Cloverleaf model of tRNA
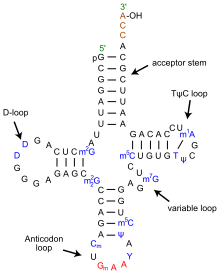
The Cloverleaf model of tRNA is a model that depict the molecular structure of tRNA.[1] The model revealed that the chain of tRNA consists of two ends, sometimes called "business ends" and three arms. Two of the arms have a loop, D-loop (dihydro U loop) and Tψ-loop with a Ribosome recognition site. The third arm known as "variable arm" has a stem with optional loop. One end of the chains (with a double stranded structure in which the 5' and 3' ends are adjacent to each other), the amino acids acceptor stem, usually attaches to Amino acids and such reactions are often catalyzed by a specific enzymes, Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase.[2] For example, if the amino acid that attach to the end is Alanine, the reaction will be catalyzed by Phenylalanine-tRNA synthase to produce tRNAphe.[3] The other end, the bottom often called, the "DNA arm" consists of a three base sequence that pairs with a complementary base sequence in a mRNA.[4]
See also
References
- ^ "Explain briefly the clover leaf model of tRNA". Preservearticle.com. Retrieved June 2, 2015.
- ^ "The Enzymes". books.google.co.uk. Retrieved June 2, 2015.
- ^ "Operators and Promoters: The Story of Molecular Biology and Its". books.google.co.uk. Retrieved June 2, 2015.
- ^ "A Survey of TRNA Mimicry: Structural Studies of Plant Viral RNA". books.google.co.uk. Retrieved June 2, 2015.
