Hafnium disulfide
Appearance
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hafnium disulfide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.038.738 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| HfS2 | |
| Molar mass | 246.62 g/mol[1] |
| Appearance | Brown solid |
| Density | 6.03 g/cm3[1] |
| Band gap | ~1.8 eV (indirect)[2] |
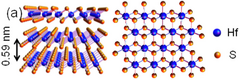
| Structure | |
| hP3, P3m1, No 164[3] | |
a = 0.363 nm, c = 0.584 nm
| |
Formula units (Z)
|
1 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Hafnium dioxide |
Other cations
|
Tungsten disulfide Molybdenum disulfide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Hafnium disulfide is an inorganic compound of hafnium and sulfur. It is a layered dichalcogenide with the chemical formula is HfS2. A few atomic layers of this material can be exfoliated using the standard Scotch Tape technique (see graphene) and used for the fabrication of a field-effect transistor.[4] High-yield synthesis of HfS2 has also been demonstrated using liquid phase exfoliation, resulting in the production of stable few-layer HfS2 flakes.[5] Hafnium disulfide powder can be produced by reacting hydrogen sulfide and hafnium oxides at 500–1300 °C.[6]
References
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hafnium disulfide.
- ^ a b Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 4.66. ISBN 1-4398-5511-0.
- ^ Terashima, K.; Imai, I. (1987). "Indirect absorption edge of ZrS2 and HfS2". Solid State Communications. 63 (4): 315. Bibcode:1987SSCom..63..315T. doi:10.1016/0038-1098(87)90916-1.
- ^ Hodul, David T.; Stacy, Angelica M. (1984). "Anomalies in the properties of Hf(S2−xTex)1-y and Hf(Se2−xTex)1-y near the metal-insulator transition". Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 54 (3): 438. Bibcode:1984JSSCh..54..438H. doi:10.1016/0022-4596(84)90176-2.
- ^ Kanazawa, Toru; Amemiya, Tomohiro; Ishikawa, Atsushi; Upadhyaya, Vikrant; Tsuruta, Kenji; Tanaka, Takuo; Miyamoto, Yasuyuki (2016). "Few-layer HfS2 transistors". Scientific Reports. 6: 22277. Bibcode:2016NatSR...622277K. doi:10.1038/srep22277. PMC 4772098. PMID 26926098.
- ^ Kaur, Harneet (2017). "High Yield Synthesis and Chemical Exfoliation of Two-Dimensional Layered Hafnium Disulphide". Nano Research. arXiv:1611.00895. doi:10.1007/s12274-017-1636-x.
- ^ Kaminskii, B. T.; Prokof'eva, G. N.; Plygunov, A. S.; Galitskii, P. A. (1973-07-01). "Manufacture of zirconium and hafnium sulfide powders". Soviet Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics. 12 (7): 521–524. doi:10.1007/BF00796747.
