Carisoprodol: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 64.107.96.18 to last version by 75.185.125.118 (HG) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| legal_status = Schedule III in these U.S. states: Alabama, Arkansas, Arizona, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Indiana, Kentucky, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Nevada, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Oregon and West Virginia. |
| legal_status = Schedule III in these U.S. states: Alabama, Arkansas, Arizona, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Indiana, Kentucky, Massachusetts, Minnesota, Nevada, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Oregon and West Virginia. |
||
| routes_of_administration = Oral |
| routes_of_administration = Oral |
||
}}boobtityboobboob |
|||
}} |
|||
'''Carisoprodol''' is a centrally-acting skeletal [[muscle relaxant]] whose active [[metabolite]] is [[meprobamate]]. Although several case reports have shown that carisoprodol has [[drug abuse|abuse]] potential<ref>{{cite journal | author=Bramness JG, Furu K, Engeland A, .|title=Carisoprodol use and abuse in Norway. A pharmacoepidemiological study|journal=Br J Clin Pharmacol|year=2007|vol=64|issue=2|pages=210–218 | volume=64 | doi=10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.02847.x}}</ref> both by itself and as a potentiator of [[hydrocodone]], [[dihydrocodeine]], [[codeine]] and similar drugs, it continues to be widely [[Medical prescription|prescribed]] in North America. In Europe, doctors favor [[cyclobenzaprine]] due to its lower abuse factor. In the United Kingdom, benzodiazepines are preferred instead. Carisoprodol is a colorless, crystalline powder, having a mild, characteristic odor and a bitter taste. It is slightly [[soluble]] in [[Water (molecule)|water]] and freely soluble in [[alcohol]], [[chloroform]] and [[acetone]]. Its solubility is practically independent of [[pH]]. |
'''Carisoprodol''' is a centrally-acting skeletal [[muscle relaxant]] whose active [[metabolite]] is [[meprobamate]]. Although several case reports have shown that carisoprodol has [[drug abuse|abuse]] potential<ref>{{cite journal | author=Bramness JG, Furu K, Engeland A, .|title=Carisoprodol use and abuse in Norway. A pharmacoepidemiological study|journal=Br J Clin Pharmacol|year=2007|vol=64|issue=2|pages=210–218 | volume=64 | doi=10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.02847.x}}</ref> both by itself and as a potentiator of [[hydrocodone]], [[dihydrocodeine]], [[codeine]] and similar drugs, it continues to be widely [[Medical prescription|prescribed]] in North America. In Europe, doctors favor [[cyclobenzaprine]] due to its lower abuse factor. In the United Kingdom, benzodiazepines are preferred instead. Carisoprodol is a colorless, crystalline powder, having a mild, characteristic odor and a bitter taste. It is slightly [[soluble]] in [[Water (molecule)|water]] and freely soluble in [[alcohol]], [[chloroform]] and [[acetone]]. Its solubility is practically independent of [[pH]]. |
||
Revision as of 20:14, 19 September 2008
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 60% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic (CYP2C19-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 8 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.017 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
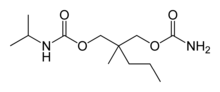
| Formula | C12H24N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 260.33 g/mol g·mol−1 |
boobtityboobboob
Carisoprodol is a centrally-acting skeletal muscle relaxant whose active metabolite is meprobamate. Although several case reports have shown that carisoprodol has abuse potential[1] both by itself and as a potentiator of hydrocodone, dihydrocodeine, codeine and similar drugs, it continues to be widely prescribed in North America. In Europe, doctors favor cyclobenzaprine due to its lower abuse factor. In the United Kingdom, benzodiazepines are preferred instead. Carisoprodol is a colorless, crystalline powder, having a mild, characteristic odor and a bitter taste. It is slightly soluble in water and freely soluble in alcohol, chloroform and acetone. Its solubility is practically independent of pH.
Carisoprodol is marketed in the United States under the brand name Soma, and in the United Kingdom and other countries under the brand names Sanoma and Carisoma. Carisoprodol is especially useful against various types of pain (whether or not related to muscle spasm) because of its analgesic-sparing (potentiating) effect on opioid analgesics. Carisoprodol is available by itself or mixed with aspirin and in one preparation (Soma Compound With Codeine) along with codeine and caffeine as well.
As of November 2007 Carisoprodol (Somadril, Somadril comp.) has been taken off the market in Sweden due to problems with dependence, abuse and side effects. The agency overseeing pharmaceuticals has considered other drugs used with the same indications as carisoprodol to have the same or better effects without the risks of the drug.[1] In the EU, the European Medicines Agency has issued a release recommending that member states suspend marketing authorization for this product. [2]
History
On June 1, 1959 several American pharmacologists convened at Wayne State University in Detroit, Michigan to discuss a new drug. The drug, originally thought to have antiseptic properties, was found to have central muscle relaxing properties.[3] It had been developed by Dr. Frank M. Berger at Wallace laboratories and had been named carisoprodol (trade name Soma).
Carisoprodol was developed on the basis of meprobamate, in the hope that it would have better muscle relaxing properties, less potential for abuse, and less risk of overdose than meprobamate.[4] The substitution of one hydrogen atom with an isopropyl group on one of the carbamyl nitrogens was intended to yield a molecule with new pharmacological properties.
The brand name Soma is shared with the Soma/Haoma of ancient India, a drug mentioned in ancient Sanskrit writings which various classical and modern researchers have theorised could be anything from ephedra to mushrooms of the genus Amanita with hallucinogenic and psychedelic properties related to the muscarinic drugs contained therein to various anticholinergic plants to opium -- or a still unknown hallucinogen, stimulant and/or narcotic of unknown chemical class and origin or even coca or other drugs ported from the Western Hemisphere by an as yet unknown pre-Viking, pre-Columbian contact. Soma is also the name of the fictional drug featured in Aldous Huxley's Brave New World.[5]
Chemistry
It is a carbamic acid ester. Carisoprodol is a racemic mixture of two stereoisomers.
Effects
- Analgesia
- Relief from hypertonia
Side effects
Carisoprodol seems to be more effective as a muscle relaxant than meprobamate but it also has the side effects of the latter drug (trade name Miltown) which is a related non-barbiturate and non-benzodiazepine sedative-hypnotic which has been largely replaced by Carisoprodol. Both carisoprodol and meprobamate can produce a glutethimide-like euphoria in certain dose ranges; a euphoriant dose of either drug will also rapidly produce somnolence and the patient can be in a deep sleep shortly after euphoria, anxiolysis, ataxia and other side effects manifest. However, the usual dose of 350 mg is unlikely to engender prominent side effects. At higher doses, in some patients, and/or early in therapy, carisoprodol can have the full spectrum of sedative-hypnotic side effects (and often to an extent to which the patient may not be fully aware) and can dangerously impair the patient's ability to operate a firearm, automobile, motorcycle, and other machinery of various types; slurred speech is also a side effect which manifests rather rapidly. The intensity of the side effects of carisoprodol tends to lessen and/or become very predictable as therapy continues, as is the case with many other drugs.
The interaction of carisoprodol with opioids, essentially all opioids and other centrally-acting analgesics, but especially those of the codeine-derived subgroup of the semi-synthetic class (codeine, ethylmorphine, dihydrocodeine, hydrocodone, oxycodone, nicocodeine, benzylmorphine, the various acetylated codeine derivatives including thebacon and acetyldihydrocodeine, dihydroisocodeine, nicodicodeine and others) which allows the use of a smaller dose of the opioid to have a given effect, is useful in general and especially where injury and/or muscle spasm is a large part of the problem. The potentiation effect is also useful in other pain situations and is also especially useful with opioids of the open-chain class such as methadone, levomethadone, ketobemidone, phenadoxone and others.
The use of methadone with carisoprodol and an NSAID such as diclofenac where indicated is a treatment for chronic low back pain which is gaining in popularity in the United States and other countries. After significant somonolence in some patients in the first few days of this protocol for pain control, patients are able to regain overall function very well in a lot of cases and the interaction of carisoprodol and methadone with the NMDA system in the CNS may be part of the excellent pain relief and attenuation of some opioid side effects usually obtained by using this protocol. In European countries, ketobemidone is a good and even superior replacement for the methadone.
The potentiation effect is also something noted by recreational drugs users, and is accompanied by an economy of scale increase of the euphoria and deaths have resulted from carelessly combining overdoses of hydrocodone and carisoprodol.
Meprobamate and other muscle relaxing drugs often were subjects of misuse and abuse in the 1950s and 1960s.[6][7] Overdose cases were reported as early as 1957 and have been reported on several occasions since then.[8][9][10][11][12][13][14]
Carisoprodol, meprobamate, and related drugs such as tybamate have the potential to produce physical dependence with prolonged use and this group of sedatives has a spectacular withdrawal syndrome with death as a potential endpoint; therefore withdrawal of the drug after extensive use should be supervised in hospital in the fashion appropriate with the barbiturates, glutethimide and other such agents.
Pharmacokinetics
Carisoprodol has a rapid, 30 minute onset of action, with the aforementioned effects lasting for approximately 2–6 hours. It is metabolized in the liver via the cytochrome P450 oxidase isozyme CYP2C19, excreted by the kidneys and has an approximate 8 hour half-life. A considerable proportion of carisoprodol is metabolized to meprobamate, which is a known drug of abuse and dependence; this could account for the abuse potential of carisoprodol.
Notes
- ^ Bramness JG, Furu K, Engeland A, . (2007). "Carisoprodol use and abuse in Norway. A pharmacoepidemiological study". Br J Clin Pharmacol. 64 (2): 210–218. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.02847.x.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|vol=ignored (|volume=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Carisprodol press release = EMEA" (PDF). Retrieved 2008-05-12.
- ^ Miller JG, ed. The pharmacology and clinical usefulness of carisoprodol. Detroit:Wayne State University; 1959.
- ^ Berger F, Kletzkin M, Ludwig B, Margolin S. The history, chemistry, and pharmacology of carisoprodol. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1959;86:90-107
- ^ "Brave New Soma - TIME". Retrieved 2007-08-20.
- ^ Kamin I, Shaskan D. (1959). "Death due to massive overdose of meprobamate". Am J Psychiatry. 115 (12): 1123–1124.
- ^ Hollister LE (1983). "The pre-benzodiazepine era". J Psychoactive Drugs. 15 (1–2): 9–13.
- ^ Gaillard Y, Billault F, Pepin G (1997). "Meprobamate overdosage: a continuing problem. Sensitive GC-MS quantitation after solid phase extraction in 19 fatal cases". Forensic Sci.Int. 86 (3): 173–180. doi:10.1016/S0379-0738(97)02128-2.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Allen MD, Greenblatt DJ, Noel BJ (1977). "Meprobamate overdosage: a continuing problem". Clin Toxicol. 11 (5): 501–515.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Kintz P, Tracqui A, Mangin P, Lugnier AA (1988). "Fatal meprobamate self-poisoning". Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 9 (2): 139–140.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Eeckhout E, Huyghens L, Loef B, Maes V, Sennesael J (1988). "Meprobamate poisoning, hypotension and the Swan-Ganz catheter". Intensive Care Med. 14 (4): 437–438. doi:10.1007/BF00262904.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lhoste F, Lemaire F, Rapin M (1977). "Treatment of hypotension in meprobamate poisoning". N Engl J Med. 296 (17): 1004.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Bedson H (1959). "Coma due to meprobamate intoxication. Report of a case confirmed by chemical analysis". Lancet. 273 (1): 288–290. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(59)90209-0.
- ^ Blumberg A, Rosett H, Dobrow A (1959). "Severe hypotension reactions following meprobamate overdosage". Ann Intern Med. 51: 607–612.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
References
- APhA Drug Information Handbook
