Time in France
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2010) |
Metropolitan France uses Central European Time (heure d'Europe centrale, HEC: UTC+01:00) and Central European Summer Time (heure d'été d'Europe centrale: UTC+02:00). Daylight saving time is observed from the last Sunday in March (02:00 CET) to the last Sunday in October (03:00 CEST).
Until 1940 metropolitan France used GMT (and GMT+1 in summer). However, the German military authorities switched the country to "German time" and it has never switched back.
Notation
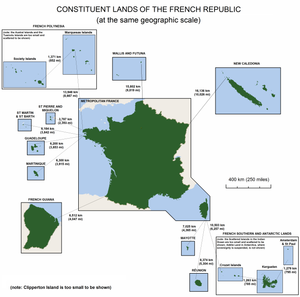
Overseas Territories
The overseas territories of France, use different timezones.
History
Until the Second World War France used Greenwich Mean Time. However, the German occupation switched France to German time immediately after the occupation for practical military reasons.[1] After the war France stayed on "German time" and remains in the Central European Time Zone to this day. From 1923 until the Second World War France observed summer time from the last Saturday in March until the first Saturday in October. During the war France also observed summer time. However, after the war the practice was abandoned (since the country changed time zones instituting de facto permanent summer time. In 1975, summer time was reimplemented because of the oil crisis.[1] In 1996, daylight saving time was harmonized throughout the European Union by Directive 2000/84/EC, which moved the end of DST to the last Sunday in October.
Since GMT (now UTC) is France's "natural" time zone its use of UTC+1 in winter can be seen as a form of daylight saving time in winter, while Central European Summer Time (UTC+2) can be seen as a form of "double summer time."[2]
References
- ^ a b Poulle, Yvonne (1999). "La France à l'heure allemande" (PDF). Bibliothèque de l'école des chartes. 157 (2): 493–502. Retrieved 11 January 2012.
- ^ Thorsen, Steffen. "France and Spain kicks into "Double Summer Time"". Time and Date.com. Retrieved 11 January 2012.
