Occipital lobe: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
==Anatomy== |
==Anatomy== |
||
[[File:Occipital lobe animation small.gif|thumb|left|Animation. Occipital lobe (red) of left cerebral hemisphere.]] |
[[File:Occipital lobe animation small.gif|thumb|left|Animation. Occipital lobe (red) of left cerebral hemisphere.]] |
||
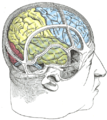
The two occipital lobes are the smallest of four paired lobes in the human cerebral cortex. Located in the rearmost portion of the skull, the occipital lobes are part of the [[Cerebral hemisphere|forebrain]]. The cortical lobes are not defined by any internal structural features, but rather by the bones of the skull that overlie them. Thus, the occipital lobe is defined as the part of the cerebral cortex that lies underneath the occipital bone. (See the [[human brain]] article for more information. |
The two occipital lobes are the smallest of four paired lobes in the human cerebral cortex. Located in the rearmost portion of the skull, the occipital lobes are part of the [[Cerebral hemisphere|forebrain]]. The cortical lobes are not defined by any internal structural features, but rather by the bones of the skull that overlie them. Thus, the occipital lobe is defined as the part of the cerebral cortex that lies underneath the occipital bone. (See the [[human brain]] article for more information. |
||
SUBSCRIBE TO CANDIEDPOPCORN on Youtube. http://www.youtube.com/user/candiedpopcorn |
|||
The lobes rest on the [[tentorium cerebelli]], a process of dura mater that separates the cerebrum from the [[cerebellum]]. They are structurally isolated in their respective cerebral hemispheres by the separation of the [[cerebral fissure]]. At the front edge of the occipital are several lateral [[occipital gyri]], which are separated by lateral [[occipital sulcus]]. |
The lobes rest on the [[tentorium cerebelli]], a process of dura mater that separates the cerebrum from the [[cerebellum]]. They are structurally isolated in their respective cerebral hemispheres by the separation of the [[cerebral fissure]]. At the front edge of the occipital are several lateral [[occipital gyri]], which are separated by lateral [[occipital sulcus]]. |
||
Revision as of 17:21, 6 October 2011
This article needs additional citations for verification. (June 2009) |
| Occipital lobe | |
|---|---|
 Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere. (cuneus and lingual gyrus are at left.) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | cerebrum |
| Artery | posterior cerebral artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | lobus occipitalis |
| MeSH | D009778 |
| NeuroNames | 140 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1136 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.132 |
| TA2 | 5480 |
| FMA | 67325 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
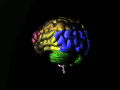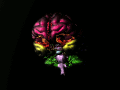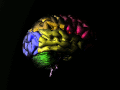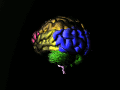
The occipital lobe is the visual processing center of the mammalian brain containing most of the anatomical region of the visual cortex.[1] The primary visual cortex is Brodmann area 17, commonly called V1 (visual one). Human V1 is located on the medial side of the occipital lobe within the calcarine sulcus; the full extent of V1 often continues onto the posterior pole of the occipital lobe. V1 is often also called striate cortex because it can be identified by a large stripe of myelin, the Stria of Gennari. Visually driven regions outside V1 are called extrastriate cortex. There are many extrastriate regions, and these are specialized for different visual tasks, such as visuospatial processing, color discrimination and motion perception. The name derives from the overlying occipital bone, which is named from the Latin oc- + caput, "back of the head".
Anatomy

The two occipital lobes are the smallest of four paired lobes in the human cerebral cortex. Located in the rearmost portion of the skull, the occipital lobes are part of the forebrain. The cortical lobes are not defined by any internal structural features, but rather by the bones of the skull that overlie them. Thus, the occipital lobe is defined as the part of the cerebral cortex that lies underneath the occipital bone. (See the human brain article for more information.
SUBSCRIBE TO CANDIEDPOPCORN on Youtube. http://www.youtube.com/user/candiedpopcorn
The lobes rest on the tentorium cerebelli, a process of dura mater that separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum. They are structurally isolated in their respective cerebral hemispheres by the separation of the cerebral fissure. At the front edge of the occipital are several lateral occipital gyri, which are separated by lateral occipital sulcus.
The occipital aspects along the inside face of each hemisphere are divided by the calcarine sulcus. Above the medial, Y-shaped sulcus lies the cuneus, and the area below the sulcus is the lingual gyrus.
Function
Significant functional aspects of the occipital lobe is that it contains the primary visual cortex and is the part of the brain where dreams come from.
Retinal sensors convey stimuli through the optic tracts to the lateral geniculate bodies, where optic radiations continue to the visual cortex. Each visual cortex receives raw sensory information from the outside half of the retina on the same side of the head and from the inside half of the retina on the other side of the head. The cuneus (Brodmann's area 17) receives visual information from the contralateral superior retina representing the inferior visual field. The lingula receives information from the contralateral inferior retina representing the superior visual field. The retinal inputs pass through a "way station" in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus before projecting to the cortex. Cells on the posterior aspect of the occipital lobes' gray matter are arranged as a spatial map of the retinal field. Functional neuroimaging reveals similar patterns of response in cortical tissue of the lobes when the retinal fields are exposed to a strong pattern.
If one occipital lobe is damaged, the result can be homonomous vision loss from similarly positioned "field cuts" in each eye. Occipital lesions can cause visual hallucinations. Lesions in the parietal-temporal-occipital association area are associated with color agnosia, movement agnosia, and agraphia.
Functional anatomy
The occipital lobe is divided into several functional visual areas. Each visual area contains a full map of the visual world. Although there are no anatomical markers distinguishing these areas (except for the prominent striations in the striate cortex), physiologists have used electrode recordings to divide the cortex into different functional regions.
The first functional area is the primary visual cortex. It contains a low-level description of the local orientation, spatial-frequency and color properties within small receptive fields. Primary visual cortex projects to the occipital areas of the ventral stream (visual area V2 and visual area V4), and the occipital areas of the dorsal stream—visual area V3, visual area MT (V5), and the dorsomedial area (DM).
Additional images
-
Base of brain.
-
Drawing to illustrate the relations of the brain to the skull.
-
Occipital lobe in blue
See also
References
- ^ "SparkNotes: Brain Anatomy: Parietal and Occipital Lobes". Archived from the original on 2007-12-31. Retrieved 2008-02-27.