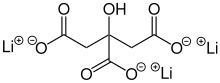
Lithium citrate
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Trilithium citrate
trilithium 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.860 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Li3C6H5O7 | |
| Molar mass | 209.923 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | Odorless white powder |
| Melting point | decomposes at 105 °C (221 °F; 378 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Toxic |
| Flash point | N/A |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lithium citrate (Li3C6H5O7) is a chemical compound of lithium and citrate that is used as a mood stabilizer in psychiatric treatment of manic states and bipolar disorder.[1][2] There is extensive pharmacology of lithium, the active component of this salt.
Lithia water contains various lithium salts, including the citrate. An early version of Coca-Cola available in pharmacies' soda fountains called Lithia Coke was a mixture of Coca-Cola syrup and lithia water. The soft drink 7Up was originally named "Bib-Label Lithiated Lemon-Lime Soda" when it was formulated in 1929 because it contained lithium citrate. The beverage was a patent medicine marketed as a cure for hangover. Lithium citrate was removed from 7Up in 1948.[3]
References
- ^ Medication description
- ^ Medical use Archived 2006-06-15 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Gielen, Marcel; Edward R. T. Tiekink (2005). Metallotherapeutic drugs and metal-based diagnostic agents: The use of metals in medicine. John Wiley and Sons. p. 3. ISBN 0-470-86403-6.
