German spring offensive
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (February 2014) |
| German Spring Offensive, 1918 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Western Front of World War I | |||||||
 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 688,341[1] |
| ||||||
The 1918 Spring Offensive or Kaiserschlacht (Kaiser's Battle), also known as the Ludendorff Offensive, was a series of German attacks along the Western Front during the First World War, beginning on 21 March 1918, which marked the deepest advances by either side since 1914. The Germans had realised that their only remaining chance of victory was to defeat the Allies before the overwhelming human and matériel resources of the United States could be fully deployed. They also had the temporary advantage in numbers afforded by the nearly 50 divisions freed by the Russian surrender (the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk).
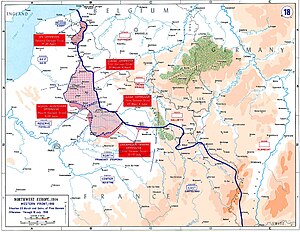
There were four German offensives, codenamed Michael, Georgette, Gneisenau and Blücher-Yorck. Michael was the main attack, which was intended to break through the Allied lines, outflank the British forces which held the front from the Somme River to the English Channel and defeat the British Army. Once this was achieved, it was hoped that the French would seek armistice terms. The other offensives were subsidiary to Michael and were designed to divert Allied forces from the main offensive on the Somme.
No clear objective was established before the start of the offensives and once the operations were underway, the targets of the attacks were constantly changed according to the battlefield (tactical) situation. The Allies concentrated their main forces in the essential areas (the approaches to the Channel Ports and the rail junction of Amiens), while leaving strategically worthless ground, devastated by years of combat, lightly defended.
The Germans were unable to move supplies and reinforcements fast enough to maintain their advance. The fast-moving stormtroopers leading the attack could not carry enough food and ammunition to sustain themselves for long and all the German offensives petered out, in part through lack of supplies.
By late April 1918, the danger of a German breakthrough had passed. The German Army had suffered heavy casualties and now occupied ground of dubious value which would prove impossible to hold with such depleted units. In August 1918, the Allies began a counter-offensive with the support of 1–2 million fresh American troops and using new artillery techniques and operational methods. This Hundred Days Offensive resulted in the Germans retreating or being driven from all of the ground taken in the Spring Offensive, the collapse of the Hindenburg Line and the capitulation of the German Empire that November.
German preparations
Strategy

The German High Command—in particular General Erich Ludendorff, the Chief Quartermaster General at Oberste Heeresleitung, the supreme army headquarters—has been criticised by military historians[who?] for the failure to formulate sound and clear strategy. Ludendorff privately conceded that Germany could no longer win a war of attrition, yet he was not ready to give up the German gains in the West and East and was one of the main obstacles to the German government's attempts to reach a settlement with the Western Allies.
Although Ludendorff was unsure whether the Americans would enter the war in strength, at a meeting of the Chiefs of Staff of the German armies on the Western Front on 11 November 1917, he decided to launch an offensive.[6] The German government and Field Marshal Paul von Hindenburg, nominally the Chief of the General Staff, were not party to the planning process. Eventually it was decided to launch Operation Michael near Saint-Quentin, at the hinge between the French and British armies, and strike north to Arras. The main reason for the choice was tactical expediency. The ground on this sector of the front would dry out much sooner after the winter and spring rains and would therefore be easier to advance across. It was also a line of least resistance as the British and French armies were weak in the sector.
The intention was not to reach the English Channel coast, but to break through the Allied lines and roll up the flank of the British army from the south, pushing it back against the Channel Ports or destroying it if the British chose to stand and fight. Further operations such as Operation Georgette and Operation Mars were designed to strike further north to seize the remaining Allied ports in Belgium and France while diverting Allied forces from Michael. However, these remained only secondary and weaker operations, subordinate to Michael.[7]
The constant changing of operational targets once the offensive was underway gave the impression the German command had no coherent strategic goal. Any capture of an important strategic objective, such as the Channel ports, or the vital railway junction of Amiens would have occurred more by chance than by design.[8][9]
Supply constraints
Logistics were a key issue in the Spring Offensives, owing to the German failures in that area. Operation Michael in particular repeated the apparent mistakes of the Schlieffen Plan, in that it forced German infantry to advance too deep and fight too far away from supplying railheads. The stormtrooper units leading the advance were unable to carry enough supplies to sustain themselves for more than a few days as it would slow them down and defeat the object of deploying a unit built for a speedy advance. Instead, they relied on logistical support brought up quickly from the rear to allow them to continue rapid advances. This was not achieved; the advance was slowed by supply shortages, which then gave Allied commanders the time to reinforce the threatened areas and slow the advance still more.[10] Exacerbating the problem, the Germans were trying to advance over areas which had been devastated during the Battle of the Somme in 1916 or to which the Germans themselves had applied scorched earth techniques during their retreat to the Hindenburg Line in February–March 1917, where communications were difficult.[11]
Tactical change
The German army had concentrated many of its best troops into stormtrooper units, trained in infiltration tactics to infiltrate and bypass enemy front line units, leaving these strong points to be "mopped-up" by follow-up troops. The stormtrooper tactic was to attack and disrupt enemy headquarters, artillery units and supply depots in the rear areas, as well as to occupy territory rapidly.[12] Each major formation "creamed off" its best and fittest soldiers into storm units; several complete divisions were formed from these elite units. This process gave the German army an initial advantage in the attack, but meant that the best formations would suffer disproportionately heavy casualties, while the quality of the remaining formations declined as they were stripped of their best personnel to provide the storm troops. The Germans also failed to arm their forces with a mobile exploitation force, such as cavalry, to exploit gains quickly. This tactical error meant the infantry had to keep up an exhausting tempo of advance.[13] Notwithstanding the effectiveness of the stormtroopers, the following German infantry often made attacks in large traditional waves and suffered heavy casualties.[14]
To enable the initial breakthrough, Lieutenant Colonel Georg Bruchmüller,[15] a German artillery officer, developed the Feuerwalze, an effective and economical artillery bombardment scheme.[16] There were three phases: first, a brief bombardment on the enemy's command and communications (headquarters, telephone exchanges, etc.); then, destruction of their artillery; lastly an attack upon the enemy front-line infantry defences. Bombardment would always be brief so as to retain surprise. Bruchmüller's tactics were made possible by the vast numbers of heavy guns—with correspondingly plentiful amounts of ammunition for them—which Germany possessed by 1918.
Allied preparations
Defensive tactics
In their turn, the Allies had developed defences in depth, reducing the proportion of troops in their front line and pulling reserves and supply dumps back beyond German artillery range. This change had been made after experience of the successful German use of defence in depth during 1917.
In theory, the front line was an "outpost zone" (later renamed the "forward zone"), lightly held by snipers, patrols and machine-gun posts only. Behind, out of range of German field artillery, was the "battle zone" where the offensive was to be firmly resisted, and behind that again, out of range of all but the heaviest German guns, was a "rear zone" where reserves were held ready to counter-attack or seal off penetrations. In theory, a British infantry division (with nine infantry battalions) deployed three battalions in the outpost zone, four battalions in the battle zone and two battalions in the rear zone.[17]
This change had not been completely implemented by the Allies. In particular, in the sector held by the British Fifth Army, which they had recently taken over from French units, the defences were incomplete and there were too few troops to hold the complete position in depth. The rear zone existed as outline markings only, and the battle zone consisted of battalion "redoubts" which were not mutually supporting (allowing stormtroopers to penetrate between them).
Operation Michael
On 21 March 1918, the Germans launched a big offensive against the British Fifth Army and the right wing of the British Third Army.
The artillery bombardment began at 4.40am on March 21. The bombardment [hit] targets over an area of 150 square miles, the biggest barrage of the entire war. Over 1,100,000 shells were fired in five hours...[18]

The German armies involved were—from north to south—the Seventeenth Army under Otto von Below, the Second Army under Georg von der Marwitz and the Eighteenth Army under Oskar von Hutier, with a Corps (Gruppe Gayl) from the Seventh Army supporting Hutier's attack. Although the British had learned the approximate time and location of the offensive, the weight of the attack and of the preliminary bombardment was an unpleasant surprise. The Germans were also fortunate in that the morning of the attack was foggy, allowing the stormtroopers leading the attack to penetrate deep into the British positions undetected.
By the end of the first day, the British had lost nearly 20,000 dead and 35,000 wounded and the Germans had broken through at several points on the front of the British Fifth Army. After two days Fifth Army was in full retreat. As they fell back, many of the isolated "redoubts" were left to be surrounded and overwhelmed by the following German infantry. The right wing of Third Army became separated from the retreating Fifth Army, and also retreated to avoid being outflanked.
Ludendorff failed to follow the correct stormtroop tactics, as described above. His lack of a coherent strategy to accompany the new tactics was expressed in a remark to one of his Army Group commanders, Rupprecht, Crown Prince of Bavaria, in which he stated, "We chop a hole. The rest follows." Ludendorff's dilemma was that the most important parts of the Allied line were also the most strongly held. Much of the German advance was achieved where it was not strategically significant. Because of this, Ludendorff continually exhausted his forces by attacking strongly entrenched British units. At Arras on 28 March, he launched a hastily prepared attack (Operation Mars) against the left wing of the British Third Army, to try to widen the breach in the Allied lines, and was repulsed.
The German breakthrough had occurred just to the north of the boundary between the French and British armies. The French commander-in-chief, General Pétain, sent reinforcements to the sector too slowly in the opinion of the British commander-in-chief, Field Marshal Haig, and the British government, though Elizabeth Greenhalgh disputes this, convincingly arguing that Petain sent the six additional divisions quicker than had been arranged with Haig – in 2 days instead of 4 – and arranging for extra divisions several times – 12 divisions on 23 March and 13 on the 25/26 March – before requests came in from Haig.[19] The Allies reacted by appointing the French General Ferdinand Foch to coordinate all Allied activity in France, and subsequently as commander-in-chief of all Allied forces everywhere.

After a few days, the German advance began to falter, as the infantry became exhausted and it became increasingly difficult to move artillery and supplies forward to support them. Fresh British and Australian units were moved to the vital rail centre of Amiens and the defence began to stiffen. After fruitless attempts to capture Amiens, Ludendorff called off Operation Michael on 5 April. By the standards of the time, there had been a substantial advance. It was, however, of little value; a Pyrrhic victory in terms of the casualties suffered by the crack troops, as the vital positions of Amiens and Arras remained in Allied hands. The newly won territory was difficult to traverse, as much of it consisted of the shell-torn wilderness left by the 1916 Battle of the Somme, and would later be difficult to defend against Allied counter-attacks.
The Allies lost nearly 255,000 men (British, British Empire and French). They also lost 1,300 artillery pieces and 200 tanks.[20] All of this could be replaced, either from French and British factories or from American manpower. German troop losses were 239,000 men, many of them specialist shocktroops (Stoßtruppen) who were irreplaceable.[20] In terms of morale, the initial German jubilation at the successful opening of the offensive soon turned to disappointment as it became clear that the attack had not achieved decisive results.
Georgette


Michael had drawn British forces to defend Amiens, leaving the rail route through Hazebrouck and the approaches to the Channel ports of Calais, Boulogne and Dunkirk vulnerable. German success here could choke the British into defeat.
The attack started on 9 April after a Feuerwalze. The main attack was made on the open and flat sector defended by the Portuguese Expeditionary Corps. After an entire year spent in the trenches, the Portuguese were tired and had suffered heavy losses. They were being replaced in the front line by fresh British divisions, an operation that was planned to be completed on 9 April, the same day as the Germans attacked the sector. The process of relief in place was poorly organized by the British First Army's command, and the Portuguese 1st Division had been withdrawn to the rear on 6 April, leaving the Portuguese 2nd Division to defend the entire sector alone. They were left with an extensive 7 mi (11 km) front, without natural obstacles which could favour the defense.
Hit hard by the Feuerwalze bombardment and under the assault of eight German divisions, the Portuguese 2nd Division made a desperate defense, trying to hold their positions, which, however, were rapidly enveloped and overrun by the masses of German forces. The 2nd Division was virtually annihilated, losing more than 7,000 men. The British 40th Division, on the northern flank of the Portuguese, also rapidly collapsed before the attack, opening a gap that further facilitated the envelopment of the Portuguese by the Germans. However, under much less pressure from the Germans and occupying good defensive positions protected by the La Bassée Canal, the British 55th Division on the southern flank of the Portuguese were able to hold much of their position throughout the battle.
The next day, the Germans widened their attack to the north, forcing the defenders of Armentières to withdraw before they were surrounded, and capturing most of the Messines Ridge. By the end of the day, the few British divisions in reserve were hard-pressed to hold a line along the River Lys.
Without French reinforcements, it was feared that the Germans could advance the remaining 15 mi (24 km) to the ports within a week. The commander of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF), Field Marshal Sir Douglas Haig, issued an "Order of the Day" on 11 April stating, "With our backs to the wall and believing in the justice of our cause, each one of us must fight on to the end."
However, the German offensive had stalled because of logistical problems and exposed flanks. Counterattacks by British, French and Anzac forces slowed and stopped the German advance. Ludendorff ended Georgette on 29 April.
As with Michael, losses were roughly equal, approximately 110,000 men wounded or killed, each.[21] Again, the strategic results were disappointing for the Germans. Hazebrouck remained in Allied hands and the Germans occupied a vulnerable salient under fire from three sides. The British abandoned the comparatively worthless territory they had captured at vast cost the previous year around Ypres, freeing several divisions to face the German attackers.
Blücher–Yorck

While Georgette ground to a halt, a new attack on French positions was planned to draw forces further away from the Channel and allow renewed German progress in the north. The strategic objective remained to split the British and the French and gain victory before American forces could make their presence felt on the battlefield. The Americans were originally deployed in the quiet Saint-Mihiel sector in Lorraine where they had their first significant engagement in the defence of Seicheprey on 20 April.[22] After the British had held off the Michael advance on the Somme, the US 1st Division was moved to reinforce the line in that sector in mid-April and launched their first attack of the war on Cantigny on 28 May 1918.[22]
The German attack took place on 27 May, between Soissons and Reims. The sector was partly held by six depleted British divisions which were "resting" after their exertions earlier in the year. In this sector, the defences had not been developed in depth, mainly due to the obstinacy of the commander of the French Sixth Army, General Denis Auguste Duchêne.[23] As a result, the Feuerwalze was very effective and the Allied front, with a few notable exceptions, collapsed. Duchêne's massing of his troops in the forward trenches also meant there were no local reserves to delay the Germans once the front had broken. Despite French and British resistance on the flanks, German troops advanced to the Marne River and Paris seemed a realistic objective. There was a frenzied atmosphere in Paris, which German long-range guns had been shelling since 21 March, with many citizens fleeing and the government drawing up plans to evacuate to Bordeaux.[24]
Yet again, losses were much the same on each side: 137,000 Allied and 130,000 German casualties up to 6 June.[25] German losses were again mainly from the difficult-to-replace assault divisions.
Gneisenau
Although Ludendorff had intended [Blücher-Yorck] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) to be a prelude to a decisive offensive ([Hagen] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help)) to defeat the British forces further north, he made the error of reinforcing merely tactical success by moving reserves from Flanders to the Aisne, whereas Foch and Haig did not overcommit reserves to the Aisne.[26] Ludendorff sought to extend [Blücher-Yorck] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) westward with Operation [Gneisenau] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help), intending to draw yet more Allied reserves south, widen the German salient and link with the German salient at Amiens.
The French had been warned of this attack (the Battle of Matz (Template:Lang-fr)) by information from German prisoners, and their defence in depth reduced the impact of the artillery bombardment on 9 June. Nonetheless, the German advance (consisting of 21 divisions attacking over a 23 mi (37 km) front) along the Matz River was impressive, resulting in an advance of 9 miles (14 km) despite fierce French and American resistance. At Compiègne, a sudden French counter-attack on 11 June, by four divisions and 150 tanks (under General Charles Mangin) with no preliminary bombardment, caught the Germans by surprise and halted their advance. Gneisenau was called off the following day.[27]
Losses were approximately 35,000 Allied and 30,000 German.
Last German attack (Friedensturm)
Ludendorff now postponed [Hagen] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) and launched the German Seventh, First and Third Armies in the [Friedensturm] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) (Peace Offensive) of 15 July, a renewed attempt to draw Allied reserves south from Flanders and to expand the salient created by [Blücher–Yorck] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) eastwards.[27] An attack east of Rheims was thwarted by the French defence in depth. In many sectors, the Germans, deprived of any surprise as their fuel-starved air force had lost air superiority to the Allies, advanced no further than the French Forward Zone, and nowhere did they break the French Battle (Second) Zone.[28]
Although German troops southwest of Rheims succeeded in crossing the River Marne, the French launched a major offensive of their own on the west side of the salient on 18 July, threatening to cut off the Germans in the salient. Ludendorff had to evacuate most of the [Blücher–Yorck] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) salient by 7 August and [Hagen] Error: {{Lang}}: text has italic markup (help) was finally cancelled.[29] The initiative had clearly passed to the Allies, who were shortly to begin the Hundred Days Offensive which ended the war.
Aftermath
Analysis
The Kaiserschlacht offensives had yielded large territorial gains for the Germans, in First World War terms. However, victory was not achieved and the German armies were severely depleted, exhausted and in exposed positions. The territorial gains were in the form of salients which greatly increased the length of the line that would have to be defended when Allied reinforcements gave the Allies the initiative. In six months, the strength of the German army had fallen from 5.1 million fighting men to 4.2 million.[30] By July, the German superiority of numbers on the Western Front had sunk to 207 divisions to 203 Allied, a negligible lead which would be reversed as more American troops arrived.[27] German manpower was exhausted. The German High Command predicted they would need 200,000 men per month to make good the losses suffered, returning convalescents could supply 70,000–80,000/month but there were only 300,000 recruits available from the next annual class of eighteen-year-olds.[31] Even worse, they lost most of their best-trained men: stormtrooper tactics had them leading the attacks. Even so, about a million German soldiers remained tied up in the east until the end of the war.
The Allies had been badly hurt but not broken. The lack of a unified high command was partly rectified by the appointment of Marshal Foch to the supreme command, and coordination would improve in later Allied operations.[citation needed] American troops were for the first time also used as independent formations.[32]
See also
- Journey's End, a play set during the early stages of the offensive
- Spring Offensive, a poem by Wilfred Owen
Notes
- ^ Churchill, "The World Crisis, Vol. 2", p.963. German casualties from "Reichsarchiv 1918"
- ^ Churchill, "The World Crisis, Vol. 2", p.963. British casualties from "Military Effort of the British Empire"
- ^ Churchill, "The World Crisis, Vol. 2", p.963. French casualties from "Official Returns to the Chamber, March 29, 1922"
- ^ Bligny, Marne – Italian Great War Cemetery
- ^ Leonard P. Ayers, The war with Germany: a statistical summary (1919) p 104 online
- ^ Blaxland, p.25
- ^ Middlebrook 1983, pp. 30–34.
- ^ Brown 1998, p. 184.
- ^ Robson 2007, p. 93.
- ^ Brown 1998, p. 184
- ^ Middlebrook 1983, pp. 347–348.
- ^ Simpson 1995, pp. 117–118.
- ^ Simpson 1995, p. 124.
- ^ Simpson 1995, p. 123.
- ^ Bruchmüller biography.
- ^ D T Zabecki, The German 1918 Offensives: A Case Study of The Operational Level of War, Taylor & Francis, 2005, p 56
- ^ Blaxland, p.28
- ^ historyofwar.org
- ^ Greenhalgh 2004, pp. 771–820.
- ^ a b Marix Evans, p.63
- ^ Marix Evans, p.81
- ^ a b Richard W. Stewart, ed. (2005). American Military History (PDF). Vol. II. Center of Military History, US Army. p. 30.
- ^ Edmonds 1939, pp. 39–40.
- ^ Hart 2008, p.296
- ^ Marix Evans, p.105
- ^ Hart 2008, p.294
- ^ a b c Hart 2008, p.298
- ^ Hart 2008, p.299
- ^ Hart 2008, p.300
- ^ Edmonds 1939, p. 306.
- ^ Herwig 2014, p. 407.
- ^ Marshall 1976, p. 57
References
- Books
- Brown, Ian. British Logistics on the Western Front: 1914–1919. Praeger Publishers, 1998. ISBN 978-0-275-95894-7
- Blaxland, Gregory (1981) [1968]. Amiens 1918. War in the Twentieth Century. London: W. H. Allen. ISBN 0-352-30833-8.
- Edmonds, J. E. (1994) [1939]. Military Operations France and Belgium, 1918 May–July: The German Diversion Offensives and the First Allied Counter-Offensive. History of the Great War Based on Official Documents By Direction of the Historical Section of the Committee of Imperial Defence. Vol. III (Imperial War Museum & Battery Press ed.). London: Macmillan. ISBN 0-89839-211-X.
- Gray, Randal (1991) Kaiserschlacht, 1918: The Final German Offensive, Osprey Campaign Series 11, London: Osprey, ISBN 1-85532-157-2
- Griffith, Paddy (1996). Battle Tactics of the Western Front: British Army's Art of Attack. 1916–18. Yale. ISBN 0-300-06663-5.
- Hart, Peter (2008). 1918: A Very British Victory, Phoenix Books, London. ISBN 978-0-7538-2689-8
- Herwig, Holger H. (2014). The First World War: Germany and Austria-Hungary 1914–1918. A&C Black. ISBN 9781472508850.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: ref duplicates default (link) - Keegan, John (1999). The First World War, London: Pimlico, ISBN 978-0-7126-6645-9
- Marshall, George C. (1976). "Memoirs of My Service in the World War 1917–1918", Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, ISBN 0-395-20725-8
- Marix Evans, Martin (2002) 1918: The Year of Victories, Arcturus Military History Series, London: Arcturus, ISBN 0-572-02838-5
- Middlebrook, Martin. The Kaiser's Battle: 21 March 1918: The First Day of the German Spring Offensive. Penguin. 1983. ISBN 0-14-017135-5
- Simpson, Andy. The Evolution of Victory: British Battles of the Western Front, 1914–1918. Tom Donovan, 1995. ISBN 1-871085-19-5
- Robson, Stuart. The First World War. Longman. 2007. ISBN 978-1-4058-2471-2
- Zabecki, David T. (2006) The German 1918 Offensives. A Case Study in the Operational Level of War, London: Routledge, ISBN 0-415-35600-8
- Journals
- Greenhalgh, E. (July 2004). "Myth and Memory: Sir Douglas Haig and the Imposition of Allied Unified Command in March 1918". The Journal of Military History. 68 (3): 771–820. ISSN 0899-3718.
Further reading
- Pitt, Barrie (2003) [1962]. 1918 The Last Act. Pen & Sword Military Classics. Barnsley: Pen and Sword. ISBN 0-85052-974-3.
External links
- Use dmy dates from December 2012
- Conflicts in 1918
- Battles of the Western Front (World War I)
- Battles of World War I involving the United States
- Battles of World War I involving the United Kingdom
- Battles of World War I involving France
- Battles of World War I involving Australia
- Battles of World War I involving New Zealand
- Battles of World War I involving Germany
- Battles of World War I involving Portugal
- 1918 in France
- United States Marine Corps in the 20th century
- Battles of World War I involving Italy
