List of scheduled monuments in West Somerset
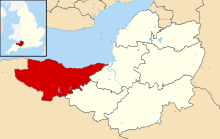
West Somerset is a local government district in the English county of Somerset. The council covers a largely rural area, with a population of 35,075[1] in an area of 740 square kilometres (290 sq mi).[2] According to figures released by the Office for National Statistics in 2009, the population of West Somerset has the oldest average age in the United Kingdom at 52.[3] The largest centres of population are the coastal towns of Minehead (population 10,000) and Watchet (4,400).
A scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or monument which is given legal protection by being placed on a list (or "schedule") by the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport; English Heritage takes the leading role in identifying such sites. The legislation governing this is the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Areas Act 1979. The term "monument" can apply to the whole range of archaeological sites, and they are not always visible above ground. Such sites have to have been deliberately constructed by human activity. They range from prehistoric standing stones and burial sites, through Roman remains and medieval structures such as castles and monasteries, to later structures such as industrial sites and buildings constructed for the World Wars or the Cold War.[4]
There are 201[note 1] scheduled monuments in West Somerset. Some of the oldest, particularly on Exmoor and the Quantock Hills are Neolithic, Bronze Age or Iron Age including hillforts, cairns, bowl barrows and other tumulis. More recent sites include several motte-and-bailey castles and church or village crosses which date from the Middle Ages. The geography with large numbers of streams is reflected by the number of packhorse and other bridges included in the list. The mining history of the area is also represented by several sections of the West Somerset Mineral Railway and associated ruins of mine buildings which are now scheduled. The most recent monuments are World War II pillboxes. The monuments are listed below using the titles given in the English Heritage data sheets.
Monuments
| Name | Location | Type | Completed [note 2] | Grid ref.[note 3] Geo-coordinates | Notes | Entry number [note 4] | Image | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agnes Fountain | Selworthy | Holy well | Middle Ages | SS 90477 47370 51°12′54″N 3°34′10″W / 51.2150°N 3.5695°W |
A medieval holy well formed from stone slabs. | 1020827 |  |
[5] |
| Alderman's Barrow N of Almsworthy Common | Exford | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | SS 83680 42326 51°10′06″N 3°39′54″W / 51.1683°N 3.6651°W |
A bowl barrow 24 metres (79 ft) in diameter. | 1006203 |  |
[6] |
| Allerford New Bridge | Luccombe | Bridge | 1630 | SS 89989 46655 51°12′31″N 3°34′34″W / 51.2085°N 3.5762°W |
A medieval stone bridge which was largely rebuilt in 1630 and again in 1866 over Horner Water. | 1006197 |  Upload Photo |
[7][8] |
| Allerford packhorse bridge, immediately north of Cross Lane Farm | Allerford | Bridge | Middle Ages | SS 90512 46923 51°12′58″N 3°34′09″W / 51.2161°N 3.5691°W |
Built as a crossing over the River Aller, it is thought to be medieval in origin. The 18 feet (5.5 m) wide pointed arch rises 8 feet (2.4 m) with a 4 feet (1.2 m) span half arch on the side for flood relief. Originally the bridge was 3.7 metres (12 ft) wide but another 1.8 metres (6 ft) was added in 1866. | 1020776 |  |
[9] |
| Almsworthy Common: a stone alignment 560 m south west of Chetsford Bridge | Exford | Stone row | Late Neolithic to middle Bronze Age | SS 84309 41698 51°09′46″N 3°39′21″W / 51.1628°N 3.6559°W |
Four rows of standing stones between 100 millimetres (3.9 in) and 700 millimetres (28 in) high. There are 14 stones in total. | 1015017 |  Upload Photo |
[10] |
| Bagley Iron Age defended settlement enclosure and deserted medieval farm | Luccombe | Earthworks | Iron Age and Middle Ages | SS 88227 42569 51°10′17″N 3°36′01″W / 51.1714°N 3.6002°W |
Earthworks from a prehistoric defended settlement and medieval village. | 1008468 |  Upload Photo |
[11] |
| Barle Bridge | Dulverton | Bridge | Middle Ages | SS 91207 27823 51°02′22″N 3°33′11″W / 51.0394°N 3.5531°W |
A medieval five arch stone bridge over the River Barle which was widened in 1819 and further restored following flooding in the 1950s. | 1006179 |  |
[12] |
| Barlinch Priory | Brompton Regis | Priory | 12th century | SS 92891 28999 51°02′45″N 3°32′05″W / 51.0457°N 3.5348°W |
Barlynch Priory (also known as St Nicholas's Priory and sometimes spelled Barlich Priory) was Augustinian priory founded, by William de Say, between 1154 and 1189 and dissolved in 1537. The only visible remains are some fragments of walling attached to Barynch farmhouse. Some of the stained glass from a Jesse window at the Priory is now in the St Peter's Church in Huish Champflower. The priory has been added to the Heritage at Risk register because of the risk of collapse. | 1006213 |  Upload Photo |
[13][14] [15][16] |
| Barrow and cairn cemetery on Black Hill, 490 m north west of Crowcombe Park Gate | Holford | Cairn and bowl barrows | Bronze Age | ST 14539 38227 51°08′13″N 3°13′22″W / 51.1369°N 3.2229°W |
Four bowl barrows and a cairn make up the site of a Bronze Age cemetery on the Quantock Hills. | 1019381 |  Upload Photo |
[17] |
| Barrow at Wilmot's Pool and a cairn 45 m to the north | Holford | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST1530838148 51°08′11″N 3°12′43″W / 51.1363°N 3.2119°W |
A Bronze Age bowl barrow which is 22 metres (72 ft) in diameter and 1.7 metres (5 ft 7 in) high. Nearby are two small cairns. | 1417361 |  Upload Photo |
[18] |
| Barrows on Longstone Hill | East Quantoxhead | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 13505 41345 51°09′53″N 3°14′18″W / 51.1648°N 3.2384°W |
Bowl barrows close to the Greenway Track. One is 19 metres (62 ft) in diameter and the others 6 metres (20 ft) although there is some uncertainty about whether they are natural or man made. | 1006157 |  Upload Photo |
[19][20] |
| Bat's Castle: a small multivallate hillfort and associated outwork | Carhampton | Hill fort | Iron Age | SS 98820 42146 51°10′11″N 3°26′55″W / 51.1696°N 3.4486°W |
Bat's Castle is an Iron Age hill fort at the top of a 213 metres (699 ft) high hill. It is on the highest point of Gallox Hill. Previously it was known as Caesar's Camp and is possibly associated with Black Ball Camp. Bat's Castle has two stone ramparts and two ditches. The ramparts are damaged in places and the hillfort is partly covered in scrub. | 1007667 |  |
[21][22] [23][24] |
| Beckham stone alignment and mound, 450 m south east of the Long Combe sheep pen | Exmoor | Stone row | Late Neolithic to middle Bronze Age | SS 80632 42382 51°10′06″N 3°42′31″W / 51.1682°N 3.7087°W |
Three parallel stone rows consisting of three standing and six recumbent stones. | 1014283 |  Upload Photo |
[25] |
| Bendel's Barrows, Exford Common | Exford | Round barrow | Bronze Age | SS 85388 40940 51°09′22″N 3°38′25″W / 51.1562°N 3.6402°W |
Two Bronze Age bowl barrows, one of 20 metres (66 ft) diameter and the other of 22 metres (72 ft). | 1006211 |  Upload Photo |
[26][27] |
| Berry Castle, Iron Age enclosure in Berry Castle Wood | Luccombe | Hillfort | Iron Age | SS 85919 44958 51°11′33″N 3°38′02″W / 51.1924°N 3.6339°W |
Berry Castle is an early Roman (possible Iron Age) hillslope enclosure. | 1006204 |  Upload Photo |
[28][29] |
| Black Ball Camp: a later prehistoric defended settlement on Gallox Hill | Dunster | Hill fort | Iron Age | SS 98428 42651 51°10′26″N 3°27′15″W / 51.1740°N 3.4543°W |
Black Ball Camp is an Iron Age hill fort . It is also known as British Camp and is possibly associated with Bat's Castle. It has a 3 metres (10 ft) high rampart and a 2 metres (7 ft) deep ditch. At the beginning of the 20th century the foundations of a stone tower were visible however this is no longer present. | 1007668 |  |
[30][31] [32][33] |
| Black Barrow | Exmoor | Round barrow | Bronze Age | SS 83211 44213 51°11′06″N 3°40′21″W / 51.1851°N 3.6724°W |
A round barrow which is 22 metres (72 ft) in diameter and 1.5 metres (4 ft 11 in) high. | 1006205 |  |
[34]
|
| Bowl barrow 80 m north of Halsway Post | Holford | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 14012 38612 51°08′25″N 3°13′50″W / 51.1403°N 3.2305°W |
A 7.5-metre (25 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1015084 |  Upload Photo |
[35] |
| Bowl barrow 100 m north west of Halsway Post | Holford | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 13962 38618 51°08′25″N 3°13′52″W / 51.1403°N 3.2312°W |
A 8.5-metre (28 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1015083 |  Upload Photo |
[36] |
| Bowl barrow 122 m NNW of Halsway Post | Holford | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 13968 38643 51°08′26″N 3°13′52″W / 51.1406°N 3.2311°W |
A bowl barrow which is 5.5 metres (18 ft) in diameter. | 1015082 |  Upload Photo |
[37] |
| Bowl barrow 225 m north west of Halsway Post | Holford | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 13860 38706 51°08′28″N 3°13′58″W / 51.1411°N 3.2327°W |
A 9.5-metre (31 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1015081 |  Upload Photo |
[38] |
| Bowl barrow 260 m north east of Ralegh's Cross Hotel | Nettlecombe | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 04142 34544 51°06′08″N 3°22′13″W / 51.1022°N 3.3704°W |
A 41-metre (135 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1020721 |  Upload Photo |
[39]
|
| Bowl barrow 470 m north of Brendon Hill Farm | Brompton Regis | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 01269 33964 51°05′47″N 3°24′41″W / 51.0965°N 3.4113°W |
A 14-metre (46 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1020918 |  Upload Photo |
[40] |
| Bowl barrow 610 m ESE of the fire tower on Monkham Hill | Luxborough | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 99214 39134 51°08′33″N 3°26′32″W / 51.1426°N 3.4421°W |
A 19-metre (62 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1021227 |  Upload Photo |
[41] |
| Bowl barrow 650 m north west of Elworthy Barrows hillfort | Elworthy | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 06724 34262 51°06′00″N 3°20′01″W / 51.1000°N 3.3335°W |
A 19.5-metre (64 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1020725 |  Upload Photo |
[42] |
| Bowl barrow 700 m north east of Burrow Farm | Brompton Regis | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 01298 34620 51°06′09″N 3°24′40″W / 51.1024°N 3.4111°W |
A 14.5-metre (48 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1020777 |  Upload Photo |
[43] |
| Bowl barrow 780 m ESE of the fire tower on Monkham Hill | Luxborough | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 99357 39016 51°08′29″N 3°26′24″W / 51.1415°N 3.4400°W |
A 13.2-metre (43 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1021231 |  Upload Photo |
[44] |
| Bowl barrow and round cairn on Withypool Hill, 850 m and 820 m east of Portford Bridge | Withypool and Hawkridge | Bowl barrow and round cairn | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 83983 34411 51°05′50″N 3°39′30″W / 51.0972°N 3.6582°W |
A bowl barrow and round cairn 50 metres (160 ft) apart on Withypool Hill. The barrow is 20.5 metres (67 ft) and the cairn 3.5 metres (11 ft) in diamater. | 1021262 |  |
[45] |
| Bowl barrow called Chains Barrow | Exmoor | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 73458 41904 51°09′44″N 3°48′40″W / 51.1623°N 3.8111°W |
A 25-metre (82 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1006206 |  Upload Photo |
[46] |
| Bowl barrow on Longstone Hill, 270 m NNE of Bicknoller Post | East Quantoxhead | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 13033 40562 51°09′28″N 3°14′42″W / 51.1577°N 3.2450°W |
A 15-metre (49 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1014131 |  Upload Photo |
[47] |
| Bowl barrow on Longstone Hill, 270 m north east of Bicknoller Post | East Quantoxhead | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 13100 40485 51°09′25″N 3°14′38″W / 51.1570°N 3.2440°W |
A 11-metre (36 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1014130 |  Upload Photo |
[48] |
| Bowl barrow on Lype Hill, 550 m north west of Lype Farm | Cutcombe | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 95035 37112 51°07′25″N 3°30′04″W / 51.1236°N 3.5012°W |
A 21-metre (69 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1021062 |  Upload Photo |
[49] |
| Bowl barrow on Lype Hill, 750 m ENE of Heath Pault Cross | Cutcombe | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 94780 37046 51°07′23″N 3°30′18″W / 51.1230°N 3.5049°W |
A 15.8-metre (52 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1021063 |  Upload Photo |
[50] |
| Bowl barrow on Thorncombe Hill | Bicknoller | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 13162 39214 51°08′44″N 3°14′34″W / 51.1456°N 3.2428°W |
A bowl barrow which is approximately 12 metres (39 ft) north to south, 10 metres (33 ft) from east to west and is 1 metre (3 ft 3 in) high. | 1014129 |  Upload Photo |
[51] |
| Bowl barrow on Thorncombe Hill, 1.03 km north east of Paradise Farm | Bicknoller | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 13018 39461 51°08′52″N 3°14′42″W / 51.1478°N 3.2449°W |
A 9.3-metre (31 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1015079 |  Upload Photo |
[52]
|
| Bowl barrow on Thorncombe Hill, 1.07 km north east of Paradise Farm | Bicknoller | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 13030 39495 51°08′53″N 3°14′41″W / 51.1481°N 3.2447°W |
A 7.5-metre (25 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1015078 |  Upload Photo |
[53] |
| Bowl barrow on Thorncombe Hill 500 m north west of Halsway Post | East Quantoxhead | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 13668 38892 51°08′34″N 3°14′08″W / 51.1427°N 3.2355°W |
A 16-metre (52 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1015208 |  Upload Photo |
[54]
|
| Bowl barrow on Thorncombe Hill known as `Thorncombe Barrow' | Bicknoller | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 12733 39418 51°08′50″N 3°14′56″W / 51.1473°N 3.2489°W |
A 17-metre (56 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1014408 |  |
[55] |
| Bowl barrow on Weacombe Hill, 300 m SSW of Bicknoller Post | Bicknoller | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 12835 40036 51°09′10″N 3°14′52″W / 51.1529°N 3.2477°W |
A bowl barrow which is 13 metres (43 ft) in diameter. | 1014125 |  Upload Photo |
[56] |
| Brewer's Castle | Withypool and Hawkridge | Hillfort | Iron Age | SS 88314 29769 51°03′23″N 3°35′42″W / 51.0563°N 3.5949°W |
Earthworks from a 0.4-hectare (0.99-acre) Iron Age Hillfort surrounded by a bank and ditch. | 1021358 |  Upload Photo |
[57] |
| Brightworthy Barrows on Withypool Common | Withypool | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 81740 35095 51°06′10″N 3°41′26″W / 51.1029°N 3.6905°W |
Two bowl barrows one of which is the site for an Ordnance Survey triangulation station. | 1021264 |  |
[58] |
| Burrow Farm iron mine and section of mineral railway trackbed, 350 m north east of Burrow Farm | Brompton Regis | Mine workings | 1863 | ST 00963 34490 51°06′04″N 3°24′57″W / 51.1011°N 3.4158°W |
The remains of Mine workings from a 19th century Iron ore mine, including the standing beam engine house. The West Somerset Mineral Railway was built to carry the ore from the Brendon Hills to Watchet for export. | 1021353 |  |
[59] |
| Bury Bridge | Brompton Regis | Packhorse bridge | Middle Ages | SS 94467 27456 51°02′12″N 3°30′23″W / 51.0367°N 3.5065°W |
A medieval stone bridge with four arches, carrying a small track over the River Haddeo. | 1006242 |  |
[60]
|
| Bury Castle | Brompton Regis | Hillfort | Iron Age reused in Middle Ages | SS 93841 26966 51°01′56″N 3°30′54″W / 51.0321°N 3.51512°W |
Bury Castle is an Iron Age Hillfort and 12th century castle. The hillfort covers 0.2 hectares (0.49 acres) in internal area. The main enclosure has a single rampart and ditch, with steep drops on the north, east and south sides. There is an additional rampart 30 metres (98 ft) to the west, with a deep ditch. The rampart is revetted with drystone walling. In the late 1130s, a civil war, known as the Anarchy, broke out in England between the supporters of King Stephen and the Empress Matilda. A motte and bailey castle was built on the Bury Castle side, probably by William de Say. In 1198 Richard I confirmed that Brompton should be part of the inheritance of Matilda. The motte measures 23 metres (75 ft) and was placed on the southern tip of the promontory, with the bailey beyond around 60 metres (197 ft) across. | 1006170 |  Upload Photo |
[61][62] [63][64] |
| Bury Castle, an Iron Age defended settlement | Selworthy | Enclosure | Iron Age | SS 91744 47171 51°12′48″N 3°33′05″W / 51.2134°N 3.5513°W |
An enclosure covering 0.21 hectares (0.52 acres) surrounded by a bank and ditch. | 1008808 |  |
[65] |
| Butter Cross at Dunster | Dunster | Wayside Cross | Late 14th or early 15th century | SS9881243873 51°11′06″N 3°26′57″W / 51.185099°N 3.449189°W |
The Butter Cross has an octagonal base and polygonal shaft which probably date from the 15th century. The cross once stood in the High Street, possibly near the Yarn Market, and was moved to its current location on the edge of the village possibly in 1825, however a drawing by JMW Turner made in 1811 suggests it was in its present position by then. | 1014409 |  |
[66][67] [68][69] [70] |
| Cairn 90 m SSE of the Ordnance Survey triangulation point on Beacon Hill | West Quantoxhead | Cairn | Bronze Age | ST 12493 40909 51°09′39″N 3°15′10″W / 51.1607°N 3.2528°W |
The cairn is around 5.5 metres (18 ft) in diameter and 0.7 metres (2 ft 4 in) high. It is part of a wider cemetery with both cairns and round barrows. | 1014123 |  Upload Photo |
[71] |
| Cairn 150 m SSE of the Ordnance Survey triangulation point on Beacon Hill | West Quantoxhead | Cairn | Bronze Age | ST 12543 40858 51°09′37″N 3°15′07″W / 51.1602°N 3.2520°W |
The cairn is around 0.5 metres (1 ft 8 in) high, 6 metres (20 ft) north to south and 7 metres (23 ft) from east to west. It is part of a wider cemetery with both cairns and round barrows. | 1014124 |  Upload Photo |
[72] |
| Cairn 250 m SSE of the Ordnance Survey triangulation point on Beacon Hill | West Quantoxhead | Cairn | Bronze Age | ST 12575 40764 51°09′34″N 3°15′06″W / 51.1594°N 3.2516°W |
The cairn is around 12 metres (39 ft) in diameter and 0.2 metres (7.9 in) high. It is part of a wider cemetery with both cairns and round barrows. | 1014127 |  Upload Photo |
[73] |
| Cairn 480 m north of Little Quantock Farm | Crowcombe | Cairn | Bronze Age | ST 14915 36972 51°07′33″N 3°13′02″W / 51.1257°N 3.2172°W |
An irregular mound around 26 metres (85 ft) in diameter and 2 metres (6 ft 7 in) high. | 1017294 |  Upload Photo |
[74] |
| Cairn 850 m north east of Dunkery Bridge | Cutcombe | Cairn | Bronze Age | SS 90127 41213 51°09′35″N 3°34′23″W / 51.1596°N 3.5730°W |
The cairn is around 14 metres (46 ft) in diameter and 1.5 metres (4 ft 11 in) high. | 1020829 |  Upload Photo |
[75]
|
| Cairn on Bossington Hill, 1.12 km north east of Lynch Mead | Bossington | Cairn | Bronze Age | SS 90839 48625 51°13′35″N 3°33′54″W / 51.2263°N 3.565°W |
The cairn is around 12 metres (39 ft) in diameter and 10.9 metres (36 ft) high. | 1020795 |  |
[76] |
| Cairn on Thorncombe Hill, 990 m north west of Halsway Post | Bicknoller | Cairn | Bronze Age | ST 13212 39105 51°08′41″N 3°14′32″W / 51.1446°N 3.2421°W |
The cairn is around 0.7 metres (2 ft 4 in) high, 11.6 metres (38 ft) north to south and 10.7 metres (35 ft) from east to west. | 1015080 |  Upload Photo |
[77] |
| Cairn on Thorncombe Hill | Bicknoller | Cairn | Bronze Age | ST 12679 39310 51°08′47″N 3°14′59″W / 51.1464°N 3.2497°W |
The cairn is around 0.75 metres (2 ft 6 in) high, 13 metres (43 ft) north to south and 17 metres (56 ft) from east to west. | 1014128 |  Upload Photo |
[78] |
| Caratacus Stone: an inscribed stone 140 m east of Spire Cross | Winsford | inscribed stone | 6th century | SS 88970 33557 51°05′26″N 3°35′12″W / 51.0905°N 3.5867°W |
The Caratacus Stone, sometimes known as the Caractacus Stone, is an inscribed stone thought to date from the 6th century. The inscription, in Latin, can be translated as "grandson or immediate descendant of Caratacus", has led to the general opinion that the stone was probably erected as a memorial to a person who claimed the first-century British chieftain Caratacus as an ancestor. The first mention of the stone was in 1219, when it was described in a perambulation of the Royal Forest of Exmoor as "the Langeston". In 1890 the letter N (which is reversed) was missing from the inscription, but by 1919 the missing piece had been found and was cemented back in place. In 1906 a shelter was erected over the stone, and an excavation in 1937 revealed that the stone was not associated with a burial site. | 1021228 |  |
[79][80] [81][82] |
| Carnarvon New Pit iron mine and section of mineral railway trackbed, 300 m south west of Heather House | Brompton Regis | Mine workings | 1860s | ST 02057 34260 51°05′57″N 3°24′01″W / 51.0993°N 3.4002°W |
The remains of the Carnarvon New Pit iron mine and a section of the West Somerset Mineral Railway which served it. The mine was worked in the 1860s and 1870s before being closed as uneconomic. The ruin of the winding house, main shaft, two airshafts and parts of the railway infrastructure. | 1021352 |  |
[83] |
| Chains Valley stone alignment 400 m north west of Exe Head | Exmoor | Stone row | Late Neolithic to middle Bronze Age | SS 74915 41775 51°09′41″N 3°47′25″W / 51.1615°N 3.7902°W |
Ten standing and four recumbent stones which are between 120 millimetres (4.7 in) and 630 millimetres (25 in) high. | 1014278 |  Upload Photo |
[84]
|
| Churchyard cross | Bicknoller | Cross | Late 14th century | ST 11106 39428 51°08′50″N 3°16′20″W / 51.1472°N 3.2722°W |
The cross was built in the late 14th century. The tapering octagonal shaft is supported by a three-step base. | 1006202 |  |
[85] |
| Churchyard cross immediately south of Holy Ghost Church | Crowcombe | Cross | Middle Ages | ST 14069 36694 51°07′23″N 3°13′45″W / 51.1231°N 3.2292°W |
The remains of a medieval cross. The octagonal 2.8 metres (9 ft 2 in) high shaft sits on a base of three steps. | 1017221 |  |
[86] |
| Cist and associated mound in Langridge Wood, 410 m north west of Treborough Lodge | Withycombe | Cist | Bronze Age | ST 01407 37330 51°07′36″N 3°24′37″W / 51.1267°N 3.4103°W |
A stone built rectangular cist, approximately 2 metres (6 ft 7 in) long which contained a human skeleton until it was removed in 1820. | 1020689 |  |
[87] |
| Clatworthy hillfort | Clatworthy | Hillfort | Iron Age | ST 04586 31500 51°04′28″N 3°22′02″W / 51.0744°N 3.3672°W |
Clatworthy Camp is an Iron Age Hillfort. It is situated on a promontory of the Brendon Hills above Clatworthy Reservoir. It is roughly triangular in shape with an area of 5.8 hectares (14 acres). It has a single bank and ditch, cut through solid rock. There may have been an entrance on the west and two on the east. | 1006149 |  Upload Photo |
[88] [89] |
| Cleeve Abbey | Washford | Remains of Cistercian abbey | 1198 | ST0474440703 51°09′27″N 3°21′49″W / 51.157623°N 3.363499°W |
Cleeve Abbey was a medieval monastery. The abbey was founded in the late twelfth century as a house for monks of the austere Cistercian order. In 1536 Cleeve was closed by Henry VIII in the course of the Dissolution of the Monasteries and the abbey was converted into a country house. Subsequently, the status of the site declined and the abbey was used as farm buildings until the latter half of the nineteenth century when steps were taken to conserve the remains. In the twentieth century Cleeve was taken into state care; the abbey is now looked after by English Heritage and is open to the public. While the church is no longer standing, the conventual buildings are still roofed and habitable and contain many features of particular interest including the 'angel' roof in the refectory and the wall paintings in the painted chamber. | 1014824 |  |
[90][91] [92][93]
|
| Cow Castle | Exmoor | Hillfort | Iron Age | SS 79437 37350 51°07′22″N 3°43′27″W / 51.12270°N 3.7241°W |
Cow Castle is an Iron Age Hillfort which occupies an isolated hilltop and has a single rampart and ditch, enclosing 0.9 hectares (2.2 acres). It is in the valley of the River Barle. It has been added to the heritage at Risk register because of the risk from bracken. | 1002955 |  |
[94][95] |
| Cross 15 m north of St Peter's Church | Williton | Cross | 13th century | ST 07522 40772 51°07′05″N 3°24′54″W / 51.1181°N 3.415°W |
The base and lower part of the shaft of a 13th century stone cross. | 1017293 |  |
[96] |
| Cross in the churchyard of All Saints' Church | Selworthy | Cross | Late 14th century | SS 91995 46793 51°12′37″N 3°32′51″W / 51.2102°N 3.5476°W |
A medieval cross with a 2-metre (6 ft 7 in) stone shaft on an octagonal base with three octagonal steps. | 1020775 |  |
[97][98] [99] |
| Cross in the churchyard of St George's Church | Dunster | Cross | Middle Ages | SS 98995 43662 51°11′00″N 3°26′47″W / 51.1832°N 3.4465°W |
The remains of a stone cross which was constructed in or before the 15th century. The remaining part of the shaft is 0.5 millimetres (0.020 in) high and sits on a circular base with three steps. | 1021061 |  |
[100]
|
| Cross in the churchyard of the Church of St Mary the Virgin | Luccombe | Cross | 15th century | SS 91118 44531 51°11′22″N 3°33′34″W / 51.1895°N 3.5594°W |
A 15th century cross with a 1 metre (3 ft 3 in) stone shaft set in an octagonal three step base. | 1020917 |  |
[101] |
| Cross in the churchyard of St Mary the Virgin's Church | Nettlecombe | Cross | Late 14th century | ST 05696 37742 51°07′52″N 3°20′57″W / 51.1312°N 3.3491°W |
The remains of a 14th century cross with a stone shaft set in a two-step base. | 1020691 |  Upload Photo |
[102] |
| Cross in the churchyard of St Peter's Church | Exton | Cross | Late 14th century | SS 92585 33693 51°05′33″N 3°32′07″W / 51.0925°N 3.5352°W |
The remains of a 14th century cross with a tapering octagonal stone shaft. The upper part of the shaft was restored in 1875. | 1021156 |  Upload Photo |
[103] |
| Cross in the churchyard of the Church of St Decuman | Watchet | Cross | 14th or 15th century | ST 06493 42684 51°10′47″N 3°19′49″W / 51.1796°N 3.3302°W |
The remains of a 14th or 15th century cross with a tapering octagonal stone shaft on an octagonal base. The upper part of the shaft was restored with wood in the mid 20th century. | 1020919 |  |
[104] |
| Cross in the churchyard of St Mary's Church | Luxborough | Cross | 13th or 14th century | SS 97385 38005 51°07′56″N 3°28′04″W / 51.1321°N 3.4679°W |
A medieval inscribed stone cross which is 1.6 metres (5 ft 3 in) high and stands on a partially buried plinth. | 1021155 |  Upload Photo |
[105] |
| Cross in the churchyard of St Peter's Church | Treborough | Cross | Late 13th century | ST 01067 36365 51°07′05″N 3°24′54″W / 51.1180°N 3.4149°W |
A medieval cross with a stone shaft on an octagonal base with three octagonal steps. The head of the cross with a figure of St Peter is a 19th century addition. | 1020690 |  |
[106]
|
| Crowcombe village cross 170 m north west of Holy Ghost Church | Crowcombe | Cross | Middle Ages | ST 13906 36765 51°07′25″N 3°13′54″W / 51.1237°N 3.2316°W |
A medieval cross of red sandstone. The octagonal shaft is 3 metres (9.8 ft) high, topped by a Greek cross added in the 19th century, standing on an octagonal base. | 1017220 |  |
[107] |
| Curdon Wood camp | Stogumber | Hillfort | Iron Age | ST 10201 38515 51°08′05″N 3°17′28″W / 51.1347°N 3.2911°W |
Curdon Camp is a univallate Iron Age hillfort. It was nearly completely destroyed by quarrying and bulldozing. A section of the camp remains that is still 2.5 metres (8 ft 2 in) high on the southern and western sides. | 1006158 |  Upload Photo |
[108][109] |
| Daw's Castle | Watchet | Hillfort | Iron Age | ST 06141 43181 51°10′53″N 3°20′39″W / 51.1814°N 3.3442°W |
Daw's Castle is a sea cliff Hillfort just west of Watchet. The fort is situated on an east-west cliff about 80 metres (260 ft) above the sea, on a tapering spur of land bounded by the Washford River. The ramparts of the fort would have formed a semicircle backing on to the sheer cliffs, but coastal erosion has reduced the size of the enclosure, and later destruction by farming, limekilns, and the B3191 road, have left only about 300 metres (980 ft) of ramparts visible today. The fort may be of Iron Age origin, but was (re)built and fortified as a burh by King Alfred, as part of his defence against Viking raids from the Bristol Channel around 878 AD. It would have been one of a chain of forts and coastal lookout posts, connected by the Herepath, or military road, which allowed Alfred to move his army along the coast, covering Viking movements at sea. | 1020882 |  |
[110][111] |
| Deserted medieval farm, W of Bramble Combe | Minehead Without | Earthworks | Middle Ages | SS 94045 47920 51°13′14″N 3°31′07″W / 51.2206°N 3.5186°W |
Earthworks of a medieval farmhouse 22 metres (72 ft) by 5 metres (16 ft). It is known to have been occupied around 1279 and in decline by 1487. | 1006126 |  Upload Photo |
[112] |
| Dovecote 60 m north of St George's Church | Dunster | Dovecote | Late 16th century | SS9901843725 51°11′02″N 3°26′46″W / 51.183805°N 3.4462°W |
Dunster Dovecote was probably built in the late 16th century. It is situated on Priory Green opposite the Tithe Barn and close to the walls of the Priory Church of St George. It is approximately 5.8 metres (19 ft) high and 5.8 metres (19 ft) in diameter, with walls around 1.2 metres (4 ft) thick. There are five hundred and forty nest-holes. In the 18th century the floor level and door were raised among several major alterations. The lower tiers of nest holes were blocked to protect against Brown Rats which had arrived in the Britain in 1720 and reached Somerset by 1760. A revolving ladder, known as a "potence", was installed to allow the pigeon keeper to search the nest holes more easily. In the 19th century two feeding platforms were added to the axis of the revolving ladder. | 1020408 |  |
[113][114][115][116] |
| Dovecote at Little Blackford | Selworthy | Dovecote | 11th century | SS 92475 45284 51°11′48″N 3°32′25″W / 51.1967°N 3.5403°W |
The Dovecot At Blackford Farm was built in the 11th century. It is now owned by the National Trust and used as a store for the neighbouring farm. The earliest written record of the Dovecote was in 1393 although the exact date of construction is not known. It is built of local Devonian sandstone, with walls are 1.2 metres (4 ft) thick and contains over 300 nest holes. | 1020774 |  |
[117][118][119] |
| Doverhay Down round barrow, Porlock | Luccombe | Round barrow | Bronze Age | SS 88566 45241 51°11′44″N 3°35′46″W / 51.1955°N 3.5962°W |
Two round barrows one of which is 9.6 metres (31 ft) in diameter and the other 6.4 metres (21 ft). | 1006191 |  Upload Photo |
[120]
|
| Dowsborough hillfort and associated round barrow | Holford | Hillfort | Iron Age | ST 16017 39113 51°08′43″N 3°12′05″W / 51.1454°N 3.2015°W |
Dowsborough Camp (or Danesborough or Dawesbury) is an Iron Age Hillfort on the Quantock Hills near Nether Stowey. The fort has an oval shape, with a single rampart and ditch (univallate) following the contours of the hill top, enclosing an area of 2.7 hectares (6.7 acres). The fort and associated round barrow has been added to the Heritage at Risk register due to vulnerability to vehicle damage and erosion. | 1010494 |  Upload Photo |
[121][122] [123][124] |
| Dunkery Beacon and adjacent mounds | Cutcombe | Burial mounds | Bronze Age | SS 89143 41590 51°09′46″N 3°35′12″W / 51.1627°N 3.5868°W |
Dunkery Beacon is the summit of Dunkery Hill, and the highest point on Exmoor and in Somerset. Dunkery Beacon was given to the National Trust in 1935 by Sir Thomas Acland, Colonel Wiggin and Allan Hughes along with the rest of the Holnicote Estate an event commemorated by the summit memorial cairn known as Robin How. | 1003026 | [125][126] | |
| Early Christian to medieval settlement and cemetery | Carhampton | Earthworks | Early Middle Ages | ST 01108 42677 51°10′29″N 3°24′58″W / 51.1748°N 3.4160°W |
Earthworks remains of houses and a metal working site dating from the 5th to 8th century. Skeletons from a medieval cemetery have also been recovered from the site. | 1013589 |  Upload Photo |
[127] |
| Earthwork enclosure on Rodhuish Common, 300 m west of Moor Barn | Withycombe | Hillfort | Iron Age | SS 99901 39225 51°08′37″N 3°25′56″W / 51.1435°N 3.4323°W |
Rodhuish Common is a univallate Iron Age Hillfort. There is a small oval enclosure which is thought to be of Iron Age date. | 1021122 |  Upload Photo |
[128][129] |
| Earthwork enclosure on Monkslade Common, 860 m east of Fire Tower | Luxborough | Earthworks | Iron Age | SS 99468 39174 51°08′35″N 3°26′19″W / 51.1430°N 3.4385°W |
Earthworks from an Iron Age enclosure 68 metres (223 ft) long and 54 metres (177 ft) wide surrounded by a bank and ditch. | 1021121 |  Upload Photo |
[130] |
| Earthwork enclosure on Winsford Hill, 200 m south east of Wambarrows | Winsford | Earthworks | Late Middle Ages | SS 87789 34204 51°05′46″N 3°36′14″W / 51.0961°N 3.6038°W |
Earthworks from a medieval enclosure 17.6 metres (58 ft) long and 13.2 metres (43 ft) wide. | 1021274 |  Upload Photo |
[131] |
| Earthworks W of Bury | Brompton Regis | Earthworks | Unknown | SS9434027296 51°02′07″N 3°30′30″W / 51.0353°N 3.5083°W |
Earthworks from an enclosure of unknown date with banks on either side; however it is unlikely this was a defensive structure. | 1003031 |  Upload Photo |
[132] |
| East Pinford: a stone alignment on the west side of East Pinford 700 m west of Long Combe sheep pen | Exmoor | Stone row | Late Neolithic to middle Bronze Age | SS 79658 42730 51°10′16″N 3°43′22″W / 51.1711°N 3.7227°W |
An alignment of two parallel rows of six standing stones. The stones are between 350 millimetres (14 in) and 720 millimetres (28 in) high. | 1014263 |  Upload Photo |
[133] |
| Edgerley Stone | Exmoor | Inscribed stone | Before 1207 | SS 71959 40700 51°09′04″N 3°49′56″W / 51.1512°N 3.8321°W |
A wedge shaped stone which is 1.5 metres (4 ft 11 in) high. The inscribed text is of unknown date. | 1020883 |  Upload Photo |
[134] |
| Elworthy Barrows hillfort | Brompton Ralph | Hill fort | Iron Age | ST 07033 33718 51°05′44″N 3°19′43″W / 51.0956°N 3.3286°W |
Elworthy Barrows is an unfinished Iron Age hill fort rather than Bronze Age barrows. It covers an area of 3.5 hectares (8.6 acres) and is surrounded by a bank and ditch. | 1020724 |  Upload Photo |
[135][136][137] |
| Enclosure and associated outworks on Staddon Hill | Winsford | Enclosure | Iron Age | SS 88143 37524 51°07′34″N 3°35′59″W / 51.1260°N 3.5998°W |
Staddon Hill Camp is an hill slope enclosure. It covers 0.1 hectares (0.25 acres) and is surrounded by a bank and ditch. | 1021359 |  Upload Photo |
[138] |
| Entrenchment on Heydon Hill | Huish Champflower | Earthworks | Unknown | ST 03391 28215 51°02′42″N 3°22′46″W / 51.0451°N 3.3794°W |
A bank and ditch. The site has been added to the Heritage at Risk register because of the risks of arable ploughing. | 1006173 |  Upload Photo |
[139][140] |
| Exe Plain stone alignment 425 m north east of the sheepfold | Exmoor | Stone row | Late Neolithic to middle Bronze Age | SS 74970 42629 51°10′09″N 3°47′23″W / 51.1692°N 3.7897°W |
A 27.8-metre (91 ft) long stone row of two vertical and one recumbent stones. | 1014262 |  Upload Photo |
[141] |
| Four cairns on Hurley Beacon | Crowcombe | Cairn | Bronze Age | ST 14112 37999 51°08′05″N 3°13′44″W / 51.1348°N 3.2289°W |
The central cairn at the highest point is known as Hurley Beacon and is 24 metres (79 ft) in diameter and 2 metres (6 ft 7 in) high. | 1017218 |  Upload Photo |
[142] |
| Four medieval fish weirs 500 m east of the Harbour | Minehead | Fishing weir | Middle Ages | SS 97644 47052 51°12′49″N 3°28′00″W / 51.2135°N 3.4668°W |
A series of V shaped stone fish weirs. The date on which they were built is not documented however there is documentary evidence of the weirs in the 1420, but they may date back to the 11th century. | 1020017 |  Upload Photo |
[143] |
| Four round barrows on The Allotment, 520 m south east of Spire Cross | Winsford | Round barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 89284 33287 51°05′18″N 3°34′56″W / 51.0882°N 3.5822°W |
Four round barrows each between 5 metres (16 ft) and 12.5 metres (41 ft) in diameter. | 1021230 |  Upload Photo |
[144] |
| Four round cairns on Dunkery Hill 400 m south east of Joaney How Cairn | Wootton Courtenay | Cairn | Bronze Age | SS 91052 42642 51°10′21″N 3°33′35″W / 51.1726°N 3.5598°W |
Two pairs of cairns ranging from 7.4 metres (24 ft) to 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1020931 |  Upload Photo |
[145] |
| Gallox Bridge | Dunster | Bridge | 15th century | SS9895143213 51°10′45″N 3°26′49″W / 51.179191°N 3.447015°W |
The Gallox Bridge is a narrow stone packhorse bridge, on the southern outskirts of Dunster, with two arches over the River Avill. It has a roadway width of 1.2 metres (3.9 ft), a total width of 1.9 metres (6.2 ft) and is 13.5 metres (44.3 ft) long. The bridge is in the guardianship of English Heritage. | 1014410 |  |
[146][147] |
| Green Barrow on Hawkridge Common | Withypool and Hawkridge | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 81791 34564 51°05′54″N 3°41′23″W / 51.0982°N 3.6896°W |
A 13.3-metre (44 ft) diameter bowl barrow. | 1021263 |  Upload Photo |
[148]
|
| Group of four barrows and cairns known as 'Rowbarrows' including Great Rowbarrow and Little Rowbarrow | Cutcombe | Cairns and barrows | Bronze Age | SS 87417 41473 51°09′41″N 3°36′41″W / 51.1614°N 3.6114°W |
A cairn which is 25 metres (82 ft) diameter and associated barrows. | 1003677 |  |
[149][150] |
| Group of round barrows | North Molton | Round barrow | Bronze Age | SS 74635 36212 51°06′41″N 3°47′32″W / 51.1114°N 3.7923°W |
A group of ten Round barrows | 1002626 |  |
[151] |
| Halscombe stone setting 790 m SSW of Simonsbath Bridge | Exmoor | Standing stones | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 77022 38336 51°07′52″N 3°45′32″W / 51.1311°N 3.7589°W |
Two rows of standing stones, up to 600 millimetres (24 in) high, some of which are now recumbent. | 1014281 |  Upload Photo |
[152] |
| Hillfort on Grabbist Hill, 275 m south west of St Leonard's Well | Dunster | Hillfort | Iron Age | SS 98294 43686 51°11′00″N 3°27′23″W / 51.1832°N 3.4565°W |
Grabbist hillfort is an Iron Age oval hillfort. The fort is 270.0 metres (885.8 ft) long and 219.8 feet (67.0 m) wide, and is surrounded by a counterscarp, which measures 4.2 to 6.2 feet (1.3 to 1.9 m) in height. It is also surrounded by a ditch, which ranges up to 10.0 metres (32.8 ft) wide and 2.2 metres (7.2 ft) deep. The bank has a peak height of 3 metres (9.8 ft), and, on the northern and western sides, there is a second bank, which leads to the northeastern corner being the most strongly defended. |  Upload Photo |
[153][154]
| |
| Holy well at St Pancras Chapel | Old Cleeve | Well | Middle Ages | ST 04143 39888 51°09′01″N 3°22′18″W / 51.1502°N 3.3718°W |
A stone lined holy well in the grounds of the former St Pancras Chapel which is now a private house. | 1020720 |  Upload Photo |
[155] |
| Horner packhorse bridge | Luccombe | Packhorse bridge | Middle Ages | SS 89733 45541 51°11′54″N 3°34′47″W / 51.1984°N 3.5796°W |
A stone packhorse bridge over Horner Water. | 1006228 |  |
[156] |
| Huish Champflower Barrow | Huish Champflower | Bowl barrow | Late Neolithic to middle Bronze Age | ST 02860 34168 51°05′55″N 3°23′19″W / 51.0986°N 3.3887°W |
A bowl barrow which is 21 metres (69 ft) in diameter. | 1020692 |  |
[157] |
| Incised stone W of Stent Hill | Oare | Standing stone | Possibly 7th to 9th century | SS 83210 47374 51°12′49″N 3°40′24″W / 51.2136°N 3.6734°W |
The Culbone Stone, an early mediaeval standing stone approximately one metre in height. It lies in woodland close to the parish boundary, and features an incised wheeled cross, the style of which suggests it dates from 7th to 9th century. The stone is legally protected as a scheduled ancient monument. It has been suggested that the stone has been moved from its original site as part of the Culbone Hill Stone Row. | 1006141 |  |
[158][159] [160][161] [162][162] |
| Iron Age defended settlement above Sweetworthy (eastern of two) | Luccombe | Hillfort | Iron Age | SS 88991 42408 51°10′12″N 3°35′21″W / 51.1701°N 3.5892°W |
One of two Iron Age hillforts within 80 metres (260 ft) of each other. This one is around 37 metres (121 ft) in diameter and surrounded by a bank up to 0.4 metres (1 ft 4 in) high. | 1008471 |  Upload Photo |
[163] |
| Iron Age defended settlement above Sweetworthy (western of two) | Luccombe | Hillfort | Iron Age | SS 88877 42361 51°10′11″N 3°35′27″W / 51.1696°N 3.5908°W |
One of two Iron Age hillforts within 80 metres (260 ft) of each other. This one is around 35 metres (115 ft) in diameter and surrounded by a bank up to 0.5 metres (1 ft 8 in) high. | 1008472 |  Upload Photo |
[164] |
| Iron Age defended settlement, Furzebury Brake | Minehead Without | Enclosure | Iron Age | SS 93590 48299 51°13′26″N 3°31′31″W / 51.2239°N 3.5252°W |
An enclosure and settlement covering 0.22 hectares (0.54 acres) and surrounded by a bank. | 1008809 |  |
[165] |
| Ironstone mine ventilation flue in Chargot Wood, 1150 m south west of Langham Farm | Luxborough | Chimney | 19th century | SS 97346 35779 51°06′44″N 3°28′04″W / 51.1121°N 3.4678°W |
A ventilation chimney at the disused Bearland Wood Iron Mine. A fire at the base of the shaft was used to draw air and gasses from the mine. The chimney is 6.5 metres (21 ft) high and 1.75 metres (5 ft 9 in) in diameter at the base. | 1020189 |  |
[166]
|
| Katherine's Well | Selworthy | Well | Middle Ages | SS 91425 46897 51°12′39″N 3°33′21″W / 51.2109°N 3.5558°W |
A natural spring which has been converted into a well by the use of stone slabs. | 1020826 |  Upload Photo |
[167] |
| Kit Barrows Cairns | Cutcombe | Cairn | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 90033 42010 51°10′00″N 3°34′27″W / 51.1667°N 3.5742°W |
Two cairns one of which is 24 metres (79 ft) in diameter and the other 12.5 metres (41 ft). Each is around 0.5 metres (1 ft 8 in) high. | 1020828 |  Upload Photo |
[168] |
| Kittuck stone setting and cairn, 200 m south west of Three Combes Foot | Exmoor | Cairn | Bronze Age | SS 82034 43885 51°10′55″N 3°41′21″W / 51.1820°N 3.6892°W |
A cairn and standing stones (some of which are now recumbent). | 1014284 |  Upload Photo |
[169] |
| Lanacombe 1: a stone setting and two cairns on the east side of Lanacombe | Exmoor | Cairn and menhirs | Bronze Age | SS 78117 42770 51°10′16″N 3°44′41″W / 51.1711°N 3.7448°W |
A collection of two cairns, and several standing stones (some of which are now recumbent). | 1014273 |  Upload Photo |
[170] |
| Lanacombe 2: a stone setting and cairn on the east side of Lanacombe | Exmoor | Cairn and menhirs | Bronze Age | SS 78432 42873 51°10′20″N 3°44′25″W / 51.1721°N 3.7403°W |
A collection of cairns, and several standing stones (some of which are now recumbent). | 1014274 |  Upload Photo |
[171]
|
| Lanacombe 3: a stone setting and cairn on the east side of Lanacombe | Exmoor | Cairn and menhirs | Bronze Age | SS 78630 42998 51°10′24″N 3°44′15″W / 51.1733°N 3.7375°W |
A collection of cairns, and several standing stones (some of which are now recumbent). | 1014275 |  Upload Photo |
[172] |
| Lanacombe 4: a stone setting on the ENE side of Lanacombe | Exmoor | Menhirs | Bronze Age | SS 78654 43151 51°10′29″N 3°44′14″W / 51.1747°N 3.7372°W |
A collection of several standing stones (some of which are now recumbent). | 1014276 |  Upload Photo |
[173] |
| Lanacombe 5: a stone alignment on the south east side of Lanacombe | Exmoor | Menhirs | Bronze Age | SS 77995 42569 51°10′09″N 3°44′47″W / 51.1693°N 3.7465°W |
A collection of several standing stones (some of which are now recumbent) arranged into three rows | 1014277 |  Upload Photo |
[174] |
| Landacre Bridge | Withypool | Arch bridge | Late Middle Ages | SS8164936129 51°06′44″N 3°41′32″W / 51.112196°N 3.692103°W |
A stone bridge over the River Barle with five arches each with a span of 2.7 metres (9 ft). It was built in the late medieval period with the first documentary evidence being from 1610. Restoration work was undertaken in 1875, and again following damage during flooding in 1952. | 1021125 |  |
[175][176] [177] |
| Later prehistoric defended enclosure, Long Wood | Carhampton | Enclosure | Iron Age | SS 98125 40385 51°09′13″N 3°27′29″W / 51.1536°N 3.4580°W |
An Enclosure which may have been a univallate Iron Age hill fort. The enclosure is approximately 40 metres (130 ft) in diameter and covers around 0.15 hectares (0.37 acres). It is surrounded by a bank and ditch about 6.5 metres (21 ft) wide and 1.9 metres (6 ft 3 in) high. The hill fort has been damaged in recent years due to forestry plantation. | 1008255 |  |
[178][179] [180] |
| Leather Barrow | Luxborough | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 98906 35534 51°06′37″N 3°26′44″W / 51.1102°N 3.4455°W |
A bowl barrow with a diameter of 23 metres (75 ft) and height of 3.3 metres (11 ft). | 1021158 |  Upload Photo |
[181] |
| Lock up 60 m south east of St Mary's Church | Brompton Regis | Village lock-up | Late 18th century | SS 95176 31441 51°04′22″N 3°29′51″W / 51.0727°N 3.4976°W |
A small stone building used as the village lock-up. The original door has been blocked up and a new doorway constructed. | 1021157 |  |
[182] |
| Long Chains Combe North: a stone setting 120 m WNW of the sheepfold | Exmoor | Standing stones | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 74570 42358 51°10′00″N 3°47′43″W / 51.1667°N 3.7954°W |
Three standing stones between 300 millimetres (12 in) and 450 millimetres (18 in) high. | 1014280 |  Upload Photo |
[183] |
| Long Chains Combe South: two standing stones 380 m south west of the sheepfold | Exmoor | Standing stones | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 74387 42093 51°09′51″N 3°47′52″W / 51.1643°N 3.7979°W |
Two standing stones between 300 millimetres (12 in) and 530 millimetres (21 in) high. | 1014279 |  Upload Photo |
[184] |
| Malmsmead Bridge | Oare | Packhorse bridge | 17th century | SS 79193 47723 51°12′57″N 3°43′52″W / 51.2159°N 3.7311°W |
A stone two arch packhorse bridge carrying a minor road over Badgworthy Water. | 1006229 |  |
[185][186] |
| Motte and bailey at Dunster Castle | Dunster | Castle | 11th century | SS9919643490 51°10′54″N 3°26′37″W / 51.181724°N 3.443589°W |
Dunster Castle is a former motte and bailey castle and now a country house on the top of a steep hill called the Tor. It has been fortified since the late Anglo-Saxon period. After the Norman conquest of England in the 11th century, William de Mohun constructed a timber castle on the site as part of the pacification of Somerset. A stone shell keep was built on the motte by the start of the 12th century, and the castle survived a siege during the early years of the Anarchy. At the end of the 14th century the de Mohuns sold the castle to the Luttrell family, who continued to occupy the property until the late 20th century. In 1976 Colonel Walter Luttrell gave Dunster Castle and most of its contents to the National Trust, which operates it as a tourist attraction. | 1020410 |  |
[187] |
| Mounsey Castle and an associated outwork 100 m to the north | Dulverton | Hillfort | Iron Age | SS 88555 29561 51°03′16″N 3°35′36″W / 51.0544°N 3.5933°W |
Earthworks of Mounsey Castle, an Iron Age irregular triangular earthwork. It is surrounded by the remains of coursed stone walling, with an entrance to the west. It overlooks the River Barle. | 1021357 | 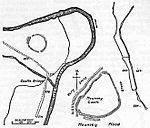 |
[188] [189][190] |
| Oare Bridge | Oare | Bridge | Possibly 18th century | SS 80211 47452 51°12′18″N 3°41′24″W / 51.205°N 3.690°W |
Robber's Bridge is an old masonry arch bridge in the royal forest of Exmoor, carrying the minor road from Porlock Hill to Oare. It crosses Weir Water and is located down a steep, wooded lane beneath overhanging trees. | 1006196 |  |
[191][192] [193] |
| Old Barrow on Old Barrow Down | Withypool and Hawkridge | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 84085 32447 51°04′47″N 3°39′22″W / 51.0796°N 3.6561°W |
A bowl barrow which is 20.9 metres (69 ft) in diameter and 1.5 metres (4 ft 11 in) high. | 1021356 |  Upload Photo |
[194] |
| Oldberry Castle | Dulverton | Hillfort | Iron Age | SS 90942 28226 51°02′35″N 3°33′25″W / 51.0430°N 3.5570°W |
Oldberry Castle (sometimes called Oldbury Castle) is an Iron Age hill fort. The site overlooks the town and the ancient crossing point of the River Barle. It is an irregular oval shape measuring 220 metres (720 ft) by 300 feet (91 m). It is defended by a bank measuring 3.0 metres (10 ft) wide and 6 feet (1.8 m) high, and a 5.5 metres (18 ft) wide ditch. | 1006168 | 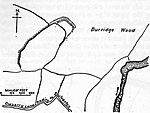 |
[195][196] [197] |
| Packhorse bridge 60 m north east of Royal Oak Farm | Winsford | Bridge | Middle Ages | SS 90551 34885 51°06′10″N 3°33′53″W / 51.1028°N 3.5646°W |
A stone packhorse bridge over Winn Brook. | 1021124 |  |
[198] |
| Packhorse bridge 75 m south east of The Old Vicarage | Winsford | Packhorse bridge | Middle Ages | SS 90570 35160 51°06′19″N 3°33′52″W / 51.1053°N 3.5644°W |
A medieval stone packhorse bridge, with two arches, over the River Exe. | 1021123 |  |
[199] |
| Porlock Allotment stone alignment and cairn, 450 m west of Porlock stone circle | Porlock | Standing stones and a cairn | Bronze Age | SS 84055 44701 51°11′23″N 3°39′38″W / 51.1897°N 3.6605°W |
A collection of standing stones and a cairn. | 1014268 |  Upload Photo |
[200] |
| Porlock Allotment 1: a stone alignment 450 m SSE of Black Barrow | Porlock | Standing stones | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 83359 43784 51°10′53″N 3°40′13″W / 51.1813°N 3.6702°W |
Three standing and five recumbent stones. | 1014270 |  Upload Photo |
[201] |
| Porlock Hill stone setting, 150 m north west of the cattle grid on the A39 at the top of Porlock Hill | Porlock | Standing stones | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 86450 46135 51°12′11″N 3°37′36″W / 51.2031°N 3.6267°W |
Three standing stones. | 1014267 |  Upload Photo |
[202] |
| Post-medieval pottery kiln 360 m NNE of the Castle | Dunster | Kiln | 18th century | SS 99226 43862 51°11′06″N 3°26′36″W / 51.1851°N 3.4433°W |
A stone pottery kiln. | 1020409 |  Upload Photo |
[203] |
| Ralegh's Cross | Nettlecombe | Cross | 13th century | ST 03886 34415 51°06′04″N 3°22′26″W / 51.1010°N 3.3740°W |
The remains of a cross dating from around 1300. A stone base supports the remains of the shaft which is now 0.7 metres (2 ft 4 in) high. | 1020722 |  Upload Photo |
[204] |
| Raleigh's Cross iron mine, 310 m south east of Heather House | Huish Champflower | Earthworks | 1850s | ST 02526 34212 51°05′56″N 3°23′36″W / 51.0989°N 3.3934°W |
Earthworks and ruins from an iron mine opened in the 1850s. The buildings were demolished in 1907. | 1021351 |  Upload Photo |
[205]
|
| Remains of 14th century chantry at Kilve | Kilve | Chantry Chapel | 1329 | ST 14644 44021 51°11′20″N 3°13′22″W / 51.1890°N 3.2228°W |
The ruins of a Chantry Chapel formed in 1329. The stonework is Blue Lias but is now ruined and covered in ivy. Little of the slate roof remains. The building was previously thatched. | 1002960 |  |
[206] |
| Remains of St Andrew's Chapel, 80 m north west of Chapel Cross | Luccombe | Earthworks | Middle Ages | SS 90577 44865 51°11′33″N 3°34′02″W / 51.1925°N 3.5673°W |
The remaining walls and footings of a medieval chapel | 1021120 |  |
[207] |
| Rexy Barrow, Little Buscombe | Exmoor | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | SS 77019 41950 51°09′49″N 3°45′37″W / 51.1635°N 3.7602°W |
A bowl barrow which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1006208 |  Upload Photo |
[208]
|
| Ring cairn on West Hill | East Quantoxhead | Cairn | Bronze Age | ST 12327 41573 51°10′00″N 3°15′19″W / 51.1666°N 3.2553°W |
A stone cairn with a surrounding rim of 15.3 metres (50 ft) diameter. | 1014121 |  Upload Photo |
[209] |
| Road Castle | Winsford | Hill fort | Iron Age | SS 86289 37578 51°07′34″N 3°37′35″W / 51.1262°N 3.6263°W |
Road Castle is an Iron Age bank and ditch enclosure. The ditch is almost square in plan with rounded corners and covers an area of approximately 0.28 hectares (0.7 acres). | 1021360 |  Upload Photo |
[210][211] |
| Round barrow 200 ft (60 m) NW of Setta Barrow, Bray Common | Brayford | Round barrow | Bronze Age | SS 72523 38098 51°07′40″N 3°49′23″W / 51.1279°N 3.8231°W |
A 32-metre (105 ft) diameter mound which has been described as both a round barrow and bowl barrow. | 1003855 |  Upload Photo |
[212] |
| Round barrow 720 m NNW of Spire Cross | Winsford | Round barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 88639 34246 51°05′48″N 3°35′30″W / 51.0966°N 3.5917°W |
A round barrow which is 15.5 metres (51 ft) in diameter. | 1021229 |  Upload Photo |
[213]
|
| Round barrow 500 yd (460 m) WSW of Exe Head | Exmoor | Round barrow | Bronze Age | SS 74702 41411 51°09′30″N 3°47′35″W / 51.1582°N 3.7931°W |
A bowl barrow south of The Chains, which is 12.3 metres (40 ft) in diameter and 0.8 metres (2 ft 7 in) high. | 1006212 |  Upload Photo |
[214] |
| Round barrow 800 yd (730 m) SW of Dunkery Beacon | Cutcombe | Round barrow | Bronze Age | SS 88592 41151 51°09′31″N 3°35′40″W / 51.1587°N 3.5945°W |
A round barrow which is 12.3 metres (40 ft) in diameter. | 1006232 |  Upload Photo |
[215] |
| Round barrow cemetery at Battle Gore immediately west of North Road | Williton | Round barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 07444 41392 51°09′51″N 3°19′30″W / 51.1643°N 3.3251°W |
Three round barrows and the Neolithic burial chamber. | 1019032 |  Upload Photo |
[216] |
| Round barrow cemetery incorporating Wambarrows on Winsford Hill | Winsford | Round barrow | Bronze Age | SS 87616 34301 51°05′49″N 3°36′23″W / 51.0970°N 3.6063°W |
A round barrow cemetery at Wambarrows on Winsford Hill. There are at least five barrows ranging in diameter from 17.6 metres (58 ft) to 28.8 metres (94 ft). | 1021273 |  |
[217] |
| Round barrow on Great Tom's Hill | Exmoor | Round barrow | Bronze Age | SS 80496 43113 51°10′29″N 3°42′39″W / 51.1747°N 3.7109°W |
A 12.5-metre (41 ft) diameter stony mound covered in turf. | 1003032 |  Upload Photo |
[218] |
| Round barrow on Roosthitchen | Exmoor | Cairn | Prehistoric | SS 72192 40151 51°08′47″N 3°49′43″W / 51.1463°N 3.8286°W |
A turf covered mound with stones protruding from it. It was previously classified as a barrow. | 1006164 |  Upload Photo |
[219] |
| Round cairn 280 m south of Rex Stile Head | Wootton Courtenay | Cairn | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 90447 42282 51°10′09″N 3°34′06″W / 51.1693°N 3.5683°W |
A 9.4-metre (31 ft) diameter stoney mound. | 1020932 |  Upload Photo |
[220] |
| Round cairn 550 m north east of Joaney How Cairn | Wootton Courtenay | Cairn | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 91265 43105 51°10′36″N 3°33′24″W / 51.1768°N 3.5568°W |
A round cairn which is 15 metres (49 ft) in diameter. | 1020927 |  Upload Photo |
[221] |
| Round cairn 750 m south east of Joaney How Cairn | Wootton Courtenay | Cairn | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 91445 42371 51°10′13″N 3°33′15″W / 51.1702°N 3.5541°W |
An earth and stone mound, 8 metres (26 ft) in diameter and 1 metre (3 ft 3 in) high. | 1020928 |  Upload Photo |
[222] |
| Round cairn 1000 m ESE of Joaney How Cairn | Wootton Courtenay | Cairn | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 91732 42385 51°10′13″N 3°33′00″W / 51.1704°N 3.5500°W |
A cairn of 9 metres (30 ft) diameter. | 1020929 |  Upload Photo |
[223] |
| Round cairn cemetery, 570 m east of Selworthy Beacon | Minehead Without | Cairns | Late Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 92175 48044 51°13′18″N 3°32′42″W / 51.2218°N 3.545°W |
A collection of nine round cairns on a ridge of Selworthy Beacon. | 1020794 |  Upload Photo |
[224] |
| Round cairn cemetery on Dunkery Hill | Luccombe | Cairn | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 90883 42778 51°10′26″N 3°33′44″W / 51.1738°N 3.5623°W |
A collection of five round cairns each of which is between 21.5 metres (71 ft) and 24 metres (79 ft) in diameter. | 1020930 |  Upload Photo |
[225] |
| Round cairn known as Pixie's Mound | Stogursey | Cairn | Bronze Age | ST 20907 45575 51°12′14″N 3°08′01″W / 51.2039°N 3.1335°W |
A cairn which is 27 metres (89 ft) in diameter and 1.7 metres (5 ft 7 in) high. Excavations have found the remains of several bodies and flint tools. | 1006226 |  Upload Photo |
[226] |
| Ruined cairn on Higher Hare Knap | Holford | Cairn | Bronze Age | ST 14844 39516 51°08′55″N 3°13′08″W / 51.1485°N 3.2188°W |
A cairn or round barrow which is between 21 metres (69 ft) and 26.5 metres (87 ft) in diameter. | 1006144 |  Upload Photo |
[227]
|
| Selworthy Beacon cairn | Minehead Without | Cairn | Neolithic to Bronze Age revised 16th century | SS 91868 47981 51°13′15″N 3°32′59″W / 51.2208°N 3.5497°W |
A cemetery cairn which was adapted in the 16th century for use as a fire beacon. The original earth and stone mound is topped with a 7 metres (23 ft) diameter stone heap. | 1020793 | [228] | |
| Setta Barrow and three round barrows to the south | Brayford Exmoor | Round barrow | Bronze Age | SS 72545 37699 51°07′28″N 3°49′21″W / 51.1244°N 3.8226°W |
Several bowl and round barrows ranging from 10 metres (33 ft) to 28 metres (92 ft) in diameter. | 1003856 |  Upload Photo |
[229][230][231] |
| Standing stones on Manor allotment | Oare | Standing stones | Prehistoric | SS 80180 43287 51°10′34″N 3°42′56″W / 51.1762°N 3.7155°W |
A line of three small stones. | 1006165 |  Upload Photo |
[232] |
| St Leonard's Well | Dunster | Holy well | Middle Ages | SS 98504 43867 51°11′04″N 3°27′13″W / 51.18450°N 3.4536°W |
A 16th century stone well house over a medieval holy well. It may have been the water supply for Dunster Priory. | 1021154 |  |
[233] |
| Stogursey Castle | Stogursey | Motte-and-bailey castle | 11th or 12th century | ST 20326 42575 51°10′36″N 3°08′32″W / 51.1766°N 3.1422°W |
Stogursey Castle was built in the late 11th or early 12th century. The castle was a motte-and-bailey design with a 60 metre wide, two metre tall motte and two bailey enclosures, surrounded by a water-filled moat. The castle was controlled by King John of England during the First Barons' War, and was ordered to be destroyed in 1215, but survived; John's lieutenant Falkes de Breauté took control of the castle, and after his death a second order to destroy the property was given in 1228, again apparently ignored. The castle was extended in stone in 1300 by the Fitzpayne family, but was destroyed in the 1450s by the Yorkist faction during the War of the Roses. | 1019035 |  |
[234][235] |
| Stone circle, Porlock Common | Porlock | Stone circle | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 84520 44656 51°11′22″N 3°39′14″W / 51.1894°N 3.6538°W |
A stone circle which originally had 21 stones. 14 stones remain half of which are upright and the other half recumbent. The tallest of the standing stones is 0.8 metres (2 ft 7 in) high. | 1006189 |  |
[236][237] |
| Stone circle on Withypool Hill 670 m ESE of Portford Bridge | Withypool and Hawkridge | Stone circle | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 83827 34313 51°05′47″N 3°39′37″W / 51.0963°N 3.6604°W |
A stone circle which has 25 standing stones, some which were previously part of the circle are no longer present. The circle has a diameter of 36 metres (118 ft). | 1021261 |  |
[238] |
| Stringston churchyard cross | Stringston | Cross | Late 14th century | ST 17647 42388 51°10′29″N 3°10′46″W / 51.1748°N 3.1794°W |
A cross dating from the 14th century, which is on the Heritage at Risk register. It has two steps and an octagonal shaft supporting a canopied head. | 1006171 |  |
[239][240][241] |
| Swap Hill standing stone 200 m south east of the Long Combe sheep pen | Exmoor | Standing stone | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 80513 42669 51°10′15″N 3°42′38″W / 51.1707°N 3.7105°W |
A 23-centimetre (9.1 in) high standing stone and a split fragment from the stone. | 1014272 |  Upload Photo |
[242]
|
| Swap Hill stone setting, 275 m south east of the Long Combe sheep pen | Exmoor | Standing stones | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS805426 51°10′12″N 3°42′35″W / 51.1701°N 3.7096°W |
Six standing stones the tallest of which are 90 centimetres (35 in) high. | 1014282 |  Upload Photo |
[243] |
| Sweetworthy deserted medieval settlement | Luccombe | Earthworks | Middle Ages | SS 88783 42383 51°10′11″N 3°35′32″W / 51.1698°N 3.5922°W |
Earthworks of several buildings cut into the terraces on the side of the hill. It has been added to the Heritage at Risk register because of the vulnerability to plant growth. | 1008469 |  Upload Photo |
[244][245][246] |
| Sweetworthy Iron Age defended settlement | Luccombe | Hillfort | Iron Age | SS 89050 42534 51°10′17″N 3°35′25″W / 51.1714°N 3.5903°W |
A defended settlement on the north-facing slope of Dunkery Hill. It has a single rampart and external ditch, enclosing 0.25 hectares (0.62 acres). The rampart is still visible and the ditch on the east side is used as a trackway. | 1008470 |  Upload Photo |
[247][248][249] |
| Tarr Steps | Dulverton | Clapper bridge | Middle Ages | SS8677032116 51°04′38″N 3°37′04″W / 51.077161°N 3.617719°W |
The Tarr Steps are a clapper bridge across the River Barle in the Exmoor National Park. A typical clapper bridge construction, the bridge possibly dates to around 1000 BC. The stone slabs weigh up to 1-2 tons apiece. The bridge is 55 metres (180 ft) long and has 17 spans. | 1021325 |  |
[250][251][252] |
| The Incline, lying between Brendon Hill and Comberow, and the remains of Combe Row Station | Old Cleeve | Inclined plane | 1861 | ST 02648 34928 51°06′19″N 3°23′31″W / 51.1054°N 3.3919°W |
A rope-worked inclined plane 997 metres (3,272 ft) long to bring the ore down a 230 metres (770 ft) vertical interval on a 1 in 4 gradient on the West Somerset Mineral Railway. | 1021350 |  |
[253][254][255] |
| The Mound, Stoke Ridge, Stoke Pero | Luccombe | Round barrow | Bronze Age | SS 88098 43108 51°10′34″N 3°36′08″W / 51.1762°N 3.6022°W |
A possible round barrow which is 7 metres (23 ft) long and 6 metres (20 ft) wide. | 1006190 |  |
[256] |
| The Whit Stones: two standing stones 230 m west of Whitstone Post | Porlock | Standing stones | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 85330 46250 51°12′14″N 3°38′34″W / 51.2039°N 3.6428°W |
Two standing stones 7 metres (23 ft) apart. Each is 85 centimetres (33 in) to 90 centimetres (35 in) high. | 1014269 |  |
[257]
|
| The Yarn Market | Dunster | Market cross | 1609 | SS9915243812 51°11′05″N 3°26′40″W / 51.184611°N 3.444308°W |
The octagonal Yarn Market has a central stone pier which supports a heavy timber framework for the structure. The slate roof has a central wooden lantern topped by a weather vane. The roof is interrupted by a series of dormer windows. Around the periphery is a low stone wall and vertical timber supports. One of the roof beams has a hole in it, a result of cannon fire in the Civil War, when Dunster Castle was a besieged Royalist stronghold. Following the damage, it was restored in 1647 to its present condition. | 1015706 |  |
[258][259] [260][261] [262] |
| Three bowl barrows on Black Hill, 590 m north west of Crowcombe Park Gate | Holford | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 14738 38364 51°08′18″N 3°13′12″W / 51.1382°N 3.2201°W |
Three bowl barrows which are between 5 metres (16 ft) and 13 metres (43 ft) in diamater. | 1017219 |  Upload Photo |
[263] |
| Three round barrows on Withycombe Common, 360 m north of Fire Tower | Withycombe | Round barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 98668 39592 51°08′47″N 3°27′00″W / 51.1465°N 3.4500°W |
Three round barrows two of which are approximately 12 metres (39 ft) in diameter. The largest, most southerly is the largest at approximately 28 metres (92 ft) in diameter and has an Ordnance Survey trig point on it. | 1021119 |  |
[264] |
| Trendle Ring hillfort and associated outwork | Bicknoller | Hill fort | Bronze Age to Iron Age | ST 11825 39359 51°08′48″N 3°15′43″W / 51.1467°N 3.2619°W |
Trendle Ring is a late prehistoric earthwork. The site, which covers 0.8 hectares (2.0 acres), is surrounded by a single rampart with a ditch and has a simple opening on the east, uphill side. The hillside is steep and there are two areas which may have been more level platforms. It is situated on the slope of a hill which rises 130 metres (430 ft) above the ring. | 1008249 |  |
[265][266] |
| Tripp round barrow NW of Tripp Farm | Clatworthy | Round barrow | Bronze Age | ST 03771 33408 51°05′31″N 3°22′32″W / 51.0919°N 3.3755°W |
A round barrow approximately 20 metres (66 ft) in diameter. | 1006125 |  |
[267] |
| Trout Hill 1: a stone setting on the north east end of Trout Hill 550 m south west of the foot bridge over Badgworthy Water | Exmoor | Standing stone | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 79399 43226 51°10′32″N 3°43′36″W / 51.1755°N 3.7266°W |
Five standing stones, one of which is broken, in two intersecting rows. The largest is 70 centimetres (28 in) high. | 1014264 |  Upload Photo |
[268] |
| Trout Hill 2: a stone setting on the north east end of Trout Hill 610 m south of the foot bridge over Badgworthy Water | Exmoor | Standing stone | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 79554 43124 51°10′29″N 3°43′27″W / 51.1746°N 3.7243°W |
Three standing and one recumbent stones. One other stone was demolished by an unexploded shell in the 1970s leaving a crater on the site. | 1014265 |  Upload Photo |
[269] |
| Trout Hill 3: a stone setting on the north east end of Trout Hill 850 m SSW of the foot bridge over Badgeworthy Water | Exmoor | Standing stone | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 79412 42885 51°10′21″N 3°43′35″W / 51.1724°N 3.7263°W |
Two standing and two recumbent stones. The tallest standing stone is 30 centimetres (12 in) high. | 1014266 |  Upload Photo |
[270] |
| 'Two Barrows', group of barrows (Hangley Cleave) | North Molton | Bowl barrows | Bronze Age | SS 74635 36212 51°06′41″N 3°47′32″W / 51.1114°N 3.7923°W |
A group of four bowl barrows which straddles the border between Somerset and Devon. | 1006210 |  |
[271] |
| Two bowl barrows on Beacon Hill | West Quantoxhead | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 12444 40997 51°09′41″N 3°15′13″W / 51.1615°N 3.2535°W |
Two bowl barrows each approximately 24 metres (79 ft) in diameter. An Ordnance Survey trig point is on the more southerly of the two barrows. | 1014122 | [272] | |
| Two cairns on Great Hill, 470 m south and 750 m south west of Quantock Farm | Crowcombe | Cairn | Bronze Age | ST 15657 36251 51°07′09″N 3°12′23″W / 51.1193°N 3.2064°W |
Two cairns approximately 300 metres (980 ft) apart. The mound on the summit of the hill is 21 metres (69 ft) in diameter and the other 28 metres (92 ft). | 1020364 |  |
[273]
|
| Two cairns and two bowl barrows on Weacombe Hill, 440 m south of Bicknoller Post | Bicknoller | Cairns and bowl barrows | Bronze Age | ST 12862 39893 51°09′06″N 3°14′50″W / 51.1516°N 3.2472°W |
Two cairns and two bowl barrows dating from the Bronze Age three of them have been disturbed or partially excavated in the past. | 1014126 |  Upload Photo |
[274] |
| Two round barrows on Culbone Hill | Oare | Round barrows or cairns | Bronze Age | SS 82400 47603 51°12′56″N 3°41′06″W / 51.2155°N 3.6851°W |
Grass covered stony mounds previously classified as cairns and now as round barrows. Each approximately 10 metres (33 ft) in diameter. | 1006207 |  Upload Photo |
[275][276] |
| Two round barrows on Heydon Hill | Huish Champflower | Round barrow | Bronze Age | ST 03624 27978 51°02′35″N 3°22′34″W / 51.0430°N 3.3761°W |
Two barrows, partially excavated in 1896. | 1006143 |  Upload Photo |
[277] |
| Two round cairns on Dunkery Hill, 390 m and 420 m south east of Rex Stile Head | Wootton Courtenay | Cairn | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 90779 42302 51°10′10″N 3°33′49″W / 51.1695°N 3.5636°W |
Two mounds, one of 11 metres (36 ft) in diameter and the other 9 metres (30 ft). | 1020926 |  Upload Photo |
[278]
|
| Two standing stones and a mound 200 m WSW of Black Barrow, Hoscombe | Exmoor | Standing stones | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 83011 44163 51°11′05″N 3°40′31″W / 51.1847°N 3.6753°W |
Two stones 4.7 metres (15 ft) apart. One is 25 centimetres (9.8 in) high and the other 10 centimetres (3.9 in) high. The 5 metres (16 ft) wide mound is 11.7 metres (38 ft) from the nearest stone. | 1014271 |  Upload Photo |
[279] |
| Village cross 75 m north of St Andrew's Well | Stogursey | Cross | 13th or 14th century | ST 20241 42891 51°10′47″N 3°08′33″W / 51.1797°N 3.1424°W |
The remains of a Hamstone village cross on the High Street is from the Middle Ages. Approximately 1 metre (3 ft 3 in) of the original shaft is still in the socket stone. | 1019034 |  Upload Photo |
[280][281] |
| Wayside cross 100 m south east of Doniford Farm | Williton | Cross | Middle Ages | ST 08838 42897 51°10′41″N 3°18′20″W / 51.1780°N 3.3055°W |
The socket stone and part of the shaft of a medieval cross on the main street in Doniford. | 1019292 |  |
[282] |
| Wayside cross at junction of High Street and Bank Street | Williton | Cross | Middle Ages | ST 07737 40924 51°09′36″N 3°19′15″W / 51.1601°N 3.3208°W |
The remains of a medieval cross which still has its octagonal base and 0.75 metres (2 ft 6 in) of the shaft. | 1017292 |  |
[283] |
| West Luccombe packhorse bridge | Luccombe | Packhorse bridge | Middle Ages | SS 89886 46119 51°12′13″N 3°34′39″W / 51.2036°N 3.5775°W |
A single arch packhorse bridge built of red sandstone. | 1006227 |  |
[284][285] |
| Wilmersham Common West: a stone row 120 m south east of the confluence of Chetsford and Embercombe waters | Luccombe | Stone row | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 85544 42131 51°10′01″N 3°38′18″W / 51.1669°N 3.6384°W |
Two standing and one recumbent stones. | 1014258 |  Upload Photo |
[286] |
| Wilmersham Common stone row 320 m south east of the confluence of Embercombe and Chetsford waters | Luccombe | Stone row | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 85670 41976 51°09′56″N 3°38′11″W / 51.1656°N 3.6365°W |
A 68-metre (223 ft) long row of 50 standing stones. The tallest of which is 60 centimetres (24 in) high. | 1014257 |  Upload Photo |
[287] |
| Wiveliscombe Barrow | Brompton Regis | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 00553 34857 51°06′16″N 3°25′18″W / 51.1044°N 3.4218°W |
Wiveliscombe Barrow. which was previously known as Eastern Barrow is 20.5 metres (67 ft) in diameter. | 1020773 |  |
[288] |
| Wood Barrow round barrow | Challacombe | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | SS 71631 42506 51°10′03″N 3°50′15″W / 51.1674°N 3.8374°W |
A bowl barrow approximately 28 metres (92 ft) in diameter. | 1003838 1006209 |
 |
[289] |
| World War II pillbox 100 m west of Ralegh's Cross Hotel | Clatworthy | Pillbox | 1940 | ST 03837 34397 51°06′03″N 3°22′29″W / 51.1008°N 3.3748°W |
A Type 24 pillbox made of reinforced concrete. | 1020723 |  Upload Photo |
[290] |
| World War II pillbox at Vale House, 120 m north east of Glasses Farm | Old Cleeve | Pillbox | 1940 | ST 02792 38004 51°07′59″N 3°23′27″W / 51.1330°N 3.3907°W |
A concrete pillbox which is 2.6 metres (8 ft 6 in) high. | 1020726 |  |
[291] |
See also
- Scheduled Monuments in Somerset
- Grade I listed buildings in West Somerset
- Grade II* listed buildings in West Somerset
Notes
- ^ Wood Barrow round barrow is included twice in the National Heritage List for England as it straddles the border between Somerset and Devon.
- ^ The date given is the date used by Historic England as significant for the initial building or that of an important part in the structure's description.
- ^ Sometimes known as OSGB36, the grid reference is based on the British national grid reference system used by the Ordnance Survey.
- ^ The "List Entry Number" is a unique number assigned to each listed building and scheduled monument by Historic England.
References
- ^ "Community and Living". West Somerset Council. Retrieved 24 January 2015.
- ^ "West Somerset (Local Authority): Key Figures for Physical Environment". Neighbourhood Statistics. Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 23 April 2009.
- ^ "Maps chart UK's ageing population". BBC News. 1 October 2009. Retrieved 3 October 2009.
- ^ "Sites of Special Scientific Interest and historical monuments". Gov.uk. Natural England. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ^ "Agnes Fountain". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "MSO6730 - Alderman's Barrow, Almsworthy Common". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Allerford New Bridge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "MSO8006 - New Bridge, Allerford". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Packhorse Bridge". Images of England. Retrieved 5 January 2008.
- ^ "Almsworthy Common: a stone alignment 560 m south west of Chetsford Bridge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bagley Iron Age defended settlement enclosure and deserted medieval farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "MSO9331 - Barle Bridge, Dulverton". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Barlynch Priory". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 24 January 2015.
- ^ "Houses of Augustinian canons: The priory of Barlynch". Houses of Augustinian canons: The priory of Barlynch', A History of the County of Somerset: Volume 2 (1911), pp. 132-134. British History Online. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- ^ "Barlich Farmhouse". Images of England. Historic England. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- ^ "Barlinch Priory, Brompton Regis, West Somerset - Exmoor (NP)". Heritage at Risk. Historic England. Retrieved 20 October 2013.
- ^ "Barrow and cairn cemetery on Black Hill, 490 m north west of Crowcombe Park Gate". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Barrow at Wilmot's Pool and a cairn 45 m to the north". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Monument No. 189871". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 11 January 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 189876". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 11 January 2015.
- ^ "Bat's Castle: a small multivallate hillfort and associated outwork". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Bats Castle". Crown Estates. Retrieved 20 November 2010.
- ^ "Bat's Castle, Gallox Hill, Carhampton". Exmoor Historic Environment Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ^ Bush, Robin (1994). Somerset: The complete guide. Wimborne, Dorset: Dovecote Press. p. 55. ISBN 1-874336-26-1.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "Beckham stone alignment and mound, 450 m south east of the Long Combe sheep pen". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bendels Barrows". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "MSO6716 - Bendels Barrows, Exford Common, Exford". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Berry Castle". National Monuments Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ^ "Berry Castle". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ^ "Black Ball Camp: a later prehistoric defended settlement on Gallox Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Black Ball Camp". Exmoor Historic Environment Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ^ "Black Ball Camp". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 15 November 2010.
- ^ "Black Ball Camp". Exmoor Historic Environment Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ^ "MSO7900 - Black Barrow". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 80 m north of Halsway Post". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 100 m north west of Halsway Post". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 122 m NNW of Halsway Post". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 225 m north west of Halsway Post". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 260 m north east of Ralegh's Cross Hotel". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 470 m north of Brendon Hill Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 610 m ESE of the fire tower on Monkham Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 650 m north west of Elworthy Barrows hillfort". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 700 m north east of Burrow Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 780 m ESE of the fire tower on Monkham Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow and round cairn on Withypool Hill, 850 m and 820 m east of Portford Bridge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow called Chains Barrow". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow on Longstone Hill, 270 m NNE of Bicknoller Post". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow on Longstone Hill, 270 m north east of Bicknoller Post". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 March 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow on Lype Hill, 550 m north west of Lype Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow on Lype Hill, 750 m ENE of Heath Pault Cross". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow on Thorncombe Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow on Thorncombe Hill, 1.03 km north east of Paradise Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow on Thorncombe Hill, 1.07 km north east of Paradise Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow on Thorncombe Hill 500 m north west of Halsway Post". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow on Thorncombe Hill known as `Thorncombe Barrow'". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bowl barrow on Weacombe Hill, 300 m SSW of Bicknoller Post". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Brewer's Castle". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Brightworthy Barrows on Withypool Common". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Burrow Farm iron mine and section of mineral railway trackbed, 350 m north east of Burrow Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "MSO8842 - Bury Bridge, Bury, Brompton Regis". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Bury Castle". National Monument Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ^ "Bury Castle, an Iron Age defended settlement, No:24025". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- ^ Bury Castle, Brompton Regis, Gatehouse website, accessed 16 July 2011.
- ^ Dunning, Robert (1995). Somerset Castles. Tiverton: Somerset Books. pp. 30–31. ISBN 978-0-86183-278-1.
- ^ "Bury Castle, an Iron Age defended settlement". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 3 March 2015.
- ^ "Butter Cross". National heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 14 July 2013.
- ^ "Butter Cross at Dunster — ancient monument". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 15 June 2014.
- ^ "Butter Cross, Dunster". Exmoor Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park.
- ^ "History and Research: Dunster Butter Cross". Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ^ "Dunster: The Butter Cross, St George's Church, the Castle and Conygar Tower". TATE. Retrieved 25 March 2015.
- ^ "Cairn 90 m SSE of the Ordnance Survey triangulation point on Beacon Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cairn 150 m SSE of the Ordnance Survey triangulation point on Beacon Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cairn 250 m SSE of the Ordnance Survey triangulation point on Beacon Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cairn 480 m north of Little Quantock Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cairn 850 m north east of Dunkery Bridge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cairn on Bossington Hill, 1.12 km north east of Lynch Mead". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cairn on Thorncombe Hill, 990 m north west of Halsway Post". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cairn on Thorncombe Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Caratacus Stone". Pastscape. English Heritage. Retrieved 3 June 2011.
- ^ Thomas, Charles (1994). And Shall These Mute Stones Speak? Post Roman Inscriptions in Western Britain. University of Wales Press. pp. 288–9. ISBN 0-7083-1160-1.
- ^ "Caratacus Stone". National heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 9 June 2013.
- ^ Bruton, F. A. (1919). "The Caratacus Stone on Exmoor". The Journal of Roman Studies. 9: 208–210. doi:10.2307/296006.
- ^ "Carnarvon New Pit iron mine and section of mineral railway trackbed, 300 m south west of Heather House". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Chains Valley stone alignment 400 m north west of Exe Head". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Churchyard Cross, 8 metres East of chancel, Church of St George, Church Lane (South side), Bicknoller". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Churchyard cross immediately south of Holy Ghost Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Cist and associated mound in Langridge Wood, 410 m north west of Treborough Lodge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Clatworthy Camp". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 22 March 2011.
- ^ "Clatworthy Camp". National Monuments Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 22 March 2011.
- ^ "Cleeve Abbey". Historic England. Retrieved 9 August 2013.
- ^ William Page (editor) (1911). "House of Cistercian monks: The abbey of Cleeve". A History of the County of Somerset: Volume 2. Institute of Historical Research. Retrieved 11 May 2013.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ "Cleeve Abbey, Washford". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 13 July 2008.
- ^ "Cleeve Abbey". Historic England. Retrieved 23 May 2013.
- ^ "Cow Castle, Exmoor, West Somerset - Exmoor (NP)". Heritage at Risk. Historic England. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
- ^ "Cow Castle". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 16 January 2011.
- ^ "Cross 15 m north of St Peter's Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ Adkins, Lesley; Roy Adkins (1992). A Field Guide to Somerset Archaeology. Wimborne, Dorset: Dovecote Press. p. 101. ISBN 0-946159-94-7.
- ^ "Remains of churchyard cross". Images of England. Retrieved 26 January 2008.
- ^ "Cross in the churchyard of All Saints' Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cross in the churchyard of St George's Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cross in the churchyard of the Church of St Mary the Virgin". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cross in the churchyard of St Mary the Virgin's Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cross in the churchyard of St Peter's Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cross in the churchyard of the Church of St Decuman". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cross in the churchyard of St Mary's Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Cross in the churchyard of St Peter's Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Crowcombe village cross 170 m north west of Holy Ghost Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 November 2014.
- ^ "Curdon Wood Camp". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 22 March 2011.
- ^ "Curdon Camp". National Monuments Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 22 March 2011.
- ^ "Daws Castle". National Monuments Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 16 March 2011.
- ^ "Daws Castle, Watchet". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 14 January 2011.
- ^ "MMO213 - Deserted medieval farmstead on western side of Bramble Combe". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 30 November 2014.
- ^ "Dovecote". National heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ^ Ballard, Barbara. "Dunster Somerset". Britain Express. Retrieved 4 June 2009.
- ^ Cooke, A.O. "Somerset and Devon". Book of Dovecotes. Chapter 17. Retrieved 4 June 2009.
- ^ "Dovecote, Dunster". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 4 June 2009.
- ^ "Dovecot at Blackford Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 9 April 2014.
- ^ "Dovecote at Little Blackford". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- ^ "Dovecote at Little Blackford". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 11 April 2014.
- ^ "MSO7317 - Two Bowl Barrows, Doverhay". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 3 December 2014.
- ^ "Dowsborough hillfort and associated round barrow, Holford — West Somerset". Heritage at Risk. Historic England. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
- ^ "Dowsborough Camp". National Monuments Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 23 March 2011.
- ^ "Dowsborough hillfort, Holford". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 28 December 2010.
- ^ "Dowsborough hillfort and associated round barrow". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 3 December 2014.
- ^ "MSO9187 - Dunkery Beacon". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 3 December 2014.
- ^ "Robin How". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 3 December 2014.
- ^ "Early Christian to medieval settlement and cemetery". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 3 December 2014.
- ^ "Earthwork enclosure on Rodhuish Common, 300 m west of Moor Barn". English Heritage. Retrieved 24 July 2011.
- ^ "Rodhuish Common". National Monuments Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ^ "Earthwork enclosure on Monkslade Common, 860 m east of Fire Tower". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 3 December 2014.
- ^ "Earthwork enclosure on Winsford Hill, 200 m south east of Wambarrows". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 3 December 2014.
- ^ "MSO8844 - Enclosure on southern bank of River Haddeo". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 3 December 2014.
- ^ "East Pinford: a stone alignment on the west side of East Pinford 700 m west of Long Combe sheep pen". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 December 2014.
- ^ "Edgerley Stone". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Elworthy Barrows Hillfort". National Monuments Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 23 March 2011.
- ^ "Elworthy Barrows hillfort, Brompton Ralph". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 9 March 2010.
- ^ "Elworthy Barrows hillfort". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Enclosure and associated outworks on Staddon Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 December 2014.
- ^ "Entrenchment on Heydon Hill, Huish Champflower - West Somerset". Heritage at Risk. Historic England. Retrieved 5 December 2014.
- ^ "Linear Earthwork, Heydon Hill, Huish Champflower". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 10 December 2014.
- ^ "Exe Plain stone alignment 425 m north east of the sheepfold". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 December 2014.
- ^ "Four cairns on Hurley Beacon". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 December 2014.
- ^ "Four medieval fish weirs 500 m east of the Harbour". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Four round barrows on The Allotment, 520 m south east of Spire Cross". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 December 2014.
- ^ "Four round cairns on Dunkery Hill 400 m south east of Joaney How Cairn". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 December 2014.
- ^ "Gallox Bridge". Historic England. Retrieved 24 January 2015.
- ^ "Gallox Bridge". Images of England. Historic England. Retrieved 13 April 2009.
- ^ "Green Barrow on Hawkridge Common". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 December 2014.
- ^ "Great Rowbarrow". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 27 December 2014.
- ^ "Monument No 35934". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 27 December 2014.
- ^ "Five Barrows". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 27 December 2014.
- ^ "Halscombe stone setting 790 m SSW of Simonsbath Bridge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 December 2014.
- ^ "Monument No. 36851". National Monuments Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 23 March 2011.
- ^ "Grabbist Hillfort". Exmoor Historic Environment Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 23 March 2011.
- ^ "Holy well at St Pancras Chapel". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 December 2014.
- ^ "Horner Bridge". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 27 December 2014.
- ^ "Huish Champflower Barrow". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Culbone Stone". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Incised stone W of Stent Hill". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "MSO7891 - Culbone Stone, Culbone Hill". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Culbone Stone". Megalithic Portal. Retrieved 24 October 2007.
- ^ a b "Culbone Stone". The Modern Antiquarian. Retrieved 24 October 2007.
- ^ "Iron Age defended settlement above Sweetworthy (eastern of two)". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ "Iron Age defended settlement above Sweetworthy (western of two)". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ "Iron Age defended settlement, Furzebury Brake". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ "Ironstone mine ventilation flue in Chargot Wood, 1150 m south west of Langham Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ "Katherine's Well". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ "Kit Barrows Cairns". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ "Kittuck stone setting and cairn, 200 m south west of Three Combes Foot". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ "Lanacombe 1: a stone setting and two cairns on the east side of Lanacombe". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ "Lanacombe 2: a stone setting and cairn on the east side of Lanacombe". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ "Lanacombe 3: a stone setting and cairn on the east side of Lanacombe". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ "Lanacombe 4: a stone setting on the ENE side of Lanacombe". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ "Lanacombe 5: a stone alignment on the south east side of Lanacombe". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ "Landacre Bridge". National heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ^ Otter, R.A. (1994). Civil Engineering Heritage: Southern England. Thomas Telford Ltd. pp. 91–92. ISBN 978-0727719713.
- ^ "MSO8670 - Landacre Bridge". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 11 October 2014.
- ^ "Later prehistoric defended enclosure, Long Wood". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 December 2014.
- ^ "MSO9087 - Long Wood Enclosure". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 1 December 2014.
- ^ "Longwood". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 1 December 2014.
- ^ "Leather Barrow". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 29 December 2014.
- ^ "Lock up 60 m south east of St Mary's Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 November 2014.
- ^ "Long Chains Combe North: a stone setting 120 m WNW of the sheepfold". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 30 December 2014.
- ^ "Long Chains Combe South: two standing stones 380 m south west of the sheepfold". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 30 December 2014.
- ^ "Malmsmead Bridge". Pastscape. Historic England.
- ^ "Malmsmead Bridge". Images of England. Historic England. Retrieved 30 December 2014.
- ^ "Dunster Castle and gatehouse". Historic England. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ "Mounsey Castle". National Mounments Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 24 March 2011.
- ^ "Mounsey Castle". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 16 January 2011.
- ^ "Mounsey Castle and associated outwork 100 m to the north". Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 28 February 2011.
- ^ Montgomery, Elizabeth. "Robbers Bridge". Everything Exmoor. Retrieved 2 October 2013.
- ^ Ross, David. "Oare, Somerset Lorna Doone Country". Historic Somerset Guide. Retrieved 2 October 2013.
- ^ "Oare Bridge". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 30 December 2014.
- ^ "Old Barrow on Old Barrow Down". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 30 December 2014.
- ^ "Oldbury (or Oldberry) Castle, NW of Dulverton". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 16 January 2011.
- ^ Gathercole, Clare. "Dulverton" (PDF). English Heritage Extensive Urban Survey. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 17 August 2016.
- ^ "Oldberry Castle, Oldbury Castle". Fortified England. Retrieved 15 January 2011.
- ^ "Packhorse bridge 60 m north east of Royal Oak Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- ^ "Packhorse bridge 75 m south east of The Old Vicarage". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Porlock Allotment stone alignment and cairn, 450 m west of Porlock stone circle". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- ^ "Porlock Allotment 1: a stone alignment 450 m SSE of Black Barrow". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- ^ "Porlock Hill stone setting, 150 m north west of the cattle grid on the A39 at the top of Porlock Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- ^ "Post-medieval pottery kiln 360 m NNE of the Castle". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- ^ "Ralegh's Cross". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- ^ "Raleigh's Cross iron mine, 310 m south east of Heather House". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 31 December 2014.
- ^ "Kilve chantry, Kilve". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 7 January 2010.
- ^ "Remains of St Andrew's Chapel, 80 m north west of Chapel Cross". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Rexy Barrow". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 6 January 2015.
- ^ "Ring cairn on West Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 January 2015.
- ^ "Pastscape: Road Castle". Pastscape. Retrieved 12 May 2011.
- ^ "Road Castle". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 35030". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ^ "Round barrow 720 m NNW of Spire Cross". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 January 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 35331". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 11 January 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 35331". Pastscpae. Historic England. Retrieved 13 January 2015.
- ^ "Round barrow cemetery at Battle Gore immediately west of North Road". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Round barrow cemetery incorporating Wambarrows on Winsford Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 11 January 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 36255". Pastscpae. Historic England. Retrieved 13 January 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 35336". Pastscpae. Historic England. Retrieved 13 January 2015.
- ^ "Round cairn 280 m south of Rex Stile Head". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ^ "Round cairn 550 m north east of Joaney How Cairn". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Round cairn 750 m south east of Joaney How Cairn". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ^ "Round cairn 1000 m ESE of Joaney How Cairn". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ^ "Round cairn cemetery, 570 m east of Selworthy Beacon". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Round cairn cemetery on Dunkery Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ^ "Round cairn known as Pixie's Mound". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ^ "Monument No.189581". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 16 January 2015.
- ^ "Selworthy Beacon cairn". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ^ "Setta Barrow". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 35033". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 35052". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ^ "Stone setting". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ^ "St Leonard's Well". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ^ Stogursey Castle, the Gatehouse website, accessed 22 April 2011.
- ^ "Stogursey Castle". Images of England. English Heritage. Retrieved 9 May 2011.
- ^ "Porlock Stone Circle". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ^ "MSO7898 - Porlock Stone Circle". Exmoor Historic Environment Record. Exmoor National Park. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ^ "Stone circle on Withypool Hill 670 m ESE of Portford Bridge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 19 January 2015.
- ^ "Stringston churchyard cross, Stringston - West Somerset". Heritage at Risk. Historic England. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
- ^ "Churchyard Cross". Images of England. Retrieved 6 January 2008.
- ^ "Monument No. 189779". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 20 January 2015.
- ^ "Swap Hill standing stone 200 m south east of the Long Combe sheep pen". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 20 January 2015.
- ^ "Swap Hill stone setting, 275 m south east of the Long Combe sheep pen". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 20 January 2015.
- ^ "Sweetworthy deserted medieval settlement". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 20 October 2013.
- ^ "Sweetworthy Deserted Medieval Settlement". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 16 January 2011.
- ^ "Sweetworthy deserted Medieval settlement, Luccombe, West Somerset - Exmoor (NP)". Heritage at Risk. Historic England. Retrieved 28 October 2015.
- ^ "Sweetworthy". National Monuments Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 16 March 2011.
- ^ "Sweetworthy". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 16 January 2011.
- ^ "Sweetworthy Enclosure". Exmoor National Park Historic Environment Record. English Heritage. Retrieved 16 January 2011.
- ^ "Tarr Steps". Historic England. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ "Tarr Steps". Images of England. Retrieved 9 May 2007.
- ^ Leete-Hodge, Lornie (1985). Curiosities of Somerset. Bodmin: Bossiney Books. pp. 63–64. ISBN 0-906456-98-3.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ "West Somerset Mineral Railway Extension". North Devon Journal. British Newspaper Archive. 29 September 1864. Retrieved 19 July 2014.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|subscription=ignored (|url-access=suggested) (help) - ^ R.W. Dunning (editor), A.P. Baggs, R.J.E. Bush, M.C. Siraut (1985). "Parishes: Old Cleeve". A History of the County of Somerset: Volume 5. Institute of Historical Research. Retrieved 22 July 2014.
{{cite web}}:|author=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "The Incline, lying between Brendon Hill and Comberow, and the remains of Combe Row Station". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 35951". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 20 January 2015.
- ^ "The Whit Stones: two standing stones 230 m west of Whitstone Post". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 20 January 2015.
- ^ "Yarn Market". Historic England. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ Heritage Unlocked. Historic England. 2004. p. 66. ISBN 1850748756.
- ^ Brown, Patrick (1981). Buildings of Britain 1550-1750: South West England. Moorland. pp. 100–101. ISBN 0861900308.
- ^ "Brief History of Dunster". Dunster Tithe Barn. Retrieved 26 May 2009.
- ^ "The Yarn Market". Historic England. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ "Three bowl barrows on Black Hill, 590 m north west of Crowcombe Park Gate". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Three round barrows on Withycombe Common, 360 m north of Fire Tower". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Trendle Ring hillfort and associated outwork". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Trendle Ring hillfort, Bicknoller Hill, Bicknoller". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 1 February 2011.
- ^ "Tripp Barrow". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Trout Hill 1: a stone setting on the north east end of Trout Hill 550 m south west of the foot bridge over Badgworthy Water". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Trout Hill 2: a stone setting on the north east end of Trout Hill 610 m south of the foot bridge over Badgworthy Water". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Trout Hill 3: a stone setting on the north east end of Trout Hill 850 m SSW of the foot bridge over Badgeworthy Water". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Two Barrows". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Two bowl barrows on Beacon Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Two cairns on Great Hill, 470 m south and 750 m south west of Quantock Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Two cairns and two bowl barrows on Weacombe Hill, 440 m south of Bicknoller Post". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 January 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 35896". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 35893". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 188228". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Two round cairns on Dunkery Hill, 390 m and 420 m south east of Rex Stile Head". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Two standing stones and a mound 200 m WSW of Black Barrow, Hoscombe". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Village cross 75 m north of St Andrew's Well". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Remains of Village cross". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Wayside cross 100 m south east of Doniford Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Wayside cross at junction of High Street and Bank Street". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Packhorse Bridge at NGR SS 8987 4608". Images of England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 35855". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Wilmersham Common West: a stone row 120 m south east of the confluence of Chetsford and Embercombe waters". National heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Wilmersham Common stone row 320 m south east of the confluence of Embercombe and Chetsford waters". National heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Wiveliscombe Barrow". National heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "Wood Barrow". Pastscape. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "World War II pillbox 100 m west of Ralegh's Cross Hotel". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ^ "World War II pillbox at Vale House, 120 m north east of Glasses Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 23 January 2015.



