend ever served me, and no enemy ever wronged me, whom I have not repaid in full".[73]
Plutarch claims he had seen Sulla's personal motto carved on his tomb on the Campus Martius. The personal motto was 'no better friend, no worse enemy'.[74]
Legacy
This section needs additional citations for verification. (October 2016) |
Sulla is generally seen as having set the precedent for Caesar's march on Rome and dictatorship. Cicero comments that Pompey once said "If Sulla could, why can't I?".[75] Sulla's example proved that it could be done, and therefore inspired others to attempt it; and in this respect, he has been seen as another step in the Republic's fall. Further, Sulla failed to frame a settlement whereby the army (following the Marian reforms allowing non-landowning soldiery) remained loyal to the Senate rather than to generals such as himself. He attempted to mitigate this by passing laws to limit the actions of generals in their provinces, and although these laws remained in effect well into the imperial period, they did not prevent determined generals such as Pompey and Julius Caesar from using their armies for personal ambition against the Senate, a danger that Sulla was intimately aware of.
While Sulla's laws such as those concerning qualification for admittance to the Senate and reform of the legal system and regulations of governorships remained on Rome's statutes long into the Principate, much of his legislation was repealed less than a decade after his death. The veto power of the tribunes and their legislating authority were soon reinstated, ironically during the consulships of Pompey and Crassus.[76]
Sulla's descendants continued to be prominent in Roman politics into the imperial period. His son, Faustus Cornelius Sulla, issued denarii bearing the name of the dictator,[77] as did a grandson, Quintus Pompeius Rufus. His descendants among the Cornelii Sullae would hold four consulships during the imperial period: Lucius Cornelius Sulla in 5 BC, Faustus Cornelius Sulla in AD 31, Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix in AD 33, and Faustus Cornelius Sulla Felix (the son of the consul of 31) in AD 52. The latter was the husband of Claudia Antonia, daughter of the emperor Claudius. His execution in AD 62 on the orders of emperor Nero would make him the last of the Cornelii Sullae.
Cultural references
- The dictator is the subject of four Italian operas, two of which take considerable liberties with history: Lucio Silla by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and the Silla by George Frideric Handel. In each he is portrayed as a bloody, womanizing, ruthless tyrant who eventually repents his ways and steps down from the throne of Rome. Also Pasquale Anfossi and Johann Christian Bach wrote operas on this subject.
- Sulla is an important character in the first three Masters of Rome novels of Colleen McCullough. Sulla is depicted as ruthless and amoral, very self-assured, personally brave, and charming, especially with women. His charm and ruthlessness make him a valuable aide to Gaius Marius. Sulla’s desire to move out of the shadow of aging Marius eventually leads to civil war. Sulla softened considerably after the birth of his son and was devastated when he died at a young age. The novels depict Sulla full of regrets about having had to put aside his homosexual relationship with a Greek actor to take up his public career.
- Sulla is played by Richard Harris in the 2002 miniseries Julius Caesar.
- Lucius Cornelius Sulla is also a character in the first book of the Emperor novels by Conn Iggulden, which are centred around the lives of Gaius Julius Caesar and Marcus Brutus.
- Sulla is a major character in Roman Blood, the first of the Roma Sub Rosa mystery novels by Steven Saylor.
Marriages and children
- First wife, "Ilia" (according to Plutarch). If Plutarch's text is to be amended to "Julia", then she is likely to have been one of the Julias related to Julius Caesar, most likely Julia Caesaris, Caesar's first-cousin once-removed.[78]
- Cornelia, married first Quintus Pompeius Rufus the Younger and later Mamercus Aemilius Lepidus Livianus; mother of Pompeia (second wife of Julius Caesar) with the former.
- Lucius Cornelius Sulla, died young
- Second wife, Aelia.
- Third wife, Cloelia. Sulla divorced her due to sterility.
- Fourth wife, Caecilia Metella
- Faustus Cornelius Sulla
- Fausta Cornelia, married first to Gaius Memmius (praetor in 58 BC), then later to Titus Annius Milo (praetor in 54 BC). Mother of Gaius Memmius, suffect consul in 34 BC.
- Fifth wife, Valeria
- Cornelia Postuma (born after Sulla's death)
Appearance and character
Sulla was red-blond,[79] blue-eyed, and had a dead-white face covered with red marks.[80] Plutarch notes that Sulla considered that "his golden head of hair gave him a singular appearance".[81]
He was said to have a duality between being charming and easily approachable, able to joke and cavort with the most simple of people while also assuming a dictatorial stern demeanor when he was leading armies and as dictator. An example of the extent of his charming side was that his soldiers would sing a ditty about Sulla's one testicle, although without truth, to which he allowed as being "fond of a jest."[82] This duality, or inconsistency, made him very unpredictable and "at the slightest pretext he might have a man crucified, but on another occasion would make light of the most appalling crimes; or he might happily forgive the most unpardonable offenses and then punish trivial, insignificant misdemeanors with death and confiscation of property."[83] His excesses and penchant for debauchery could be attributed to the difficult circumstances of his youth, such as losing his father while he was still in his teens, retaining a doting step mother, necessitating an independent streak from an early age. The circumstances of his relative poverty as a young man left him removed from his patrician brethren, enabling him to consort with revelers and experience the baser side of human nature. This "first hand" understanding of human motivations and the ordinary Roman citizen may explain why he was able to succeed as a general despite lacking any significant military experience before his 30s.[84]
Chronology
- c. 138 BC: Born in Rome
- 110 BC: Marries first wife
- 107-05 BC: Quaestor and pro quaestore to Gaius Marius in the war with Jugurtha in Numidia
- 106 BC: End of Jugurthine War
- 104 BC: legatus to Marius cos.II in Gallia Transalpina
- 103 BC: tribunus militum in army of Marius cos.III in Gallia Transalpina
- 102-01 BC: legatus to Quintus Lutatius Catulus consul and pro consule in Gallia Cisalpina
- 101 BC: took part in the defeat of the Cimbri at the battle of Vercellae
- 97 BC: Praetor urbanus
- 96 BC: Propraetor of Cilicia province pro consule
- 90-89 BC: senior officer in the Social War as legatus pro praetore
- 88 BC:
- Holds the consulship (for the first time) with Quintus Pompeius Rufus as colleague
- Invades Rome and outlaws Gaius Marius
- 87 BC: Command of Roman armies to fight King Mithridates of Pontus
- 86 BC: Sack of Athens, Battle of Chaeronea, Battle of Orchomenus
- 85 BC: Liberation of Macedonia, Asia and Cilicia provinces from Pontic occupation
- 84 BC: Reorganization of Asia province
- 83 BC: Returns to Italy and undertakes civil war against the factional Marian government
- 83-82 BC: War with the followers of Gaius Marius the Younger and Cinna
- 82 BC: Victory at the Battle of the Colline Gate
- 82/1 BC: Appointed "dictator legibus faciendis et rei publicae constituendae causa"
- 81 BC: Resigns the dictatorship before the end of the year
- 80 BC: Holds the consulship (for the second time) with Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius as colleague
- 79 BC: Retires from political life, refusing the post consulatum provincial command of Gallia Cisalpina he was allotted as consul, but retaining the curatio for the reconstruction of the temples on the Capitoline Hill
- 78 BC: Dies, perhaps of an intestinal ulcer. Funeral held in Rome
See also
- Apellicon of Teos – Ancient Greek philosopher in Athens
Notes
- ^ Crawford, Roman Republican Coinage, pp. 456, 457.
- ^ Valerius Maximus 9. 3. 8; Appian 1. 105; Plutarch Sulla 6. 10; Velleius Paterculus 2. 17. 2
- ^ a b Vervaet, pp. 60–68.
- ^ L•CORNELIVS•L•F•P•N•SVLLA•FELIX in Latin inscriptions, the meaning in English is "Lucius Cornelius Sulla, son of Lucius, grandson of Publius, the Fortunate." His agnomen Felix — the fortunate — was attained later in life, as the Latin equivalent of the Greek nickname he had acquired during his campaigns, ἐπαφρόδιτος epaphroditos, beloved-of-Aphrodite or (to Romans who read Sulla's Greek title) Venus — due to his skill and luck as a general.
- ^ a b "Plutarch • Life of Sulla". penelope.uchicago.edu. Retrieved 2015-12-09.
- ^ Smith, William (1870). Dictionary of Greek and Roman biography and mythology. Vol. 3. Boston, Little. p. 933.
- ^ Smith, William. Dictionary of Greek and Roman biography and mythology. p. 665.
- ^ a b Arthur Keaveney, Sulla: The Last Republican, p. 165
- ^ Keaveney, Arthur. Sulla: the last Republican. p. 6.
- ^ Keaveney, Arthur. Sulla: the last Republican. pp. 9, 10.
- ^ Plutarch: Sulla.
- ^ Plutarch (2006). Fall of the Roman Republic. Penguin Classics. p. 59.
- ^ Plutarch: Sulla, Sect 2.
- ^ Plutarch: Sulla, Sect 3
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 41.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 42.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, pp 42-43.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, pp 45-51.
- ^ a b Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p.58.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, pp 57-58.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p.60.
- ^ a b Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p.61.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, pp 60-61.
- ^ a b Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 65; Philip Matyszak, Sertorius and the Struggle for Spain, pp 14-15.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 67.
- ^ Keaveney, p. 30.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 72.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, pp 72-74.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, pp 75-76; Olbrycht 2009: 174-9.
- ^ Olbrycht 2009: 173.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 77.
- ^ Plutarch, Parallel Lives; Life of Sula
- ^ Philip Matyszak, Cataclysm 90 BC, pp 95-96; Lynda Telford, Sulla, p. 89.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, pp 89-90.
- ^ Philip Matyszak, Cataclysm 90 BC, p. 105.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, pp 91-92.
- ^ a b c Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 93; Philip Matyszak, Cataclysm 90 BC, p. 107.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 93.
- ^ [1].
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, pp 90-94; Stefano Giuntoli, Art & History of Herculaneum.
- ^ Philip Matyszak, Cataclysm 90 BC, p. 109; Tom Holland, Rubicon, p. 65.
- ^ Lynda Telford, A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 97.
- ^ a b Lynda Telford, A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 99.
- ^ Lynda Telford, A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 100.
- ^ a b Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 96; Tom Holland, Rubicon, p. 66; Philip Matyszak, Cataclysm 90 BC, p. 116.
- ^ Tom Holland, Rubicon, p. 66.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 100; Tom Holland, Rubicon, p. 67; Philip Matyszak, Cataclysm 90 BC, pp 116-117.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, pp 98-99; Tom Holland, Rubicon, p. 66; Philip Matyszak, Cataclysm 90 BC, p. 116.
- ^ a b c Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, pp 100-101; Tom Holland, Rubicon, pp 67-68; Philip Matyszak, Cataclysm 90 BC, pp 116-118.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, pp 101-102; Tom Holland, Rubicon, pp 68-69; Philip Matyszak, Cataclysm 90 BC, pp 117-118.
- ^ Plutarch, [Life of] Sulla, c.35
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, pp 101-104;Tom Holland, Rubicon, pp 69-73.
- ^ Plutarch, Life of Sulla, 14
- ^ Philip Matyszak, Mithridates the Great: Rome's Indomitable Enemy, p. 77.
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 157; Philip Matyszak, Cataclysm 90 BC, p. 113.
- ^ Mark Davies; Hilary Swain (22 June 2010). Aspects of Roman history, 82 BC-AD 14: a source-based approach. Taylor & Francis. pp. 33–. ISBN 978-0-415-49693-3. Retrieved 10 August 2011.
- ^ Cicero, Anthony Everitt, p.41
- ^ Plutarch, Roman Lives. Oxford University Press, 1999, translation by Robin Waterfield. p 210
- ^ Suetonius, The Life of Julius Caesar, 1 Archived 2012-05-30 at archive.today
- ^ Plutarch, The Life of Caesar , 1
- ^ a b c d Abbott, 104
- ^ Abbott, 103
- ^ a b c d Abbott, 105
- ^ LacusCurtius, Pomerium
- ^ Plutarch, Sulla, 34
- ^ Suetonius, Julius 77 Archived 2012-05-30 at archive.today. "... No less arrogant were his public utterances, which Titus Ampius records: that the state was nothing, a mere name without body or form; that Sulla did not know his A. B. C. when he laid down his dictatorship; that men ought now to be more circumspect in addressing him, and to regard his word as law. So far did he go in his presumption, that when a soothsayer once reported direful inwards [sic] without a heart, he said: "They will be more favourable when I wish it; it should not be regarded as a portent, if a beast has no heart ..."
- ^ Plutarch, "The Life of Sulla", 37.
- ^ Valerius Maximus, ix. 3. § 8.
- ^ Pliny the elder, (N'H, VII, XLIV) says that "was not the close of his life more horrible than the sufferings which had been experienced by any of those who had been proscribed by him? His very flesh eating into itself, and so engendering his own punishment."
- ^ Valerius Maximus, Memorable Deeds and Sayings IX.3.8; Plutarch, Sulla 36-37; Appian, Civil Wars I.12.105; A. Keaveney (2005) Sulla: the Last Republican (2nd edition) p.175.
- ^ "Plutarch, Sulla, chapter 36". www.perseus.tufts.edu. Retrieved 2015-12-09.
- ^ Robin Seager, 'Sulla', in The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume IX (2nd Edition), Cambridge University Press, 1994, p.207
- ^ Heroes of History : A Brief History of Civilization from Ancient Times to the Dawn of the Modern Age (2001) by Will Durant
- ^ Lynda Telford, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, p. 199
- ^ Cicero, Ad Atticum IX 10.2. Arthur Keaveney (1982). Sulla, the last republican. pp. 228–. ISBN 978-0-7099-1507-2. Retrieved 10 August 2011.
- ^ Plutarch, Pompey 22.3.
- ^ Michael Crawford, Roman Republican Coinage, 1974, vol. 1, p. 449-451.
- ^ Keaveney, p. 8
- ^ Keaveney, p. 10
- ^ Erik Hildinger, Swords Against the Senate: The Rise of the Roman Army and the Fall of the Republic, Da Capo Press, 2003, p.99
- ^ "Plutarch, Life of Sulla". May 2008. Retrieved 2011-07-03.
- ^ Keaveney
- ^ Plutarch, Roman Lives. Oxford University Press, 1999, Translation by Robin Waterfield, p. 181.
- ^ Keaveney, p. 11
References
- Crawford, Michael, Roman Republican Coinage, Cambridge University Press, 1974.
- Fröhlich, Franz, "Cornelius 392", Realencyclopädie der classischen Altertumswissenschaft, volume 7 (IV.1), Metzlerscher Verlag (Stuttgart, 1900), columns 1522–1566.
- Keaveney, Arthur (2005) [1982]. Sulla: The Last Republican (2nd ed.). London: Routledge. ISBN 0-415-33660-0.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Seager, Robin (1994). "Sulla". In J.A. Crook; Andrew Lintott; Elizabeth Rawson (eds.). The Cambridge Ancient History IX: The Last Age of the Roman Republic, 146–43 B.C. (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 165–207. ISBN 0-521-25603-8.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - Telford, Lynda, Sulla: A Dictator Reconsidered, Pen and sword; 1st edition (April 19, 2014). ISBN 978-1-783-03048-4.
- Vervaet, Frederik Juliaan (2004). "The lex Valeria and Sulla's empowerment as dictator (82–79 BCE)". Cahiers du Centre Gustave Glotz. 15: 37–84. eISSN 2117-5624.
Further reading
- Sulla the Fortunate: Roman general and dictator by G. P. Baker (1927, 2001: ISBN 0815411472)
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 26 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
External links
- Sulla
- 138 BC births
- 78 BC deaths
- 2nd-century BC Romans
- 1st-century BC Romans
- 1st-century BC rulers
- Ancient Roman dictators
- Ancient Roman generals
- Cornelii
- Leaders who took power by coup
- Optimates
- Roman patricians
- Roman Athens
- Roman governors of Cilicia
- Roman governors of Hispania
- Roman Republican consuls
- Romans who received the grass crown
- Senators of the Roman Republic
